Professional Documents
Culture Documents
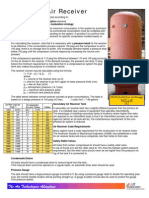
Air Receivers Volume Calculation
Uploaded by
Kenny RuizCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Receivers Volume Calculation
Uploaded by
Kenny RuizCopyright:
Available Formats
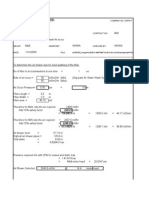
Air receiver volume Compressor mass flow rate
Ambient pressure m
comp
= V
comp
*
n
P
amb
= 80 kPa V
comp
= 0.56
Nm
3
/s
Ambient temperature
n
= 1.29
kg/Nm
3
t
amb
= 10 C m
comp
= 0.728 kg/s
Normal conditions Receiver
P
N
= 1.01325 bar Pressure difference op. range
T
N
= 273.15 K This is the difference betwee the
Normal density maximum an minimum pressures
n
= p / ( R * T) AP
op
= 0.7 bar
p = 101,325 Pa Air temperature in receiver
R = 286.9 J/(kg*K) t
rcv
= t
comp_out
T = 273 K t
rcv
= 25 C
n
= 1.29
kg/Nm
3
P
rcv_initial
= P
comp_out
Compressor P
rcv_initial
= 6.5 bar (g)
Refrigerated type P
rcv_final
= P
rec_initial
- AP
op
Required volumetric flow rate P
rcv_initial
= 6.5 bar (g)
V
req_N
= 0.45 Nm/s AP
op
= 0.7 bar
Ratio compresor flow rate "V
comp
" P
rcv_final
= 5.8 bar (g)
to required flow rate "V
req
" Receiver inlet mass flow rate
F = V
comp_N
/ V
req_N
V
rcv_in
= 0.56 Nm/s
F = 1.25 Receiver outlet mass flow rate
V
comp_N
= 0.56 Nm/s V
rcv_out
= 0.45 Nm/s
Required prressure at receiver exit
P
rec_out
= 6 bar (g) Required mass flow rate
Pressure drop Compressor-Receiv. leaving the receiver
DP
comp-rec
= 0.5 bar m
rcv_out
= V
rec_out
*
n
Presure at compressor exit V
rcv_out
= 0.45
Nm
3
/s
P
comp_out
= P
rec_out
+ DP
comp_rec
n
= 1.29
kg/Nm
3
P
rec_out
= 6 bar (g) m
rcv_out
= 0.582 kg/s
DP
comp-rec
= 0.5 bar
P
comp_out
= 6.5 bar (g) Receiver inlet mas flow rate
Temperature at exit of refr. comp. m
rcv_in
= m
comp
t
comp_out
= 25 C m
comp
= 0.728 kg/s
m
rcv_in
= 0.728 kg/s
Inlet conditions Air required by the
V
n
= #REF! Nm/s system (or consumption)
P
comp_in
= #REF! kPa V
req
= 0.45 Nm/s
T
comp_in
= #REF! K
Receiver
bar
AP = 6 Average values of pressure
#REF! and temperature
#REF! P
m
= #REF! Pa
Cooleded compressor T
m
= #REF! K
Outlet conditions
V
n
= #REF! Nm/s
P
comp_out
= #REF! Pa
T
comp_out
= #REF! K
bar
Pin = b
Pout b
Rev.cjc. 1.08.2013
Operating time (to fill the receiver) The time required for the pressure
Time required for the compressor to reach this condition is defined
to bring the receiver from the low by the equation:
pressure
Am =
m
rec_out
*t
deliver
P
final
= 5.8 bar (g) t
deliver
= Am / m
rec_out
to the initial pressure Am = 8.7 kg
P
initial
= 6.5 bar (g) m
rec_out
= 0.582 kg/s
when the receiver is being filled t
deliver
= 15.0 s
by the compressor at the rate
"m
in
" and at the same time the The total cycle time is
system is consuming air at the t
cycle
= t
Fill
+ t
deliver
flow rate "m
out
". t
Fill
= 60 s
The operating time to fill the t
deliver
= 15 s
receiver under these conditions t
cycle
= 75 s
is assumed selected as
t
Fill
= 60 s
Air mass required in a cycle V =
t
Fill
*P
N
*[V
comp_N
V
rcv_N
]*(T
rcv
/T
N
*(1/AP
op
)
Am =
(m
rec_in
- m
rec_out
) *t
Fill
t
Fill
= 60 s
m
rec_in
= 0.728 kg/s P
N
= 1.01325 bar
m
rec_out
= 0.582 kg/s V
