Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Retail market segmentation and consumer product examples
Uploaded by
PbawalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Retail market segmentation and consumer product examples
Uploaded by
PbawalCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Explain process of retail market segmentation and discuss segmentation based on consumer products. Give examples.
Ans;- Retail market segmentation is the process of aggregating customers with similar wants, needs, preferences, or buying behaviour. The segmentation process is divided into a heterogeneous process follows four broad steps: i) The definition of the market to be addressed. ii. iii. The identification of alternative bases for segmentation. An examination of these based and the choice of the best base or base for segmentation. iv. The identification of individual market segments, an assessment of their attractiveness and the selection of specific target market.
A market is a group of potential customers with similar needs who are willing to exchange something of value with sellers offering various goods and services that can satisfy these needs. The marketer has the option of either approaching the entire set of customers with a uniform marketing approach or adopting a differentiated approach for different sets of customers. hile the former refers to mass marketing, the latter refers to the strategy of market segmentation !egmentation : "eterogeneous total market to small groups of homogenous segments with similar wants , needs and characteristics that responds to specific marketing mix # $ %) &xamples total market : 'en and women omen: orking women and housewives orking women: (oung, middle aged A segment is a relatively homogeneous group and hence responds to a marketing mix in a similar way. )ifferent groups or segments re*uire different promotional strategies and marketing mixes because they have different wants and needs. +f you are marketing fashion garments above segmentation is useful. ,ut if you are marketing rice then this segmentation may not serve the purpose
-iche : A niche is a more narrowly defined group seeking a distinctive mix of benefits. 'arketers usually identify niches by dividing a segment into sub.segments. /uture group has special outlets called 0 All1 for those +ndian men and women typically short , overweight with higher income group. -ormally niche market is not served by large scale competitors working on volumes. &ntrepreneur finds a gap and develop -iche market giving customi2ed marketing mix. Segmentation based on Consumer products:
3onsumer products are those products that are intended for the ultimate consumer. 3onsumer products can be sub.divided into four sub.groups: 4. 5. 6. $. 3onvenience products !hopping products !pecialty items 7nsought items
Convenience products 3onvenience products are products that are purchased fre*uently but on which the consumer not willing to spend much time or effort. These include staples like packaged foods, milk, bread, and emergency products like medicine. Shopping products( comparison products) : !hopping products are products that a customer feels are worth the time and effort to compare with competing products. These include furniture, clothing, washing machines, television sets, etc. Specialty items: !pecialty products are consumer products that the customer makes a special effort to purchase. The consumer is willing to search for such specialty products. Any branded product that customers insist on by name is a specialty product. Unsought items: 7nsought goods are products that potential customers do not yet want or know about. 3ustomers do not buy such products unless promotion shows their value. 8ife insurance and encyclopedias are examples of unsought products. 5. Explain any four theories of institutional changes taking place in retail. Give examples.
Ans;- Theories of institutional changes 4. 5. 6. $. 9. :. Dialectic process Gravity model Retail accordion theory Wheel of retailing theory Natural selection theory Central place theory
1- ialectic process !Dialectics are based around three concepts: 1: Everything is made out of opposing forces/opposing sides !: Gradual changes lead to turning points" #here one force overcomes the other $: Change moves in spirals not circles%
&n evolutionary theory based on the premise that retail institutions evolve
