Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bending: Nri Institute of Information Science & Technology Bhopal (M.P)
Uploaded by
Tare Er KshitijOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bending: Nri Institute of Information Science & Technology Bhopal (M.P)
Uploaded by
Tare Er KshitijCopyright:
Available Formats
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.
P)
BENDING
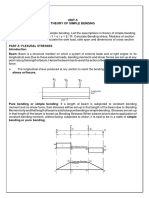
INTRODUCTION: When some external load acts on a beam, the Shear force and bending moments are set up at all sections of the beam. Due to shear force and bending moment, the beam under-goes certain deformation; the material of the beam will offer resistance or stresses against these deformations. The stresses introduced by bending moment are known as bending stresses. PURE BENDING OR SIMPLE BENDING: If a length of a beam is subjected to a constant bending moment and no shear force (i.e., zero force), then the stresses will be set up in that length of the beam due to B.M. only and that length of the beam is said to be in pure bending or simple bending. The stresses set up in that length of the beam are known as bending stresses.
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 1
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
THEORY OF SIMPLE BENDING WITH ASSUMPTION MADE: The following are the assumption made in the theory of simple bending. The material of the beam is homogenous (the material is of the same kind throughout) and isotropic (the elastic properties in all direction are equal). The value of Youngs modulus of elasticity is the same in tension and compression. The transverse sections which were plane before bending remain plane after bending also. The beam is initially straight and all longitudinal filaments bend into circular area with a common center of curvature. The radius of curvature is large compared with the dimension of the crosssection. Each layer of the beam is free to expand or contact, independently of the layer, above or below it.
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 2
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
THEORY OF SIMPLE BENDING
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 3
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 4
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
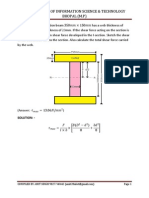
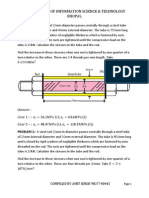
MOMENT OF RESISTANCE: Due to pure bending, the layers above N.A. are subjected to compressive stresses whereas the layers below the N.A. are subjected to tensile stresses. Due to theses stresses, the forces will be acting on the layers. There forces will have the moment about the N.A. The total moment about the N.A. for a section is known as the moment of resistance of that section.
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 5
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 6
NRI INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY BHOPAL (M.P)
COMPILED BY AMIT SINGH 9827740442 (amit28niist@gmail.com)
Page 7
You might also like
- Stiffness Calculation For PileDocument2 pagesStiffness Calculation For PilePriyabrata Mahata100% (10)
- SolutionDocument13 pagesSolutionTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Composite Slab DesignDocument6 pagesComposite Slab DesignFranklyn GenoveNo ratings yet
- Farhan Akhtar Poem From ZNMDDocument3 pagesFarhan Akhtar Poem From ZNMDTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Set 8Document5 pagesSet 8Tare Er Kshitij100% (1)
- Set 7Document11 pagesSet 7Tare Er Kshitij100% (1)
- Set 2 (Unit 2)Document13 pagesSet 2 (Unit 2)Tare Er Kshitij64% (11)
- Set 3 - Unit 3Document6 pagesSet 3 - Unit 3Tare Er Kshitij100% (3)
- Bending of BeamsDocument17 pagesBending of Beamskusangichandana100% (1)
- Mom PPT-1Document28 pagesMom PPT-1Syed Muzammil AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document8 pagesUnit 1harinathNo ratings yet
- Module-4: Stresses in BeamsDocument41 pagesModule-4: Stresses in BeamsVIVEKNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2design Against Static LoadDocument33 pagesCHAPTER 2design Against Static LoadmanishtopsecretsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 LeverDocument4 pagesChapter 03 Leverrajendra20No ratings yet
