Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ED1
Uploaded by
Vikash TiwariCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ED1
Uploaded by
Vikash TiwariCopyright:
Available Formats
Set No: 1 Course/Branch: B.Tech.
/EN Subject Name & Code: Electric Drives [EEE-035] Semester/Section: VII [A] Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100 Section A (Note: Section A shall have ten compulsory parts, each of two marks) Q1. Attempt all questions of this section in brief. [10 x 2=20]
(a) Define Electric Drives. Ans. Systems employed for motion control are called drives and they employ any of the prime movers such as diesel or petrol engines, gas or steam turbines, hydraulic motors and electric motors for supplying mathematical energy for motion control. Drives employing electric motion are called electric drives. (b) Mention the different factors influencing the choice of an electric drives? Ans. 1) Steady state operation requirements. 2) Transient operation requirements. 3) Requirements related to the source. 4) Capital and running cost, maintenance needs life. 5) Space and weight restriction. 6) Environment and location. 7) Reliability. (c) Define heating time constant &cooling time constant? Ans. The time required to heat the machine parts to 63.3% of its final temperature rise is called as heating time constant. The time required to cool the machine parts to 36.6% of its final temperature fall is called as cooling time constant. (d) Why the losses at starting are not a factor of consideration in acontinuous duty motor? Ans.While selecting a motor for this type of duty it is not necessary togive importance to the heating caused by losses at starting even thoughthey are more than the losses at rated load. This is because the motordoes not require frequent starting it is started only once in its duty cycle and the losses during starting do not have much influence on heating. (e) What is meant by regenerative braking? Ans.In this method motor speed exceeds the rated speed. In this case the motor works as a generator and converts the mechanical power into electrical power which is delivered back to the electrical system. This method of braking is known as regenerative braking.
(f) Compare electrical and mechanical braking.
1
Ans. S.no. Mechanical Breaking Brakes require frequent maintenance 1 Not smooth 2 Can be applied to hold the system at any position 3 (g) Mention the drawbacks of rectifier fed dc drives? Ans. (i) Distortion of supply. (ii) Low power factor. (iii) Ripple in motor current
Electrical Breaking very little maintenance smooth cannot produce holding torque.
(h) Why self commutated devices are preferred over thyristors for chopper circuits? Ans. Self commutated devices such as power MOSFETs power transistors, IGBTs, GTOs and IGCTs are preferred over thyristors for building choppers because they can be commutated by a low power control signal and don't need commutation circuit. (i) What are the effects of harmonics in VSI fed induction motor drive? Ans.The output voltage of VSI has harmonic components. The harmonics of the stator current cause additional losses and heating. These harmonics are also responsible for torque pulsations. (j) State the principle of operation of switched reluctance motor? Ans.The SRM develops an electromagnetic torque due to variable reluctance principle. When air gapis minimum, the reluctance will be minimum. Hence inductance will be maximum, so the rate of changeof inductance is zero. When the reluctance varies, there will be a change in inductance so when aparticular stator winding of SRM is excited, the rotor pole comes in alignment with that stator pole andthus the rotor rotates. Section B (Note: Section B shall have five parts, each of ten marks;only three are to be attempted by student.) Q2. Attempt any three parts. [310=30] (a) Explain the four quadrant operation of motor applicable for hoist. Ans.
(b) Derive the equation for temperature rise in an electric drive. Ans.
(c) Derive the expression for energy loss in DC shunt motor during starting. Ans.
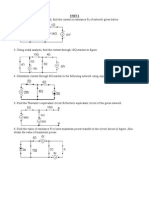
(d) Explain the operation of single phase fully controlled rectifier fed DC separately excited motor drive. Ans. Figure shows the setup for single phase controlled rectifier fed separately excited dc motor drive. Field circuit is also excited by a dc source, which is not shown in the figure just for simplicity.
(e) Explain Static Scherbius drive using Slip power recovery scheme. Ans.