comp_N
= 0.56 Nm/s
t
Fill
= 60 s V
rcv_N
= 0.45 Nm/s
Am =
8.7 kg T
rcv
= 298.15 K
This is the air mass that will T
N
= 273.15 K
go in and out of the receiver AP
op
= 0.7 bar
V = 10.66 m
After this time, the compressor
stops. Tank volume
The receiver starts to deliver air H = 1.5 * d
at the required flow rate. d = 2.1 m
m
rec_out
= 0.582 kg/s H = 3.15 m
until the pressure decreses to V = (pi()/4) * d^2 * H
the minimum pressure d = 2.1 m
P
rec_final
= 5.8 bar (g) H = 3.15 m
V = 10.9 m
| |
op N
rcv
N rec N comp N Fill
P T
T
V V P V
A
=
1
_ _
t
Mass change during a cycle in receiver
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
op N
rcv
N rec N comp N Fill
op
rcv
N
N rec N comp N Fill
op
rcv
N
N rec N comp N Fill
Fill
N
N
N rec N comp
N
N
N
Fill N N rec N comp
Fill N N rec N N comp
N N rec out rec
N N comp in rec
comp in rec
Fill out rec in rec
P T
T
V V P V
P
T R
R T
V V P V
P
T R m V
R T
V V P m
T R
P
V V m
T R
P
V V m
V V m
V m
V m
m m
m m m
receiver in cycle a during change Mass
A
=
A
=
A
A =
= A
= A
=
= A
= A
=
=
=
= A
1
1 1 1
1
____ __________ __________ __________
1 1
: _ _ _ _ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_
_ _
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
Time to fill, initally, the receiver
Densities
P
final
= P
comp_out
Initial density
P
comp_out
= 6.5 bar (g)
initial
= p
initial
/ ( R * T
initial
)
P
atm
= 0.8 bar P
initial
= 80000 Pa
P
comp_out
= 7.3 bar T
initial
= 298.15 K
P
final
= 7.3 bar R = 286.9 J/(kg*K)
initial
= 0.935 kg/m
P
initial
= P
amb
P
amb
= 0.8 bar Final density
P
initial
= 0.8 bar
final
= P
final
/ ( R * T
final
)
P
final
= 730000 Pa
Isothermal process T
final
= 298.15 K
t
rcv =
25 C R = 286.9 J/(kg*K)
t
initial
= t
rcv
final
= 8.534 kg/m
t
initial
= 25 C
t
final
= 25 C Mass to fill reveiver
m = m
final
- m
initial
Receiver volume m = V *
final
- V *
initial
V = 10.66 m m = V * (
final
-
initial
)
V = 10.66 m
final
= 8.534 kg/m
initial
= 0.935 kg/m
m = 81.04 kg
Air constant
R = Rg / MM
Rg = 8314.41 [ J / (kmol*K)]
MM = 28.97 kg/kmol
R = 287.0 (J/(kg*K)
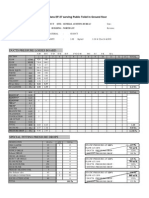
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
0 50 100
m (kg)
220
225
230
235
240
245
250
255
260
261.4
Compressor mass flow rate Mass remaining in receiver when the
Normal flow rate pressure reaches the defined minimum
V
comp_N
= 0.56 Nm/s value
Normal density P
rcv_final
= 5.8 bar (g)
n
= p / ( R * T) P
rcv_final
= 6.6 bar
p = 101,325 Pa Density
R = 286.9 J/(kg*K)
final
= P
rcv_final
/ ( R * T
final
)
T = 273 K P
rcv_final
= 660,000 Pa
N
= 1.29
kg/Nm
3
R = 286.9 J/(kg*K)
T
final
= 298.15 K
m
comp
= V
comp_N
*
N
final
= 7.72 kg/m
V
comp_N
= 0.56 Nm/s Final mass for minimum pressure
N
= 1.29
kg/Nm
3
m
final
= V * (
final
-
initial
)
m
comp
= 0.73 kg/s V = 10.66 m
final
= 7.72 kg/m
Time to fill initially the receiver
initial
= 0.935 kg/m132
t
0
= m / m
comp
m
final
= 72.31 kg
m = 81.04
m
comp
= 0.73 kg/s Mass decrease in this phase
t
0
= 111.4 s
Am =
m
initial -
m
final
m
initial
= 81.04 kg
t V m
final
= 72.31 kg
s m Am = 8.73 kg
0 0
15 11
30 22
45 33
60 44
75 55
90 65
105 76
111.4 81
112 81
115 79
