Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAR Process PDF
Uploaded by
da azcurOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SAR Process PDF
Uploaded by
da azcurCopyright:
Available Formats
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
Basic SAR Processing and Analysis Files Used in this Tutorial Background Single-Band SAR Processing Read and Display RADARSAT CEOS Data Review CEOS Header Apply Square-Root Contrast Stretch Remove Speckle Using Adaptive Filters Density Slice Edge Enhancement Data Fusion Image-Map Output 2 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 6 7 8 9
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
This tutorial is designed to give you a working knowledge of ENVIs basic tools for processing singleband synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data such as RADARSAT, ERS-1, and JERS-1.
Files Used in this Tutorial
ENVI Resource DVD: Data\rsat_sub File
lea_01.001 rsi_f1.img (.hdr) dslice.dsr rsi_f2.img (.hdr) rsi_f3.img (.hdr) rsi_fus.img (.hdr) rsi_map.jpg
Description RADARSAT leader file Frost filter result Density slice file Laplacian filter result Laplacian filter result with 90% add-back Simulated fused TM and RADARSAT RADARSAT map composition example
bonnrsat.img (.hdr) RADARSAT image subset
Background
Use the Radar menu in ENVI to access standard and advanced tools for analysis of detected radar images and advanced SAR systems such as NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory's (JPL's) fully polarimetric AIRSAR and SIR-C systems. ENVI can process ERS-1, JERS-1, RADARSAT, SIR-C, X-SAR, and AIRSAR data and any other detected SAR dataset. In addition, ENVI is designed to handle radar data distributed in the CEOS format. Most standard ENVI processing functions are inherently radar-capable, including all display capabilities, stretching, color manipulations, classification, registration, filters, geometric rectification, and so on. Additional specialized tools are provided for analyzing polarimetric radar data. A typical processing flow may include reviewing the CEOS header, reading the CEOS data, displaying and contrast stretching, removing speckle using an adaptive filter, density slicing, edge enhancement, data fusion, and map composition.
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
Single-Band SAR Processing
This section describes a typical single-band SAR processing scenario from data input through processing and analysis, to publication-quality or map output. You will use a subsetted RADARSAT 1 Path Image, Fine Beam 2, from December 17, 1995, Bonn, Germany.
Read and Display RADARSAT CEOS Data
ENVI provides the tools to read generic CEOS data tapes and RADARSAT data from both tape and CD-ROM. To read data from tape, select File > Tape Utilities > Read Known Tape Formats > RADARSAT CEOS. To read original RADARSAT data from disk or CD, select Radar > Open/Prepare Radar File > RADARSAT. For this tutorial, a RADARSAT image subset has already been extracted. 1. From the ENVI main menu bar, select File > Open Image File . A file selection dialog appears. 2. Navigate to Data\rsat_sub and select bonnrsat.img. Click Open. 3. In the Available Bands List, select the Gray Scale radio button and click Load Band. The following figure shows the subsetted RADARSAT image of Bonn, Germany, with a 2% linear stretch applied. This dataset was acquired during the RADARSAT commissioning phase and should not be used for scientific analysis or interpretation. Data are copyright, RADARSAT, 1995.
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
Review CEOS Header
Many SAR datasets are distributed in CEOS format. ENVI provides generic tools to read CEOS headers and display CEOS header information on the screen. ENVI also has tools specifically designed to read RADARSAT CEOS headers, which contain additional information. 1. From the ENVI main menu bar, select Radar > Open/Prepare Radar File > View RADARSAT Header . A file selection dialog appears. 2. Select the RADARSAT leader file lea_01.001. A CEOS Header Report dialog appears. 3. Browse the information in the CEOS Header Report, then close the dialog when you are finished.
Apply Square-Root Contrast Stretch
Radar data typically cover a large range of data values. As seen above, default linear stretches do not perform a very good job of enhancing the contrast in most radar images. ENVIs square-root stretch spreads out radar data over a given range of gray scales better than other types of stretches, resulting in an improved display of radar images. 1. From the Display group menu bar, select Enhance > [Image] Square Root. The stretch is applied based on the statistics of the data in the Image window. The following figure shows a square-root stretch of the Bonn RADARSAT image. Compare to the linear contrast stretch above.
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
2. In the Available Bands List, click Display #1 and select New Display. Click Load Band again to display the image with the default 2% linear stretch. 3. From a Display group menu bar, select Tools > Link > Link Displays. Click OK to link the square-root image with the 2% linear stretch image. Click in an Image window to toggle between the two images.