- MOM Module 3Document24 pagesMOM Module 3Ramesh Reddy B TNo ratings yet
- Simple Bending1Document10 pagesSimple Bending1programmingprofessor01No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Ending StressesDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 3 Ending StresseshaymanotNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies IIDocument124 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies IIkarlajane0350% (2)
- Design of Machine ElementsDocument53 pagesDesign of Machine ElementsRajeswari DhamotharanNo ratings yet
- Bending and Shear Stresses in BeamDocument20 pagesBending and Shear Stresses in BeamJiya ShindeNo ratings yet
- Mech206 - 2014-15 Spring - l04 - Pure BendingDocument28 pagesMech206 - 2014-15 Spring - l04 - Pure BendingYazan HarbNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2: Shear and Bending in BeamsDocument37 pagesUnit - 2: Shear and Bending in BeamsRobert DownieNo ratings yet
- MEMSDocument71 pagesMEMSSantosh VishnuNo ratings yet
- MOS-2 MarksDocument18 pagesMOS-2 MarksGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- When A Beam Is Subjected To A Loading System or by A Force Couple Acting On A Plane Passing Through The AxisDocument4 pagesWhen A Beam Is Subjected To A Loading System or by A Force Couple Acting On A Plane Passing Through The AxisLakshika SubodhaniNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAnonymous ML4hh4MOyBNo ratings yet
- Mom PPT-2Document27 pagesMom PPT-2Syed Muzammil AliNo ratings yet
- Verification of Bending Stress and Shear Stress Distribution Across The Depth For Slender BeamDocument6 pagesVerification of Bending Stress and Shear Stress Distribution Across The Depth For Slender BeamAditiDeshpandeNo ratings yet
- KCG College of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Ce 6306-Strength of Materials (Sem: 3) Question Bank For Unit 2Document4 pagesKCG College of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Ce 6306-Strength of Materials (Sem: 3) Question Bank For Unit 2adamodaraNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements PageDocument203 pagesDesign of Machine Elements PageKrishnan P MNo ratings yet
- Verification of Bending Stress and Shear Stress Distribution Across The Depth For Slender BeamDocument7 pagesVerification of Bending Stress and Shear Stress Distribution Across The Depth For Slender BeamAditiDeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19Document11 pagesLecture 19Adam SurtiNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument15 pagesFaculty of Engineering and TechnologyAditya Kumar GautamNo ratings yet
- Strength 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument27 pagesStrength 2 Marks All 5 UnitsparathNo ratings yet
- BSC103C Pre-recordedLecture Topic8 v3.2Document71 pagesBSC103C Pre-recordedLecture Topic8 v3.2fxl62920No ratings yet
- What Is Engineering Arch Theory?Document2 pagesWhat Is Engineering Arch Theory?Jeewanshu UttamNo ratings yet
- 6 BeamsDocument116 pages6 BeamsIrish TambisNo ratings yet
- Title of Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument1 pageTitle of Shear Force and Bending MomentMuhammad Yusoff ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Flexural Formula or Bending Equation & Shearing EquationDocument16 pagesFlexural Formula or Bending Equation & Shearing Equationmaniram7No ratings yet
- Members Subjected To BendingDocument5 pagesMembers Subjected To BendingRonald obasieNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityDocument78 pagesUnit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityNirav LakhaniNo ratings yet
- 17me64 Dme-2 Module 1Document15 pages17me64 Dme-2 Module 1GgghhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Columns and Strut: Failure of A ColumnDocument10 pagesChapter 7: Columns and Strut: Failure of A ColumnAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Beton Prategang: Members Analysis Under ShearDocument45 pagesBeton Prategang: Members Analysis Under Shearzacoeb_a1669No ratings yet
- Civil Engg Interview QuestionsDocument41 pagesCivil Engg Interview QuestionspraveenNo ratings yet
