Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quick Quiz
Uploaded by
Laert Velia50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
591 views5 pagesquiz physic
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentquiz physic
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
591 views5 pagesQuick Quiz
Uploaded by
Laert Veliaquiz physic
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Quick Quiz 23.
1
If you rub an inflated balloon against your hair, the two materials attract each other, as shown in Figure 23.2. Is the amount of charge present in the balloon and your hair after rubbing (a) less than, (b) the same as, or (c) more than the amount of charge present before rubbing?
Quick Quiz 23.2
Object A is attracted to object B. If object B is known to be positively charged, what can we say about object A? (a) It is positively charged. (b) It is negatively charged. (c) It is electrically neutral. (d) Not enough information to answer.
Quick Quiz 23.3
Object A has a charge of _+2 NC, and object B has a charge of _+6 N true? (a) FAB=-3FBA. (b)FAB=-FBA . (c)3FAB=-FBA C. Which statement is
Quick Quiz 23.4
A charge of _3 NC is at a point P where the electric field is directed to the right and has a magnitude of 4 _ 106 N/C. If the charge is replaced with a _3- NC charge, what happens to the electric field at P ? Nothing,
Quick Quiz 23.5
Rank the magnitude of the electric field at points A, B, and C shown in Figure 23.22a (greatest magnitude first). A, B , C
Quick Quiz 24.1
Suppose that the charge in Example 24.1 is just outside the sphere, 1.01 m from its center. What is the total flux through the sphere? Zero,
Quick Quiz 24.2
For a gaussian surface through which the net flux is zero, the following four statements could be true. Which of the statements must be true? (a) There are no charges inside the surface. (b) The net charge inside the surface is zero. (c) The electric field is zero everywhere on the surface. (d) The number of electric field lines entering the surface equals the number leaving the surface.
Quick Quiz 24.3
How would the electric flux through a gaussian surface surrounding the shell in Example 24.10 change if the solid sphere were off-center but still inside the shell? NO CHANGE the same.
Quick Quiz 25.1
If the path between A and B does not make any difference in Equation 25.1, why don t we just use the expression where d is the straight-line distance between A and B? We do if the electric field is uniform. (This is precisely what we do in the next section.) In general, however, an electric field changes from one place to another.
Quick Quiz 25.2
The labeled points in Figure 25.3 are on a series of equipotential surfaces associated with an electric field. Rank (from greatest to least) the work done by the electric field on a positively charged particle that moves from A to B; from B to C; from C to D; from D to E. B C, CD, AB, DE.
Quick Quiz 25.3
A spherical balloon contains a positively charged object at its center. As the balloon is inflated to a greater volume while the charged object remains at the center, does the electric potential at the surface of the balloon increase, decrease, or remain the same? How about the magnitude of the electric field decreases? The electric flux remains constant?
Quick Quiz 25.4
(a) Is it possible for the magnitude of the electric field to be zero at a location where the electric potential is not zero? (b) Can the electric potential be zero where the electric field is nonzero? (a) Yes. (b) Yes
Quick Quiz 26.1
Many computer keyboard buttons are constructed of capacitors, as shown in Figure 26.4. When a key is pushed down, the soft insulator between the movable plate and the fixed plate is compressed. When the key is pressed, the capacitance (a) increases, (b) decreases, or (c) changes in a way that we cannot determine because the complicated electric circuit connected to the keyboard button may cause a change in _V.
Quick Quiz 26.2
What is the magnitude of the electric field in the region outside the spherical capacitor described in Example 26.3? Zero.
Quick Quiz 26.3
You have three capacitors and a battery. How should you combine the capacitors and the battery in one circuit so that the capacitors will store the maximum possible energy? parallel
Quick Quiz 26.4
You charge a parallel-plate capacitor, remove it from the battery, and prevent the wires connected to the plates from touching each other. When you pull the plates apart, do the following quantities increase, decrease, or stay the same? (a) C decreases; (b) Q the same ; (c) E between the plates constant; (d) _V increases ; (e) energy stored in the capacitor. increases
Quick Quiz 26.5
Repeat Quick Quiz 26.4, but this time answer the questions for the situation in which the battery remains connected to the capacitor while you pull the plates apart.
