Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Technicals
Uploaded by
xjyang01Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Technicals
Uploaded by
xjyang01Copyright:
Available Formats
DJIA 15843 Up at all time highs S&P 1782 Gold: 1254 1200 low back in beginning of July.
y. 1400 in September but downhill from there
Increase Interest Rate Increase in USD Decrease in Gold prices 5 yr 1.53 10 year 2.88 30 year 3.89 WTI 97.64 Brent 108.71 EV/EBITDA Multiple used in conjunction with other ratios like P/E Enterprise Value = MV of Equity + MV of Preferred Stock + Market Value of Debt Cash/Investments EBITDA = EBIT + Dep & Amortization - Low ratio could indicate undervaluation unless its a high capital intensive business - Multiple takes into account debt, so its a good multiple for finding takeover candidates - Biotech would have high multiples EV/EBITDA VS P/E When and why?
How non-cash items move through financial statement ROE vs Op Margin - Provides information about how profitable and efficient a company can be o Op Margin shows you how much revenue is left after deducting your cost of revenue o ROE shows you how much the company generates for the owners of the company NI/Shareholders Equity The higher the ROE, the better. But you have to consider debt. You can boost your ROE higher by borrowing money. And as long as the revenue you generate is more than the interest you pay on those debt, NI will increase more than equity. Nothing wrong with debt, but too much can be a problem if theres a downturn. Reinvest ROE or distribute? Net Debt = ST debt + LT debt Cash FCF = NI + Dep A/R + A/P Capex FCF = Cash flow from operations Capex Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT/Int Exp Diluted EPS = Total Income Preferred Div Payment / Weighted avg shares os + diluted shares
CF statement is the most crucial, but you need the Income Statement and Balance Sheet to do the CF statement Income Statement - How profitable is the firm. Net income - bottom line - flows to Retained Earnings on the balance sheet. Net income - bottom line - flows to first line on Cash Flow from Operations on the Cash Flow Statement *Cumulative record over a period of time Income Revenue Other Income Expense CofGS Sales, General, Admin Dep Loan Interest Taxes
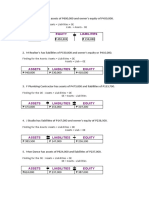
Statement of RE - Portion of NI not paid out to investors as dividends Retained earning - Net income taken from Income Statement to calculate ending Retained Earning. Also states dividends paid out if any to get to ending RE. *Explains change in RE account and in dividends over a period of time. RE from prior year +NI from Income Statement -Dividends Balance Sheet - Act as a record for the firm's assets and liabilities. The rest is Shareholders Equity. Cash balance - first line under Current Assets - taken from ending cash balance on Cash Flow Statement *Snapshot of a moment in time Assets Cash Accounts Receivable Inventory Plant, Property, Equipment Less: Depreciation Liabilities Accounts Payable Loans Stockholder Equity Common Stock Retained Earnings
Cash Flow - Connects the statements together Take the net income and depreciation from income statement for use in Operating Activities Take the comparative balance sheets to create your CF statements. - Increase in assets means decrease in cash and increase in liabilities means increase in cash Ending CF is put into Cash and Cash Equivalents on Balance Sheet Op Activity - most important as it indicates how successful the business is at maintaining a positive cash flow Operating activities - day to day transactions that brings in revenues or expenses Consolidated NI Depreciation Changes in receivables, payables, liabilities, income tax, Investing activities - buy/sell long term assets to be used by the company Payments for PPE Investments and business acquisitions Financing activities - raising cash by taking out loans or bringing in more equity Change in short term borrowing Proceeds from long term debt Dividends paid Purchase of company stock Cash and Cash Equivalents at end of year
