Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 12 Bkey
Uploaded by
sohaibjamilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 12 Bkey
Uploaded by
sohaibjamilCopyright:
Available Formats
BA 205 section 002 Chapter 1 and 2 Quiz B
Multiple Choice 1. Making a clearly unethical or illegal choice is termed an: a. ethical lapse b. ethical dilemma c. ethical crime d. ethical misdeed
Spring 2009
ANSWER: a. An ethical lapse is the term used for a clearly unethical or illegal choice. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: &! '()%CTI*%: +! T "%: concept ,. Miscommunication bet-een cultures o.ten occurs because a. the senders and recei/ers are encoding and decoding messages using the assumptions o. their di..erent cultures. b. the senders are encoding messages that the recei/ers -ill not be able to decode. c. the recei/ers are decoding messages that the senders -ere not able to encode. d. the senders and recei/ers are encoding and decoding messages that o..end each other. ANSWER: a. When you communicate with someone from another culture, you encode your message using the assumptions of your own culture. However, the audience will decode your message using the assumptions of their culture. DIFFICULT : di..icult! "#$%: 0! '()%CTI*%: 1! T "%: concept 2. 3ecogni4ing and accommodating cultural di..erences in/ol/es all o. the .ollo-ing except: a. social customs b. ethics and la-s c. non/erbal communication d. impact ANSWER: d. mpact is not one of the cultural differences to consider. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 0! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: concept 1. Communication is the process o. a. trans.erring kno-ledge. b. listening acti/ely. c. sending and recei/ing messages. d. -riting e..ecti/e messages. ANSWER: c. !ommunication is the process of sending and receiving messages. "nly answer #c$ contains the %ey dynamics of communication: sending and receiving. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: ,! '()%CTI*%: 1! T "%: concept +. 'ne o. the greatest challenges that communicators .ace in the ne- age o. in.ormation is a. e..ecti/ely .ormatting their documents. b. success.ully analy4ing their audience. c. e..ecti/ely catching their audience6s attention.
d. success.ully editing .or clarity. ANSWER: c. &eople are so inundated with information that they tend to ignore messages they see as less important. t is a challenge to catch their attention. DIFFICULT : di..icult! "#$%: 2! '()%CTI*%: ,! T "%: concept 5. In the communication process all o. the .ollo-ing occur7 except: a. the sender has an idea. b. the sender transmits the message. c. the recei/er has an idea. d. the recei/er decodes the message. ANSWER: c. 'he receiver sends feed(ac%, (ut the initial idea is the sender)s. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: + '()%CTI*%: 2! T "%: concept &. Identi.y the characteristic that is not a part o. ethical communication. a. It includes all rele/ant in.ormation. b. It is designed to hide some negati/e in.ormation. c. It is true in e/ery sense. d. It is not decepti/e in any -ay. ANSWER: (. Ethical communication must always include the *ualities noted in answers #a$, #c$, and #d$. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 5! '()%CTI*%: 1! T "%: application 8. Choosing bet-een alternati/es that aren6t clear9cut is termed an: a. ethical lapse b. ethical dilemma c. ethical crime d. ethical misdeed ANSWER: (. An ethical dilemma occurs when you must weigh the relative merits of the situation+there is no clear answer. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 5! '()%CTI*%: +! T "%: concept 0. :hen one person takes credit .or the -ords and -riting o. another7 it is called a. ethics. b. cultural di/ersity. c. plagiarism. d. ethnocentrism. ANSWER: c. &lagiarism is claiming someone else)s wor% as your own. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 5! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: application 1;. $ood communication skills are /ital today because a. people need to adapt to a constantly changing -orkplace. b. o. an aging population. c. there are multiple sets o. generations in the -orkplace that ha/e di..erent methods o. communication. d. o. the numerous kinds o. media used to communicate. ANSWER: a. 'here are many challenges in the wor%place. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$% 2! '()%CTI*%: 1! T "%: concept
