Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes For Perioperative Nursing
Uploaded by
Jearanell LabraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes For Perioperative Nursing
Uploaded by
Jearanell LabraCopyright:
Available Formats
Perioperative Nursing Definition of Terms Surgery is any procedure performed on the human body that uses instruments to alter
tissue or organ integrity. SURGEON - A physician who treats disease, injury, or deformity by operative or manual methods. *A medical doctor specialized in the removal of organs, masses and tumors and in doing other procedures using a knife (scalpel) STERILE - free from living germs or microorganisms; aseptic: sterile surgical instruments ASEPSIS - The state of being free of pathogenic microorganisms. SEPSIS - a toxic condition resulting from the spread of bacteria or their toxic products from a focus of infection DISINFECTANT- any chemical agent used chiefly on inanimate objects to destroy or inhibit the growth of harmful organisms. ANTISEPTICS - is a substance that prevents or arrests the growth or action of microorganisms either by inhibiting their activity or by destroying them. STERILIZATION -the destruction of all living microorganisms, as pathogenic bacteria, vegetative forms, and spores. BACTERIOSTATIC -Capable of inhibiting the growth or reproduction of bacteria. BACTERICIDAL - Capable of killing bacteria. BACTERIOCIDES - is a substance that kills bacteria .Bactericides are either disinfectants, antiseptics or antibiotics Prefixes and Suffixes PREFIXES Supra above ; beyond Ortho joint Chole bile or gall Cysto bladder Encephalo- brain Entero intestine Hystero uterus Mast breast Meningo membrane; meninges Myo muscle Nephro kidney Neuro nerve Oophor ovary Pneumo lungs Pyelo kidney pelvis Salphingo fallopian tube Thoraco chest Viscero organ esp. abdomen SUFFIXES Oma tumor ; swelling Ectomy removal of an organ or gland Rhapy suturing or stitching of a part or an organ Scopy looking into Ostomy making an opening or a stoma Otomy cutting into Plasty to repair or restore Cele tumor ; hernia ; swelling Itis inflammation of Perioperative Nursing
Phases Preoperative phase begins when the decision to have surgery is made and ends when the client is transferred to the OR table. Intraoperative phase begins when the client is transferred to the OR table and ends when the client is admitted to the PACU. Postoperative phase begins with the admission of the client to the PACU and ends when the healing is complete. Fundamental purposes of the O.R. : It is a place. . . To correlate theory & practice. To develop skills in assisting the surgeon in the
operation. To create a suitable sterile field for surgical procedures to prevent complications.
Perioperative Nursing
Purpose/reasons Degree of urgency necessity to preserve the clients life, body part, or body function. Degree of risk involved in surgical procedure is affected by the clients age, general health, nutritional status, use of medications, and mental status. Extent of surgery Simple and radical CLASSIFICATIONS OF SURGERY According to Urgency : EMERGENT patient requires immediate attention ; disorder maybe life- threatening. URGENT patient requires prompt attention. > indications for surgery : within 24-30 hours. REQUIRED patient needs to have surgery. > indications for surgery: plan within few weeks or months. ELECTIVE patient should have surgery. > indications for surgery: Failure to have surgery is not catastrophic. OPTIONAL decision rests with pt. > indications for surgery : Personal preference Accdg. To Degree Of Risk : MAJOR high degree of risk : >maybe complicated / prolonged, large losses of blood may occur, vital organs maybe involved, post-op complications may be likely. MINOR little risk with few complications. - often performed in a day surgery. Accdg. To Purpose : DIAGNOSTIC verifies suspected diagnosis EXPLORATORY estimates the extent of the disease or injury. CURATIVE removes or repairs damaged tissues . ABLATIVE removing diseased organ that cant wait anymore. - emergency surgery. PALLIATIVE relieves symptoms but does not cure the underlying disease process. RECONSTRUCTIVE partial or complete restoration of a damaged organ/tissue to bring back the original appearance & function. CONSTRUCTIVE repairing the damaged tissue or congenitally defective organ. Accdg. To Location : INTERNAL inside the body . Ex. Hysterectomy EXTERNAL outside the body .Ex. Skin grafting
Perioperative Nursing- connotes the delivery of patient care in the
preoperative,intraoperative, and postoperative periods of the patients surgical experience through the framework of the nursing process.