Section C (Note: Section C shall have five questions with internal choice, each of ten marks.) Q3. Attempt any twoparts. [2x5=10] (a) What are the advantages of an Electrical Drives? Ans. Advantages of Electrical Drive 1. They have flexible control characteristics. The steady state and dynamic characteristics of electric drives can be shaped to satisfy the load requirements. 2. Drives can be provided with automatic fault detection systems. Programmable logic controller and computers can be employed to automatically control the drive operations in a desired sequence. 3. They are available in wide range of torque, speed and power. 4. They are adaptable to almost any operating conditions such as explosive and radioactive environments 5. It can operate in all the four quadrants of speed-torque plane 6. They can be started instantly and can immediately be fully loaded 7. Control gear requirement for speed control, starting and braking is usually simple and easy to operate.
(b) Give the comparison between AC drives and DC drives. Ans. DC Drives The power circuit and control circuit is simple and inexpensive It requires frequent maintenance The commutator makes the motor bulky, costly and heavy AC drives The power circuit and control circuit are complex Less Maintenance These problems are not there in these motors and are inexpensive, particularly squirrel cage induction motors Fast response and wide speed range of In solid state control the speed range is wide control, can be achieved smoothly by conventional and solid state control Speed and design ratings are limited due to commutations Speed and design ratings have upper limits and conventional method is stepped and limited
(c) Explain the characteristics of different types of loads. Ans. loads can be classified into the following four categories. Constant torque type load Torque proportional to speed (Generator Type load) Torque proportional to square of the speed (Fan type load) Torque inversely proportional to speed (Constant power type load) Constant Torque type load: Most of the working machines that have mechanical nature of work like shaping, cutting, grinding or shearing, require constant torque irrespective of speed. Torque Proportional to speed: Separately excited dc generators connected to a constant resistance load, eddy current brakes have speed torque characteristics given by T=k
Torque proportional to square of the speed: Another type of load met in practice is the one in which load torque is proportional to the square of the speed.Eg Fans rotary pumps, compressors and ship propellers. Torque Inversely proportional to speed: Certain types of lathes, boring machines, milling machines, steel mill coiler and electric traction load exhibit hyperbolic speed-torque characteristics
Q4.Attempt any two parts.
[2x5=10]
(a) Determine the equivalent moment of inertia and equivalent load torque, if loads are rotational. Ans.
10
(b)
Ans.
(c) Explain the dynamics of electric drive system. Ans.
11
Q5. Attempt any twoparts. (a) Explain the different type of breaking methods. Ans.
[2x5=10]
12
(b) Explain the rheostatic breaking of DC shunt motor. Ans.
13
(c) A 220 V DC shunt motor having an efficiency of 85% drives a hoist having an efficiency of 80%. Calculate the current drawn from the supply to raise a load of 400 kg at 2.5 m/s. what resistance must be added in the armature circuit in order to lower the load at 2.5 m/s, using rheostatic breaking. Ans.
Q6. Attempt any two parts.
[2x5=10]
(a) A 220 V, 1500 rpm, 10 A separately excited DC motor is fed from a single phase fully controlled rectifier with AC source voltage 230 V, 50Hz. Ra=2. Assuming continuous conduction determine firing angle for,
14
(i) (ii) Ans.
Half the rated torque, 500 rpm Rated motor torque and -1000 rpm
(b) Explain the two modes in which a dual converter is used to control the DC motor speed. Ans.
15
(c) A 230 V, 1100 rpm, 220 Amps separately excited DC motor has an armature resistance of 0.02 M. The motor is fed from a chopper, which provides both motoring and braking operations. Calculate i. The duty ratio of chopper for motoring operation at rated torque and 400 rpm ii. The maximum permissible motor speed obtainable without field weakening, if the maximum duty ratio of the chopper is limited to 0.9 and the maximum permissible motor current is twice the rated current
16
Q7. Attempt any two parts.