11. Communicating in team9based organi4ations re<uires that you a. listen -ell and understand ho- groups interact. b. be asserti/e and take charge. c. speed up the decision9making process. d. all o. the abo/e ANSWER: a. 'o function effectively in team,(ased organi-ations you need to understand communication in groups, listen closely and interpret (ody language. DIFFICULT : di..icult! "#$%: 1! '()%CTI*%: ,! T "%: concept 1,. Cultures like =outh >orea and Tai-an that rely less on /erbal communication and more on conte?t and setting to con/ey meaning are considered @@@@@@@ cultures. a. basic9conte?t b. moderate9conte?t c. high9conte?t d. lo-9conte?t ANSWER: c. South .orea and 'aiwan are #high,conte/t$ cultures where conte/t and setting convey meaning and where people are e/pected to recogni-e situational cues 0such as gestures and tone of voice1. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 0! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: concept 12. :hich o. the .ollo-ing is the best de.inition o. ethicsA a. stealing someone else6s -ords or -ork and claiming it as your o-n b. the accepted principles o. conduct that go/ern a person or a group c. the belie. that one6s o-n culture is superior to others d. predicting indi/iduals6 beha/ior on the basis o. their membership in a particular group ANSWER: (. Ethics are the accepted principles of conduct that govern a person or a group. DIFFICULT : di..icult! "#$%: 5! '()%CTI*%: 1! T "%: concept 11. :hen belonging to a team is more important to members than making the right decision7 that team may de/elop -hat is termed a. di/ersity o. /ie-s. b. increased per.ormance le/els. c. groupthink. d. e..ecti/e team -ork. ANSWER: c. When (elonging to a team is more important to mem(ers than ma%ing the right decision, that team may develop what is termed #groupthin%.$ DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: ,0! '()%CTI*%: 1! T "%: concept 1+. Cultural conte?t is a. a pattern o. physical cues. b. implicit understanding that con/eys meaning. c. a pattern o. en/ironmental stimuli. d. all o. the abo/e ANSWER: d. !ultural conte/t is the pattern of cues and stimuli that convey meaning (etween mem(ers of a culture.
DIFFICULT : di..icult! "#$%: 0! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: concept 15. #ll o. the .ollo-ing are e?amples o. unethical communication practices except: a. distorting /isuals b. using Bargon c. plagiarism d. mis<uoting ANSWER: (. While using 2argon is not always an effective means of communication, it is not unethical. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 5! '()%CTI*%: 1! T "%: concept 1&. Listeners -ho engage in selecti/e perception a. .ocus on the speaker6s appearance. b. mold messages to .it -hat they already belie/e about the subBect. c. let their attention -ander. d. do all o. the abo/e ANSWER: (. Selective perception involves molding a spea%er)s message to fit what the listener already (elieves a(out the su(2ect. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 20! '()%CTI*%: +! T "%: concept 18. The pattern o. physical cues7 en/ironmental stimuli7 and implicit understanding that con/eys meaning bet-een t-o members o. the same culture is termed: a. ethics b. conte?t c. social customs d. non/erbal communication ANSWER: (. !onte/t is the shared pattern of physical cues, environmental stimuli, and implicit understanding that convey meaning (etween two mem(ers of the same culture. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 0! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: concept 10. The t-o main types o. meetings are a. in.ormational and decision9making. b. problem and solution. c. analytical and comprehensi/e. d. .ocused and .ree9.orm. ANSWER: a. 3ost meetings are either informational or decision,ma%ing. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 2,! '()%CTI*%: ,! T "%: concept ,;. 3ules and e?pectations are usually spelled out in @@@@@@@ cultures. a. basic9conte?t b. moderate9conte?t c. high9conte?t d. lo-9conte?t ANSWER: d. n #low,conte/t$ cultures, rules and e/pectations are usually spelled out through e/plicit statements. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 1;! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: concept ,1. #n e..ecti/e agenda ans-ers -hich o. the .ollo-ing <uestionsA
a. b. c. d.