Quick Quiz 26.7
A fully charged parallel-plate capacitor remains connected to a battery while you slide a dielectric between the plates. Do the following quantities increase, decrease, or stay the same? (a) C decreases; (b) Q decreases; (c) E between the plates decreases (d) _V constant ; (e) energy stored in the capacitor. Decreases
Quick Quiz 27.1
Consider positive and negative charges moving horizontally through the four regions shown in Figure 27.4. Rank the current in these four regions, from lowest to highest. d, b = c, a.
Quick Quiz 27.2
Suppose that a current-carrying ohmic metal wire has a cross-sectional area that gradually becomes smaller from one end of the wire to the other. How do drift velocity increase, current density increase, and electric field vary along the wire increase? Note that the current must have the same value everywhere in the wire so that charge does not accumulate at any one point.
Quick Quiz 27.3
What does the slope of the curved line in Figure 27.7b represent? The curvature of the line indicates that the device is nonohmic (that is, its resistance varies with potential difference).
Quick Quiz 27.4
Your boss asks you to design an automobile battery jumper cable that has a low resistance. In view of Equation 27.11, what factors would you consider in your design?(small l ), (large A), low resistivity p.
Quick Quiz 27.5
When does a lightbulb carry more currentjust after it is turned on and the glow of the metal filament is increasing, or after it has been on for a few milliseconds and the glow is steady? Just after it is turned on.
Quick Quiz 27.6
The same potential difference is applied to the two lightbulbs shown in Figure 27.16. Which one of the following statements is true? (a) The 30-W bulb carries the greater current and has the higher resistance. (b) The 30-W bulb carries the greater current, but the 60-W bulb has the higher resistance. (c).
Quick Quiz 27.7
For the two lightbulbs shown in Figure 27.17, rank the current values at points a through f , from greatest to least.
I a = I b I c = I d I e = I f .
Quick Quiz 28.1
If a piece of wire is used to connect points b and c in Figure 28.4b, does the brightness of bulb R1 increase, decrease, or stay the same? What happens to the brightness of bulb R2 ? Bulb R1 becomes brighter.
Quick Quiz 28.2
Assume that the battery of Figure 28.1 has zero internal resistance. If we add a second resistor in series with the first, does the current in the battery increase, decrease, or stay the same? How about the potential difference across the battery terminals increase? Would your answers change if the second resistor were connected in parallel to the first one? Current increase , the potential difference decrease
Quick Quiz 28.3
Are automobile headlights wired in series or in parallel? How can you tell? because if one burns out, the other continues to operate.
Quick Quiz 28.4
Is a circuit breaker wired in series or in parallel with the device it is protecting? it must be in series to sense the appropriate current
Quick Quiz 29.1
What is the maximum work that a constant magnetic field B can perform on a charge q moving through the field with velocity v? Zero.
Quick Quiz 29.2
The north-pole end of a bar magnet is held near a positively charged piece of plastic. Is the plastic attracted, repelled, or unaffected by the magnet? Unaffected.
Quick Quiz 29.3
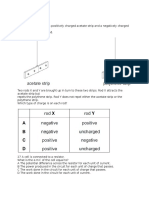
The four wires shown in Figure 29.11 all carry the same current from point A to point B through the same magnetic field. Rank the wires according to the magnitude of the magnetic force exerted on them, from greatest to least. C, B, A, D
Quick Quiz 29.4
Describe the forces on the rectangular current loop shown in Figure 29.13 if the magnetic field is directed as shown but increases in magnitude going from left to right. F3 > F1. Therefore, in addition to the torque resulting from the two forces, a net force is exerted downward on the loop.
Quick Quiz 29.5
Rank the magnitude of the torques acting on the rectangular loops shown in Figure 29.15, from highest to lowest. All loops are identical and carry the same current. C , B , A
Quick Quiz 29.6
When a photographic plate from a mass spectrometer like the one shown in Figure 29.23 is developed, the three patterns shown in Figure 29.25 are observed. Rank the particles that caused the patterns by speed and m/q ratio. C , B , A
Quick Quiz 30.1
For I1=2A, I2=6A and in Figure 30.7, which is true: (a) F1=F3(b) F1=F2/3 or (c)F1 =F2 ?
