Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hesi Study Guide
Uploaded by
angie10231Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hesi Study Guide
Uploaded by
angie10231Copyright:
Available Formats
Study Recommendations for HESI Admissions
Assessment Test
BIOLOGY
Please refer to your textbooks used in BIOL 105 (formerly BIOL100) and your
Anatomy & Physiology courses.
Properties of Water (an Inorganic Compound)
PoIarity of MoIecuIes
BioIogicaI MoIecuIes ("Organic Compounds"):
Carbohydrates, including glycogen and starch
Lipids
Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fats
Phospholipids
Steroids
Proteins
Structural (Fibrous) vs. Functional (Globular, including Enzyme) Proteins
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA
Enzymes as Catalysts for Metabolic Processes
ATP
CeII Structure and Function
Nucleus
Chromosomes (Chromatin)
Ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):
Rough ER
Smooth ER
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
2
Gogi Apparatus
Lysosomes
nclusions (Vacuoles)
Mitochondria
Plasma (Cell) Membrane
Proteins of the Cell Membrane and their functions
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Diffusion
Osmosis
Filtration
(AsexuaI) CeIIuIar Growth and Reproduction
(see also "Binary Fission," for bacteria, below)
Mitosis: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
cytokinesis
SexuaI CeIIuIar Reproduction:
Meiosis: Meiosis and Meiosis
Genetic Code
DNA
A, T, G and C nitrogenous bases
Double Helix structure
RepIication
Transcription
TransIation:
Codon
Anticodon
.
Necessary Life Functions (Characteristics of Cells/Living Organisms)
Homeostasis
Positive Feedback versus Negative Feedback
MetaboIism:
Anabolism
Catabolism
CeIIuIar Respiration:
Aerobic:
Glycolysis
Kreb's Cycle:
NADH, FADH2
Electron Transport Chain
Anaerobic (Fermentation)
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
3
The following topics may not be found in your Human Anatomy &
Physiology texts, but may be reviewed using the listed web links.
Genetics: http://library.thinkquest.org/C004367/be1.shtml
Genotype versus Phenotype
Dominant and Recessive Traits
Alleles
Homozygous vs. Heterozygous Traits
Punnett Squares: http://anthro.palomar.edu/mendel/mendel_2.htm
Pedigree
Polygenes and Environmental Factors (Multifactorial nheritance)
Organization of Species:
Know aII Kingdoms, incIuding Monera (bacteria) and AnimaIia
(incIudes humans)
This site will help you understand the Kingdoms. t is a bit confusing to study this topic at
this time, as science is in a transitional stage of re-classifying all living creatures, due to
recent new information. Understand that the single-celled bacteria (former Kingdom
Monera) belong to the Prokaryotes, and differ from the Eukaryotes (which include most
plants and all animals, including humans). Note that the term "Prokaryote," which you
may understand to be basically single-celled bacteria, is not mentioned at the first site
below, but is understood to be the combination of Archea and Eubacteria...every other
being on earth is in the Domain Eukarya, and is thus a Eukaryote. The second site listed
below will also be helpful, as it distinguishes the characteristics of Eukaryotes from those
of the Prokaryotes.
http://www.palaeos.com/Kingdoms/kingdoms.htm#kingdoms
Theory of EvoIution:
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/educators/course/session2/explain_c_
pop2.html
Scientific Method:
http://teacher.nsrl.rochester.edu/phy_labs/AppendixE/AppendixE.html
Density:
http://physics.about.com/od/fluidmechanics/f/density.htm
Specific Heat:
http://www.iun.edu/~cpanhd/C101webnotes/matter-andenergy/
specificheat.html
SoIutions: http://www.sparknotes.com/chemistry/solutions/composition
click on "Terms" "Solution Composition" and "Problems and Solutions"
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
4
Photosynthesis and ChIoropIasts:
Describe the basic chemicaI equation:
http://www.life.uiuc.edu/bio100/lectures/s97lects/07Photosynthesis/photosynsumm.html
http://biology.about.com/od/plantbiology/a/aa050605a.htm
Binary Fission: a type of AsexuaI CeIIuIar Reproduction used by bacteria,
not humans
The method by which bacteria reproduce. The circular DNA molecule is
replicated; then the cell splits into two identical cells, each containing an exact
copy of the original cell's DNA.
CHEMISTRY
The following topics are may not be found in your Human Anatomy &
Physiology texts, but may be reviewed using the listed web links.