118 77
121 75
124 74
126.4 72
130 73
135 74
140 74
145 75
150 76
155 76
160 77
165 78
150 200 250
Time (s)
Mass in receiver vs. time
170 79
175 79
180 80
185 81
186.4 81
190 79
193 77
196 75
199 74
200 73
201.4 72
205 73
210 74
215 74
220 75
225 76
230 76
235 77
240 78
245 79
250 79
255 80
260 81
261.4 81
Time for this mass decrease
t
dec
= Am / m
rcv_out
Am =
8.73 kg
m
rcv_out
= 0.582 kg/s
t
dec
= 15.0 s
At this stage, the compressor starts
again an will run for a time
t
Fill
= 60 s
250 300
2.- Receiver volume
V = Am * R * T
rcv
/ AP
op
( )
| |
| |
) T R ( / P
) T R ( / P
1
Re
:
:
:
3
3
final final final
ini ini ini
final ini
final ini
final ini
Densities
m V
m
V
volume ceiver
m
kg
time given a at receiver in density air
m volume receiver V
kg receiver in change mass m
V m
cycle a during change Mass
VOLUME RECEIVER
=
=
A =
A
=
(
A
= A
op
rcv
op final ini
final ini
rcv
final ini
final ini
op
rcv
final ini
op final ini
final ini
rcv
final ini
rcv
final ini
final ini
rcv final rcv ini final ini
rcv final final
rcv ini ini
rcv final ini
P
T R
m V
P
change pressure operation Allowed
T R
m V
m V
m
V
P
T R
P
change pressure operation Allowed
T R
T R
T T
T
T
T
A
A =
A =
A =
A =
A
=
A
A =
=
=
=
=
= =
P - P
P - P
1
1
P - P
P - P
1
P - P
) R ( / P - ) R ( / P
) R ( / P
) R ( / P
T T
process isothermal an Assuming
op
rcv
P
T R
m V
A
A =
3.- Mass change during a cycle in receiver
[Ec. B]
V = t
Fill
* P
N
* [V
comp_N
- V
rcv_N
] * (T
rcv
/T
N
) * (1/AP
op
)
[Ec. A]
op
rcv
op final ini
final ini
rcv
final ini
final ini
op
rcv
final ini
op final ini
final ini
rcv
final ini
rcv
final ini
final ini
rcv final rcv ini final ini
rcv final final
rcv ini ini
rcv final ini
P
T R
m V
P
change pressure operation Allowed
T R
m V
m V
m
V
P
T R
P
change pressure operation Allowed
T R
T R
T T
T
T
T
A
A =
A =
A =
A =
A
=
A
A =
=
=
=
=
= =
P - P
P - P
1
1
P - P
P - P
1
P - P
) R ( / P - ) R ( / P
) R ( / P
) R ( / P
T T
process isothermal an Assuming
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
op N
rcv
N rec N comp N Fill
op
rcv
N
N rec N comp N Fill
op
rcv
N
N rec N comp N Fill
Fill
N
N
N rec N comp
N
N
N
Fill N N rec N comp
Fill N N rec N N comp
N N rec out rec
N N comp in rec
comp in rec
Fill out rec in rec
P T
T
V V P V
P
T R
R T
V V P V
P
T R m V
R T
V V P m
T R
P
V V m
T R
P
V V m
V V m
V m
V m
m m
m m m
receiver in cycle a during change Mass
A
=
A
=
A
A =
= A
= A
=
= A
= A
=
=
=
= A
1
1 1 1
1
____ __________ __________ __________
1 1
: _ _ _ _ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_ _
_
_ _
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
| |
op N
rcv
N rec N comp N Fill
P T
T
V V P V
A
=
1
_ _
t
2.- Receiver volume 3.- Mass change during a cycle in receiver
V
n
= 0.56 Nm/s
P
atm_loc
= 80 kPa
t
loc
= 10 C
Normal flow rate data Operation absolute pressure
P
op
= P
atm_loc
+ P
op
V
n
= 2,025
Nm
3
/h
P
atm_loc
= 80
P
n
= 101,325 Pa P
op
= 0
T
n
= 273.15 K P
op
= 80.00
P
op
= 80,000
Local atmospheric pressure
P
atm_loc
= 80 kPa Real volumetric flow rate
V = (P
n
/P
op
) * (T
op
/T
n
) * V
n
Operating conditions P
n
= 101,325
P
op
= 0 kPa (g) T
n
= 273.15
t
op
= 10 C P