Remove Speckle Using Adaptive Filters
Adaptive filters remove radar speckle from images without seriously affecting the spatial characteristics of the data. The Frost-filtered image shown below is a considerable improvement over the unfiltered data. The Frost filter, an exponentially damped, circularly symmetric filter that uses local statistics, is used to reduce speckle while preserving edges in the data. The pixel being filtered is replaced with a value calculated based on the distance from the filter center, the damping factor, and the local variance. 1. From the ENVI main menu bar, select Radar > Adaptive Filters > Frost. A Frost Filter Input File dialog appears. 2. Select bonnrsat.img and click OK. A Frost Filter Parameters dialog appears. 3. Use the default Filter Size (3x3) and Damping Factor (1.0). Enter an output filename and click OK. 4. In the Available Bands List, select the new Frost-filtered image and click Load Band. Or, load the pre-generated file rsi_f1.img to a new display group and apply a square-root stretch.
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
5. From a Display group menu bar, select Tools > Link > Link Displays. Click OK to link the Frost-filtered image with the 2% linear stretch image. Click in an Image window to toggle between the two images.
Density Slice
Density slicing visually enhances radar differences based on image brightness. The density-sliced image below has four levels, with higher radar backscatter in the warmer colors. 1. From the Display group menu bar associated with the Frost-filtered image, select Tools > Color Mapping > Density Slice . A Density Slice Band Choice dialog appears. 2. Select the name of your Frost-filtered image and click OK. A Density Slice dialog appears. 3. From the Density Slice dialog menu bar, select File > Restore Ranges. A file selection dialog appears. 4. Select dslice.dsr and click Open. 5. Click Apply in the Density Slice dialog. Use image-linking and dynamic overlays to compare the density-sliced image to the gray scale images.
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
6. When you are finished, close the Density Slice dialog.
Edge Enhancement
A Laplacian filter is a convolution filter that enhances edges in SAR and other data types. A 5 x 5 filter has the following kernel:
1. From the ENVI main menu bar, select Filter > Convolutions and Morphology. 2. From the Convolutions and Morphology Tool dialog menu bar, select Convolutions > Laplacian. 3. Set the Kernel Size field to 5. 4. Click Quick Apply. An input band selection dialog appears. 5. Select bonnrsat.img and click OK. Or, view the pre-generated file rsi_f2.dat. Applying the kernel in this manner strongly enhances the edges while losing most of the radiometric information in the image.
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
6. Repeat Steps 1-4, but set the Image Add Back field to 90. 7. Click Quick Apply. Or, view the pre-generated file rsi_f3.dat. The following figure shows Laplacian filter results (left) and 90% Add Back results (right):
8. Use image linking and dynamic overlays to compare these results with the original gray scale images. 9. When you are finished, close the Convolutions and Morphology Tool dialog. 10. From the ENVI main menu bar, select File > Exit.
Data Fusion
SAR data complement other types of data by providing spatial information that other data do not contain. Conversely, SAR data do not have the composition expressed in multispectral, optical data. Therefore, a combined SAR/optical data analysis is usually required. You can use an intensity-hue-saturation (IHS) transform to combine a multispectral, color-composite image with a monochromatic SAR-sharpening band. ENVI provides a simple tool to conduct data merging using IHS. See the Landsat TM and SAR Data Fusion tutorial for more information, and view the pre-generated, fused TM/SAR file rsi_fus.img.
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
Image-Map Output
Output from ENVI image processing usually consists of a map-oriented, scaled image-map for presentation or visual analysis and interpretation. Radar data can be used in a map composition, just like any other dataset. See the Image Georeferencing and Registration and Map Composition tutorials for more information.