[2x5=10]
17
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Assignment: SESSION-2019-20 SEM-6 (ODD)Document2 pagesAssignment: SESSION-2019-20 SEM-6 (ODD)Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Question PaperDocument1 pageQuestion PaperVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Demagnetizing Characteristics Using B-H LoopDocument2 pagesDemagnetizing Characteristics Using B-H LoopVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Assignment: Demagnetizing Characteristics Using B-H LoopDocument2 pagesAssignment: Demagnetizing Characteristics Using B-H LoopVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Assignment: Assignment Sheet No. 1 Subject Name: Special Electrical Machines Subject Code: REE-064Document1 pageAssignment: Assignment Sheet No. 1 Subject Name: Special Electrical Machines Subject Code: REE-064Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- X1 = 2.0 Ω/phase; X2' = 2.0 Ω/phase; Xm = 47.34 Ω/phaseDocument1 pageX1 = 2.0 Ω/phase; X2' = 2.0 Ω/phase; Xm = 47.34 Ω/phaseVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Assignment Sheet No. 1 Subject Name: Special Electrical Machines Subject Code: REE-064Document1 pageAssignment Sheet No. 1 Subject Name: Special Electrical Machines Subject Code: REE-064Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- QP2 SEM First SessionalDocument1 pageQP2 SEM First SessionalVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Deep Bar and Double Cage RotorDocument34 pagesDeep Bar and Double Cage RotorVikash Tiwari0% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- QP 1Document1 pageQP 1Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet No. 1 Subject Name: Special Electrical Machines Subject Code: REE-064Document2 pagesAssignment Sheet No. 1 Subject Name: Special Electrical Machines Subject Code: REE-064Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Third Sessional Qp1 SemDocument1 pageThird Sessional Qp1 SemVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Special Electrical Machines: Unit-3: Stepper Motor & Switched Reluctance MotorDocument51 pagesSpecial Electrical Machines: Unit-3: Stepper Motor & Switched Reluctance MotorVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Niet - Greater Noida B.Tech.-EN-VI SEM. (A+B+C) Assignment-2/ Ree-602/Microprocessor Doa: DosDocument1 pageNiet - Greater Noida B.Tech.-EN-VI SEM. (A+B+C) Assignment-2/ Ree-602/Microprocessor Doa: DosVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Sessional Set 17Document1 pageSessional Set 17Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Third Sessional Qp2 SemDocument1 pageThird Sessional Qp2 SemVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- QP1 SEM SecondSessionalDocument1 pageQP1 SEM SecondSessionalVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Three Phase AC Circuit FundamentalsDocument9 pagesThree Phase AC Circuit FundamentalsVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Noida Institute of Engineering & Technology, Greater Noida: Section - ADocument3 pagesNoida Institute of Engineering & Technology, Greater Noida: Section - AVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- QP1 SEM First SessionalDocument1 pageQP1 SEM First SessionalVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Questions: DC AnalysisDocument4 pagesQuestions: DC AnalysisVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Vishveshwarya Group of Institutions: First Sessional Test, Even Semester Examination 2016-17Document2 pagesVishveshwarya Group of Institutions: First Sessional Test, Even Semester Examination 2016-17Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument4 pagesQuestion BankVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. (VI Semester) PUT Examination Digital Control SystemDocument3 pagesB.Tech. (VI Semester) PUT Examination Digital Control SystemVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ii. All The Questions Carry Equal MarksDocument1 pageIi. All The Questions Carry Equal MarksVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- System.: Z 1 G (Z) T 0.1 SecDocument2 pagesSystem.: Z 1 G (Z) T 0.1 SecVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Digital Control SystemDocument3 pagesDigital Control SystemVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Answer Tutorial 1Document1 pageAnswer Tutorial 1Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- BHELDocument49 pagesBHELm4mayankrocksNo ratings yet
