Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP S
Uploaded by
Marvie CadenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP S
Uploaded by
Marvie CadenaCopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING CARE PLAN
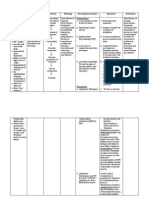
Name: Address: Chief Complaint: ASSESSMENT Nursing Diagnosis Age: Clinical Impression: PLANNING Goals & Desired Outcome At the end of my shift, after medical and nursing intervention the patients airway will slightly be cleared as evidenced by patient will have normal rate and depth of breathing, will have normal breath sounds, will less use accessory muscle for breathing and will not anymore experience dyspnea. Sex: Male Rm. No.: Religion: Bed No.: Date of Admission: EVALUATION
Cues/Evidence
Scientific Rationale
IMPLEMENTATION Nursing Order/Action Rationale for Action Assess rate/depth of respirations and chest movement. Tachypnea, shallow respirations, and asymmetric chest movement are frequently present because of discomfort of moving chest wall and/or fluid in lung. Decreased airflow occurs in areas consolidated with fluid. Bronchial breath sounds (normal over bronchus) can also occur in consolidated areas. Crackles, rhonchi, and wheezes are heard on inspiration and/or expiration in response to fluid accumulation, thick secretions, and airway spasm/obstruction. Lowers diaphragm,
Subjective data:
Ineffective airway Infectious agents clearance related to increased sputum Patients normal flora production in response altered to respiratory infection secondary to pneumonia Inflammatory reaction Objective: as evidenced by occurs in the alveoli - Changes in Restlessness, Presence of producing an exudates rate, depth sputum, Difficulty of that interferes with the breathing, RR- 63, SpO2 - diffusion of oxygen and of Positive chest carbon dioxide respirations. 78, retractions, Pale, Using - Abnormal ventilatory support. White blood cells breath migrate into the alveoli sounds - Use of Secretions and mucosal edema causes partial accessory occlusion of the muscles bronchi making the - Dyspnea lungs not adequately - Use of ventilated mechanical ventilator Decrease in alveolar
Auscultate lung fields, noting areas of decreased/absent airflow and adventitious breath sounds, e.g., crackles, wheezes.
oxygen tension Bronchospasm Altered airway ***MSN by Brunner and Suddarth p.525
Elevate head of bed, change position frequently.
promoting chest expansion, aeration of lung segments, mobilization and expectoration of secretions. Stimulates cough or mechanically clears airway in patient who is unable to do so because of ineffective cough or decreased level of consciousness.
Suction as indicated (e.g., frequent or sustained cough, adventitious breath sounds, desaturation related to airway secretions). Monitor serial chest x-rays, ABGs, pulse oximetry readings.
Follows progress and effects of disease process/therapeutic regimen, and facilitates necessary alterations in therapy.
Dependent: Administer medications as indicated: mucolytics, expectorants, bronchodilators,
Aids in reduction of bronchospasm and mobilization of secretions. Analgesics are given to improve cough effort by reducing discomfort, but should be used cautiously
analgesics.
because they can decrease cough effort/depress respirations. Fluids are required to replace losses (including insensible) and aid in mobilization of secretions. Note: Some studies indicate that room humidification has been found to provide minimal benefit and is thought to increase the risk of transmitting infection.
Provide supplemental fluids, e.g., IV, humidified oxygen, and room humidification.
Cues/Evidence
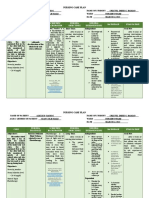
ASSESSMENT Nursing Diagnosis
Scientific Rationale
PLANNING Goals & Desired Outcome After 3 days of rendering nursing and medical intervention the patient will demonstrate improved ventilation and oxygenation of tissues by ABGs within patients acceptable range and absence of symptoms of respiratory distress, will not experience dyspnea and tachycardia, no nasal flaring and will have normal rate, rhythm and depth of breathing.
IMPLEMENTATION Nursing Order/Action Rationale for Action Maintain client airway. Place client in position of comfort with head of bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees. Monitor respiratory rate and depth. Note use of accessory muscles or work of breathing. Elevating the head of bed enhances lung expansion and reduces respiratory effort.
EVALUATION
Subjective data:
Impaired Gas Exchange r/t collection of secretions affecting oxygen exchange across alveolar membrane.
Pneumonia
Objective: - Dyspnea - Tachycardia - Nasal flaring - Abnormal rate, rhythm and depth of breathing
Inflammation of the parenchyma of the lung (that is, the alveoli)
Abnormal alveolar filling with fluid (consolidation and exudation)
cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty in breathing.