States of Matter, and Changes of State of Matter: SoIid, Liquid and Gas
Mixtures: Homogeneous versus Heterogeneous
http://www.iun.edu/~cpanhd/C101webnotes/matter-and-energy/elscmpdsmxts.html
Atomic Structure:
http://www.smuhsd.k12.ca.us/bhs/science-dept/marcan/APpdfs/chap02notes.pdf
Protons, Electrons, Neutrons:
mass, location and charge of each
Orbitals versus Nucleus of Atom
Atomic Number
Atomic Mass
Isotopes
Ions: Cations versus Anions
ChemicaI Bonding:
Covalent versus onic
Polar versus Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Single-, Double-, and Triple-Covalent Bonds
Hydrogen Bonding
http: www.sparknotes.com
Click on "Sparknotes Free Study Guide" tab (top left corner)
Click on Study Guide Category "Chemistry"
Select topic from items in "Bonding" list
Acids and Bases:
Characteristics of Acids
Characteristics of Bases
Neutralization
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
5
pH scale
http://lrs.ed.uiuc.edu/students/erlinger/water/background/ph.html
ChemicaI versus PhysicaI Changes/Properties
http://www.iun.edu/~cpanhd/C101webnotes/matter-and-energy/properties.html
http://www.learner.org/channel/courses/essential/physicalsci/session4/closer1.html
Periodic TabIe of EIements:
http://www.iun.edu/~cpanhd/C101webnotes/composition/elements.html
A Periodic Table to print out, when reading about "Trends," below:
http://www.webelements.com/
Characteristics of Groups and Rows in the Periodic Table, including ons
and Noble Gases Trends in the Periodic Table:
http://chemistry.about.com/library/weekly/aa071802a.htm
ChemicaI Equations: Reactants versus Products
http://www.iun.edu/~cpanhd/C101webnotes/chemical%20reactions/chemicalrxn.html
ChemicaI Reactions: synthesis, decomposition, combustion (oxidationreduction,
or "redox"), single- and double- exchange (or replacement, or
displacement)
http://misterguch.brinkster.net/6typesofchemicalrxn.html
Rates of ChemicaI Reactions
Reversible versus rreversible Reactions
Effects Due to Changes in: Temperature, Particle Size (Surface Area),
Concentration of Reactants, Addition of a Catalyst
http://www.purchon.com/chemistry/rates.htm
MoIes: Definition
MoIar CaIcuIations:
Calculation of number of molecules of a substance, given the
number of moles; Calculation of number of grams of a substance, given the
number of moles of that substance; Calculate the number of moles of a
substance, given the weight in grams:
http://dbhs.wvusd.k12.ca.us/webdocs/Solutions/Molarity.html
http://antoine.frostburg.edu/chem/senese/101/moles/index.shtml
NucIear Chemistry: radioactivity, and reIease of aIpha, beta and gamma
radiation
http://www.lbl.gov/abc/Basic.html
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
6
Law of Conservation of Matter (Mass):
http://www.iun.edu/~cpanhd/C101webnotes/matter-and-energy/masscons.html
http://www.iun.edu/~cpanhd/C101webnotes/chemical%20reactions/massconservation.html
Van der WaaIs Forces:
http://www.ausetute.com.au/intermof.html
Stoichiometry: BaIancing simpIe chemicaI equations
http://www.ausetute.com.au/balcheme.html
Oxidation States:
Definition: An oxidation number (oxidation state) is the charge an
atom wouId carry if the moIecuIe or ion were compIeteIy ionic
RuIes for Determining Oxidation States:
For elements, the oxidation number is the number of electrons the
element would have to lose or gain in order to have a complete outer
shell. (e.g., Oxygen would be assigned "-2" as it would have to accept two
additional negatively charged electrons to complete its outer shell).
http://www.ausetute.com.au/oxistate.html
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
The following information can be found in your Anatomy & Physiology
texts.
Homeostasis
LeveIs of StructuraI Organization (cells to organisms)
DirectionaI Terms:
Superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral
Planes of the Body:
Median (Sagittal), Coronal (Frontal), Transverse (Horizontal)
Body Cavities (Know location and organ contents):
Dorsal: cranial and spinal
Ventral: orbits, nasal, oral, thoracic, mediastinum, pericardial, pleural and
abdominopelvic (peritoneal)
Membranes of Body Cavities
(pleural, pericardial, peritoneal)
Know the Four Major Tissues and the Function of Each:
Epithelial Tissue:
Types of Membranes and their Definitions:
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
7
Mucous, Serous, Synovial and Cutaneous
Connective Tissues:
Cartilage, Bone, Blood, Adipose, Dense, Loose
Muscle Tissue:
voluntary and involuntary; smooth, cardiac and skeletal
Nerve Tissue
Glands: sudoriferous, sebaceous, ceruminous
Review of Parts (OrganeIIes) of the CeII (see Iisting under BioIogy, above)
Integumentary System
Epidermal and Dermal Structures
What is keratin, and keratized epithelium?
Strata of the Epidermis: stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum
granulosum and stratum germinativum/basale (mitotic layer)
Subcutaneous Tissue (Hypodermis): know definition
Sebaceous and Sudoriferous Glands
Functions of the Skin
Appendages of the Skin: hair, nails
SkeIetaI System
Functions of the skeletal system
Classification of bones by shape
Osteocytes/Osteoblasts/Osteoclasts
Spongy versus Compact bone
Axial versus Appendicular bones
Number of bones in the body, Names of all the bones and numbers of
each type (including numbers and types of vertebrae, names and numbers
of cranial bones, facial bones).
Term to Know: foramen magnum and its significance
MuscuIar System
Organization:
muscles, muscle cell, myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomeres
Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction:
role of actin, myosin, ATP, calcium
Muscle Types:
Voluntary versus nvoluntary versus Cardiac
Prime Mover, Agonists, Antagonists
Classification of Muscles as Flexors, Extensors, Abductors, Adductors
Naming of Muscles Related to location, origin, insertion, shape, function
(action)
Know the names of all major contour (surface) muscles of body.