'he theory suggests that ne# retail formats emerge by adopting characteristics from other forms of retailers in much the same #ay that a child is the product of the pooled genes of t#o different individuals (elting pot : t#o institutional forms #ith different advantages modify their format till they develop a format that combine the advantages of both &dvantages of ne# competitors are copied by e)isting businesses by adopting same strategies *ence both companies practically gets in distinguishable unless competitor changes The ialectic "rocess
T#E$%$ epartment store #igh margin &o' turnover #igh price (ull service o'nto'n location "lush facilities $)*T#E$%$ iscount department store Average margins Average turnover +oderate prices &imited services $uburban locations +odest facilities A*T%T#E$%$ iscount store &o' margin #igh turnover &o' price $elf-service &o' rent location $partan facilities
Examples of dielectric process +ndian udipi and specialty restaurants no# trend is +ndian udipi restaurants serves south +ndian" ,un-abi and Chinese dishes" pi..a etc
While (cDonald is going for +ndian dishes such as Wada /pav Cheap air line lo# service 0 *igh end airline #ith high service Will change both so that both are middle price middle service airline
+ndian udipi and specialty restaurants no# trend is +ndian udipi restaurants serves south +ndian" ,un-abi and Chinese dishes" pi..a etc While (cDonald is going for +ndian dishes such as Wada /pav Cheap air line lo# service 0 *igh end airline #ith high service Will change both so that both are middle price middle service airline Gravity model & theory about the structure of mar1et areas: 'he model states that the volume of purchases by consumers and the fre2uency of trips to the outlets are a function of the si.e of the store and the distance bet#een the store and the origin of the shopping trip
Gravity is pull it depends upon the mass of item 3igger the mass " it has capacity to attract smaller masses 4orce of attraction depends upon mass and inversely proportional to s2uare of distance
+n Retail more assortment and larger the store means more pull to attract customers &nd more the distance of store from customer lesser is the pull 'his means customers have inertia to move 5nless the pull 6large format" large assortment% is more they #ill prefer to buy at a closer location 6 small format" less assortment% +n 17$1 a gentleman name William 8 Reilly #rote a retail a)iom that is still used today for mar1et planning of retail stores +t is commonly 1no#n as Reilly9s :a# of Retail Gravitation and #as inspired by Ne#ton9s la# of Gravitation #hich stated ;t#o bodies attract each other #ith a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the s2uare of the distance bet#een them ; Reilly9s formula is used to predict the li1ely division bet#een t#o trade centers at #hich shoppers #ill go one #ay or the other
Reilly recogni.ed that trade centers produce gravitational pull 4urther he reali.ed that bigger trade centers had more mass and therefore" as stated in Ne#ton9s :a#" more gravity *ere9s a ne# scoop" though <our store produces a gravitational field as #ell 'he gravitation that your store produces is based on a number of elements" not the least of #hich is its si.e =no#ing this fact can aid you in the management of your business
,heel of -etailing Theory +t is a theory of retail institutional changes that e)plains retail evolution #ith an institutional life cycle concept escribes ho' ne' types of retailers enter the market as lo'-status. lo'-margin. lo'-price operators; ho'ever. as they meet 'ith success. these ne' retailers gradually ac/uire more sophisticated and elaborate facilities. and thus become vulnerable to ne' types of lo'-margin retail competitors 'ho progress through the same patter. efinition0 The ,heel of -etailing is a theory to explain the institutional changes that take place 'hen innovators enter the retail arena.
The Wheel of Retailing concept states that ne' types of retailers usually begin as lo'-margin. lo'-price. lo'-status operations. but later evolve into higher-priced. higher-service operations. eventually becoming like the conventional retailers they replaced
>ome #ould argue that (cDonald?s has become a victim of the #heel of retailing When (cDonald?s started out" it served a select menu @ver the years" the (cDonald?s product offering has e)panded to the inclusion of playgrounds" thus opening the #ay for ne#" lo#Acost fastAfood providers" such as Chec1ers
*atural $election Theory +t is a theory of retail institutional changes that states that retailing institutions that can most effectively adapt to environmental changes are the ones that are most li1ely to prosper or survive 3ased on Dar#in theory of evolution &dopting to changing environment or perish Retail institution that are fle)ible to adopt " survive and prosper 'hey need to change all B ,s 4. 5. ,roduct ,rice
6. $.