- Beams: by - Ir.Sugeng P Budio, MSC 1Document18 pagesBeams: by - Ir.Sugeng P Budio, MSC 1ragil_purnamasariNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Presentation PDFDocument30 pagesStructural Analysis Presentation PDFArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Deflection of Beam - 2sDocument19 pagesDeflection of Beam - 2sDave Harrison FloresNo ratings yet
- Flexural Stresses in Beams - IDocument3 pagesFlexural Stresses in Beams - IZewdieNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Beams-Loads and StressesDocument60 pagesUnit II - Beams-Loads and StressesMonesh kumarNo ratings yet
- CE2401 - Design of Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument4 pagesCE2401 - Design of Reinforced Concrete DesignSabarinath MuruganNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements: Unit - I Steady Stresses and Variable Stress in Machine MembesDocument53 pagesDesign of Machine Elements: Unit - I Steady Stresses and Variable Stress in Machine MembesDinesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-MENG 313Document45 pagesMechanics of Materials-MENG 313Kelly GbandehNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document50 pagesCH 4Doğukan KurtuluşNo ratings yet
- Basic Mech ConceptDocument13 pagesBasic Mech Conceptdavesh jadonNo ratings yet
- 07 Flexure in Beams Fundamentals 01Document20 pages07 Flexure in Beams Fundamentals 01S. M. ZAHIDUR RAHMAN 1301129No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materia1 Combined Bending and TorsionDocument4 pagesMechanics of Materia1 Combined Bending and Torsionhammad ghaffarNo ratings yet
- Maximum Deflection of Different Types of BeamsDocument3 pagesMaximum Deflection of Different Types of BeamsVivek SonkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Bending and Shearing StressesDocument70 pagesChapter Three Bending and Shearing StressesYalem MesfinNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDocument27 pagesStrength of Materials - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M89% (38)
- UNIT4-MEC236-Bending Stresses in BeamsDocument18 pagesUNIT4-MEC236-Bending Stresses in Beamsintustan leeNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Stresses in BeamsDocument14 pagesModule 5 - Stresses in Beamswag naNo ratings yet
- Bending of Beams SolleroDocument34 pagesBending of Beams SolleroPedroLemosNo ratings yet
- CEE485 Lect5 2009Document6 pagesCEE485 Lect5 2009Jack IanNo ratings yet
- GATE Aerospace Study Material Book 3 Aircraft StructureDocument16 pagesGATE Aerospace Study Material Book 3 Aircraft StructureAham BrahmasmiNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Strength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainFrom EverandStrength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Jhelum Exp Jammu To Pune Time TableDocument4 pagesJhelum Exp Jammu To Pune Time TableTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular ShaftDocument12 pagesTorsion of Circular ShaftTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- RC Design V 2.0 UN: Rebar PS: NewtonDocument1 pageRC Design V 2.0 UN: Rebar PS: NewtonTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Sunday, September 14, 2014 9:19 PMDocument2 pagesSunday, September 14, 2014 9:19 PMTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Jhelum Exp PUne To JammuTime TableDocument4 pagesJhelum Exp PUne To JammuTime TableTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Thin Wall Pressure VesselsDocument20 pagesThin Wall Pressure VesselsTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument6 pagesSolutionTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Design Example For PrestressedDocument8 pagesComprehensive Design Example For PrestressedTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Set 6Document15 pagesSet 6Tare Er Kshitij60% (5)
- Set 4 - Unit 3Document5 pagesSet 4 - Unit 3Tare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Set 1 - Unit 4Document8 pagesSet 1 - Unit 4Tare Er Kshitij0% (1)
- Set 2 - Unit 3Document8 pagesSet 2 - Unit 3Tare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Deflection of BeamDocument18 pagesDeflection of BeamTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Set 1 (Unit 2)Document15 pagesSet 1 (Unit 2)Tare Er Kshitij67% (9)
- Set 1 - Unit 3Document8 pagesSet 1 - Unit 3Tare Er Kshitij67% (3)
- NICMAR Exam Ques Paper - June 2010Document10 pagesNICMAR Exam Ques Paper - June 2010Vithal Katrodiya100% (6)