Terms to Know: Joint, Tendon, Ligament, Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
8
Nervous System
Basic Functions
Anatomy of Neuron
Conduction of a Nerve mpulse through the Neuron
Sensory (afferent) versus Motor (efferent) Neurons
Central Nervous System versus Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic (Voluntary) Nervous System versus Autonomic Nervous System
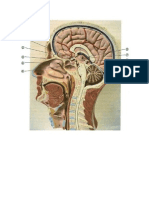
Major Parts of the Brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla oblongata) and
their Functions
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves:
Simple spinal reflexes versus reflexes modified by ascending and
descending tracts
Sensory versus motor impulses
Dorsal horns versus ventral horns
Definitions: foramen magnum, spinal (vertebral) column
Endocrine System
Definition of a Hormone
Hierarchical Levels of Control:
Hypothalamus, pituitary (master gland), other endocrine gland(s),
target tissue(s)
Pituitary:
Anterior (Adenohypophysis) versus Posterior (Neurohypophysis)
Locations in the Body, Hormones Secreted by Each, Hormone Actions,
and Disorders Associated with Abnormal Levels of each Hormone, for
each of the following:
Anterior Pituitary:
Pay particular attention to: GH/STH, ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH,
PRL
Posterior Pituitary:
ADH, oxytocin
Major Endocrine Organs: Thyroid, Parathyroids, Adrenals,
Pancreas, Gonads (Ovaries, Testes), Pineal
Organs Other Than Major Endocrine Organs
Hypothalamus
Adrenal Cortex and Functions of Cortisol
Basic Actions of Hormones:
alteration of cellular growth, differentiation, or metabolic activity
Mechanism of Action of Steroid Hormones versus Protein Hormones
Major Groups of Hormones: steroids versus protein hormones
CircuIatory System:
Composition of Whole Blood: 55% plasma, 45% formed elements
Composition of Plasma
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
9
Blood Elements and their Functions:
Erythrocytes, Leukocytes, Platelets
Genesis in Red Bone Marrow of RBC, WBC and platelets
5 types of Leukocytes and how they differ:
size, nucleus appearance, staining properties, granule type
Functions of Blood, including mmune Functions
Normal pH of Blood
Terms to Know: Antibody, Phagocytosis
Atria versus Ventricles
Systemic Circulation versus Pulmonary Circulation
Pathway of Blood Flow through the System and Pulmonary Circulatory
Systems
including names of chambers and valves of heart
names of major arteries and veins entering and leaving the heart
and lungs
Pathway of Cardiac Electrical Conduction
Systole versus Diastole
EKG rhythm
Differences between Arteries and Veins
Vasocontriction versus Vasodilation
Skeletal Muscle Pump action to assist venous return to heart; venous
return is also assisted by breathing movements and unidirectional valves
List all the major Arteries and Veins of the body
Respiratory System:
Basic Functions
Basic Structures: nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea,
bronchi, lungs, diaphragm, and rib cage muscles and bones.
Control of respiratory rate via medulla oblongata
nternal versus External Respiration
describe the process of gas exchange
nhalation versus Exhalation
Active versus Passive Process, respectively
Trace the pathways of oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the
circulatory system.
Transport of Oxygen via Erythrocytes; bound to Hemoglobin
Transport of Carbon Dioxide in the form of bicarbonate ion
Regulation of Blood pH by Respiratory System via regulation of
bicarbonate ion
Digestive System
Alimentary Canal/Digestive Tube or Tract/Gastrointestinal Tract
Basic Functions:
ingestion, propulsion, mechanical digestion, chemical
digestion, absorption, secretion, defecation (elimination)
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
10
Basic Structures, their secretions, and their specific functions:
oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine
(duodenum, jejunum, ileum), large intestine (cecum, appendix, ascending
colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon), rectum, anus
Accessory Digestive Organs, their secretions, and their
specific functions:
liver, gallbladder, pancreas
Mechanical Digestion versus Chemical Digestion
Mastication (Chewing)
Functions of Saliva; salivary amylase
Terms to Know: Bolus, Chyme, Bile
Hydrochloric Acid Secretion by Stomach
Four Layers of the Wall of the Digestive Tract:
mucous membrane, submucous layer, muscular layer and serous
layer (serosa)
Trace the pathway of food through the digestive tract, noting the enzymes
and glandular products that are mixed with the food at each step.
Understand the biomolecules that are digested by each enzyme, and the
monomer "building blocks" of each biomolecule:
amino acids, fatty acids, glucose and other simple sugars,
nucleotides
Lymphatics: absorption of fats via lacteals, and transport to bloodstream
Small intestine: absorption of nutrient building blocks by villi
Large intestine: absorption of water
Bacterial colonization of large intestine (intestinal flora)
Urinary System
Basic Functions
Basic Structures and their specific Functions:
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
Transitional Epithelium of the Urinary System
How does the male urethra differ from the female urethra?