,romotion :ocation Changes can be social" economic" political" legal " technological
ResourceAadvantage theory +s based on the idea that all firms see1 superior performance in an everAchanging environment
+llustrates t#o important lessons for retailers: >uperior performance at any point in time is a result of achieving a competitive advantage in the mar1et place as a result of some tangible or intangible entity 6CresourceD% &ll retailers cannot achieve superior results at the same time
1entral "lace Theory 'he essence of the theory is that settlements act as central places providing one or more services for their surrounding areas" and that they vary in their importance" or order" according to the number and type of other settlements dependent upon them" and according to the number and type of services" or functions" they provide >ervices are also ordered: lo#erAorder functions include the types of services provided by a village shopE higherAorder functions include department stores and hospitals Cities and large to#ns are classified as highAorder settlements because they supply both lo#A and highA order services" the latter to both their o#n inhabitants and to those living further a#ay & village #ith one small shop #ould be of a very lo# order
+t is a model that ran1s communities according to the assortment of goods available in each &t the bottom of the hierarchy are communities that represent the smallest central places 6centers of commerce% 'hey provide the basic necessities of life 4urther up the hierarchy are the larger central places" #hich carry all goods and services" found in lo#erAorder central places plus more speciali.ed ones that are not necessary
6.
efine retail strategy and discuss retail mix for ma2or retailers like ,almart. 3ig ba4ar. "une 1entral and ,est side
Ans;- -etail market strategy0 (eaning" Retail strategic planning process" retail organi.ation" management and human resource policies" >trategic positioning" developing competitive advantage
$uccess in retail 5 ,ell thought plans 6 "rocesses 6implementation
$trategy the retail perspective0 Definition: & clear and definite plan that retailer outlines to tap the mar1et and build a long term relationship #ith customers +t define purpose and provide guidance ho# retailer should face challenges in dynamic conditions Retail strategy also enables areas #ithin organi.ation to define their strategies >tore location >tore formats (erchandising (ar1eting : Retail mar1et strategy 4inance @rgani.ation
7- escribe the process of retail planning and net'orking. Give examples Ans;- >trategic retail mar1eting is the process of planning the retail concepts on effective manner 1eeping in mind the comparative environment to place the products effectively
,lanning of mar1eting program +mplementation by net#or1ing #ith 1ey partners
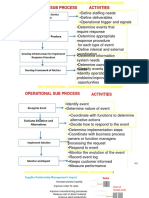
-etail "lanning *et'orking 4. 5. 6. $. 9. :. ;. <. =. Develop mission statement Establish @b-ectives Conduct situational analysis +dentify strategic alternatives >elect mar1et to compete @btain resource needed to compete Developing positioning strategy +mplement the strategy Evaluation of results
You might also like
- Finding Customers: Market Segmentation: Small Business SeriesDocument5 pagesFinding Customers: Market Segmentation: Small Business SeriesyohanchehadehNo ratings yet
- Retail Marketing Strategy 1234074502574778 1Document19 pagesRetail Marketing Strategy 1234074502574778 1Sonali PadhyeNo ratings yet
- AMG Marketing Group Discusses Business Planning ProcessDocument4 pagesAMG Marketing Group Discusses Business Planning ProcessRajetha GunturNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesSeminar Reportankurk124100% (1)
- A) Introduce Your Company and Its Products/services Capture InterestDocument8 pagesA) Introduce Your Company and Its Products/services Capture InterestGetachew MuluNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS HIGHLIGHTS REPORTDocument10 pagesBUSINESS HIGHLIGHTS REPORTSuhana ThapaNo ratings yet