:hat do -e need to do in this meeting to accomplish our goalsA :hat issues -ill be o. greatest importance to all the participantsA :hat needs do each o. the participants ha/eA both a and b
ANSWER: d. #A$ and #4$ are two of the three %ey *uestions an effective meeting agenda answers. DIFFICULT : di..icult! "#$%: 22! '()%CTI*%: ,! T "%: concept ,,. #ll o. the .ollo-ing are suggestions to help keep your message ethical -hen communicating across cultures except: a. seek mutual ground b. .ocus on pro.its c. sho- respect .or cultural di..erences d. send messages that are honest ANSWER: (. 5ocusing primarily on profits instead of on understanding will not further ethical intercultural communication. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 1;! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: concept ,2. Forming opinions on others based upon their a..iliation or membership in a particular group is called a. stereotyping. b. ethics. c. ethnocentrism. d. conte?t. ANSWER: a. Assumptions made upon the (asis of an individual)s group mem(ership come from stereotyping. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 11! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: application ,1. In part7 poor listening is caused because a. people think .aster than they speak. b. people are uninterested in the subBect matter. c. people are unable to think originally. d. all o. the abo/e
#C=:%3: a. "eople6s minds tend to -ander because they can think .aster than they speak. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 20! '()%CTI*%: +! T "%: concept
,+. %thnocentrism is a. predicting indi/iduals6 beha/ior or character based upon group a..iliation. b. the belie. that one6s culture is superior to all others. c. the promotion o. ethnic cultures. d. the .ormal rules that go/ern a culture6s social beha/iors. ANSWER: (. Ethnocentrism is the (elief that one)s culture is superior to all others. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 11! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: concept ,5. The key to producti/e meetings is care.ul planning o. a. purpose7 participants7 time7 .acilities7 and agenda. b. ethics7 purpose7 location7 and agenda. c. purpose7 participants7 location7 and protocol.
d. ethics7 purpose7 rules o. order7 and location. ANSWER: a. "nly #a$ offers the listing stated on pages 67,66. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: ,0! '()%CTI*%: ,! T "%: concept ,&. :hen -riting .or multicultural audiences7 it6s important to a. use plain %nglish. b. be clear. c. address international correspondence properly. d. all o. the abo/e ANSWER: d. All of the items listed a(ove are important in writing for multicultural audiences. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 11! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: concept ,8. @@@@@@@@@@ is the .ear o. .oreigners and strangers7 and can reduce the e..ecti/eness o. communication bet-een t-o businesspeople .rom di..erent cultures. a. %thnocentrism b. Denophobia c. =tereotyping d. Cultural "luralism ANSWER: (. 'his is the definition of /enopho(ia. DIFFICULT : easy! "#$% 11! '()%CTI*% 5! T "%: concept ,0. Identi.y the one item listed belo- that -ould not help you communicate e..ecti/ely -ith people -ho speak %nglish as a second language. a. try to eliminate noise b. al-ays hold to U.=. customs and common greetings c. obser/e body language d. rephrase sentences -here necessary ANSWER: (. 4oth parties must (e fle/i(le and avoid insisting that an interaction ta%e place strictly in terms of one culture or another. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 1,912! '()%CTI*%: 5! T "%: concept 2;. The most common method .or planning and running e..ecti/e meetings is a. the =%C =tandard6s o. %thics. b. parliamentary procedure. c. 3obert6s 3ules o. 'rder.
d. both b and c apply.
ANSWER: d. 4oth #($ and #c$ identify the valued method for planning and running effective meetings. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 21! '()%CTI*%: 2! T "%: concept 21. :hen selecting participants .or a team meeting7 you should a. include e/eryone -ho might possibly ha/e any connection to the topic at hand. b. include only the senior le/el -orkers on the proBect. c. include only those people -hose presence is essential. d. include as many people as you can .it in the room -here the meeting -ill be.