Impaired gas exchange
Rapid, shallow respirations occur because of hypoxemia, stress, and circulating endotoxins. Hypoventilation and dyspnea reflect ineffective compensatory mechanisms and are indications that ventilatory support is needed. Respiratory distress and the presence of adventitious
Note crackles, wheezes, and areas of decreased or
absent ventilation.
Reposition frequently and suction, as indicated.
sounds indicators pulmonary congestion, interstitial edema, atelectasis. -
are of
and
Good pulmonary toilet is necessary for reducing ventilation/ perfusion imbalance and for mobilizing and facilitating removal of secretions to maximize gas exchange.
Cues/Evidence
ASSESSMENT Nursing Diagnosis
Scientific Rationale
PLANNING Goals & Desired Outcome
IMPLEMENTATION Nursing Order/Action Rationale for Action
EVALUATION
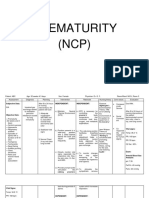
Subjective: N/A
Ineffective breathing pattern related to immature neurologic and delayed pulmonary development
Objective: With ET tube connected to mechanical ventilator RR: 44 cycles/ min O2 saturation of 91%
A premature lung is structurally underdeveloped for postnatal life. A deficiency in surfactant, which functions to decrease the surface tension within the alveoli. Without surfactant, the infant experiences diffuse atelectasis, decreased pulmonary compliance, ventilation perfusion mismatching, and significant increase in the work of breathing. Source: http://www.scribd.co m/doc/96101992/NcpNewborn
After 30 minutes of INDEPENDENT: nursing interventions, the infant will experience (1) assess RR an effective breathing pattern pattern as manifested by
and
Infants RR is between 40 and 60 Infant will experience (2) Provide respiratory no apnea assistance as needed. O2 saturation will be maintained in normal range (90-94) (3) position infant on side with a rolled blanket behind his back (4) provide tactile stimulation during periods of apnea (5) Position patient to facilitate optimum breathing patterns. (6) Maintain airway clearance.
(1) assessment provides information about neonates ability to initiate and sustain an effective breathing pattern (2) assistance helps the newborn by clearing the airway and promoting oxygenation (3) lying on the side position to facilitate breathing (4)stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system increases respiration (5) Allows gravity to assist in lowering the diaphragm, and provides greater chest expansion (6) Maintains a patent airway for gas exchange
Cues/Evidence
ASSESSMENT Nursing Diagnosis
Scientific Rationale
PLANNING Goals & Desired Outcome
IMPLEMENTATION Nursing Order/Action Rationale for Action 1. Assess mothers perception and knowledge about breastfeeding and extent of instruction that has been given. 2. Give emotional support to mother and accept decision regarding cessation/ continuation of breast feeding. 3. Demonstrate use of manual pistontype breast pump. 4. Review techniques for storage/use of expressed breast milk 5. Determine if a routine visiting schedule or advance warning can be provided 1. To know what the mother already knows and needed to know. 2. To assist mother to maintain breastfeeding as desired. 3. aid in feeding the neonate with breast milk without the mother breastfeeding the infant. 4. To provide optimal nutrition and promote continuation of breastfeeding process 5. So that infant will be hungry/ ready to feed 6. To promote successful infant feeding
EVALUATION
Subjective data:
Objective: - The newborn is diagnosed with a disease - The newborn is separated from his mother - The mother unable to provide breast milk to newborn continuously.