op
= 80,000
T
op
= 283.15
Operation absolute temperature V
n
= 2,025.0
T
op
= t
op
+ 273.15 V = 2,658.7
t
op
= 10 C
T
op
= 283.15 K V = 0.74
Rev. cjc 26.02.2013
1.- Normal flow rate to real flow rate
Operation absolute pressure
kPa
kPa (g)
kPa
Pa
(P
n
/P
op
) * (T
op
/T
n
) * V
n
Pa
K
Pa
C
Nm
3
/h
m
3
/h
m/s
Rev. cjc 26.02.2013
1.- Normal flow rate to real flow rate
[1] Drucklufttechnick
http://www.drucklufttechnik.de/www/temp/e/drucklfte.nsf/b741591d8029bb7dc1256633006a1729/5F554A457EAD0253C1256625007D993D?OpenDocument
[2] Kaeser
http://us.kaeser.com/Online_Services/Toolbox/Air_receiver_sizes/default.asp
[3] BlakeandPendleton
http://www.blakeandpendleton.com/uploadedfiles/pdf/06-010504.012%20Compressed%20Air%20Storage.pdf
[4] Air Technologies
http://www.compressedairgorilla.com/Sizing_the_air_receiver.pdf
[5] Chemical & Process Technology
http://webwormcpt.blogspot.com/2008/08/air-receiver-doubt-on-scfm-cfm.html
[6] Pneumatic Handbook
http://books.google.cl/books?id=hnfzKhMdwisC&pg=PA104&lpg=PA104&dq=air+receiver+volume+calculation&source=bl&ots=VqUwBXOWhb&sig=LA_2gJcHxYAlomgFqIMsTMg8ls4&hl=es-419&sa=X&ei=FuQnUdn3MsTX2QWG9oHAAg&ved=0CCwQ6AEwADgK#v=onepage&q=air%20receiver%20volume%20calculation&f=false
[7] Atlas Copco
Compressed_Air_Manual_tcm46-1249312
[8] Piping-Designer
http://www.piping-designer.com/Calculation:Air_Receiver_Sizing
To see hiden sheets, right click on any sheet label and unhide the desired sheet
4.- Normal state
http://www.drucklufttechnik.de/www/temp/e/drucklfte.nsf/b741591d8029bb7dc1256633006a1729/5F554A457EAD0253C1256625007D993D?OpenDocument
http://us.kaeser.com/Online_Services/Toolbox/Air_receiver_sizes/default.asp
http://www.blakeandpendleton.com/uploadedfiles/pdf/06-010504.012%20Compressed%20Air%20Storage.pdf
http://webwormcpt.blogspot.com/2008/08/air-receiver-doubt-on-scfm-cfm.html
http://books.google.cl/books?id=hnfzKhMdwisC&pg=PA104&lpg=PA104&dq=air+receiver+volume+calculation&source=bl&ots=VqUwBXOWhb&sig=LA_2gJcHxYAlomgFqIMsTMg8ls4&hl=es-419&sa=X&ei=FuQnUdn3MsTX2QWG9oHAAg&ved=0CCwQ6AEwADgK#v=onepage&q=air%20receiver%20volume%20calculation&f=false
1.- References
2.- Receiver volume
3.- Inlet compressor
4.- Normal state
http://books.google.cl/books?id=hnfzKhMdwisC&pg=PA104&lpg=PA104&dq=air+receiver+volume+calculation&source=bl&ots=VqUwBXOWhb&sig=LA_2gJcHxYAlomgFqIMsTMg8ls4&hl=es-419&sa=X&ei=FuQnUdn3MsTX2QWG9oHAAg&ved=0CCwQ6AEwADgK#v=onepage&q=air%20receiver%20volume%20calculation&f=false
http://books.google.cl/books?id=hnfzKhMdwisC&pg=PA104&lpg=PA104&dq=air+receiver+volume+calculation&source=bl&ots=VqUwBXOWhb&sig=LA_2gJcHxYAlomgFqIMsTMg8ls4&hl=es-419&sa=X&ei=FuQnUdn3MsTX2QWG9oHAAg&ved=0CCwQ6AEwADgK#v=onepage&q=air%20receiver%20volume%20calculation&f=false
You might also like
- Air Receiver Sizing Metric UnitsDocument4 pagesAir Receiver Sizing Metric UnitsAnonymous Od7nYs8No ratings yet
- Air Receivers Volume CalculationDocument98 pagesAir Receivers Volume CalculationBaskar Kannaiah100% (1)
- Air Receiver SizingDocument3 pagesAir Receiver Sizinglutfi awnNo ratings yet
- Air Receiver SizingDocument3 pagesAir Receiver Sizingmazumdar_satyajit100% (2)