- New Business Development Departments.Document4 pagesNew Business Development Departments.shoaibhassan23No ratings yet
- 50 Sample Questions (Marketing)Document4 pages50 Sample Questions (Marketing)shubham satamNo ratings yet
- Group 3: Bank MarketingDocument50 pagesGroup 3: Bank MarketingSomshubhra PalNo ratings yet
- Bank Sales PracticesDocument26 pagesBank Sales Practicesmarlane ava laurenNo ratings yet
- Certified Credit Union Financial Counselor Training Program: The Vermont StoryDocument9 pagesCertified Credit Union Financial Counselor Training Program: The Vermont StoryREAL SolutionsNo ratings yet
- 2007 Great Idea Book - Revised 4 26 2007 95771Document158 pages2007 Great Idea Book - Revised 4 26 2007 95771daaNo ratings yet
- Fifth Trimester Examination - 2009 Banking ManagementDocument7 pagesFifth Trimester Examination - 2009 Banking Managementhianshu1985No ratings yet
- Leader ExpectationsDocument2 pagesLeader ExpectationsuthguydanNo ratings yet
- Effective Leadership Skills WorkshopDocument2 pagesEffective Leadership Skills Workshopyeah108No ratings yet
- Poster 2Document1 pagePoster 2Radhiyah BaharomNo ratings yet
- Iipm Indian Institute of Planning and Management: Group AssignmentDocument33 pagesIipm Indian Institute of Planning and Management: Group Assignmentaditipathania100% (2)
- Lesson One - Banking Partners PDFDocument2 pagesLesson One - Banking Partners PDFJOHN MENDOZA GALLEGOSNo ratings yet
- Regional Sales Manager Southeast in Tampa FL Resume Jimmie DixonDocument2 pagesRegional Sales Manager Southeast in Tampa FL Resume Jimmie DixonJimmieDixonNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies and ExecutionDocument9 pagesMarketing Strategies and ExecutionRushank PatelNo ratings yet
- Leader Followers RelationshipDocument10 pagesLeader Followers RelationshipLa JiejaNo ratings yet
- All The Weekly LogsDocument12 pagesAll The Weekly Logsapi-302648238No ratings yet
- Project Planning Checklist 3aDocument4 pagesProject Planning Checklist 3aapi-307501528No ratings yet
- Rebekah Caldwell Johnson: Journal Website Annual ConferenceDocument2 pagesRebekah Caldwell Johnson: Journal Website Annual Conferencerebekah_jNo ratings yet
- Marketing PDFDocument4 pagesMarketing PDFshubham satamNo ratings yet
- Commercial Sales Associate FY - 19: Kavyaa KDocument12 pagesCommercial Sales Associate FY - 19: Kavyaa KKavya PradeepNo ratings yet
- Tools of Sales Promotion: Without Sales Promotion Something Terrible Happens .Nothing! P T BarnumDocument21 pagesTools of Sales Promotion: Without Sales Promotion Something Terrible Happens .Nothing! P T BarnumArun KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Baja Sales PresentationDocument2 pagesBaja Sales PresentationIteniumNo ratings yet
- Personal Selling For Branch Managers of Adansi Rural Bank Limited.Document21 pagesPersonal Selling For Branch Managers of Adansi Rural Bank Limited.AkwasiOsseiNkrumahNo ratings yet
- A Day in The Life of A Personnel ManagerDocument2 pagesA Day in The Life of A Personnel ManagerAbu Sama ALselmyNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy Guide for StartupsDocument5 pagesMarketing Strategy Guide for StartupsYashashavi LadhaNo ratings yet
- Marketing of Financial ServicesDocument88 pagesMarketing of Financial ServicesFaizan Ahmad100% (1)
- Marketing and Operations of The Banking SectorDocument36 pagesMarketing and Operations of The Banking SectorVineeth MudaliyarNo ratings yet
- Advertising Messages and Marketing GoalsDocument26 pagesAdvertising Messages and Marketing GoalsFrances BarenoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Plan for Galam Music LoungeDocument8 pagesStrategic Plan for Galam Music LoungeMICHAEL VINCENT CONTAOI ROBASNo ratings yet
- Personal and Household Finance ExplainedDocument5 pagesPersonal and Household Finance ExplainedMuhammad SamhanNo ratings yet