ENVI Tutorial: Basic SAR Processing and Analysis
10
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Lineaments AcaiDocument10 pagesLineaments Acaida azcurNo ratings yet
- Create Geographic Metadata and Review Arccatalog Metadata ApplicationDocument8 pagesCreate Geographic Metadata and Review Arccatalog Metadata Applicationda azcurNo ratings yet
- Branquet JSouthAmericanEarthSciences 2002 PDFDocument25 pagesBranquet JSouthAmericanEarthSciences 2002 PDFda azcurNo ratings yet
- Basso2004 1 PDFDocument14 pagesBasso2004 1 PDFda azcurNo ratings yet
- Baohong - 2007 - Cainozoic Palaeochannel-Hosted Uranium and Exploration MethodsDocument6 pagesBaohong - 2007 - Cainozoic Palaeochannel-Hosted Uranium and Exploration Methodsda azcurNo ratings yet
- ILU Mineral Sands Pricing (August 2010)Document4 pagesILU Mineral Sands Pricing (August 2010)da azcurNo ratings yet
- Hola MundoDocument1 pageHola Mundoda azcurNo ratings yet
- Types of Landslides Abbreviated Version of Varnes Classification of Slope MovementsDocument4 pagesTypes of Landslides Abbreviated Version of Varnes Classification of Slope MovementszirimiaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Scientific PaperDocument24 pagesScientific PapersharonleefulloNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Statistics For People Who Think They Hate Statistics 7th Edition Neil J SalkindDocument24 pagesSolution Manual For Statistics For People Who Think They Hate Statistics 7th Edition Neil J Salkinddonaldpollardkoatengwxj100% (38)
- LAS 7 Mean of A Discrete Random VariableDocument1 pageLAS 7 Mean of A Discrete Random VariableLorelan CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 Answer FINC Stats SASIN EmbaDocument2 pagesQuiz1 Answer FINC Stats SASIN EmbaPeak ChindapolNo ratings yet
- Skittles Project 2-6Document8 pagesSkittles Project 2-6api-302525501No ratings yet
- SamplingDocument13 pagesSamplingArun Mishra100% (1)
- Practical Research 2 Topics and RequirementsDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Topics and RequirementsKristina Cassandra TenefranciaNo ratings yet
- Statistics: The Chi Square TestDocument41 pagesStatistics: The Chi Square TestAik ReyesNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Model Drift Detection Via Weak Data SlicesDocument8 pagesMachine Learning Model Drift Detection Via Weak Data SlicesBurak TuncerNo ratings yet
- 3.binomial DistributionDocument14 pages3.binomial Distributionanshul kumarNo ratings yet
- Examining methods to improve Parkinson's disease diagnosisDocument10 pagesExamining methods to improve Parkinson's disease diagnosisBharat DedhiaNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Experiments and Binomial Distribution ExplainedDocument29 pagesBernoulli Experiments and Binomial Distribution ExplainedÇháråñ ÇhèrryNo ratings yet
- Eviews UnderstandingDocument23 pagesEviews UnderstandingarmailgmNo ratings yet
- Two Tailed & One TailedDocument5 pagesTwo Tailed & One TailedSefdy ThenNo ratings yet
- 1498238158-Research Bulletin Vol. 12-April 2014 PDFDocument356 pages1498238158-Research Bulletin Vol. 12-April 2014 PDFMAJALIWA NGURUTI SEBASTIANNo ratings yet
- Lee 1997Document6 pagesLee 1997Vitor Hugo Pontes FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Networks SlidesDocument56 pagesBayesian Networks Slidesসুনীত ভট্টাচার্যNo ratings yet
- #054 Rail Life Analysis and Its Use in Planning Track Mtce - Railway Tech Inter 1993Document11 pages#054 Rail Life Analysis and Its Use in Planning Track Mtce - Railway Tech Inter 1993Satryo Dwi SutrisnoNo ratings yet
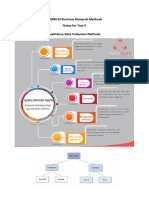
- 18MBC24 Business Research Methods Notes For Test II Qualitative Data Collection MethodsDocument35 pages18MBC24 Business Research Methods Notes For Test II Qualitative Data Collection MethodsIrfan ZubairNo ratings yet
- Research ProblemDocument13 pagesResearch ProblemNovelyn PuaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hypothesis TestingDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Hypothesis TestingMaimai PanaNo ratings yet
- Scoreplus E-BrochureDocument14 pagesScoreplus E-BrochureAlexander KilfordNo ratings yet
- Getting The Information You Need: Data CollectionDocument52 pagesGetting The Information You Need: Data CollectiontyagidonNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument21 pagesThesisJonathan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Bak A and Bartlomowicz T Conjoint Analysis Method and Its Implementation in Conjoint R PackageDocument9 pagesBak A and Bartlomowicz T Conjoint Analysis Method and Its Implementation in Conjoint R PackageBob FinlaysonNo ratings yet
- Decision Tree ClassificationDocument69 pagesDecision Tree Classificationss sriNo ratings yet
- Skills For Computing 4 September 2018 Examination PaperDocument7 pagesSkills For Computing 4 September 2018 Examination PaperpreeyalNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions For CA4Document18 pagesObjective Questions For CA4Rocket BunnyNo ratings yet
- Proceq Profometer 5 Rebar LocatorDocument2 pagesProceq Profometer 5 Rebar LocatorZulfan EffendiNo ratings yet
- Statistical Formulas and ChartsDocument29 pagesStatistical Formulas and Chartsrenaldo siregarNo ratings yet