- Calculation of Air Pipe SizeDocument6 pagesCalculation of Air Pipe SizePhyu Mar Thein Kyaw100% (1)
- Sizing Air ReceiverDocument3 pagesSizing Air ReceiverAnkon Mukherjee100% (3)
- Air Receiver SizingDocument7 pagesAir Receiver SizingKong Lingwei0% (2)
- Air Receiver SizingDocument4 pagesAir Receiver SizingAnonymous a4Jwz14WNo ratings yet
- Instrument Air Dryer Sizing CalculationDocument1 pageInstrument Air Dryer Sizing CalculationAravind Kannan100% (2)
- Compressed Air SizingDocument8 pagesCompressed Air Sizingswapnadiph100% (1)
- HX Design v1Document12 pagesHX Design v1mansourotaibiNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air ReceiversDocument6 pagesCompressed Air Receiverstruong sanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Sizing The Air ReceiverDocument1 pageSizing The Air ReceiverSreevathsa Gururaj100% (1)
- Line SizingDocument18 pagesLine SizingNathaniel Thomas100% (1)
- Compressor Capacity CalculationDocument4 pagesCompressor Capacity CalculationHoney Tiwari100% (1)
- Blower CalculatorDocument1 pageBlower CalculatorAnonymous QiMB2lBCJLNo ratings yet
- Compressor Sizing CalDocument2 pagesCompressor Sizing CalSimranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Shell Tube Heat Exchanger DesignDocument7 pagesShell Tube Heat Exchanger DesignAbhijeet JhaNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor SizingDocument11 pagesAir Compressor Sizingalquin08No ratings yet
- Tube Rupture (Two Phase-Omega Method)Document1 pageTube Rupture (Two Phase-Omega Method)Saeid Rahimi MofradNo ratings yet
- Pump Head CalculationDocument1 pagePump Head CalculationMFaiz RHamiraNo ratings yet
- Air BlowerDocument10 pagesAir Blowerewanz89100% (2)
- Line Sizing - 2PHASEDocument11 pagesLine Sizing - 2PHASEEbby Onyekwe100% (1)
- Compressed Air CalculationDocument7 pagesCompressed Air Calculationlutfi awnNo ratings yet
- Strainer Pre. Drop and Sizing CalcDocument6 pagesStrainer Pre. Drop and Sizing CalcChandrakant SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Air Consumption Rev 1Document1 pageAir Consumption Rev 1Cahyadi YadiNo ratings yet
- Separator SizingDocument9 pagesSeparator SizingTolstoy LeoNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Sizing: Unit L m3/d 1800 1.03 Bar 8.2 Bar 7.2 Bar 1 °C 120 Bar in 3 in 4Document4 pagesControl Valve Sizing: Unit L m3/d 1800 1.03 Bar 8.2 Bar 7.2 Bar 1 °C 120 Bar in 3 in 4ghandri1986No ratings yet
- Pump (English) TemplateDocument1 pagePump (English) TemplateMichael HaiseNo ratings yet
- Tank SizingDocument1 pageTank SizingSaeid Rahimi MofradNo ratings yet
- Vapor Liquid Vertical SeparatorDocument4 pagesVapor Liquid Vertical SeparatorIoana Popescu100% (1)
- Compressor and Compressed Air SystemDocument34 pagesCompressor and Compressed Air Systemrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Pump Head CalculationDocument11 pagesPump Head CalculationZoebairNo ratings yet
- TankHeatingCoil&BoilerCapacityRequirement Rev 2Document1 pageTankHeatingCoil&BoilerCapacityRequirement Rev 2sooner123456No ratings yet
- Sizing of Air ReceiverDocument6 pagesSizing of Air Receiverraghu_mn100% (1)
