Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Effective Current, Voltage, Average Power PDF
Uploaded by
mrana_56Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Effective Current, Voltage, Average Power PDF
Uploaded by
mrana_56Copyright:
Available Formats
1/31/2009
An alternating current which produces heat in a given resistance at the same average rate as I amperes of direct current is said to have a value of I amperes Average rate of heating produced by an alternating current during one cycle is
Effective Current and Voltage Average Power
Average rate of heating produced by an I amperes of direct current in the same resistance is Therefore,
The expression above gives an RMS (Root Mean Square) value for current RMS defines the alternating current in terms of its average rate of producing heat in a resistance. It is also called the effective value or virtual value.
Problem 1: Find the effective value of a current that starts at zero, rises instantaneously, then remains at a value of 20 amperes for 10 seconds, then decreases instantaneously, remaining at a value of 10 amperes for 20 seconds and then repeats this cycle.
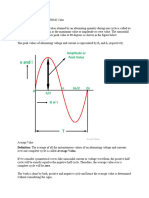
Average Value An alternating volt is the value of a wave of alternating potential which maintains an alternating current of 1 RMS ampere through a noninductive resistance of 1 ohm. Average value of an AC wave that is symmetrical about zero-axis, is zero. Thus, only one half of the cycle is considered. This value represents the DC equivalent for electrolytic action of the alternating wave abcde if the wave were rectified and made the same as wave abcfe
It therefore follows that the volt value of a wave is measured by the square root of the average square of the instantaneous values of the voltage wave.
1/31/2009
Average Value If the average values of the positive and negative loops are different, the actual average value taken over a complete cycle represents the value of a DC component in the wave. For example, the average value of the cross=hatched wave in the figure below is IDC. Inspection will show that the dotted wave is the sum of the alternating wave IAC and the direct current I DC
Effective Values and Average values of a Sinusoid
Form Factor Form factor is the ratio of the effective value to the average value of a wave. Form Factor = Effective value / Average Value
Form Factor
Hence, for a voltage wave, e, which has equal positive and negative loops
1/31/2009
Try this: What is the form factor of a Pure Sinusoidal Wave?
Problem 3: Find the form factor of the sawtooth wave form shown in the figure. Hint: Between the limits of t=0 and t=T=3 seconds, the analytical expression for the voltage is e = 50t volts. In a case of this kind,
Crest or Peak Factor
Crest or Peak Factor The crest, peak, or amplitude factor is the ratio of the maximum value of a voltage (or current) wave to the effective value. Crest Factor = Maximum value / Effective Value
The crest factor of a pure sine wave is: Em / 0.707Em = 2
Representation of Sine Waves by Vectors or Phasors
The directed lines or vectors that are employed to represent sinusoidally timevarying quantities in a coplanar system are called phasors.
A sine wave is formed by the projection of a revolving vector (OA) on the vertical axis as time progresses
Sine wave A is from projection of vector A, Sine wave B is from projection of vector B, Sine wave C is from projection of vector C, Sine wave A + Sine wave B = Sine wave C Also, Vector A + Vector B = Vector C
Therefore, vector addition of phasors is in fact reflected on the time axis as algebraic addition of sine curves
1/31/2009
Now, if we apply our knowledge of phasors to the R-L-C combinational circuits we can observe the following: Considering I (current) as the reference axis
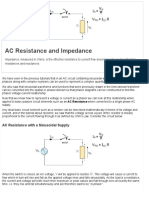
Vector Diagrams as Determined by Resistance and Reactance Drops and Impedance Functions: If a current i=Imsint is assumed to flow in a circuit containing R and L, KVL states that v=Ri+ Ldi/dt v=RImsint + ImLcost Since RImsint is of the samephase as I msint, the resistance drop is shown in phase with the current in the vector diagram of fig 12. Note also that, I mLcost is 90 degrees ahead of I msint. The sum of these two is the resultant applied potential ,V. The angle between V and I is =tan-1(L/R) The same relation can be obtained from the impedance function Z/ Positive means that applied voltage leads current (or current lags applied voltage by )
R-Branch: Current is in phase with voltage