ANSWER: c. "nly include those people who are essential to the pro2ect. 8ou will waste anyone else)s time. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 2,! '()%CTI*%: ,! T "%: application 2,. The key to producti/e meetings is care.ul planning o. a. purpose. b. participants. c. .acilities and agenda. d. all o. the abo/e ANSWER: d. 'he %ey to productive meetings is careful planning of purpose, participants, facilities and agenda. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 2,922! '()%CTI*%: ,! T "%: concept 22. "arliamentary procedure is the same as a. the =%C =tandard6s o. %thics. b. 3obert6s 3ules o. 'rder. c. the (usiness Code o. 'rder. d. Iacocca6s 3ules o. 'rder. ANSWER: (. Ro(ert)s Rules of "rder constitute parliamentary procedure. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 21! '()%CTI*%: 2! T "%: concept 21. =trictly .ollo-ing parliamentary procedure a. is especially important -ith larger groups. b. can help maintain order in a group. c. can protect indi/idual rights. d. all o. the abo/e ANSWER: d. 'hese are all true of parliamentary procedure. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 21! '()%CTI*%: 2! T "%: concept 2+. Using one6s o-n /alues7 belie.s7 ideas7 and e?pectations to assign meaning to sounds and -ords is called @@@@@@@@@ in the listening process. a. recei/ing b. e/aluating c. interpreting d. analy4ing ANSWER: c. nterpreting is assigning meaning to words. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 2&! '()%CTI*%: 1! T "%: concept 25. #ll o. the .ollo-ing are elements in the listening process except: a. interpreting b. remembering c. .ocusing d. e/aluating
ANSWER: c. 5ocusing is not an element in the listening process.
DIFFICULT : di..icult! "#$%: 2&928! '()%CTI*%: 1! T "%: concept 2&. In selecti/e listening7 the listeners
&
a. distort the message by tuning out anything that doesn6t con.irm their assumptions. b. tend to take control o. the con/ersation. c. tune out until they hear something that gets their attention. d. all o. the abo/e ANSWER: c. Selective listeners let their attention wander. 'hey remem(er what they thin% the spea%er said. DIFFICULT : moderate! "#$%: 28! '()%CTI*%: +! T "%: concept 28. %..ecti/e listeners -ill engage in all o. the .ollo-ing except: a. making eye contact -ith the speaker b. gi/ing the speaker non/erbal cues c. interrupting -hen they disagree d. looking .or opportunities to learn ANSWER: c. 'a(le 7.9 lists actions of effective listeners. DIFFICULT : di..icult! "#$% 28! '()%CTI*%: +! T "%: application. 20. Ine..ecti/e listeners -ill engage in all o. the .ollo-ing acti/ities7 except: a. not taking notes b. allo-ing their mind to -ander c. being Budgmental and becoming distracted by stylistic di..erences d. making distinctions bet-een main points and supporting details ANSWER: d. See 'a(le 7.9 for lists of actions of ineffective listeners. DIFFICULT : di..icult! "#$%: 28! '()%CTI*% +! T "%: application 1;. The .i/e stages o. group .ormation are: a. "articipating7 "urpose7 "reparing7 #genda7 and Location b. Forming7 Corming7 =torming7 "er.orming7 and #dBourning c. #naly4ing7 'rgani4ing7 Integrating7 =ynthesi4ing7 and #dBourning d. Forming7 "articipating7 "roposing7 "er.orming7 and Dismembering ANSWER: (.