- Air Cooled HX Data SheetDocument1 pageAir Cooled HX Data SheetHoney TiwariNo ratings yet
- Fgas Refrigerant CalculatorDocument10 pagesFgas Refrigerant CalculatorKumar sssssNo ratings yet
- Liquid Line SizingDocument12 pagesLiquid Line Sizinglolofm25No ratings yet
- Thermal Insulation Thickness Calculation (By James)Document1 pageThermal Insulation Thickness Calculation (By James)Ah BengNo ratings yet
- Steam Pipe SizingDocument16 pagesSteam Pipe SizingsamvendanNo ratings yet
- Fgas Refrigerant CalculatorDocument12 pagesFgas Refrigerant CalculatorKhadija MirajNo ratings yet
- Air Receivers Volume CalculationDocument123 pagesAir Receivers Volume CalculationsdgthdtrtretNo ratings yet
- PSV SizingDocument6 pagesPSV SizingBui Khoi Nguyen100% (1)
- Pump Desing SpreadsheetDocument10 pagesPump Desing SpreadsheetAnonymous a4Jwz14WNo ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pagesCondensate Line SizingAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBNo ratings yet
- UtilityDocument8 pagesUtilityAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air PipingDocument3 pagesCompressed Air PipingManoranjan Kumar Choudhary100% (1)
- Static Pressure FansDocument35 pagesStatic Pressure FansarifkhadeerNo ratings yet
- Control Valve SizingDocument3 pagesControl Valve SizingN. S. PanditNo ratings yet
- Vent Sizing - SpreadsheetDocument2 pagesVent Sizing - SpreadsheetPradip ShindeNo ratings yet
- Pump. Slurry Selection Typical WarmanDocument44 pagesPump. Slurry Selection Typical WarmanJuan Pablo Apaza100% (1)
- PSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipDocument4 pagesPSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipAfees OlajideNo ratings yet
- Nota PemampatDocument49 pagesNota PemampatweafareezNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Test Rig Foot Mounted MotorDocument5 pagesAir Compressor Test Rig Foot Mounted MotorTinku SharmaNo ratings yet
- Performance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorDocument6 pagesPerformance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorAji V s100% (2)
- Ch3 - CompressorsDocument49 pagesCh3 - CompressorsShiau FenNo ratings yet
- Classes and Comparisons Between CompressorsDocument48 pagesClasses and Comparisons Between CompressorsVijay MeenaNo ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument19 pagesConversion of UnitsAnurag TripathyNo ratings yet
- Equation - Single - Phase - Gas - Pipeline - Flow - PreviewDocument17 pagesEquation - Single - Phase - Gas - Pipeline - Flow - PreviewmrezzaNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors - Gas IndustryDocument2 pagesConversion Factors - Gas IndustryKailas Nimbalkar100% (3)
- Condmaster Ruby 2012 User GuideDocument238 pagesCondmaster Ruby 2012 User GuideKenny Ruiz67% (6)
- Electrical Properties of Solar CellsDocument8 pagesElectrical Properties of Solar CellsKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Successful Solution: To The Challenge ofDocument2 pagesSuccessful Solution: To The Challenge ofKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- SketchsDocument1 pageSketchsKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Book-I Chapter 1: Input DataDocument3 pagesBook-I Chapter 1: Input DataKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Mba ZC417Document4 pagesMba ZC417Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Partial Report - RawanDocument23 pagesPartial Report - RawanKenny Ruiz100% (1)