- Comparative Study On RCC Structure With and Without Shear WallDocument26 pagesComparative Study On RCC Structure With and Without Shear WallTare Er Kshitij0% (1)
- I'm A Rock Chick in A Hard Rock World and Nothing Rocks Than A Rock Chick GirlDocument1 pageI'm A Rock Chick in A Hard Rock World and Nothing Rocks Than A Rock Chick GirlTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Gps/Ins: See AlsoDocument1 pageGps/Ins: See AlsoTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- Efeito Arco PDFDocument10 pagesEfeito Arco PDFGustavo VilelaNo ratings yet
- Typical Waterstop Properties: Hardness - ASTM D2240Document4 pagesTypical Waterstop Properties: Hardness - ASTM D2240Dicky PramonoNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Quasi Fermi EnergyDocument3 pagesDefinition of The Quasi Fermi EnergyFlor EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Welded ConnectionDocument37 pagesWelded ConnectionRajib MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Defect Engineering of ZnO - Review On Oxygen and Zinc VacanciesDocument20 pagesDefect Engineering of ZnO - Review On Oxygen and Zinc VacanciesHalimah YusoffNo ratings yet
- Discrete Dislocation DynamicsDocument10 pagesDiscrete Dislocation DynamicsFabian de Jesus Orozco MartinezNo ratings yet
- IJETR041973Document5 pagesIJETR041973erpublicationNo ratings yet
- Nptel: Advanced Marine Structures - Video CourseDocument4 pagesNptel: Advanced Marine Structures - Video CourseSuman.SNo ratings yet
- Nickel Super Alloy INCONEL 713LC - Structural Characteristics After Heat TreatmentDocument9 pagesNickel Super Alloy INCONEL 713LC - Structural Characteristics After Heat TreatmentelmiraNo ratings yet
- Session13 Henkel SoritaDocument41 pagesSession13 Henkel Soritahsaini19762387No ratings yet
- Surface & Coatings Technology: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesSurface & Coatings Technology: SciencedirectVikrant Saumitra mm20d401No ratings yet
- Icsid2019 Program Overview v0.1Document1 pageIcsid2019 Program Overview v0.1Radu IuliaNo ratings yet
- Draft StructuralSteel DesignGuideDocument79 pagesDraft StructuralSteel DesignGuideSheila Rose Bacerra-VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Burns, Parry - Effect of Mean Shear Stress On The Fatigue IDocument9 pagesBurns, Parry - Effect of Mean Shear Stress On The Fatigue IDavid C HouserNo ratings yet
- (Appendix 1) Solids: Oelze ECE/TAM 373 Notes - Chapter 5 PG 27Document8 pages(Appendix 1) Solids: Oelze ECE/TAM 373 Notes - Chapter 5 PG 27AlinaBogoiNo ratings yet
- Steel Properties, Limit State Design and Introduction To EurocodesDocument51 pagesSteel Properties, Limit State Design and Introduction To EurocodesLilyNo ratings yet
- Realize The Potential: Apparent Hardness vs. Thickness in Over-Mold ApplicationsDocument2 pagesRealize The Potential: Apparent Hardness vs. Thickness in Over-Mold Applicationsisraelevy1No ratings yet
- Pham 2018Document33 pagesPham 2018Mohamed YasserNo ratings yet
- Physical and Mechanical Properties of ConcreteDocument5 pagesPhysical and Mechanical Properties of ConcreteInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ipc 2022 87078 A Comprehensive New Look at Type B SleevesDocument7 pagesIpc 2022 87078 A Comprehensive New Look at Type B SleevesOswaldo MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Resin Cation AnionDocument11 pagesPerhitungan Resin Cation AnionkhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Material Science: Unit Wise Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesMaterial Science: Unit Wise Lecture NotesLogesh GovindNo ratings yet
- Effect of Multi-Pass SMAW Welding On The Surface HDocument7 pagesEffect of Multi-Pass SMAW Welding On The Surface HYousab CreatorNo ratings yet
- CHE 2131 Module 2 Unit 2Document7 pagesCHE 2131 Module 2 Unit 2Poison PinkNo ratings yet
- MOSDocument366 pagesMOSMr.S UpenderNo ratings yet
- Modulus NewDocument35 pagesModulus NewSanaullah BalochNo ratings yet
- Bibliografia - Desgaste em Matrizes de ForjamentoDocument1 pageBibliografia - Desgaste em Matrizes de ForjamentoFerramentalNo ratings yet
- Modeling and FE Analysis of Column To Beam End-Plate Bolted ConnectionDocument17 pagesModeling and FE Analysis of Column To Beam End-Plate Bolted ConnectionAhmed MoniemNo ratings yet