FOUR BASIC PATHOLOGIC CONDITIONS THAT REQUIRE SURGERY (OPET): OBSTRUCTION a blockage ; are dangerous because they block the flow of blood, air, CSF, urine & bile through the body. PERFORATION is a rupture of the organ, artery or bleb. EROSION break in the continuity of tissue surface. It can damage the walls of blood vessels resulting in serious bleeding. TUMORS abnormal growth of tissue that serves no physiologic function in the body. Who are the the SURGICAL RISK PATIENTS? *Extremes of age ( very young & very old ) *Extremes of weight (emaciation, obesity) *Dehydrated pts. *Nutritional deficits *Pts. with severe trauma or injury, infection/sepsis *Pts. with cardiovascular disease *Endocrine dysfunction (diabetes mellitus) *Hypertensive & hypotensive pts. *Hypovolemia *Hepatic disease *Pre-existing mental or physical disability PROBLEMS THAT MAY ARISE IN SURGERY: Surgical risk pts probability of mortality Pain Hemorrhage Infection UTI PHASES OF O.R. NURSING : PREOPERATIVE PHASE The rendering of nursing care to the surgical client as soon as he is admitted & the decision to undergo surgery is made. It ends on the time the client is transferred to the O.R. NURSING ACTIVITIES : Assessment of the client Identification of potential/actual health problems. Pre-op teaching involving client & support persons. Day of surgery : pt. teaching reviewed informed consent confirmed pt.s identity & surgical site verified IVF started. Assessment (Nursing History) Current health statusAllergies Medications- list all current medications Previous surgeries Understanding of the surgical procedure and anesthesia Smoking Alcohol and other-altering substances Coping Social resources Cultural considerations PREPARATION FOR SURGERY Psychological Support : Assess clients fears, anxieties, support systems & patterns of coping. Establish trusting relationship with client & significant others.
Explain routine procedures, encourage verbalization of fears & allow client to ask questions. Demonstrate confidence in surgeon & staff. Provide for spiritual care if appropriate.
PREOPERATIVE TEACHING Assess clients level of understanding of surgical procedure & its implications. >Answer questions, clarify & reinforce explanations given by the surgeon. Explain routine pre- & post-op procedures & any special equipment to be used. PREOPERATIVE TEACHING Preoperative experience Preoperative medication Breathing exercises, coughing, incentive spirometer Leg exercises Position changes and movement Pain management Reducing anxiety and fear, support of coping Special considerations related to outpatient surgery Diaphragmatic Breathing and Splinting When Coughing Leg Exercises and Foot Exercises Preoperative Nursing Interventions PHYSICAL PREPARATIONS: Obtain history of past medical conditions, surgical procedures, dietary restrictions & medications. Perform baseline head-to-toe assessment, including VS, height & weight. Ensure that diagnostic procedures pertinent to surgery are performed as ordered NPO Bowel prep Skin prep Immediate preoperative preparation Transporting the pt. to the pre-surgical area about 30 to 60 minutes before anesthetics is to be given. Attend to family needs LEGAL PREPARATION: Surgeon obtains operative permit (informed consent) Surgical procedures, alternatives , possible complications & disfigurements or removal of body parts are explained. It is part of the nurses role as client advocate to confirm that the client understands information given. INFORMED CONSENT is necessary in the ff. Circumstances: Invasive procedures Procedures requiring sedation or anesthesia A non-surgical procedure Procedures involving radiation Adult client (over 18 y/o) signs own permit unless unconcious or mentally incompetent. Consents are not needed for emergency care if all 4 of the ff. criteria are met: There is an immediate threat to life. Experts agree that it is an emergency. Client is unable to consent. A legally authorized person cannot be reached. *Minors (under 18 y/o) must have consent signed by an adult (i.e. Parent or legal guardian) PREOPERATIVE MEDICATIONS PURPOSES: To relieve fear & anxiety. To reduce dose needed for induction & maintenance of anesthesia.