- Equipment Dossier R0Document50 pagesEquipment Dossier R0Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Fly AcDocument7 pagesFly AcKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- VB 29 - 10Document5 pagesVB 29 - 10Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Annexure 1 Mass Flow RajashreeDocument3 pagesAnnexure 1 Mass Flow RajashreeKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Test Report 10034-1 Raw Material Grasim Rawan IndiaDocument6 pagesTest Report 10034-1 Raw Material Grasim Rawan IndiaKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- WE 12742 Grasim Rawan Table: Mixing Calculation Mixture With Coal B As FuelDocument1 pageWE 12742 Grasim Rawan Table: Mixing Calculation Mixture With Coal B As FuelKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- cdk1 Coal B-EDocument1 pagecdk1 Coal B-EKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- List of DOE - Unaided Schools (1278) : S.No District Zone School ID School NameDocument2 pagesList of DOE - Unaided Schools (1278) : S.No District Zone School ID School NameKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- 139 FPDocument7 pages139 FPKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- 142 EaDocument3 pages142 EaKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- 148 FPDocument2 pages148 FPKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Document5 pagesCentre of Mass & Consv of Momentum (Nitin M Sir)Kenny Ruiz0% (1)
- IIT JEE Molecular Orbital Theory Study MaterialDocument4 pagesIIT JEE Molecular Orbital Theory Study MaterialKenny Ruiz100% (1)
- Work, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesWork, Energy&Power (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Emi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesEmi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Nya Cement Company Limited: Daily Production ReportDocument1 pageNya Cement Company Limited: Daily Production ReportIrshad HussainNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Natural Fibre Polymer Composites For Structural ApplicationDocument159 pagesCharacterization of Natural Fibre Polymer Composites For Structural ApplicationAsia YahyaNo ratings yet
- Brochure AmbaramDocument13 pagesBrochure AmbaramAman GoyalNo ratings yet
- Building Materials Laboratory Test Request & Worksheet For Compressive Strength of Concrete CubesDocument4 pagesBuilding Materials Laboratory Test Request & Worksheet For Compressive Strength of Concrete CubessajjaduetNo ratings yet
- Precast-Handbook-Dayton Superior PDFDocument163 pagesPrecast-Handbook-Dayton Superior PDFJulio Eder LopezNo ratings yet
- BoqDocument2 pagesBoqJohn Carlo TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Cantilever Sheet Pile Wall DesignDocument7 pagesCantilever Sheet Pile Wall Designต้นหญ้าNo ratings yet