- Eurorider 430Document2 pagesEurorider 430fatalgamersNo ratings yet
- Sistema Petrolero Del Campo GullfaksDocument8 pagesSistema Petrolero Del Campo GullfaksPepe MtzNo ratings yet
- Baotian BT49QT 12 Rebel 50 User Manual With LegendaDocument26 pagesBaotian BT49QT 12 Rebel 50 User Manual With LegendaMoppie Hofstede100% (2)
- DF 300Document6 pagesDF 300ruge13484246No ratings yet
- One Mans Quest For LS Power in His 3rd GenDocument115 pagesOne Mans Quest For LS Power in His 3rd GenAngel palaciosNo ratings yet
- Diverter Procedure While Drilling Fixed: Last Updated On Tue, 24 Jun 2014Document4 pagesDiverter Procedure While Drilling Fixed: Last Updated On Tue, 24 Jun 2014AmitabhaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- TM 10-4930-236-13P Tank and Pump Unit For TruckDocument231 pagesTM 10-4930-236-13P Tank and Pump Unit For TruckAdvocate100% (3)
- DDC 12 & 16 V 2000 C&I WS Manual 6se2000 - 02-802 P 1 To 816Document816 pagesDDC 12 & 16 V 2000 C&I WS Manual 6se2000 - 02-802 P 1 To 816Edison Cortes100% (4)
- AFRISO Watchdog en 05-14 PDFDocument8 pagesAFRISO Watchdog en 05-14 PDFb400013No ratings yet
- Parts YamahaDocument63 pagesParts YamahahuguslourNo ratings yet
- MTU 10V1600 DS450: Diesel Generator SetDocument4 pagesMTU 10V1600 DS450: Diesel Generator SetJorge Eraldo Albarran PoleoNo ratings yet
- Fuel and Combustion-ChemistryDocument20 pagesFuel and Combustion-ChemistryJevaa KharthickNo ratings yet
- Spe 93594 MS PDocument5 pagesSpe 93594 MS PGustavoMillaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Performance VehiclesDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Performance VehiclesDennis Esik MaligayaNo ratings yet
- Scooptram ST1520LP: Atlas CopcoDocument4 pagesScooptram ST1520LP: Atlas CopcosamuelahpNo ratings yet
- Stirling Engine Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesStirling Engine Literature Reviewtog0filih1h2100% (1)
- Lubrication System Maintenance2Document37 pagesLubrication System Maintenance2Zalmiers SarterezNo ratings yet
- Flash Steam ... : What Is Flash Steam..? How Is It Formed..? What Can We Do With It..?Document20 pagesFlash Steam ... : What Is Flash Steam..? How Is It Formed..? What Can We Do With It..?rafiradityaNo ratings yet
- Dum Truck Komatsu hd465-7hd605-7 PDFDocument395 pagesDum Truck Komatsu hd465-7hd605-7 PDFamin100% (1)
- Saufer Danfoss Load Sensing Steering UnitsDocument92 pagesSaufer Danfoss Load Sensing Steering UnitsaapereirazNo ratings yet
- HazopDocument5 pagesHazopMohammed KhatibNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instalação - Perkins 2800S - (ING)Document134 pagesManual de Instalação - Perkins 2800S - (ING)Jair Ferreira Angelo JuniorNo ratings yet
- Summer Vocational Training: Gujarat Refinery, Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. Duration:15/05/2022-14/06/2022Document76 pagesSummer Vocational Training: Gujarat Refinery, Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. Duration:15/05/2022-14/06/2022Akash YadavNo ratings yet
- P0773Document5 pagesP0773Noel Alejandro Cordova RangelNo ratings yet
- AC250 Data SheetDocument5 pagesAC250 Data SheetAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- NH TD SpecificationsDocument3 pagesNH TD SpecificationsCristian StoicaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Onsite Hydrogen Generation For Power Plants - India - 2011 - PDFDocument67 pagesAdvanced Onsite Hydrogen Generation For Power Plants - India - 2011 - PDFkaruna346100% (1)
- Fuel Technology 2 Lab ManualDocument17 pagesFuel Technology 2 Lab Manualjohn powerNo ratings yet
- FME OP BrochureDocument2 pagesFME OP BrochureMartin KratkyNo ratings yet
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceFrom EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- A Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeFrom EverandA Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (53)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)