- Team Building Training: Prepared For The Horticultural Industry With Johnson Gitonga: Director, Derimex Food TechnologiesDocument25 pagesTeam Building Training: Prepared For The Horticultural Industry With Johnson Gitonga: Director, Derimex Food TechnologiesJohnson Gitonga NderiNo ratings yet
- Bersamira, Melanie G.: Examples Include Debates Over The AppropriateDocument4 pagesBersamira, Melanie G.: Examples Include Debates Over The AppropriateMelanie BersamiraNo ratings yet
- Planning Your Marketing StrategyDocument6 pagesPlanning Your Marketing StrategyPrashant SatputeNo ratings yet
- Sales Promotion NotesDocument5 pagesSales Promotion NotesLebbe PuthaNo ratings yet
- Goup 5 LeadershipDocument80 pagesGoup 5 LeadershipAidil-Nur ZainalNo ratings yet
- Dcos A Daily Management Huddle Template V 4-21-20Document12 pagesDcos A Daily Management Huddle Template V 4-21-20api-516216369No ratings yet
- Lloyd Balanced ScorecardDocument4 pagesLloyd Balanced Scorecardvimalsairam100% (1)
- Guide To Developing The Elements of A Marketing PlanDocument11 pagesGuide To Developing The Elements of A Marketing PlanArlene TingsonNo ratings yet
- Project+Planning+&+Client+Management+ +Team+Contract+ +group+3Document11 pagesProject+Planning+&+Client+Management+ +Team+Contract+ +group+3Stacey lukeNo ratings yet
- Dave Ramsey's Monthly Cash-Flow Plan: INCOME Worksheet INCOME WorksheetDocument9 pagesDave Ramsey's Monthly Cash-Flow Plan: INCOME Worksheet INCOME WorksheetgelubotNo ratings yet
- Leadership PortfolioDocument7 pagesLeadership PortfolioKaylea AlgireNo ratings yet
- Marketing TipsDocument6 pagesMarketing TipsParas ShahNo ratings yet
- Strategic customer service management process and metrics frameworkDocument28 pagesStrategic customer service management process and metrics frameworkDwaraka MayeeNo ratings yet
- Bank Asia MCB BranchDocument64 pagesBank Asia MCB Branchding_dong_001No ratings yet
- Role Transition Plan Template: Instructions: How To Use This ToolDocument5 pagesRole Transition Plan Template: Instructions: How To Use This ToolDelsie Belle AcoboNo ratings yet
- For Sales Supervisor and Sales ManagerDocument18 pagesFor Sales Supervisor and Sales Managerprince husainNo ratings yet
- Weekly - Sales PipelineDocument102 pagesWeekly - Sales PipelineĐào Anh BanNo ratings yet
- The Robert Donato Approach to Enhancing Customer Service and Cultivating RelationshipsFrom EverandThe Robert Donato Approach to Enhancing Customer Service and Cultivating RelationshipsNo ratings yet
- Retail Industry ReportDocument60 pagesRetail Industry ReportPbawalNo ratings yet
- Doppler PresentationDocument51 pagesDoppler PresentationPbawal100% (2)
- Project Report Minda HRDDocument106 pagesProject Report Minda HRDPbawal79% (24)
- Project Report On Big BazaarDocument77 pagesProject Report On Big BazaarPbawal85% (46)
- 7 Alerts For A Money CrunchDocument4 pages7 Alerts For A Money CrunchPbawalNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: Pankaj Kr. SrivastavaDocument17 pagesDecision Making: Pankaj Kr. SrivastavaPbawalNo ratings yet
- HCL BPO Interview Support MaterialDocument37 pagesHCL BPO Interview Support MaterialPbawalNo ratings yet
- Wealth ManagementDocument144 pagesWealth ManagementPbawal100% (6)
- STANDARD ChartDocument103 pagesSTANDARD ChartPbawal100% (9)
- LGDocument23 pagesLGPbawal100% (17)
- HR DictionaryDocument23 pagesHR DictionaryProf. Lakshman Madurasinghe100% (22)
- Project On LGDocument79 pagesProject On LGViPul82% (17)
- Entertainment IndustryDocument12 pagesEntertainment IndustryPbawal100% (14)
- Process YDocument8 pagesProcess YPbawalNo ratings yet
- Best PicturesDocument39 pagesBest PicturesmkgchemNo ratings yet
- RBI MoneyKumar ComicDocument24 pagesRBI MoneyKumar Comicbhoopathy100% (1)
- Faces of NatureDocument15 pagesFaces of NaturePbawalNo ratings yet
- Barriers To CommunicationDocument36 pagesBarriers To CommunicationPbawal100% (4)