Interrupted breastfeeding related to neonates present illness as evidenced by separation of mother to infant
Abnormal condition of Short-term: After 3 hours the newborn of nursing intervention and health teachings the mother will identify and Need of special demonstrate techniques intervention and close to sustain lactation until monitoring. breastfeeding is initiated Long Term: After 3 days Admission of newborn of NI, the mother shall to NICU still be able to identify and demonstrate techniques to sustain Separation from the lactation and identify mother techniques on how to provide the newborn with breast milk. Interrupted breastfeeding
6. Provide privacy, calm surroundings when mother breast feeds. 7. Recommend for infant sucking on a regular basis 8. Encourage mother to obtain adequate rest, maintain fluid and nutritional intake, and schedule breast pumping every 3 hours while awake
7. Reinforces that feeding time is pleasurable and enhances digestion. 8. to sustain adequate milk production and breast feeding process
You might also like
- 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument8 pages1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceEsel Mae DinamlingNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanJose Mari F. Esguerra0% (1)
- Premature Infant Breathing DifficultiesDocument5 pagesPremature Infant Breathing DifficultiesRustan FrozenNo ratings yet
- NICU Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNICU Nursing Care Planlorence_cachoNo ratings yet
- Neonatal NCPDocument7 pagesNeonatal NCPMaria Delia SalvadoNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper 1Document6 pagesNCP Proper 1Noreen PinedaNo ratings yet
- Post-maturity Nursing Assessment and InterventionDocument6 pagesPost-maturity Nursing Assessment and InterventionJeanne Mari CostalesNo ratings yet
- NCP Rds 2Document1 pageNCP Rds 2Angelokeizer Gavino0% (1)
- New Born NCPDocument8 pagesNew Born NCPCarl Vincent Marrion Rejuso100% (1)
- Nursing Plan for Preterm Infant with Respiratory IssuesDocument2 pagesNursing Plan for Preterm Infant with Respiratory IssuesJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Power Point For The Case Study About PneumoniaDocument16 pagesPower Point For The Case Study About PneumoniaJai - Ho86% (7)
- NCP Meningitis Sure NaniDocument2 pagesNCP Meningitis Sure NaniARISNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Goals for Post-Surgical PatientsDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan Goals for Post-Surgical PatientsJyotiNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome TreatmentDocument12 pagesNeonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome TreatmentRazelVillanueva67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan: PotentialDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan: PotentialNna ANn CastleNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LDocument2 pagesSt. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Pneumonia With Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan Pneumonia With Congenital Heart DiseaseKarri Ann Tonel100% (2)
- Neo Sepsis NCPDocument15 pagesNeo Sepsis NCPmelodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 NCPDocument14 pagesGroup 4 NCPitsmeaya100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS HIVDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For AIDS HIVFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNeonatal Jaundice Nursing Care PlanCristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus NCP - DayanghirangDocument2 pagesHydrocephalus NCP - DayanghirangEdnar DayanghirangNo ratings yet
- Postpartum NCPDocument20 pagesPostpartum NCPireneNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue and Back Pain NCP PresentationDocument18 pagesFatigue and Back Pain NCP PresentationTine Guibao100% (1)
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaNo ratings yet
- NCP On Nerborn CareDocument7 pagesNCP On Nerborn CareMandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Planning 3 NCPSDocument5 pagesPlanning 3 NCPSCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Interventions RationaleDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Interventions RationaleJose Rey BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Peritonsillar AbscessDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Peritonsillar AbscessKevin Leo Lucero AragonesNo ratings yet
- Care Plan PedsDocument7 pagesCare Plan PedsdjbhetaNo ratings yet
- MCN NCPDocument4 pagesMCN NCPPEARL CHRISTINE CUDALNo ratings yet
- NCP (LTB, Abortion, MI, DM)Document8 pagesNCP (LTB, Abortion, MI, DM)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans - NurseryDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans - NurserySusie PadaoanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Special ChildrenDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Special Childrenharas_dcsaisNo ratings yet
- NCP Viral MeningitisDocument7 pagesNCP Viral MeningitisvincevilNo ratings yet
- NCP For Insomnia PDFDocument2 pagesNCP For Insomnia PDFEca0% (1)
- NCP Baby DDocument3 pagesNCP Baby DYna LafuenteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Johndelle Banlasan Hernan100% (1)
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Care of The NewbornDocument10 pagesCare of The NewbornValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument1 pageCourse in The WardGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Prematurity and Lung Surfactant TherapyDocument27 pagesPrematurity and Lung Surfactant TherapyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- "My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingDocument3 pages"My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanAnthea ValinoNo ratings yet