Nephron Structure and Function:
trace the pathway of filtered blood through all the structures of the
kidney and their nephrons (starting with the renal artery), then trace
the pathway of urine through the remaining organs of the urinary
system from collecting ducts through the urethra. Know the terms
Bowman's capsule and glomerulus.
Movement of substances across the nephron: filtration, secretion,
reabsorption. Both active and passive movement (diffusion) occurs.
Role of Kidney in Regulating Blood pH: Acidosis and Alkalosis
Reproductive System
Functions: produce hormones, produce sex cells (gametes)
List all the Organs of the Reproductive Tract in Both Sexes
Control by Pituitary Gland
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
11
Comparison of Male and Female Reproductive Tracts, including
cyclic nature of sex cell production and hormone levels in female
versus continuous nature in males
Secondary Sex Characteristics in both sexes
Know the Layers of the Uterine Wall, and how they change under
hormonal control
Control of Production of Male and Female Gametes by Hormones:
FSH, CSH, LH, testosterone, estrogen, progesterone
Review of Meiosis
Trace the pathway of Sperm Development and Emission through the male
reproductive tract.
Trace the origin and path of the ovum during Fertilization and mplantation
(as the blastocyst); fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube (oviduct).
Review the changes in the uterine lining, and the changes in hormonal
levels, during the Menstrual Cycle; ovulation occurs at Day 14.
Role of the Corpus Luteum
Review the Development of the Embryo during pregnancy: placenta,
formation of embryonic tissues (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm).
How do hormonal levels change throughout pregnancy, and what are all
the tissues they affect in the mother?
Role of Placenta in Maintaining Milk Production; Role of Prolactin
Terms to Know: Embryo, Chromosome, Zygote
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
12
MATH
Without using a caIcuIator, take the following Math Quiz, then check your
answers against the Answer Key, below.
You will also find it helpful to memorize the foIIowing information:
Understanding Roman NumeraIs:
http://www.factmonster.com/ipka/A0769547.html
Conversion between Fahrenheit and CeIsius:
C = (5/9) x (F - 32) or F = [(9/5) x C] + 32
C = degree in Celsius, F = degrees in Fahrenheit]
Boiling Point of Water: 100 degrees Celsius; 212 degrees Fahrenheit
Freezing Point of Water: 0 degrees Celsius; 32 degrees Fahrenheit
http://avc.comm.nsdlib.org/cgi-bin/wiki_grade_interface.pl?Converting_Temperatures
http://www.fordhamprep.org/gcurran/sho/sho/lessons/lesson29.htm
Metric Conversions: Conversion between units in the metric system
1 miIIiIiter = 1 cubic centimeter (cc)
http://vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/Miscellaneous/ConversionTables/conversion_table.html
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
13
Math Quiz
Basic Addition:
1. 359+ 2,204
2. 247+ 4,309
Basic Subtraction:
3. 4,907- 3,478
4. 5,812- 2,434
5. 369 - 241 = _______________
6. 2,345 - 2008 = ______________
Basic Multiplication:
7. 319x 914
8. 888x 296
9. 825 x 14 = _______________
10. 788 x 139 = _______________
For problems 11 - 13, round to the nearest whole number.
11. 4,056 5 = ______________
12. 4,443 12 = _______________
13. = _____________
Addition of Decimals (report all decimal places in your answer):
14. 2.278 + 1.4 + 22 = _____________
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
14
15. 98.0 + 27 + 1.2 + 0.34 = _______________
Subtraction of Decimals:
16. 15 - 5.43 = ______________
17. 44.56 - 12 = _______________
For problems 18 and 19, round to the tenths place.
Multiplication of Decimals:
18. 439.1 x 34 = _____________
19. 0.032 x 435.2 = ______________
For problems 20 - 22, round your answer to the hundredths place.
Division with Decimals:
20. 56 0.3 = _______________
21. 3.445 0.25 = _______________
22. 3.25 5.6 = _______________
Addition of Fractions:
23. 2 + 4 = ____________
7 5
24. 2 5 + 6 8 = ____________
7 9
25. 3 4 + 12 1 = ____________
5 3
Subtraction of Fractions:
26. 22 - 4 = ____________
37 37
27. 21 13 - 2 6 = ____________
14 7
28. 6 4 - 1 1 = ____________
5 10
Multiplication of Fractions:
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
15
29. 2 x 4 = ____________
7 7
30. 1 13 x 2 2 = ____________
14 3
31. 6 3 x 2 = ____________
4
Division of Fractions:
32. 6 4 = ____________
7 5
33. 6 1 = ____________
8
34. 9 4 3 = ____________
7
For problems 35 and 36, round to the hundredths place.
Change these fractions to decimals:
35. 5 = ____________
6
36. 19 1 = ____________
7
Change these decimals to fractions:
37. 5.032 = _____________
38. 0.02 = _____________
39. 7.29 = _____________
Change each number from a fraction into a ratio:
40. 12 = ____________
15
41. 17 = ____________
20
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
16
Solve for x:
42. 4:3 :: 16:x x = _____________
43. 18:27 :: 9:x x = _____________
Change each decimal to a percent:
44. 0.98 = _____________
45. .00043 = _____________
Change each percent into a decimal:
46. 65% = _____________
47. 0.03% = _____________
48. 14.3% = _____________
Round to the tenths place for problems 49 and 50.