You might also like
- SJ-20130814154658-001-ZXSDR R8862A (HV1.0) Product Description - 592255Document24 pagesSJ-20130814154658-001-ZXSDR R8862A (HV1.0) Product Description - 592255Nouvric IntNo ratings yet
- ZXDU68 T601 (V5.0R01M01) Quick Installation & Commissioning Guide PDFDocument4 pagesZXDU68 T601 (V5.0R01M01) Quick Installation & Commissioning Guide PDFsohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- Zxdu68 t301 (v4.1r01m01) User ManualDocument194 pagesZxdu68 t301 (v4.1r01m01) User ManualRamiz Rzaoglu100% (2)
- RET Quality Standards & Installation Guide V (1.0)Document14 pagesRET Quality Standards & Installation Guide V (1.0)sohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- GUL - DER - ZXSDR R8882 Product Description - UR13 - V1.01 - 20140609 PDFDocument23 pagesGUL - DER - ZXSDR R8882 Product Description - UR13 - V1.01 - 20140609 PDFsohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- SJ-20130814154658-001-ZXSDR R8862A (HV1.0) Product Description - 592255Document24 pagesSJ-20130814154658-001-ZXSDR R8862A (HV1.0) Product Description - 592255Nouvric IntNo ratings yet
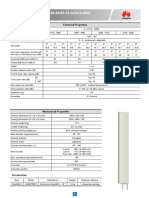
- DXX-1710-2200/1710-2200-65/65-19.5i/ 19.5i-M/M: Electrical Electrical Properties PropertiesDocument2 pagesDXX-1710-2200/1710-2200-65/65-19.5i/ 19.5i-M/M: Electrical Electrical Properties PropertiessohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- Indoor Antenna - KatherienDocument1 pageIndoor Antenna - KatheriensohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- Ts Channel CombDocument1 pageTs Channel CombsohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- GUL - DER - ZXSDR R8882 Product Description - UR13 - V1.01 - 20140609 PDFDocument23 pagesGUL - DER - ZXSDR R8882 Product Description - UR13 - V1.01 - 20140609 PDFsohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- Rs Easy Gprsv2Document11 pagesRs Easy Gprsv2sohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- DXX-1710-2200/1710-2200-65/65-19.5i/ 19.5i-M/M: Electrical Electrical Properties PropertiesDocument2 pagesDXX-1710-2200/1710-2200-65/65-19.5i/ 19.5i-M/M: Electrical Electrical Properties PropertiessohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- DXX-1710-2200/1710-2200-65/65-19.5i/ 19.5i-M/M: Electrical Electrical Properties PropertiesDocument2 pagesDXX-1710-2200/1710-2200-65/65-19.5i/ 19.5i-M/M: Electrical Electrical Properties PropertiessohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Comissiong and Alarm SimulationDocument12 pagesRectifier Comissiong and Alarm SimulationsohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- Rs Easy Gprsv2Document11 pagesRs Easy Gprsv2sohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- GSM QuestionsDocument22 pagesGSM QuestionsAbu Abdullah YaserNo ratings yet
- GSM BasicsDocument19 pagesGSM BasicsTamseel ChowdhryNo ratings yet
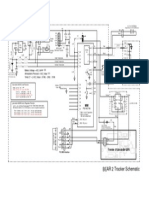
- Aprs SCHDocument1 pageAprs SCHsohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- HW 19634d6Document17 pagesHW 19634d6KenNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: William J. StevensonDocument40 pagesOperations Management: William J. StevensonsohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- GSM BasicsDocument19 pagesGSM BasicsTamseel ChowdhryNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Final Report1Document31 pagesMechatronics Final Report1sohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- Chap002 - Competitiveness, Strategy, and ProductivityDocument34 pagesChap002 - Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivityshivram20No ratings yet
- 30 Hadeeth For RamdanDocument10 pages30 Hadeeth For RamdanabulaylachartierNo ratings yet
