Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Strength of Materials July 2013
Uploaded by
Prasad C M0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views0 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views0 pagesStrength of Materials July 2013
Uploaded by
Prasad C MCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 0
USN
Third Semester B.E. Degree Examination, June/July 2013
=
:r,
;
Y{J
;i
FO-
6no
U<
.-i
;
E
2a.
b.
3a.
b.
and shear stresses on an oblique plane are given by on - o cos2 0 and o,
0
:
Angle made by oblique plane with the normal cross section of the bar.
Strength of Materials
Time: 3 hrs.
Max. Marks:100
Notez Answer FIVEfull questions, selecting
ot leost TWO questions
from
each porl
PART
_
A
I a. Brielly explain the behaviour ofductile material under gradually increasing tensile load.
(05 Marks)
b. Derive the relationship between modulus of rigidity and modulus of elasticity. (05 Marks)
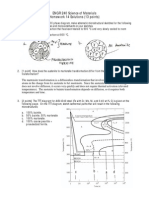
c. A member ABCD is subjected to point loads Pr, Pz, P: and P4 as shown in Fig.Q1(c).
Calculate the force P2 necessary for equilibrium, if Pr
:
45 kN, P3
:
450 kN and
P+
:
130 kN.-Determine the total elongation of the member, assuming the modulus of
elasticity to be 2.1 x 10s N/mm2. (10 Marks)
Fig.Ql(c)
Define: i) Modular ratio, ii) Volumetric strain. (04 Marks)
c.
A load of 2 MN is applied on a column 500 mm x 500 mm. The column is reinforced with
lbur steel bars of l0 mm diameter. one in each comer. Find the stresses in the concrete and
steel bars. Take "E" for steel as 2. I x 105 N/mm2 and ftir concrete as 1 .4 x 104 N/mrn2.
(08 Marks)
A steel rod of 20 mm diameter passes centrally through a copper tube of 50 mm external
diameter and 40 mm internal diameter. The tube is closed at each end by rigid plates of
negligible thickness. The nuts are tightened lightly home on the protecting pans ofthe rod.
It the temperature oI the assembly is raised by 50"C. calculate rhe srresses developed in
copper and steel. Take E lbr steel and copper as 200 GN/m2 and 100 N/m2 and a for steel
and copper as 12 x 10-6/nC and 18 x 10-6fC. (08 Marks)
Define: i) Principal planes, ii) Principal stresses. (04 Marks)
A rectangular bar is subjected to a direct stress (o) in one plane only. Prove that the normal
lOCV/EV33
=
9sin
20.
t
(06 Marks)
615 nnl
c. Two wooden pieces 100 mm x 100 mm in cross section are glued together along line AB as
For More Question Papers Visit - www.pediawikiblog.com
For More Question Papers Visit - www.pediawikiblog.com
r
I
\
\
4a.
b.
Define: i) Shear force, ii) Bending moment.
Tluough sketch list the imporlant tlpe of beams.
Fig.Q4(c) shown the shear force diagram for a simply supporled beam.
pattem and also draw the bending moment diagram.
t
Fig.Qa(c)
PART
_
B
Define: i) Neutral axis, ii) Section modulus, iii) Moment of resistance.
beam.
Define: Torsional rigidity, ii) Polar moment of inertia.
10cv/EV33
(04 Marks)
(05 Marks)
Obtain the loading
(l I Marks)
(06 Marks)
(06 Marks)
(0,1 Marks)
5a.
b.
c.
6a.
b.
c.
Calculate the maximum bending stress induced in a cast iron pipe of external diameter
40 mm, internal diameter 20 mm and of length 4 metre when the pipe is simply supported at
its ends and carries a
point load of80 N at its centre.
(06 Marks)
A beam is simply supported and carries a uniformly distributed load of 40 kN/m over the
entire span. The section ofthe beam is rectangular- having depth as 500 mm. Ifthe maximum
stress in the material of the beam is 120 N/mm2 and moment of inertia of the section is
7 x 108 mma, find the span of the beam.
(08 Marks)
Define: i) Deflection, ii) Elastic curve.
(04 Marks)
Derive an expression for the slope and deflection of a simply supported beam carrying a
point load at the centre.