To prevent reflex bradycardia that happens during induction of anesthesia. To minimize oral secretions.
INTRAOPERATIVE PHASE Giving nursing care to client undergoing surgery. It starts from the time the pt. was admitted to the O.R. , during operation until it ends & transferred to the PACU. NURSING ACTIVITIES: Activities providing for pts safety. Maintenance of aseptic environment. Ensuring proper function of equipments. Providing surgeons with specific instruments & supplies for surgical field. Completing documentation. Positioning pts. Acting as scrub/circulating nurse. Members of the Surgical Team Patient Anesthesiologist or anesthetist Surgeon Nurses (Scrub & Circulating) Surgical technologists PATIENT the most important member of the surgical team. May feel relaxed & prepared, or fearful & highly stressed. is also subject to several risks. OPERATING SURGEON pre-op dx & care. performance of operation. post-op mgt & care assumes all responsibility for all medical acts of judgement & mgt. SURGEON & ASSISTANTS scrub & perform the surgery. REGISTERED NURSE 1ST ASST. practices under the direct supervision of the surgeon. (handling tissue, suturing, maintaining hemostasis) ANESTHESIOLOGIST / NURSE ANESTHETIST administers the anesthetic agent & monitors the pts physical status throughout the surgery. SCRUB NURSE provides sterile instruments & supplies to the surgeon during the procedure. performs surgical hand scrub. CIRCULATING NURSE coordinates the care of the pt. in the O.R. care provided includes assisting with pt. positioning , skin prep, managing surgical specimens & documenting intraoperative events. Prevention of Infection The surgical environment stark appearance & cool temperature. Located central to all supporting services. Unrestricted zone where street clothes are allowed.
Semirestricted zone where attire consists of scrub clothes & caps. Restricted zone where scrub clothes, shoe covers, caps & masks are worn.
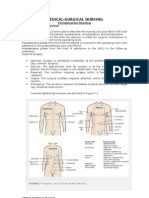
THE OPERATING ROOM Basic Guidelines for Surgical Asepsis All materials in contact with the wound and within the sterile field must be sterile. Gowns are sterile in the front from chest to the level of the sterile field, and sleeves from 2 inches above the elbow to the cuff. Only the top of a draped table is considered sterile. During draping, the drape is held well above the area and is placed from front to back. Items are dispensed by methods to preserve sterility. Movements of the surgical team are from sterile to sterile and from unsterile to sterile only. Movement around the sterile field must not cause contamination of the field. At least a 1-foot distance from the sterile field must be maintained. Whenever a sterile barrier is breached, the area is considered contaminated. Every sterile field is constantly maintained and monitored. Items of doubtful sterility are considered unsterile. Sterile fields are prepared as close as possible to time of use.
SURGICAL ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE BEFORE AN OPERATION, it is necessary to sterilize and keep sterile all instruments, materials, and supplies that come in contact with the surgical site. Every item handled by the surgeon and the surgeon's assistants must be sterile. The patient's skin and the hands of the members of the surgical team must be thoroughly scrubbed, prepared, and kept as aseptic as possible. DURING THE OPERATION, the surgeon, surgeon's assistants, and the scrub nurses must wear sterile gowns and gloves and must not touch anything that is not sterile. Maintaining sterile technique is a cooperative responsibility of the entire surgical team. Each member must develop a surgical conscience, a willingness to supervise and be supervised by others regarding the adherence to standards. Intraoperative Nursing Care Roles of team members Surgeon responsible for determining the preoperative diagnosis, the choice and execution of the surgical procedure, the explanation of the risks and benefits, obtaining inform consent and the postoperative management of the patients care. Scrub nurse (RN or Scrub tech)- preparation of supplies and equipment on the sterile field; maintenance of pt.s safety and integrity: observation of the scrubbed team for breaks in the sterile fields; provision of appropriate sterile instrumentation, sutures, and supplies; sharps count Circulating Nurse responsible for creating a safe environment, managing the activities outside the sterile field, providing nursing care to the patient. Documenting intraoperative nursing care and ensuring surgical specimens are identified and place in the right media. In charge of the instrument and sharps count
and communicating relevant information to individual outside of the OR, such as family members. Anesthesiologist and anesthetist anesthetizing the pt. providing appropriate levels of pain relief, monitoring the pts physiologic status and providing the best operative conditions for the surgeons.