Quick Quiz 30.2
A loose spiral spring is hung from the ceiling, and a large current is sent through it. Do the coils move closer together or farther apart?
Quick Quiz 30.3
Rank the magnitudes of _B_ ds for the closed paths in Figure 30.9, from least to greatest. WITH AMPERS B, D, A, C
Quick Quiz 30.4
Rank the magnitudes of _B_ ds for the closed paths in Figure 30.10, from least to greatest. B, A=C=D
Quick Quiz 30.5
Is a net force acting on the current loop in Example 30.7? A net torque? Net force, yes; net torque, no
Quick Quiz 30.6
What is the displacement current for a fully charged 3-NF capacitor? Zero;
Quick Quiz 30.7
A current in a solenoid having air in the interior creates a magnetic field Describe qualitatively what happens to the magnitude of B as (a) aluminum, (b) copper, and (C)iron are placed in the interior. (a) Increases slightly; (b) decreases slightly; (c) increases greatly.
Quick Quiz 30.8
Which material would make a better permanent magnet, one whose hysteresis loop looks like Figure 30.31a or one whose loop looks like Figure 30.31b? One whose loop looks like Figure 30.31a because the remanent magnetization at the point corresponding to point b in Figure 30.30 is greater.
Quick Quiz 30.9
If we wanted to cancel the Earths magnetic field by running an enormous current loop around the equator, which way would the current have to flow: east to west or west to east?
Quick Quiz 31.1
Equation 31.3 can be used to calculate the emf induced when the north pole of a magnet is moved toward a loop of wire, along the axis perpendicular to the plane of the loop passing through its center. What changes are necessary in the equation when the south pole is moved toward the loop? Because the magnetic field now points in the opposite direction, you must replace KETA with KETA + PI
Quick Quiz 31.2
As an airplane flies from Los Angeles to Seattle, it passes through the Earth s magnetic field. As a result, a motional emf is developed between the wingtips. Which wingtip is positively charged? The one on the west side of the plane.
Quick Quiz 31.3
Figure 31.14 shows a magnet being moved in the vicinity of a solenoid connected to a galvanometer. The south pole of the magnet is the pole nearest the solenoid, and the gal- vanometer indicates a clockwise (viewed from above) current in the solenoid. Is the person inserting the magnet or pulling it out?
You might also like
- Quiz 2solutionDocument10 pagesQuiz 2solutionAdarsh ChhajedNo ratings yet
- Test: Section 2 Quiz 1 - L1-L7 ReviewDocument6 pagesTest: Section 2 Quiz 1 - L1-L7 ReviewJawahar MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration 2Document6 pagesElectron Configuration 2268953No ratings yet
- Quiz For Small Business SuccessDocument4 pagesQuiz For Small Business SuccessJohn PratheeshNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document6 pagesQuiz 3Dronadula Venkata Sumanth SumanthNo ratings yet
- Economics QuizDocument3 pagesEconomics Quizdesi_paris100% (1)
- Self Generating Sensors Quiz Exam Sr. No. Answer 1. A 2. C 3. CDocument2 pagesSelf Generating Sensors Quiz Exam Sr. No. Answer 1. A 2. C 3. CMeghayu Adhvaryu100% (1)
- Conservation of Mass WorksheetDocument3 pagesConservation of Mass WorksheetDJ - 10GB 742966 Glenforest SSNo ratings yet
- Act.10 Content Quiz # 3 ListeningDocument5 pagesAct.10 Content Quiz # 3 ListeningJ Etb Castro AlzateNo ratings yet
- 20 Tips For Creating A Safe Learning EnvironmentDocument3 pages20 Tips For Creating A Safe Learning Environmentghulam sabirNo ratings yet
- 3 - Pulpal and Periradicular PathosisDocument10 pages3 - Pulpal and Periradicular PathosisZaid AKNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Behaviourist Developmental TheoriesDocument24 pagesTopic 2 Behaviourist Developmental Theoriesadamskbd100% (1)
- Physics 124A Practice Quiz VectorsDocument4 pagesPhysics 124A Practice Quiz VectorsReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Water QuizDocument11 pagesWater QuizMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- Action Research FormatDocument1 pageAction Research FormatEden EscaloNo ratings yet
- CHAP 1 - Zener DiodeDocument65 pagesCHAP 1 - Zener Diodeksreddy2002No ratings yet
- Practice Test 2 - Nuclear ChemistryDocument5 pagesPractice Test 2 - Nuclear ChemistryRauMuống XàoTỏi VắtChanhNo ratings yet
- Greek Mythology Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesGreek Mythology Lesson PlanDave BarthNo ratings yet