(10 Marks)
A beam 3m long, simply supported at its ends, is canying a
point load "W" at the centre. If
the slope at the nds ofthe beam should not exceed 1o, find the deflection at the centre ofthe
7a.
b. For: a circular shaft subjected to torsion, derive the relationship between the torque
transmitted and shear stress induced in the shaft.
(06 Marks)
A hollow circular shaft is to transmit 300 kW power at 80 rpm. If the shear stress is not to
exceed 60 N/mm2 and the intemal diameter is 0.6 of the external diameter, find the external
and internal diameter assuming that the maximum torque is 1.4 times the mean. (10 Marks)
a.
b.
Differentiate between long and short columns.
Using Euler's theory, derive an equation for the crippling load of a long column pinned at
(04 Marks)
both ends.
(06 Marks)
c. A simply supported beam of length 4 metre is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of
30 kN/mt over the whole span and deflects 15 mm at the centre. Determine the crippling
load when this beam is used as a column with both the ends hinged.
2 of2
,
t,g
(10 Marks)
For More Question Papers Visit - www.pediawikiblog.com
For More Question Papers Visit - www.pediawikiblog.com
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MCV4U CH 8 Nelson SolutionsDocument29 pagesMCV4U CH 8 Nelson SolutionsStephanieNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Group TheoryDocument24 pagesSymmetry and Group Theorywicki0007100% (1)
- 2nd PUC PhysicsJan 2016 PDFDocument2 pages2nd PUC PhysicsJan 2016 PDFPrasad C M90% (10)
- 2nd PUC Physics Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFDocument1 page2nd PUC Physics Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFPrasad C M82% (11)
- 2nd PUC English Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFDocument4 pages2nd PUC English Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFPrasad C M78% (9)
- 2nd PUC Chemistry Jan 2016 PDFDocument2 pages2nd PUC Chemistry Jan 2016 PDFPrasad C M83% (6)
- 2nd PUC Mathematics Jan 2016 PDFDocument2 pages2nd PUC Mathematics Jan 2016 PDFPrasad C M100% (3)
- 2nd PUC Biology Jan 2016 PDFDocument2 pages2nd PUC Biology Jan 2016 PDFPrasad C M89% (9)
- 2nd PUC Kannada Mide Term Nov 2015 PDFDocument2 pages2nd PUC Kannada Mide Term Nov 2015 PDFPrasad C M100% (5)
- 2nd PUC Mathematics Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFDocument3 pages2nd PUC Mathematics Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFPrasad C M60% (10)
- 2nd PUC Kannada Jan 2016 PDFDocument2 pages2nd PUC Kannada Jan 2016 PDFPrasad C M81% (16)
- 2nd PUC Chemistry Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFDocument2 pages2nd PUC Chemistry Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFPrasad C M100% (8)
- 2nd PUC English Jan 2016 PDFDocument4 pages2nd PUC English Jan 2016 PDFPrasad C M86% (14)
- 2nd Sem DIP Applied Maths 2 - Dec 2015 PDFDocument4 pages2nd Sem DIP Applied Maths 2 - Dec 2015 PDFPrasad C M89% (9)
- 2nd PUC Biology Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFDocument1 page2nd PUC Biology Mid Term Nov 2015 PDFPrasad C M78% (9)
- 2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - May 2015 PDFDocument4 pages2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - May 2015 PDFPrasad C M100% (1)
- 1st Year DIP Communication Skills in English - Dec 2015 PDFDocument4 pages1st Year DIP Communication Skills in English - Dec 2015 PDFPrasad C M100% (7)
- 2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - May 2013 PDFDocument3 pages2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - May 2013 PDFPrasad C M100% (2)
- 2nd Sem DIP Appied Mathematics 2 - May 2015 PDFDocument4 pages2nd Sem DIP Appied Mathematics 2 - May 2015 PDFPrasad C M100% (8)
- 2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - May 2011 PDFDocument3 pages2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - May 2011 PDFPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - May 2010 PDFDocument3 pages2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - May 2010 PDFPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - Dec 2012 PDFDocument4 pages2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - Dec 2012 PDFPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - Dec 2015 PDFDocument3 pages2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - Dec 2015 PDFPrasad C M100% (1)