Other personnel- pathologist, radiologist, perfusionist, EVS personnel.
Nursing Roles: Staff education Client/family teaching Support and reassurance Advocacy Control of the environment Provision of resources Maintenance of asepsis Monitoring of physiologic and psychological status Ensure sterility Alert for breaks Intraoperative Phase Anesthesia Greek word- anesthesis, meaning negative sensation. Artificially induced state of partial or total loss of sensation, occurring with or without consciousness. Blocks transmission of nerve impulses Suppress reflexes Promotes muscle relaxation Controlled level of unconsciousness Factors influencing dosage and type: Type and duration of the procedure Area of the body being operated on Whether the procedure is an emergency Options of management of post. Op. Pain How long it has been since the client ate, had any liquids, or any medications Intraoperative Phase Types of Anesthesia General method use when the surgery requires that the patient be unconscious and/or paralyzed. A general anesthetic acts by blocking awareness centers in the brain so that amnesia (loss of memory), analgesia (insensibility to pain), hypnosis (artificial sleep), and relaxation (rendering a part of the body less tense) occur. Stages of General Anesthesia Stage 1- Analgesia and sedation, relaxation Stage 2- Excitement, delirium Stage 3- Operative anesthesia, surgical anesthesia Stage 4- Danger
Types of Regional Anesthesia Topical (surface) Local Nerve Block Intravenous (Bier Block) Spinal Epidural (peridural) Complications of Local/Regional Anesthesia Anaphylaxis Administration technique Systemic absorption Overdosage
Spinal Anesthesia Indications -surgical procedures below the diaphragm -patients with cardiac or respiratory disease Advantages -mental status monitoring -shorter recovery Disadvantages -necessary extra expertise -possible patient pain Contraindications -coagulopathy -uncorrected hypovolemia Involved medications -lidocaine -bupivacaine -tetracaine Patient assessment -continuous heart rate, rhythm, and pulse oximetry monitoring -level of anesthesia -motor function and sensation return monitoring Complications -hypotension -bradycardia -urine retention -postural puncture headache -back pain Spinal analgesia Indications -postoperative pain from major surgery Involved medications -lipid-soluble drugs -preservative-free morphine Monitoring recovery -respiratory depression -urine depression -pruritus -nausea and vomiting Conscious Sedation Administration of IV sedative, hypnotic, and opioid medications. Produces a depressed level of consciousness Retains ability to maintain a patent airway Able to respond to verbal commands or physical stimulation Used for relatively short procedures
Complications of General Anesthesia Overdose Hypoventilation Related to anesthetic agents Malignant hyperthermia Related to intubation
Local or Regional Anesthesia Temporarily interrupts the transmission of sensory nerve impulses from a specific area or region. Motor function may or may not be affected Client does not lose consciousness Gag reflex remains intact Supplemented with sedatives, opioids, or hypnotics
Postoperative Nursing Care Nursing assessment in the PACU Vital signs- presence of artificial airway, 02 sat,BP,pulse, temperature. LOC- ability to follow command, pupillary response Urinary output Skin integrity Pain Condition of surgical wound Presence of IV lines Position of patient Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective airway clearance- increased secretions 2 to anesthesia, ineffective cough, pain Ineffective breathing pattern- anesthetic and drug effects, incisional pain Acute pain Urinary retention Risk for infection Assessment of the Postanesthesia Client Airway Vital signs Cardiac monitoring Peripheral vascular assessment Level of consciousness (LOC) Fluid and electrolytes GI system Integumentary system Discomfort/pain Postoperative Management Maintain a patent airway Stabilize vital signs Ensure patient safety Provide pain relief Recognize & manage complications When caring for post-surgical patient, think of the 4 Ws Wind: prevent respiratory complications Wound: prevent infection Water: monitor I & O Walk: prevent thrombophlebitis
Treatment: Call for help Cover with sterile NS soaked gauze/towels Keep moist DO NOT ATTEMPT TO REINSERT ORGANS. Keep in supine position with knees/hips bent Assessment/VS q 5 min. until MD arrive Prepare for surgery.