Change each fraction into a percent.
49. 4 = ____________
7
50. 2 = ____________
13
Round to the nearest whole number for problem 51.
51. What is 3 out of 7, as a percent? ____________
52. What is 20 out of 100, as a percent? ____________
53. What is 15% of 900? ____________
For problem 54, report your answer to the tenths place.
54. What is 3.5% of 24? ____________
55. 4 is 1% of what number? ____________
56. 3 is 15% of what number? ____________
57. What is the numerical value of the Roman number V? ____________
58. What is the numerical value of the Roman number X? ____________
HES A2 Study Recommendations
Rev 12/08 CPM
17
Answer Key to Math Quiz
1. 2,563
2. 4,556
3. 1,429
4. 3,378
5. 128
6. 337
7. 291,566
8. 262,848
9. 11,550
10. 109,532
11. 811
12. 370
13. 108
14. 25.678
15. 126.54
16. 9.57
17. 32.56
18. 14,929.4
19. 13.9
20. 186.67
21. 13.78
22. 0.58
23. 1 3
35
24. 9 38
63
25. 16 2
15
26. 18
37
27. 19 1
14
28. 5 7
10
29. 8
49
30. 5 1
7
31. 13 1
2
32. 1 1
14
33. 48
34. 3 4
21
35. 0.83
36. 19.14
37. 5 4
125
38. 1
50
39. 7 29
100
40. 4:5
41. 17:20
42. 12
43. 13.5
44. 98%
45. 0.043%
46. 0.65
47. 0.0003
48. 0.143
49. 57.1%
50. 15.4%
51. 43%
52. 20%
53. 135
54. 0.84
55. 400
56. 20
57. 8
58. 11
1/07 KC
HESI A2 PreTest PLATO
If you have a PLATO login, go to the " LnC Quick Links on the LnC pages and
click on PLATO, or go directly to http://plato.davenport.edu and log in by entering
your PLATO Name, Group Name (HES) and your password.
If you do not have a PLATO login, follow the directions under "Create a PLATO
login at this web page:
http://dnn4.davenport.edu/LibrarynformationCommonsLnC/TutoringServices/Tut
orials/PLATO/tabid/190/Default.aspx
PLATO BioIogy Series
Click on the following sections. Unless indicated by bullets, complete the entire
tutorial's menu in order to cover the basics of Biology.
ntroduction to Biology
Biology the Study of Life
Signs of Life
V Scientific Method
The Energy and Chemistry of Life
Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis
Enzymes
Biochemistry
Cell Structure and Specialization
The plasma membrane and cellular transport
Mitosis
Meiosis
Genetics and Evolution
Mendel's Principles of Heredity
nvestigating Heredity
DNA: The Molecules of Life
From DNA to Protein
The Diversity of Life
Classification of Living Things
ntroduction
Criteria for Classification
V The 5 Kingdom Classification
V The 6 Kingdom Classification
1/07 KC
PLATO Chemistry Series
Click on the following sections. Unless indicated by bullets, complete the entire
tutorial's menu in order to cover the basics of Chemistry,
Introductory Chemistry
ntroduction to Chemistry
Atomic Structure
Periodic Table and Trends
ntroduction
B. Periodic Table Organizes the Elements
V. The Modern Periodic Table
Properties of Acids, Bases, and Salts
Bonding
Gases & Their Properties
Physical Properties of Gases
A. Gases are States of Matter
1 &2
B. Variables Used to Describe Gases
1 4
Solutions
Solution ntroduction
B. Heterogeneous Mixtures
C. Homogeneous Mixtures
D. Components of a Solution
V Solution Concentrations
Relative Terms
Molarity
Molality
Molar Fraction
ChemicaI Transformations
Formulas, Equations, & Stoichiometry
Chemical Equilibrium
Review of Chemical Reactions
Chemical Reactions
V Chemical Equations
All
Reaction Rates
Rates of Reactions
The Concept of Rates
Factors Affecting Reactions Rates (All)
PLATO FoundationaI Mathematics
This is a complete review of mathematics. Depending on your math skills, you
may not need to complete all tutorials within each section.