- Information About The Solutions For Flame PhotometryDocument6 pagesInformation About The Solutions For Flame PhotometrysohaibjamilNo ratings yet
- Chap002 - Competitiveness, Strategy, and ProductivityDocument34 pagesChap002 - Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivityshivram20No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- English Test 4 PDFDocument3 pagesEnglish Test 4 PDFsofiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document131 pagesLecture 4Laura Georgiana ŞiuNo ratings yet
- Healthy Relationship ChecklistDocument4 pagesHealthy Relationship ChecklistNajma Sadiq100% (1)
- Peoria County Booking Sheet 03/09/15Document5 pagesPeoria County Booking Sheet 03/09/15Journal Star police documentsNo ratings yet
- Victim or Survivor TerminologyDocument2 pagesVictim or Survivor TerminologyRohit James JosephNo ratings yet
- Philo ProjectDocument15 pagesPhilo ProjectCyrus JavierNo ratings yet
- Kida vs. SenateDocument11 pagesKida vs. SenateCassandra LaysonNo ratings yet
- Goodman.1992.History and Theory - Public Sphere and Private LifeDocument21 pagesGoodman.1992.History and Theory - Public Sphere and Private Lifeannivas13No ratings yet
- Legal Ethics ReviewerDocument18 pagesLegal Ethics ReviewerRai MenesesNo ratings yet
- RC Tones Vocabulary ListDocument6 pagesRC Tones Vocabulary ListsanskritiNo ratings yet
- Legal Forms DigestDocument2 pagesLegal Forms DigestKMNo ratings yet
- Vas ReportDocument1 pageVas ReportAjeet Thakur100% (1)
- Ideas and Ideologies Essay On MarxismDocument8 pagesIdeas and Ideologies Essay On MarxismTara SubbaNo ratings yet
- A cn4 507Document109 pagesA cn4 507amallaNo ratings yet
- The Mercy Andc Grace of GodDocument21 pagesThe Mercy Andc Grace of Godbobong9460_544444336No ratings yet
- Engineering Ethics: A Case StudyDocument2 pagesEngineering Ethics: A Case StudyMirae AlonNo ratings yet
- Environmental ClearanceDocument4 pagesEnvironmental ClearanceTanvi JainNo ratings yet
- Regional Trial Court: - VersusDocument3 pagesRegional Trial Court: - VersusBfp-ncr MandaluyongNo ratings yet
- All About WomenDocument0 pagesAll About WomenKeith Jones100% (1)
- A Model of The Effects of Colonialism - DR Michael Yellow BirdDocument2 pagesA Model of The Effects of Colonialism - DR Michael Yellow Birdhuehue2100% (1)
- Cases In-Labor-Standards-NewDocument7 pagesCases In-Labor-Standards-NewKareen BaucanNo ratings yet
- T. S. Eliot's 'Raid On The Inarticulate': A Study in His Concept of LanguageDocument170 pagesT. S. Eliot's 'Raid On The Inarticulate': A Study in His Concept of LanguageJonathan Carson100% (1)
- NuisanceDocument42 pagesNuisanceChoco Skate100% (1)
- Admin Digest - Kilusang Bayan V DominguezDocument2 pagesAdmin Digest - Kilusang Bayan V DominguezAlyssa Clarizze MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Eveline Ndlovu INDEGENOUS KNOWLEDGE ASSIGNMENTDocument4 pagesEveline Ndlovu INDEGENOUS KNOWLEDGE ASSIGNMENTPanashe EliasNo ratings yet
- Emailing PROG PINAGSAMA 3112 AT 3113 NAND2 EIN PERIODICAL PDFDocument2,600 pagesEmailing PROG PINAGSAMA 3112 AT 3113 NAND2 EIN PERIODICAL PDFNathaniele Lean CastroNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Child Adolescent and Learning PrinciplesDocument90 pagesPortfolio in Child Adolescent and Learning PrinciplesKing Louie100% (3)
- Song Fo v. Hawaiian PhilDocument2 pagesSong Fo v. Hawaiian PhilJames Evan I. ObnamiaNo ratings yet
- Management Control SystemDocument5 pagesManagement Control SystemArjun Sukumaran100% (1)
- CHAPTER 5: Quiz On FreedomDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 5: Quiz On FreedomCatalina AsencionNo ratings yet