- Practice Test KinematicsDocument10 pagesPractice Test KinematicsCool GuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27: Current and Resistance in CircuitsDocument17 pagesChapter 27: Current and Resistance in CircuitsAnita MihalakNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz 25Document23 pagesQuick Quiz 25MonishaNo ratings yet
- REVISION TEST 1 - PHYSICSDocument8 pagesREVISION TEST 1 - PHYSICSSarvan SankaranNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument17 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersprismtonicNo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 1 Physics Assertion Reasoning Electric Charges and FieldsDocument6 pagesPhysics XII CH 1 Physics Assertion Reasoning Electric Charges and FieldsNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- Physics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionDocument25 pagesPhysics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionA KNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023Document7 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023shagun sinhaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument21 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersprismtonicNo ratings yet
- Practice Test - Xii - Physics - 2021-22Document16 pagesPractice Test - Xii - Physics - 2021-22Rahul SinghNo ratings yet
- PB - II Physics Xii 2023-24Document7 pagesPB - II Physics Xii 2023-24hari008091No ratings yet
- Xii Physics - Chapter 2term 1Document17 pagesXii Physics - Chapter 2term 1RahulNo ratings yet
- Physics (Code No. 042) Maximum Marks: 40 TIME: 2 Hours General InstructionsDocument4 pagesPhysics (Code No. 042) Maximum Marks: 40 TIME: 2 Hours General InstructionsHemelatha NairNo ratings yet
- 12 PhysicsDocument8 pages12 Physicsdhritibarak548No ratings yet
- 12 Physics Sp10Document18 pages12 Physics Sp10Divydarshan MishraNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Term 1 QP Xii 2020 SeptDocument9 pagesSample Test Term 1 QP Xii 2020 SeptEdwinNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics sp02 PDFDocument25 pages12 Physics sp02 PDFaditya prabhakerNo ratings yet
- Application of Physics II For: Midterm ExamDocument66 pagesApplication of Physics II For: Midterm ExamÖmer faruk SilNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz 26Document19 pagesQuick Quiz 26Jade Abellanosa LavinNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Electric Potential and Capacitance Sheet 1Document4 pagesChapter2 Electric Potential and Capacitance Sheet 1AYUSH UPADHYAY STUDENT VKNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Test: Electricity and Magnetism-Solutions: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesAP Physics Test: Electricity and Magnetism-Solutions: Multiple Choice QuestionsChen JohnNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersDocument17 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- MasteringPhysics - Assignments10 - 9 - 11Document12 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignments10 - 9 - 11Dylan StefanskiNo ratings yet
- XII Revision Sheet 7 PhysicsDocument2 pagesXII Revision Sheet 7 PhysicsVipin VNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document20 pagesCH 1terasaini77No ratings yet
- 1121 Finals 106 NewDocument4 pages1121 Finals 106 NewPrabaharan GunarajahNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA BHOPAL REGION PRE TERM-I EXAMINATION PHYSICS (042) CLASS XIIDocument8 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA BHOPAL REGION PRE TERM-I EXAMINATION PHYSICS (042) CLASS XIIjhjhghghgghNo ratings yet
- Phy201p QPDocument9 pagesPhy201p QPAyush XI-ANo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument18 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersGyan BardeNo ratings yet
- Class 12th - QuestionBank - Physics-1-15-48Document34 pagesClass 12th - QuestionBank - Physics-1-15-48Sathya SeelanNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Prep QP 21Document14 pages12 Physics Prep QP 21alichaudaryNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz 28Document29 pagesQuick Quiz 28Hồng NhơnNo ratings yet
- Capacitors in Series and Parallel EquationsDocument4 pagesCapacitors in Series and Parallel EquationsBeverly Panganiban CadacioNo ratings yet
- Class 9 SourceDocument17 pagesClass 9 SourceDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 PP Xii PhysicsDocument4 pagesChapter 01 PP Xii Physicsstudywithak77No ratings yet