Adding and Subtracting Whole Numbers 1
Adding and Subtracting Whole Numbers 2
Multiplying Whole Numbers
Dividing Whole Numbers
Understanding Fractions
Adding and Subtracting Fractions
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
Understanding Decimals
Performing Operations with Decimals
Working with a Percentage
Understanding Ratios and Proportions
Using Geometry
Measurements
You might also like
- Nursing HESI A2: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference & Study GuideFrom EverandNursing HESI A2: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference & Study GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Study Recommendations For HESI Admissions Assessment TestDocument20 pagesStudy Recommendations For HESI Admissions Assessment TestNibin Varghese0% (1)
- HESI A2 Admission Assessment Study Guide: COMPLETE Health Information Systems A2® Study Guide and Practice Test Questions prepared by a dedicated team of test experts!From EverandHESI A2 Admission Assessment Study Guide: COMPLETE Health Information Systems A2® Study Guide and Practice Test Questions prepared by a dedicated team of test experts!No ratings yet
- Hesi Entrance Examination Study GuideDocument195 pagesHesi Entrance Examination Study Guidetken35100% (2)
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- All Hesi HintsDocument27 pagesAll Hesi Hintsangieswenson100% (34)
- A&P Target ScoresDocument72 pagesA&P Target ScoresMercurie8592% (12)
- NLN PAX Practice: PAX-RN Practice Test QuestionsFrom EverandNLN PAX Practice: PAX-RN Practice Test QuestionsNo ratings yet
- HESI Entrance Exam Study Guide - Math, Reading, Vocabulary, GrammarDocument195 pagesHESI Entrance Exam Study Guide - Math, Reading, Vocabulary, Grammarindnracn2100% (1)
- Nursing School Entrance Exams: HESI A2 / NLN PAX-RN / PSB-RN / RNEE / TEASFrom EverandNursing School Entrance Exams: HESI A2 / NLN PAX-RN / PSB-RN / RNEE / TEASNo ratings yet
- A&P Target ScoresDocument13 pagesA&P Target Scoresmailtoramann100% (1)
- Hesi Retake Exam 2023Document32 pagesHesi Retake Exam 2023Nelson Mandela100% (1)
- TEAS Test Strategy!: Winning Multiple Choice Strategies for the Test of Essential Academic SkillsFrom EverandTEAS Test Strategy!: Winning Multiple Choice Strategies for the Test of Essential Academic SkillsNo ratings yet
- ATI SecretsDocument9 pagesATI SecretsBritanny Nelson100% (11)
- NURSING SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS FOR REGISTERED AND GRADUATE NURSES (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING SCHOOL ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS FOR REGISTERED AND GRADUATE NURSES (RN): Passbooks Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CONDENSED HESI STUDY GUIDEDocument217 pagesCONDENSED HESI STUDY GUIDEggrrk781% (16)
- Ati AnatomyPhysiology QA Ati TeasDocument7 pagesAti AnatomyPhysiology QA Ati TeasNelson MandelaNo ratings yet
- abdominopelvic cavityDocument4 pagesabdominopelvic cavitydapheticNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills 1620832771Document1,429 pagesNursing Skills 1620832771Yoan PoquizNo ratings yet
- 73 77 The Nursing BibleDocument129 pages73 77 The Nursing BibleChrisana Lawrence100% (2)
- Med-Surg Nursing NotesDocument232 pagesMed-Surg Nursing NotesMaria100% (4)
- English Guide Ati TeasDocument25 pagesEnglish Guide Ati TeasMarta Sampere100% (1)
- Nursing ChoiceDocument703 pagesNursing Choicedragutin7petri7100% (1)
- Pediatric Ati RN NotesDocument20 pagesPediatric Ati RN NotesVin Lorenzo CampbellNo ratings yet
- HESIDocument6 pagesHESIDuvu99No ratings yet
- Teas Topics To StudyDocument6 pagesTeas Topics To StudyDanielle Shull100% (12)
- NCLEX-PN Exam Comprehensive Review HESI Prepared by Jeffrey B ViernesTITLENCLEX Nursing Skills and Concepts ReviewDocument38 pagesNCLEX-PN Exam Comprehensive Review HESI Prepared by Jeffrey B ViernesTITLENCLEX Nursing Skills and Concepts ReviewJeffrey Viernes100% (29)
- HESI A2 Entrance Exam Practice TestDocument9 pagesHESI A2 Entrance Exam Practice TestTestGuide100% (2)
- Hesi FundamentalsDocument14 pagesHesi Fundamentalscharitoave90% (20)
- HESI A2 Info Page For StudentsDocument3 pagesHESI A2 Info Page For Studentssunny181100% (2)
- TEAS Version 6 Real Exam Questions Bank and Practice TestDocument5 pagesTEAS Version 6 Real Exam Questions Bank and Practice TestTango Cash100% (1)
- DeWit - Studyguide - Answers - Fundamental Concepts - 4th EdDocument79 pagesDeWit - Studyguide - Answers - Fundamental Concepts - 4th Edsicu case82% (11)
- Cece S Study Guides Part 2Document26 pagesCece S Study Guides Part 2Mikaela Joson100% (1)
- ATI TEAS Survival GuideDocument9 pagesATI TEAS Survival Guidemaria torres80% (5)
- Nursing Test Taking Strategy IDocument20 pagesNursing Test Taking Strategy Iicy431100% (1)
- List of PharmacolgyDocument4 pagesList of PharmacolgySareeya ShreNo ratings yet
- Hesi Study GuidDocument44 pagesHesi Study GuidStefanie Henry80% (5)
- Ceces Study Guides Part 1Document86 pagesCeces Study Guides Part 1Patricia Mae Espinas100% (1)
- Medical Dosage Calculations Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesMedical Dosage Calculations Cheat SheetJennifer Jaworsky100% (3)