- 2nd SEM Electronics 1 - May 2012 PDFDocument2 pages2nd SEM Electronics 1 - May 2012 PDFPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - Dec 2014 PDFDocument3 pages2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - Dec 2014 PDFPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- 2nd SEM Electronics 1 - Nov 2011 PDFDocument3 pages2nd SEM Electronics 1 - Nov 2011 PDFPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - Dec 2013 PDFDocument3 pages2nd Sem DIP Electrical Circuits - Dec 2013 PDFPrasad C M100% (1)
- 2nd Sem DIP Electronics 1 - Dec 2015 PDFDocument3 pages2nd Sem DIP Electronics 1 - Dec 2015 PDFPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- 2nd SEM Electronics 1 - May 2011 PDFDocument2 pages2nd SEM Electronics 1 - May 2011 PDFPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- 2nd SEM Electronics 1 - Dec 2014 PDFDocument3 pages2nd SEM Electronics 1 - Dec 2014 PDFPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- Heat exchanger specification sheetDocument2 pagesHeat exchanger specification sheetDycka Anugerah PuryantoroNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch09 Test BankDocument15 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch09 Test BankifghelpdeskNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding II - VSEPR ModelDocument23 pagesChemical Bonding II - VSEPR ModelYokaris JTNo ratings yet
- Homework 14 Solutions Spring 2001Document2 pagesHomework 14 Solutions Spring 2001Ikhwan Wf Miscellaneous AveroesNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL ENGINEERING LICENSURE EXAM REVIEWDocument3 pagesCHEMICAL ENGINEERING LICENSURE EXAM REVIEWJayson Ordinaria100% (1)
- Split Up Syllabus Class Xii Physics 22-23Document1 pageSplit Up Syllabus Class Xii Physics 22-23ROHIT SIHRANo ratings yet
- Hertz Hgs 3 20 ManuelDocument69 pagesHertz Hgs 3 20 Manueligor_sandulenkoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2013 June - P2 PDFDocument20 pagesChemistry 2013 June - P2 PDFBinu PereraNo ratings yet
- AbaqusDocument1,535 pagesAbaqusKing1971100% (1)
- At-Rest Earth Pressure Comparison BasicsDocument9 pagesAt-Rest Earth Pressure Comparison BasicsDev MitraNo ratings yet
- Relativistic Effects Structural Chemistry: &Document32 pagesRelativistic Effects Structural Chemistry: &champ delacruzNo ratings yet
- Classified Examples of Electrical Engineering 1928Document103 pagesClassified Examples of Electrical Engineering 1928dominicrochford3068No ratings yet
- Persamaan DiferensialDocument9 pagesPersamaan DiferensialUla RidhaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Power Transfer DeviceDocument65 pagesWireless Power Transfer DevicebhagathnagarNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements 2 (Introduction)Document12 pagesMachine Elements 2 (Introduction)Melinda100% (2)
- 1415 Phy S5 Term1 Formtest1Document11 pages1415 Phy S5 Term1 Formtest1黃賡浩No ratings yet
- Rate of Change and Approximate ChangeDocument9 pagesRate of Change and Approximate ChangeThomas AlfieNo ratings yet
- 12.elastic ConstantsDocument18 pages12.elastic ConstantsaderancNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument10 pagesPhotoelectric Effect: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchSrynnENo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of The Atom - by Max BornDocument346 pagesThe Mechanics of The Atom - by Max Bornahsbon100% (2)
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledFarah EssidNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Characterization of Doxorubicin-Containing Liposomes: I. Influence of Liposome Charge and PH of Hydration Medium On Loading Capacity and Particle SizeDocument14 pagesPreparation and Characterization of Doxorubicin-Containing Liposomes: I. Influence of Liposome Charge and PH of Hydration Medium On Loading Capacity and Particle SizeSanelaNo ratings yet
- Curvature Radiation From A Quantum-Electrodynamics Point of ViewDocument22 pagesCurvature Radiation From A Quantum-Electrodynamics Point of ViewMohammed NourNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Vector Algebra: 1.1.1 ScalarsDocument7 pages1.1 Vector Algebra: 1.1.1 ScalarsreachsudhirNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 2 Chapter 1Document36 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 2 Chapter 1Adil Ahmed83% (12)
- SsssDocument17 pagesSsssPhysicsNo ratings yet
- BMS481 3.0Document45 pagesBMS481 3.0syuhadahNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument25 pagesElectricityWeb BooksNo ratings yet