- 2D Vs 3D ReviewDocument7 pages2D Vs 3D ReviewBhasker RamagiriNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Area For Fin Tube Heat Exchanger For FBDDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Area For Fin Tube Heat Exchanger For FBDPrathmesh GujaratiNo ratings yet
- Pressure ConnectionsDocument3 pagesPressure ConnectionsChandrasekhar SonarNo ratings yet
- What Are The Types of Ties Used in Building ConstructionDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Types of Ties Used in Building ConstructioncarmeloNo ratings yet
- Combined Schedule of Rates Civil Works and Electrical Mechanical Works For The Year 2018-2019 For Mumbai Pune Aurangabad & Nagpur ZonesDocument279 pagesCombined Schedule of Rates Civil Works and Electrical Mechanical Works For The Year 2018-2019 For Mumbai Pune Aurangabad & Nagpur ZonesmashaK100% (4)
- Product Information Flyer: CIMSTAR® 10-85VGDocument2 pagesProduct Information Flyer: CIMSTAR® 10-85VGsobheysaidNo ratings yet
- Apv SPXDocument34 pagesApv SPXpetrakou aglaia100% (1)
- Asme B16.21Document21 pagesAsme B16.21Anant RubadeNo ratings yet
- List Komponen Jembatan Gantung Bentang 120 M Kelas I Type RigidDocument1 pageList Komponen Jembatan Gantung Bentang 120 M Kelas I Type RigidIlham Fadel MNo ratings yet
- Recent Technology of Coke Oven Refractories: Technical ReportDocument8 pagesRecent Technology of Coke Oven Refractories: Technical ReportAmit Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Thermal Products Day-1 PDFDocument7 pagesThermal Products Day-1 PDFSachin KothariNo ratings yet
- Tappi Tip 0402-19Document21 pagesTappi Tip 0402-19GTpianomanNo ratings yet
- Air Intake SystemDocument27 pagesAir Intake SystemrahulNranaNo ratings yet
- Dishwasher Installation, Use and Care, & Warranty - 8535436Document66 pagesDishwasher Installation, Use and Care, & Warranty - 8535436rudydanielleNo ratings yet
- Stim-03.014 - en Piping Design Requirements Condensate LinesDocument9 pagesStim-03.014 - en Piping Design Requirements Condensate LinesbikendiaguirreNo ratings yet
- Sheet 04 Barrel VaultDocument1 pageSheet 04 Barrel VaultSoham SatamNo ratings yet
- HONDA - Partial List of Steel Materials at Area A & B - RBEDocument23 pagesHONDA - Partial List of Steel Materials at Area A & B - RBERhine EsperanzateNo ratings yet
- 5504Document10 pages5504hhr2412No ratings yet
- B.6 Drainage - BQDocument5 pagesB.6 Drainage - BQSHARVINDRANADAN A/L SATHANANDHAN A18KA0153No ratings yet
- Bionanocomposite: Vikram Singh Vikash Kumar Sunil Kumar Akshay PadghanDocument14 pagesBionanocomposite: Vikram Singh Vikash Kumar Sunil Kumar Akshay PadghanVikram KulriaNo ratings yet
- Lennox - Split Pared R-22Document2 pagesLennox - Split Pared R-22Saidy Jimena Plazas MarlesNo ratings yet
- Norsok Compact CL2500 Flanges With IX Ring AISI 4140 PTFE Coat and Galvanized Bolting, PCS GC100 (KA1)Document1 pageNorsok Compact CL2500 Flanges With IX Ring AISI 4140 PTFE Coat and Galvanized Bolting, PCS GC100 (KA1)Leonidas GalanisNo ratings yet
- Midas CatalogueDocument38 pagesMidas CatalogueChaudharyShubhamSachanNo ratings yet