L-Branch: Current Lags voltage, or, voltage leads current by 90 electrical degrees
C-Branch: Voltage lags current , or, current leads voltage by 90 electrical degrees
You might also like
- Bob Jones - Science 4Document254 pagesBob Jones - Science 4kage_urufu100% (4)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Pragmatic Marketing FrameworkDocument2 pagesPragmatic Marketing FrameworkohgenryNo ratings yet
- Analysing Context CluesDocument2 pagesAnalysing Context CluesSwathiNo ratings yet
- Code of Conduct GuidanceDocument17 pagesCode of Conduct GuidanceMuhammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit Notes LolDocument19 pagesAC Circuit Notes LolcatdrinkslemonadeNo ratings yet
- Concept of A. C. CircuitsDocument11 pagesConcept of A. C. CircuitsAbhishekNo ratings yet
- theory midDocument15 pagestheory midSantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Sinusoidal Alternating WaveformsDocument21 pagesLecture 01 Sinusoidal Alternating WaveformsShuvodip Das100% (1)
- AC Notes1Document12 pagesAC Notes1Varun ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesAC CircuitsJayaprasadGollaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering (BEEE101L) : Presented byDocument23 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering (BEEE101L) : Presented byAsh wanth100% (1)
- Fundamental of AC Circuits: by byDocument28 pagesFundamental of AC Circuits: by byGURMEHAK MIGLANINo ratings yet
- BE - Ac Fundamentals-14052Document28 pagesBE - Ac Fundamentals-14052DeepakDeepNo ratings yet
- Ac Power AnalysisDocument15 pagesAc Power Analysisteza maruNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AC CircuitsDocument56 pagesFundamentals of AC CircuitsSarojBankawatNo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals ExplainedDocument48 pagesAC Fundamentals ExplainedParikshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Effective Value or RDocument9 pagesEffective Value or RsurajNo ratings yet
- Single Phase AC CircuitsDocument29 pagesSingle Phase AC Circuitskali hembramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 NotesDocument15 pagesChapter 16 NotesMian EjazNo ratings yet
- CH3 LecDocument12 pagesCH3 LecAbdla DoskiNo ratings yet
- 3 A RLCDocument10 pages3 A RLCsuresh krishnanNo ratings yet
- BEE Unit-IIDocument29 pagesBEE Unit-IIharishcheeeNo ratings yet
- Ch1 AC CurrentDocument23 pagesCh1 AC CurrentAhmed ElayanNo ratings yet
- Basic AC Theory Handout 01-Mec. EngDocument10 pagesBasic AC Theory Handout 01-Mec. EngParamananda_SurangaNo ratings yet
- Ac FundamentalsDocument8 pagesAc FundamentalsPiku MajhiNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 AC NetworksDocument70 pagesCh.2 AC NetworksaattishNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electric Circuits: Sinusoidal Sources and The Concept of Phasor in Circuit AnalysisDocument20 pagesFundamentals of Electric Circuits: Sinusoidal Sources and The Concept of Phasor in Circuit AnalysisJames BejareNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument11 pagesAC CircuitsMayar ArafaNo ratings yet
- CT1 Unit 2Document29 pagesCT1 Unit 2Ali khan7No ratings yet
- Alternating Current.1Document10 pagesAlternating Current.1Jayati MittalNo ratings yet
- 1208 EEC MIcroprojectDocument16 pages1208 EEC MIcroprojectDibyas Sanjay DubeyNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current A.C.Document19 pagesAlternating Current A.C.Puran BistaNo ratings yet
- M3 PPT 1 1 Phase Ac CircuitDocument67 pagesM3 PPT 1 1 Phase Ac CircuitUDhayNo ratings yet
- Determining Average and Reactive Power Using MATLABDocument8 pagesDetermining Average and Reactive Power Using MATLABMahesh KambleNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Part 3 Sinusoidal Current and VoltageDocument46 pagesChapter5 Part 3 Sinusoidal Current and VoltageJOHN BRYNDON LANDICHONo ratings yet
- What Is Alternating Current (A.C.) ?Document16 pagesWhat Is Alternating Current (A.C.) ?ekeselNo ratings yet
- EENG 352 Lec1 To 4Document62 pagesEENG 352 Lec1 To 4teresawamboi72No ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument30 pagesAC FundamentalsSouhardya RoyNo ratings yet
- R, L and C Circuits PDFDocument42 pagesR, L and C Circuits PDFFasih Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- 11 Power in AC CircuitsDocument11 pages11 Power in AC CircuitsIt_ReviewNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits ExplainedDocument38 pagesAC Circuits ExplainedAashish SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Mod2 AC Circuits Provided by MaamDocument72 pagesMod2 AC Circuits Provided by Maamanishdeshmukh369No ratings yet