Gerontologic considerations Mental status- attributed to medications, pain, anxiety, depression. Delirium- infection, malignancy, trauma, MI, CHF, opioid use. Dementia-sundowning-sleep disturbances, lack of structure in the afternoon or early morning, sleep apnea.
Complications Respiratory- atelectasis, pulm. Embolus Cardiovascular- venous thrombosis Gastrointestinal-Hiccoughs, N/V,abd. Distention, paralytic ileus, stress ulcer. GU- urinary retention Hemorrhage-slipping of a ligature(suture) Wound infection Wound dehiscence and evisceration-
Dehiscence
Partial or complete separation of the outer layer of the wound. Possible causes: Poor suturing technique Distention Excessive vomiting Excessive coughing Dehydration Infection
Total separation of the layers & protrusion of internal organs or viscera through the open wound. Causes: same as dehiscence
Evisceration
You might also like
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDocument37 pagesBasic Surgical Instrumentsapi-2658787991% (33)
- Peri - Operative Nursing: Learning Manual DescriptionDocument41 pagesPeri - Operative Nursing: Learning Manual DescriptionCezanne Cruz100% (4)
- Perioperative Nursing LectureDocument125 pagesPerioperative Nursing LectureHazel Von S. Bravo88% (24)
- Operating Room ChartingDocument1 pageOperating Room ChartingJan Niño Estrella100% (4)
- Perioperative Nursing - 50 ItemsDocument6 pagesPerioperative Nursing - 50 Itemsapi-371817496% (26)
- Duties of Scrub Nurse & Circulating NurseDocument2 pagesDuties of Scrub Nurse & Circulating Nurseimafashionista90% (21)
- Or & DR InstrumentsDocument31 pagesOr & DR InstrumentsJustin Kristoffer Mendoza0% (1)
- Perioperative Nursing 1Document2 pagesPerioperative Nursing 1Rosie Cuasito100% (2)
- Perioperative Nursing ConceptDocument21 pagesPerioperative Nursing ConceptArgee Alonsabe100% (8)
- Perioperative Nursing 50 QuestionsDocument14 pagesPerioperative Nursing 50 QuestionsPaul Anthony Lorica100% (3)
- Perioperative Nursing - OrIGINALDocument176 pagesPerioperative Nursing - OrIGINALJamil Lorca100% (4)
- NCM 120 Decent Work Employment and Transcultural NursingDocument18 pagesNCM 120 Decent Work Employment and Transcultural NursingFrancia Toledano50% (2)
- Perioperative NursingDocument141 pagesPerioperative NursingJustin Ahorro-Dionisio100% (2)
- Perioperative NursingDocument9 pagesPerioperative NursingLouie Kem Anthony BabaranNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing: Prepared By: Annabeth K. Salonga RN, MANDocument67 pagesPerioperative Nursing: Prepared By: Annabeth K. Salonga RN, MANAnnabeth Kwong Salonga100% (2)
- Peri Operative NursingDocument214 pagesPeri Operative NursingJohn Ervin Agena100% (2)
- Reviewer in Perioperative NursingDocument12 pagesReviewer in Perioperative NursingIrish Jane Gallo100% (11)
- Exam Sa PeriopDocument5 pagesExam Sa PeriopAngelica Barcelona YumangNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument18 pagesPerioperative Nursinglagunda100% (2)
- Perioperative NursingDocument32 pagesPerioperative NursingMaria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia II100% (2)
- Operating Room Technique WordDocument9 pagesOperating Room Technique WordKaloy ZerrudoNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument12 pagesPerioperative Nursingtheglobalnursing100% (12)
- Emergency and Disaster NursingDocument20 pagesEmergency and Disaster NursingNeil Cuasito89% (9)
- 1.perioperative Nursing ConceptsDocument35 pages1.perioperative Nursing ConceptsChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument41 pagesPerioperative Nursingbajaoc100% (8)
- Perioperative Nursing Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPerioperative Nursing Practice QuestionsCharisse Lutero100% (4)
- Perioperative Nursing SkillsDocument278 pagesPerioperative Nursing SkillsNacel Celeste100% (3)