- Picmonic NCLEX Study PlanDocument38 pagesPicmonic NCLEX Study Planchellczy100% (1)
- LPN NotesDocument223 pagesLPN Notesandron1979100% (3)
- LPN PathoDocument1 pageLPN PathoBecky WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Med Surg BulletDocument12 pagesMed Surg BulletCham SaponNo ratings yet
- Boost critical thinking skills for NCLEX successDocument10 pagesBoost critical thinking skills for NCLEX successTimbo Slice100% (1)
- How To Survive Nursing School PDFDocument275 pagesHow To Survive Nursing School PDFKara Dawn Mason100% (9)
- Study Guide: Nurseboss StoreDocument9 pagesStudy Guide: Nurseboss Storezafar gharshin100% (1)
- ATI TEAS Study Bundle - The Nurse SamDocument5 pagesATI TEAS Study Bundle - The Nurse SamRrg0% (5)
- NCLEX Medications For Nurses 1 PDFDocument118 pagesNCLEX Medications For Nurses 1 PDF281175100% (4)
- Med Surg Study Guide 41 PagesDocument42 pagesMed Surg Study Guide 41 PagesVin Lorenzo Campbell100% (2)
- CNA Study Guide Modules A-I Rights, ADLs, Infection, SafetyDocument7 pagesCNA Study Guide Modules A-I Rights, ADLs, Infection, SafetyErin100% (3)
- TEAS 6 Science: Endocrine and Reproductive SystemsDocument22 pagesTEAS 6 Science: Endocrine and Reproductive SystemsLily GarciaNo ratings yet
- HESI Hints + More Chapter 1-Intro To TestingDocument29 pagesHESI Hints + More Chapter 1-Intro To TestingAngel Nwankwo100% (2)
- HESI Math and Science Answers Exam 2023Document4 pagesHESI Math and Science Answers Exam 2023Nelson MandelaNo ratings yet
- HESI Qbank from Quizzlet: Understanding Medication QuestionsDocument11 pagesHESI Qbank from Quizzlet: Understanding Medication Questionsnana100% (4)
- Nursing School Necessities Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesNursing School Necessities Cheat SheetRevNo ratings yet
- Calculating Drug Dosages A Patient Safe Approach To Nursing and MathDocument564 pagesCalculating Drug Dosages A Patient Safe Approach To Nursing and Mathkate96% (23)
- @nursingtestsbank Etsy: Reading SectionDocument18 pages@nursingtestsbank Etsy: Reading SectionTonya Barnes100% (8)
- Random Memory Notebook Pages Page 119Document1 pageRandom Memory Notebook Pages Page 119angie10231No ratings yet
- General Components of A Reflex ArcDocument6 pagesGeneral Components of A Reflex Arcangie10231No ratings yet
- Intramuscular Injection GuidelinesDocument2 pagesIntramuscular Injection Guidelinesangie10231No ratings yet
- Random Memory Notebook Pages Page 121Document1 pageRandom Memory Notebook Pages Page 121angie10231No ratings yet
- Contraction & RelaxationDocument10 pagesContraction & Relaxationangie10231No ratings yet
- Chapt17 StudentDocument30 pagesChapt17 Studentangie10231No ratings yet
- Random Memory Notebook Pages Page 128Document1 pageRandom Memory Notebook Pages Page 128angie10231No ratings yet
- Random Memory Notebook Pages Page 124Document1 pageRandom Memory Notebook Pages Page 124angie10231No ratings yet
- Random Memory Notebook Pages Page 123Document1 pageRandom Memory Notebook Pages Page 123angie10231No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Dr. Annette M. Parrott GPC BIOL1612Document34 pagesEndocrine System: Dr. Annette M. Parrott GPC BIOL1612Nathan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Hormones & HomeostasisDocument32 pagesEndocrine System: Hormones & Homeostasisangie10231No ratings yet
- Structure of The Neuromuscular JunctionDocument5 pagesStructure of The Neuromuscular Junctionangie10231No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument28 pagesEndocrine Systemangie10231No ratings yet
- 25 EndoDocument66 pages25 Endoangie10231No ratings yet
- Marieb ch7dDocument17 pagesMarieb ch7dangie10231No ratings yet
- The Roles of Calcitonin, Parathyroid Hormone & CalcitrolDocument7 pagesThe Roles of Calcitonin, Parathyroid Hormone & Calcitrolangie10231No ratings yet
- Steps in Repair of A Bone Fracture: Process Diagrams Step-by-StepDocument5 pagesSteps in Repair of A Bone Fracture: Process Diagrams Step-by-Steprambabs369No ratings yet
- Intramembranous Ossification: Process Diagrams Step-by-StepDocument5 pagesIntramembranous Ossification: Process Diagrams Step-by-Steprambabs369No ratings yet
- The Sodium-Potassium Pump: Process Diagrams Step-by-StepDocument5 pagesThe Sodium-Potassium Pump: Process Diagrams Step-by-Steprambabs369No ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Flow Sheet For Nursing StudentsDocument3 pagesCritical Thinking Flow Sheet For Nursing Studentsangie10231No ratings yet
- Signal Transmission at A Chemical SynapseDocument7 pagesSignal Transmission at A Chemical Synapseangie10231No ratings yet
- Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis: Process Diagrams Step-by-StepDocument7 pagesReceptor-Mediated Endocytosis: Process Diagrams Step-by-Steprambabs369No ratings yet
- LabValues (1) Nclex Review2Document1 pageLabValues (1) Nclex Review2angie10231No ratings yet
- Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Tract Optic Nerve Optic Chiasma Optic Tract Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Frontal LobeDocument1 pageOlfactory Bulb Olfactory Tract Optic Nerve Optic Chiasma Optic Tract Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Frontal Lobeangie10231No ratings yet
- Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland)Document1 pageHypophysis (Pituitary Gland)angie10231No ratings yet
- Anatomy Study BinderDocument13 pagesAnatomy Study Binderangie10231No ratings yet
- Dosage Calculation TutorialDocument68 pagesDosage Calculation TutorialRon AbuNo ratings yet
- Rbel60708 1-266241Document28 pagesRbel60708 1-266241angie10231No ratings yet
- 0001ha015643f3 PDFDocument5 pages0001ha015643f3 PDFAtul RajNo ratings yet
- Insulin IssuesDocument6 pagesInsulin Issuesdoctorzo0% (1)
- Ovarian Cyst Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument29 pagesOvarian Cyst Diagnosis and TreatmentMichelle Defandi ChanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document12 pagesThe Endocrine System The Endocrine System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabNo ratings yet
- Im - Chronic Kidney Disease - Dr. Lorna Wong - March 20 2021Document107 pagesIm - Chronic Kidney Disease - Dr. Lorna Wong - March 20 2021Christine MendozaNo ratings yet
- Blend CJC-1295 IpamorelinDocument2 pagesBlend CJC-1295 Ipamorelinhaydunn55No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology OF HEART FAILUREDocument2 pagesPathophysiology OF HEART FAILUREJessa AdenigNo ratings yet
- Academic Literacy Elements of a Body ParagraphDocument10 pagesAcademic Literacy Elements of a Body ParagraphSjabuliso Madlala ThandekaNo ratings yet
- The 2 Keys to Continued Growth and Size Post CycleDocument9 pagesThe 2 Keys to Continued Growth and Size Post CycleJohnnie DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Zalameda - Hypothalamic and Pituitary Agents Adrenocortical Agents Thyroid and Parathyroid Anti Diabetic AgentsDocument55 pagesZalameda - Hypothalamic and Pituitary Agents Adrenocortical Agents Thyroid and Parathyroid Anti Diabetic AgentsNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Abdalla A. A. JumaDocument15 pagesDr. Abdalla A. A. JumaR00r0 M0h4mm3dNo ratings yet
- Achiever Maza Minor-02 04 June SoDocument6 pagesAchiever Maza Minor-02 04 June SoJeetraj SoniNo ratings yet
- Physiology Magdy Sabry EndocrineDocument162 pagesPhysiology Magdy Sabry Endocrineaminata kamara89% (9)
- GroomingAssignment (Frankfinn)Document6 pagesGroomingAssignment (Frankfinn)M.Kishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer KelseyDocument12 pagesBreast Cancer Kelseyapi-3802092No ratings yet
- ImedclerksDocument389 pagesImedclerksWest AfricaNo ratings yet
- CSE Grade 10 Science Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesCSE Grade 10 Science Lesson PlanJelly Marie Baya FloresNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease GuideDocument19 pagesAddison's Disease Guidefranko fredrickNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System: 1-1. GENERALDocument5 pagesThe Female Reproductive System: 1-1. GENERALgladz25No ratings yet
- The Wisdom of Menopause by Christiane Northrup: The Physical Foundation of The Change (Excerpt)Document42 pagesThe Wisdom of Menopause by Christiane Northrup: The Physical Foundation of The Change (Excerpt)Random House Publishing Group91% (11)
- Forxiga Slide RTD 2017 - 2Document64 pagesForxiga Slide RTD 2017 - 2Budi WirawanNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia - Schermerhorn, ThomasDocument2 pagesHypoglycemia - Schermerhorn, ThomasJuanMartínezNo ratings yet
- Endometrial HyperplasiaDocument21 pagesEndometrial Hyperplasianautilus81No ratings yet
- 2018 Sec 4 Science Biology SA2 - KranjiDocument35 pages2018 Sec 4 Science Biology SA2 - Kranji19Y1H GAO CHENZHANGNo ratings yet
- Overt Diabetes in PregnancyDocument12 pagesOvert Diabetes in PregnancyGestne AureNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of ESRD: Organ Dysfunctions & Associated AbnormalitiesDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of ESRD: Organ Dysfunctions & Associated AbnormalitiesCarl JardelezaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of the OvaryDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of the OvaryJay PaulNo ratings yet
- How to Control Instincts Through AwarenessDocument5 pagesHow to Control Instincts Through AwarenessgadapremNo ratings yet
- BSC NotesDocument9 pagesBSC NotesTayyaba ShahNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryFrom EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Stuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldFrom EverandStuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (289)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Perfume Engineering: Design, Performance and ClassificationFrom EverandPerfume Engineering: Design, Performance and ClassificationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Introduction to Biological and Small Molecule Drug Research and Development: Theory and Case StudiesFrom EverandIntroduction to Biological and Small Molecule Drug Research and Development: Theory and Case StudiesC. Robin GanellinRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (150)