- Explain OC & SC Tests of A 1-Phase T/F.: Short Circuit Test On TransformerDocument10 pagesExplain OC & SC Tests of A 1-Phase T/F.: Short Circuit Test On Transformerarshadeee202No ratings yet
- Basic Elec AssignmentDocument13 pagesBasic Elec AssignmentSharyn VillarezNo ratings yet
- AC CurrentsDocument16 pagesAC CurrentsRoshan RajNo ratings yet
- Mod 3 Book 3 Ac TheoryDocument92 pagesMod 3 Book 3 Ac Theoryranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- What Is Alternating CurrentDocument49 pagesWhat Is Alternating CurrentRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Concepts: Chapter-IIIDocument12 pagesAC Circuits Concepts: Chapter-IIIatul206No ratings yet
- Publication 7 9424 628Document69 pagesPublication 7 9424 628Mary Angel YongcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Single Phase AC TheoryDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Single Phase AC TheoryJACOB MUDONHINo ratings yet
- Interpret AC Voltages & CurrentsDocument46 pagesInterpret AC Voltages & CurrentsKelvin LooiNo ratings yet
- Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT), Vellore: EEE1001 - Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument6 pagesVellore Institute of Technology (VIT), Vellore: EEE1001 - Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringEshan GuptaNo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals Introduction TheoryDocument25 pagesAC Fundamentals Introduction TheoryAlex ZulNo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals (PART 2)Document29 pagesAC Fundamentals (PART 2)Fasih Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit: Alternating Voltage and Current in An AC CircuitDocument12 pagesAC Circuit: Alternating Voltage and Current in An AC CircuitHassanNo ratings yet
- AC Impedance and Resistance Phasor DiagramsDocument6 pagesAC Impedance and Resistance Phasor DiagramsLuis PressoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document51 pagesChapter 1sahazatiNo ratings yet
- East West University Department of Computer Science and Engineering CourseDocument3 pagesEast West University Department of Computer Science and Engineering Coursearpanraj_59No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Voltages and CurrentsDocument40 pagesChapter 10 Sinusoidal Voltages and CurrentsAeron James V. Basilio100% (1)
- Instantaneous, Average, Real and Reactive PowerDocument6 pagesInstantaneous, Average, Real and Reactive PowercivaasNo ratings yet
- AC NotesDocument22 pagesAC Notesviharipavan100% (1)
- Activity 1 Ac Circuits Ac Voltage and Current - CalculationsDocument30 pagesActivity 1 Ac Circuits Ac Voltage and Current - CalculationsMonica MagnateNo ratings yet
- SINUSOIDAL AC CIRCUITSDocument35 pagesSINUSOIDAL AC CIRCUITSThiran Boy LingamNo ratings yet
- Water PurificationDocument14 pagesWater Purificationmrana_56No ratings yet
- How Water Filters WorkDocument4 pagesHow Water Filters Workmrana_56No ratings yet
- 4plasma DisplayDocument8 pages4plasma Displaymrana_56No ratings yet
- Information Source and SignalDocument61 pagesInformation Source and Signalmrana_56No ratings yet
- How Helicopter Works How Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter WorksDocument11 pagesHow Helicopter Works How Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Worksmrana_56No ratings yet
- Duplex (Telecommunications)Document4 pagesDuplex (Telecommunications)mrana_56100% (1)
- Dynamics of FlightDocument3 pagesDynamics of Flightmrana_56No ratings yet
- Jet Engines: What Is A Jet Engine?Document4 pagesJet Engines: What Is A Jet Engine?mrana_56100% (1)
- How The Train TurnsDocument4 pagesHow The Train Turnsmrana_56No ratings yet
- Bullets Working PrincipleDocument4 pagesBullets Working Principlemrana_56No ratings yet
- Why Digital?Document16 pagesWhy Digital?mrana_56No ratings yet
- Dual Tone Multi Frequency SignalingDocument4 pagesDual Tone Multi Frequency Signalingmrana_56No ratings yet
- Airplanes Airplanes Airplanes Airplanes AirplanesDocument5 pagesAirplanes Airplanes Airplanes Airplanes Airplanesmrana_56No ratings yet
- TelephonyDocument32 pagesTelephonyJoseph Velez CabiloganNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems - Telephone SystemDocument15 pagesCommunication Systems - Telephone Systemmrana_56100% (1)
- Telephone ExchangeDocument3 pagesTelephone Exchangemrana_56No ratings yet
- Cordless TelephoneDocument5 pagesCordless Telephonemrana_56No ratings yet
- 1 1 Traditional TelephonyDocument13 pages1 1 Traditional TelephonyBeOne DwiNo ratings yet
- How Telephones Work - An OverviewDocument3 pagesHow Telephones Work - An Overviewmrana_56No ratings yet