- Rle 107 Maternal and Child Health Nursing: University of The Assumption College of Nursing and PharmacyDocument6 pagesRle 107 Maternal and Child Health Nursing: University of The Assumption College of Nursing and PharmacyEvangeline Anne Macanas100% (2)
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal University: College of NursingDocument11 pagesJose Rizal University: College of NursingDhan Mark Trinidad100% (3)
- Hydrocephalus UpdatesDocument65 pagesHydrocephalus Updatescddinchimm100% (1)
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDocument3 pagesAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument79 pagesChest PhysiotherapyRabab Ahmed100% (2)
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- Ranitidine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRanitidine Drug StudyMarvie Cadena100% (3)
- PRILOSEC 20 MG: Drug study for patient with anemia and uterine bleedingDocument3 pagesPRILOSEC 20 MG: Drug study for patient with anemia and uterine bleedingMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Triderm Drug StudyDocument3 pagesTriderm Drug StudyMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Clinical Teaching Plan (San Lazaro - MKD GRP 2) Mar 7-11,2011Document3 pagesWeekly Clinical Teaching Plan (San Lazaro - MKD GRP 2) Mar 7-11,2011Marvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRanitidine Drug StudyMarvie Cadena100% (3)
- Gordons Activity Exercise PatternDocument9 pagesGordons Activity Exercise PatternMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: St. Joseph CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: St. Joseph CollegeMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Gentamycin DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesGentamycin DRUG STUDYMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesAmpicillin DRUG STUDYMarvie Cadena100% (1)
- GeriaDocument22 pagesGeriaMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Stepwise Ventilator Waveform Assessment To Diagnose Pulmonary PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesStepwise Ventilator Waveform Assessment To Diagnose Pulmonary PathophysiologyPablo Simón Narbona MenaNo ratings yet
- Health DLP STAGES OF INFECTIONDocument9 pagesHealth DLP STAGES OF INFECTIONmarielabianaNo ratings yet
- Sinusitis LectureDocument66 pagesSinusitis LectureDada Doni100% (2)
- Cvek Pulpotomy: Report of A Case With Five-YearDocument4 pagesCvek Pulpotomy: Report of A Case With Five-YearKaren SandovalNo ratings yet
- AbijitDocument3 pagesAbijitvimalNo ratings yet
- Demand For Beauty by Society (FINAL)Document10 pagesDemand For Beauty by Society (FINAL)Maryhan MukhalalatiNo ratings yet
- Using Magnets To Increase Retention of Lower DentureDocument4 pagesUsing Magnets To Increase Retention of Lower DentureFirma Nurdinia DewiNo ratings yet
- Frequency, Severity, and Distress of Dialysis-Related Symptoms Reported by Patients On HemodialysisDocument1 pageFrequency, Severity, and Distress of Dialysis-Related Symptoms Reported by Patients On HemodialysisHelvia RahayuNo ratings yet
- TTTTDocument26 pagesTTTTMoataz TrabehNo ratings yet
- OB Power Point Presentation 002Document57 pagesOB Power Point Presentation 002RitamariaNo ratings yet
- What is GastroschisisDocument6 pagesWhat is GastroschisisAnonymous MWd5UOUuiyNo ratings yet
- Newborn PQDocument6 pagesNewborn PQNurseNancy93No ratings yet
- Combined Dental Management of Patients With Medical ConditionsDocument65 pagesCombined Dental Management of Patients With Medical ConditionsJenny WangNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology - PyelonephritisFrancis Kevin Sagudo92% (13)
- Cardiovascular Pathology: Risks, Heart Failure, AMIDocument5 pagesCardiovascular Pathology: Risks, Heart Failure, AMIbmhsh100% (2)
- ICICI Lombard General Insurance Company LimitedDocument22 pagesICICI Lombard General Insurance Company LimitedAmit BansalNo ratings yet
- Petition To Remove James Wiley Conservator of The Estate of Henry C.MunozDocument2 pagesPetition To Remove James Wiley Conservator of The Estate of Henry C.MunozpropertylenderNo ratings yet
- MapehasdasdDocument2 pagesMapehasdasdAmiel Angelo BaliosNo ratings yet
- MCQ Bleeding Disorders 2nd Year2021Document6 pagesMCQ Bleeding Disorders 2nd Year2021sherif mamdoohNo ratings yet
- Erectile DysfunctionDocument31 pagesErectile Dysfunctionrahuldtc100% (1)
- Dapa-CKD - Applying Clinical Evidence To Clinical PracticeDocument45 pagesDapa-CKD - Applying Clinical Evidence To Clinical Practicedevikumar kelkarNo ratings yet
- TMG Versus DMGDocument3 pagesTMG Versus DMGKevin-QNo ratings yet
- CasopisiDocument452 pagesCasopisiGormi DurmiNo ratings yet
- The Sage Encyclopedia of Abnormal and Clinical Psychology - I36172Document5 pagesThe Sage Encyclopedia of Abnormal and Clinical Psychology - I36172Rol AnimeNo ratings yet
- AMHOP Convention LetterDocument3 pagesAMHOP Convention Letterlemonysnicket0008No ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Limb Fractures Associated With Acute Peripheral IschemiaDocument6 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Limb Fractures Associated With Acute Peripheral IschemiaramadhaniandaNo ratings yet
- Holistic Perspective of Physical TherapyDocument31 pagesHolistic Perspective of Physical TherapyShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Dr. Noel Casumpang vs. Cortejo G.R. No. 171127, March 11, 2015Document29 pagesDr. Noel Casumpang vs. Cortejo G.R. No. 171127, March 11, 2015FD BalitaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae of Professor Francesco RiaDocument9 pagesCurriculum Vitae of Professor Francesco RianoncanimussurdisNo ratings yet
- CostipitationDocument4 pagesCostipitationashmi akberNo ratings yet