- Sample Nursing Practice Test On OncologyDocument3 pagesSample Nursing Practice Test On OncologyFilipino Nurses Central100% (2)
- Perioperative Nursing 50 ItemsDocument4 pagesPerioperative Nursing 50 ItemsKrestel Saligumba Palanog100% (3)
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument6 pagesSurgical Instrumentsgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- NCM 118Document5 pagesNCM 118lalaine nadulpitNo ratings yet
- Operating RoomDocument4 pagesOperating RoomKristine Anne Liquiran Avenado100% (1)
- Operating Room TeamDocument7 pagesOperating Room TeamFaruqueHossain100% (1)
- Principles of Patient Skin PreparationDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Patient Skin PreparationKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Perioperative NursingDocument8 pagesPerioperative NursingJaney Ceniza تNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing ManagementDocument14 pagesPerioperative Nursing ManagementMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative NursingDocument41 pagesIntraoperative NursingBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (11)
- 50 Items Peripertative NursingDocument5 pages50 Items Peripertative NursingKez DomineNo ratings yet
- OR Exam July 2019Document4 pagesOR Exam July 2019Maria Sheila Belza100% (4)
- Nursing Board Exam Review Questions in Emergency Part 6/20Document15 pagesNursing Board Exam Review Questions in Emergency Part 6/20Tyron Rigor Silos100% (5)
- Diagnostic - 3answer KeyDocument35 pagesDiagnostic - 3answer KeyJune Dumdumaya100% (2)
- Instruments in Operating RoomDocument6 pagesInstruments in Operating Roomanna_villanueva_8No ratings yet
- RA 9173 Plus Other LawsDocument6 pagesRA 9173 Plus Other LawsKarl Gabriel Bonifacio100% (1)
- Intraoperative Phase 2021Document62 pagesIntraoperative Phase 2021Jmarie Brillantes PopiocoNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing1Document141 pagesPerioperative Nursing1Jordan Bautista100% (1)
- Perioperative Nursing: Rachelle M. Ganuelas RN, MANDocument66 pagesPerioperative Nursing: Rachelle M. Ganuelas RN, MANdianahazel_03No ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing UnpDocument140 pagesPerioperative Nursing Unprnrmmanphd100% (1)
- Perioperative Nursing - 2edited For BSN 3Document122 pagesPerioperative Nursing - 2edited For BSN 3JL D. BusiaNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing CDDocument66 pagesPerioperative Nursing CDJoanne ButacNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients Requiring SurgeryDocument4 pagesCare of Clients Requiring SurgeryMichelle Tamor100% (1)
- Operating Room Nursing: Vergel G. Leonardo Rn. ManDocument72 pagesOperating Room Nursing: Vergel G. Leonardo Rn. ManRalph Lorenz Avila AquinoNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument11 pagesContentSHERMINA HASANNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument15 pagesPerioperative Nursingmblanco.dchNo ratings yet
- BSN3-1 Perioperative-Nursing 2021Document236 pagesBSN3-1 Perioperative-Nursing 2021Ms MedSurg Nursin100% (2)
- 3 Phases of Operating Room Technique: Preoperative Phase Intraoperative Phase Post Operative PhaseDocument76 pages3 Phases of Operating Room Technique: Preoperative Phase Intraoperative Phase Post Operative Phasejamaica cabriga100% (1)
- Perioperative Nursing (1) 2007Document14 pagesPerioperative Nursing (1) 2007Lorraine BuelvaNo ratings yet
- MS Reviewer PrelimDocument23 pagesMS Reviewer PrelimCindy GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing: Lecturer: Mr. Renato D. Lacanilao, RN, MANDocument27 pagesPerioperative Nursing: Lecturer: Mr. Renato D. Lacanilao, RN, MANJmarie Brillantes PopiocoNo ratings yet
- Perioperative LectDocument134 pagesPerioperative LectJane Ann AlolodNo ratings yet