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Oil Refineries in 2013: ST NDDocument2 pagesOil Refineries in 2013: ST NDxjyang01No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- GMAT Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesGMAT Cheat Sheetxjyang01No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- GMAT Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesGMAT Cheat Sheetxjyang01No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Guide For RecommendersDocument3 pagesGuide For Recommendersxjyang01No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Insiders Guide FuquaDocument92 pagesInsiders Guide FuquadandemeulesNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Geometry FlashcardDocument14 pagesGeometry Flashcardxjyang01No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- WST Treasury OptionsDocument1 pageWST Treasury Optionsxjyang01No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Geometry FlashcardDocument14 pagesGeometry Flashcardxjyang01No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Chapter 10 Question Answer KeyDocument56 pagesChapter 10 Question Answer KeyBrian Schweinsteiger Fok100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Assets Equity LiabilitiesDocument2 pagesAssets Equity LiabilitiesMathew VisarraNo ratings yet
- Pearsons Federal Taxation 2018 Corporations Partnerships Estates Trusts 31St Edition Anderson Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument66 pagesPearsons Federal Taxation 2018 Corporations Partnerships Estates Trusts 31St Edition Anderson Test Bank Full Chapter PDFWilliamDanielsezgj100% (10)
- Accountancy AdjustmentsDocument17 pagesAccountancy AdjustmentsKRISHNA KUMARNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Testbank - Multinational Business Finance - Chapter 11Document14 pagesTestbank - Multinational Business Finance - Chapter 11Uyen Nhi NguyenNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Financial Statements ComponentsDocument10 pagesFinancial Statements ComponentsABHISHEK CHOUBEYNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Graduate Business School Faculty of Business ManagementDocument17 pagesGraduate Business School Faculty of Business ManagementSyahril NizamNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- International Banking Statistics OverviewDocument139 pagesInternational Banking Statistics Overviewbaburavula4756No ratings yet
- ACC GR 11 Session 11 LNDocument7 pagesACC GR 11 Session 11 LNశ్రీనివాసకిరణ్కుమార్చతుర్వేదులNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Acctg 1 - Cash8Document3 pagesIntermediate Acctg 1 - Cash8Rozen OrlinaNo ratings yet
- 3-Accounting For Management Mcqs With Answers PDF Notes For All Competitive ExamsDocument35 pages3-Accounting For Management Mcqs With Answers PDF Notes For All Competitive ExamsHammadkhan Dj89No ratings yet
- PGSC Debt obj. income statement ratios 2006-2010Document68 pagesPGSC Debt obj. income statement ratios 2006-2010Jose Luis ContrerasNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Functional AccountingDocument85 pagesFunctional AccountingUzair AhmadNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- FPAC1014 Business Accounting: Lecture WorkbookDocument107 pagesFPAC1014 Business Accounting: Lecture WorkbookTay Kai XianNo ratings yet
- ACCT 1002 Past Paper (1) SolutionsDocument9 pagesACCT 1002 Past Paper (1) SolutionsClaire CumminsNo ratings yet
- PARTNERSHIP2Document13 pagesPARTNERSHIP2Anne Marielle UyNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Falanx Interim ResultsDocument12 pagesFalanx Interim Resultsmontegue.sykesNo ratings yet
- RTP Cap III Gr-I Dec 2022Document105 pagesRTP Cap III Gr-I Dec 2022मदन कुमार बिस्टNo ratings yet
- Current Vs Non-Current AssetsDocument3 pagesCurrent Vs Non-Current AssetsTrisha GarciaNo ratings yet
- Redemption of Preference SharesDocument9 pagesRedemption of Preference SharesRahul VermaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- RATIO Analysis in Life Insurance CorporationDocument61 pagesRATIO Analysis in Life Insurance Corporationsreeja kandula789No ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Completing The Audit: Auditing, 14e (Arens)Document22 pagesChapter 18 Completing The Audit: Auditing, 14e (Arens)Miruna CiteaNo ratings yet
- Sido Muncul Consolidated Financial Statements 2019Document94 pagesSido Muncul Consolidated Financial Statements 2019Tugas UtomoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Acctg 101aDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Acctg 101aMeah LabadanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Financial StatementDocument37 pagesUnderstanding Financial StatementMagic of LifeNo ratings yet
- Chap 019Document36 pagesChap 019skuad_024216No ratings yet
- Month End Closing - List of TransactionsDocument3 pagesMonth End Closing - List of TransactionsManas Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Prepare allocation schedule and compute investment balanceDocument7 pagesPrepare allocation schedule and compute investment balancePutri anjjarwatiNo ratings yet
- PAS 36 Impairment of AssetsDocument3 pagesPAS 36 Impairment of AssetsRia GayleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReceivablesDocument22 pagesChapter 3 ReceivablesCale Robert RascoNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)