- Wirless NetworksDocument44 pagesWirless Networksmrana_56No ratings yet
- TV CameraDocument9 pagesTV Cameramrana_56No ratings yet
- Recommended Books For GATE ECEDocument2 pagesRecommended Books For GATE ECEmrana_56No ratings yet
- PhotovoltaicsDocument30 pagesPhotovoltaicsmrana_56No ratings yet
- Optical Components for Communication SystemsDocument105 pagesOptical Components for Communication Systemsmrana_56No ratings yet
- Polarization of DielectricsDocument9 pagesPolarization of Dielectricsmrana_56No ratings yet
- Multimedia CommunicationsDocument7 pagesMultimedia Communicationsmrana_56No ratings yet
- Communications SatelliteDocument9 pagesCommunications Satellitemrana_56No ratings yet
- Gate+any Written+any Viva Syllabus For ECE and EEDocument10 pagesGate+any Written+any Viva Syllabus For ECE and EEmrana_56No ratings yet
- Isometric and Orthographic ProjectionDocument13 pagesIsometric and Orthographic Projectionmrana_56No ratings yet
- EY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseDocument2 pagesEY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseAayushi AroraNo ratings yet
- Discuss in Details With Appropriate Examples What Factors Could Lead To Sympatric and Allopatric SpeciationDocument5 pagesDiscuss in Details With Appropriate Examples What Factors Could Lead To Sympatric and Allopatric SpeciationKhairul ShahmiNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 eDocument22 pagesChap 4 eHira AmeenNo ratings yet
- Ashe v. Swenson, 397 U.S. 436 (1970)Document25 pagesAshe v. Swenson, 397 U.S. 436 (1970)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- The Islam Question - Should I Become A Muslim?Document189 pagesThe Islam Question - Should I Become A Muslim?Aorounga100% (1)
- Debt Recovery Management of SBIDocument128 pagesDebt Recovery Management of SBIpranjalamishra100% (6)
- Causes and Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia in AdultsDocument88 pagesCauses and Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia in AdultsGissell LópezNo ratings yet
- Personal Weaknesses ListDocument3 pagesPersonal Weaknesses ListKinga SzászNo ratings yet
- Epithelial and connective tissue types in the human bodyDocument4 pagesEpithelial and connective tissue types in the human bodyrenee belle isturisNo ratings yet
- 3B Adverbial PhrasesDocument1 page3B Adverbial PhrasesSarah INo ratings yet
- Vinzenz Hediger, Patrick Vonderau - Films That Work - Industrial Film and The Productivity of Media (Film Culture in Transition) (2009)Document496 pagesVinzenz Hediger, Patrick Vonderau - Films That Work - Industrial Film and The Productivity of Media (Film Culture in Transition) (2009)Arlindo Rebechi JuniorNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam 2Document33 pagesMock Exam 2Althea Karmylle M. BonitaNo ratings yet
- Onsemi ATX PSU DesignDocument37 pagesOnsemi ATX PSU Designusuariojuan100% (1)
- 2 - RUBRIC PHY110 (For Student)Document3 pages2 - RUBRIC PHY110 (For Student)Puteri AaliyyaNo ratings yet
- Testing Your Understanding: The Dash, Slash, Ellipses & BracketsDocument2 pagesTesting Your Understanding: The Dash, Slash, Ellipses & BracketsBatsaikhan DashdondogNo ratings yet
- Muhammad v. Hall, 10th Cir. (2017)Document12 pagesMuhammad v. Hall, 10th Cir. (2017)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Philhis Handouts Week 1Document5 pagesPhilhis Handouts Week 1Jeen JeenNo ratings yet
- Al-Rimawi Et Al-2019-Clinical Oral Implants ResearchDocument7 pagesAl-Rimawi Et Al-2019-Clinical Oral Implants ResearchSohaib ShujaatNo ratings yet
- Medicalization of Racial Features Asian American Women and Cosmetic SurgeryDocument17 pagesMedicalization of Racial Features Asian American Women and Cosmetic SurgeryMadalina ElenaNo ratings yet
- A Case of DrowningDocument16 pagesA Case of DrowningDr. Asheesh B. PatelNo ratings yet
- Librarianship and Professional Ethics: Understanding Standards for Library ProfessionalsDocument12 pagesLibrarianship and Professional Ethics: Understanding Standards for Library ProfessionalsHALLNo ratings yet
- Urban Process Design - Hamid ShirvaniDocument1 pageUrban Process Design - Hamid ShirvaniCaramel LatteNo ratings yet
- 6 Strategies For Effective Financial Management Trends in K12 SchoolsDocument16 pages6 Strategies For Effective Financial Management Trends in K12 SchoolsRainiel Victor M. CrisologoNo ratings yet
- ESL Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesESL Lesson PlanuarkgradstudentNo ratings yet
- Origin and Development of Law of Sea PDFDocument135 pagesOrigin and Development of Law of Sea PDFkimmiahujaNo ratings yet