- Chap.-1 (Electric Charges and Filds)Document5 pagesChap.-1 (Electric Charges and Filds)lanfury45No ratings yet
- G-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2Document12 pagesG-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2annahiazNo ratings yet
- 7 SQPDocument7 pages7 SQPlanfury45No ratings yet
- PHYS 102 - Exam 1 - Spring 2015: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument6 pagesPHYS 102 - Exam 1 - Spring 2015: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNo ratings yet
- Class - Xii: (Physics)Document8 pagesClass - Xii: (Physics)kamalmeena2rkNo ratings yet
- Sample Papers SolvedDocument185 pagesSample Papers Solvedjovanbhaskaran10No ratings yet
- Schedule For ENG 102-3-4h Spring 2013 26febDocument2 pagesSchedule For ENG 102-3-4h Spring 2013 26febLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- JS Summary Example BergerDocument2 pagesJS Summary Example BergerLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Model Research Proposal BalkansDocument8 pagesModel Research Proposal BalkansLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- In-Class Writing AssignmentDocument1 pageIn-Class Writing AssignmentLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Interviewing For A Job NotesDocument19 pagesInterviewing For A Job NotesLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- MIT Cover LettersDocument2 pagesMIT Cover Lettersenzo_wooNo ratings yet
- Journal Article Summary Assignment and RubricDocument3 pagesJournal Article Summary Assignment and RubricLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Hagen Safe Just and Smart Home Education in Albania AIS Studime SocialDocument16 pagesHagen Safe Just and Smart Home Education in Albania AIS Studime SocialLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Example Paper CC325C Falun Gong and Civil Society 5-00Document15 pagesExample Paper CC325C Falun Gong and Civil Society 5-00Laert VeliaNo ratings yet
- From The Craft of Researc PergjigjeDocument6 pagesFrom The Craft of Researc PergjigjeLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research ProposalDocument3 pagesHow To Write A Research ProposalLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- HIV/AIDS Impact on Foreign Investment in South AfricaDocument22 pagesHIV/AIDS Impact on Foreign Investment in South AfricaLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Rhetoric Canon Discovery Arrangement Style Memorization Delivery Thesis Arguments Modes Logos FallaciesDocument1 pageRhetoric Canon Discovery Arrangement Style Memorization Delivery Thesis Arguments Modes Logos FallaciesLaert Velia0% (1)
- From The Craft of Researc1Document2 pagesFrom The Craft of Researc1Laert VeliaNo ratings yet
- From Classical Rhetoric For The Modern Student PergjigjeDocument4 pagesFrom Classical Rhetoric For The Modern Student PergjigjeLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CRMS Discovery of ArgumentsDocument26 pagesCRMS Discovery of ArgumentsLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Free To Learn Research Proposal ChicagoDocument15 pagesFree To Learn Research Proposal ChicagoLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Example Paper CC270 SpontaneousGenDocument14 pagesExample Paper CC270 SpontaneousGenLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Planning: From The Craft of Research by Booth, Colomb, and WilliamsDocument15 pagesPlanning: From The Craft of Research by Booth, Colomb, and WilliamsLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive and Analytical WritingDocument10 pagesDescriptive and Analytical WritingLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CRMS Looking For An ArgumentDocument10 pagesCRMS Looking For An ArgumentLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CR10 Acknowledgements and ResponsesDocument20 pagesCR10 Acknowledgements and ResponsesLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CR14 Revising Your Organization and ArgumentDocument13 pagesCR14 Revising Your Organization and ArgumentLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CRMS Introduction To RhetoricDocument14 pagesCRMS Introduction To RhetoricLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CR17 Revising StyleDocument17 pagesCR17 Revising StyleLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CR16 Introductions and ConclusionsDocument19 pagesCR16 Introductions and ConclusionsLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CR13 Drafting Your Report BDocument16 pagesCR13 Drafting Your Report BLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CR10 Acknowledgements and ResponsesDocument20 pagesCR10 Acknowledgements and ResponsesLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CR11 WarrantsDocument22 pagesCR11 WarrantsLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- CR9 Assembling Reasons and EvidenceDocument11 pagesCR9 Assembling Reasons and EvidenceLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Unit 3 - Justine T. SaldivarDocument15 pagesFluid Mechanics - Unit 3 - Justine T. SaldivarJustine Tizon SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Liquid Pressure Drop CalculationDocument9 pagesLiquid Pressure Drop CalculationMichaelMahonyNo ratings yet
- ME F211 Mechanis of SolidsDocument3 pagesME F211 Mechanis of SolidsVivekananda NandamNo ratings yet
- Standard Test Method For Tensile Properties of Geotextiles by The Wide-Width Strip MethodDocument13 pagesStandard Test Method For Tensile Properties of Geotextiles by The Wide-Width Strip MethodPaulo CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Teaching The Third Law of ThermodynamicsDocument22 pagesTeaching The Third Law of ThermodynamicsandersonNo ratings yet
- Belt Tracking GuideDocument13 pagesBelt Tracking GuideWinston NoelNo ratings yet
- Failure Criteria For Unidirectional Fiber Composites: Z. HashinDocument6 pagesFailure Criteria For Unidirectional Fiber Composites: Z. HashinrezaroohollahiNo ratings yet
- Parth Thesis 2015Document120 pagesParth Thesis 2015Darwin MoranNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Assessment As Per API 579-1ASME FFS-1 For Pressure Vessel General Metal Loss by Using FEA Techniques by Kingston.RDocument21 pagesLevel 3 Assessment As Per API 579-1ASME FFS-1 For Pressure Vessel General Metal Loss by Using FEA Techniques by Kingston.Rkingston100% (1)
- Physics Year 9 Schemes of WorkDocument12 pagesPhysics Year 9 Schemes of WorkMaoga2013100% (1)
- Nose Cone Design 2 PDFDocument76 pagesNose Cone Design 2 PDFgssrrajuNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Constants and Conversion FactorsDocument1 pageFundamental Constants and Conversion FactorsRanggaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Procedures:: P ρ gh P PDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab Procedures:: P ρ gh P Papi-244640341No ratings yet
- Aguero - Equivalent Geometric Imperfection Definition - CompressionDocument18 pagesAguero - Equivalent Geometric Imperfection Definition - CompressionDawid GabrysiakNo ratings yet
- Residual Stresses & Fatigue Life With Case StudyDocument13 pagesResidual Stresses & Fatigue Life With Case StudyDishant ShindeNo ratings yet
- Variable Area Flowmeter PresentationDocument17 pagesVariable Area Flowmeter PresentationRoger GimenesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Steel DesignDocument34 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Steel DesignTyrone PaulinoNo ratings yet
- J Values ExplndDocument20 pagesJ Values ExplndAri SinghNo ratings yet
- Linx Refresher Review: IPD PPD REFRESHERS TRIVIA EXAMINATIONDocument7 pagesLinx Refresher Review: IPD PPD REFRESHERS TRIVIA EXAMINATIONDeyn EstoqueNo ratings yet
- A Critical Assessment of Block TestDocument11 pagesA Critical Assessment of Block TestaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter 1Document16 pagesSolutions Chapter 1BluaNo ratings yet
- Compton EffectDocument4 pagesCompton EffectNatheesh TpNo ratings yet
- SpringDocument47 pagesSpringThiru NarayananNo ratings yet
- Temperature Measurement: N 1 - / 1 - / QQ TTDocument11 pagesTemperature Measurement: N 1 - / 1 - / QQ TTAhmad AbdNo ratings yet
- Shallow WaterDocument25 pagesShallow Water1111566No ratings yet
- Ch04 05 Force Problem BankDocument11 pagesCh04 05 Force Problem Banknicky1213aNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Loads NSCP 2015Document10 pagesEarthquake Loads NSCP 2015Franklyn Genove50% (2)
- Freon 134a Thermodynamic Properties Eng Units PDFDocument56 pagesFreon 134a Thermodynamic Properties Eng Units PDFRiedo YusharyahyaNo ratings yet
- Diagram Explanation X Y ZDocument7 pagesDiagram Explanation X Y Zpkgmuda6869No ratings yet
- Why Is 5% Strain Limit Used in Material Diagram For AISC - PDFDocument11 pagesWhy Is 5% Strain Limit Used in Material Diagram For AISC - PDFngocnnNo ratings yet