- Da Vinci CodeDocument17 pagesDa Vinci Codeapi-376886975% (4)
- Best PicturesDocument39 pagesBest PicturesmkgchemNo ratings yet
- Retail in IndiaDocument18 pagesRetail in Indiamahantesh12391% (11)
- Accounting DefinationsDocument17 pagesAccounting DefinationsPbawal50% (2)
- 6710 NotesDocument45 pages6710 NotesAndrés SuquilloNo ratings yet
- Fitch CLOs and Corporate CDOsRating Criteria PDFDocument57 pagesFitch CLOs and Corporate CDOsRating Criteria PDFantonyNo ratings yet
- Capillary Puncture Equipment and Procedures: Topic 7Document39 pagesCapillary Puncture Equipment and Procedures: Topic 7Angelica Camille B. AbaoNo ratings yet
- STD-Insurance Commission TRAD REVIEWER Rev1 PDFDocument24 pagesSTD-Insurance Commission TRAD REVIEWER Rev1 PDFJomar Carabot100% (1)
- TOPIC 1 - Public Speaking SkillsDocument72 pagesTOPIC 1 - Public Speaking SkillsAyan AkupNo ratings yet
- QuitclaimDocument2 pagesQuitclaimAlfred Hernandez CampañanoNo ratings yet
- Sidak 2008 FAQsDocument3 pagesSidak 2008 FAQssikhswimNo ratings yet
- Distinguish Opinion From TruthDocument12 pagesDistinguish Opinion From TruthMAR ANTERO R. CENIZA100% (2)
- Chara LesDocument5 pagesChara Lesx456456456xNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Assignment 2: (Backtracking Using Stack)Document4 pagesData Structures Assignment 2: (Backtracking Using Stack)Sai CharanNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and Symbols ExplainedDocument5 pagesMathematical Language and Symbols Explainedcyra6flores6verderaNo ratings yet
- Speaking EMN4Document61 pagesSpeaking EMN4Khánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Confidential: Turn in Exam Question PaperDocument20 pagesConfidential: Turn in Exam Question PaperRifat ManzoorNo ratings yet
- DTF - Houses of The FallenDocument226 pagesDTF - Houses of The FallenShuang Song100% (1)
- TOS-GRADE-10 EnglishDocument2 pagesTOS-GRADE-10 EnglishPRINCESS VILLASANTANo ratings yet
- GUINNESS F13 Full Year BriefingDocument27 pagesGUINNESS F13 Full Year BriefingImoUstino ImoNo ratings yet
- 01 Petrolo 224252Document7 pages01 Petrolo 224252ffontanesiNo ratings yet
- Butterfly Court SpreadsDocument24 pagesButterfly Court SpreadsAbigaïl EnderlandNo ratings yet
- Barrons High Frequency Words With Syn & AntonymsDocument48 pagesBarrons High Frequency Words With Syn & Antonymsbharatluvs100% (4)
- Bailable and Non BailableDocument10 pagesBailable and Non BailableasthaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Paper Assignment 2 Professional Practice Level 2Document3 pagesReflective Paper Assignment 2 Professional Practice Level 2api-350779667No ratings yet
- Fading Memories of Pakistan (Presentation)Document14 pagesFading Memories of Pakistan (Presentation)yfs945xpjnNo ratings yet
- Ra 6770Document8 pagesRa 6770Jamiah Obillo HulipasNo ratings yet
- Solución: R T β T R (T) = 1000 Ω ΩDocument6 pagesSolución: R T β T R (T) = 1000 Ω ΩDuvan BayonaNo ratings yet
- Coursework of Signals and Systems: Moh. Kamalul Wafi December 6, 2018Document2 pagesCoursework of Signals and Systems: Moh. Kamalul Wafi December 6, 2018kartiniNo ratings yet
- SAP Training Program Proposal for StudentsDocument2 pagesSAP Training Program Proposal for StudentsAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Report Anomalies and Normalization SummaryDocument5 pagesReport Anomalies and Normalization SummaryThomas_GodricNo ratings yet
- Marketing Communications and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) - Marriage of Convenience or Shotgun WeddingDocument11 pagesMarketing Communications and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) - Marriage of Convenience or Shotgun Weddingmatteoorossi100% (1)
- Assignment On Diesel Engine OverhaulingDocument19 pagesAssignment On Diesel Engine OverhaulingRuwan Susantha100% (3)
- Fuentes CAED PortfolioDocument32 pagesFuentes CAED PortfoliojsscabatoNo ratings yet