Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SACE Stage 1 Bonding and Structure Chemistry Notes
Uploaded by
Nhi HinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SACE Stage 1 Bonding and Structure Chemistry Notes
Uploaded by
Nhi HinCopyright:
Available Formats
SACE Stage 1 Chemistry Bonding and Structure Notes
Electronegativity is the measure of an atoms attraction for its outer shell (valence) electrons. Most atoms have a neutral charge, as the positive charge of the protons cancel out the negative charge in the electrons. However, when atoms (or groups of atoms) gain or lose electrons, they have an overall positive or negative charge, making them an ion. If an atom loses electrons, there are now more protons, and thus it becomes a positive ion. If an atom gains electrons, there are now more electrons, and thus it becomes a negative ion. Metals tend to lose electrons in bonding (they have low electronegativity). Non-metals tend to gain electrons in bonding (they have high electronegativity). Electrons tend to exist in pairs. This seems unlikely since it seems that they will repel each other. However, they can do so because they spin in opposite directions. Atoms which have either 8 electrons in their outer shell or a full outer shell are more stable than other arrangements. This is why the Noble Gases (in the 8th group) do not react easily; because they have either 8 electrons in their outer shell, or because their outer shell is full (eg. Helium has 2 electrons = full outer shell) High volatility refers to substances which do not conduct electricity in any state. They have both low melting points and low boiling points. Substances which have low volatility have both high melting points and high boiling points. There are three types of low volatility; Electrical conductivity in the solid state which means that they will conduct electricity both when they are solid or molten, Electrical conductivity in the molten state which means that they will not conduct electricity as solids, but will when molten, No conductivity in molten state which means that they do not conduct both as a solid or molten.
Although high volatility and the last type of low volatility (no conductivity in molten state) both do not conduct electricity, there is a difference.
Substances with high volatility have low melting and boiling points, whereas no conductivity in molten state has high melting and boiling points.
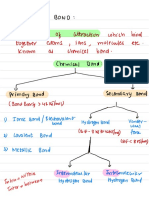
So to summarize, substances with high volatility have low melting/boiling points And substances with low volatility have high melting/boiling points There are three types of bonding between atoms: Ionic, which happens between a non-metal and metallic element, Covalent, which happens between two or more non-metals, and Metallic, which only happens between metals.
Ionic Bonding involves non-metals bonding with metals. Metals form positive ions (they lose electrons) and non-metals form negative ions (they gain electrons).
Because positive and negative ions attract each other, they then bond together in what is called an ionic bond.
Ionic bonds do not show any charge when they are written out in their chemical formulae, as the positive charges cancel out the negative charges.
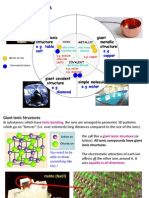
If we had NaCl (Sodium chloride), the lattice would feature 6 Cl- around one Na+ . Four Cls would be around each side of the Na, and two others would be on the front and back respectively.
Because this lattice features ionic bonds (which are equal with a neutral charge), there are also 6 Nas around each Cl.
So to summarise, Ionic bonding is the electrostatic force of attraction between the positive and negative ions in the ionic lattice.
Ionic substances have both high melting points and high boiling points. When in their ionic lattice, they are rigidly held in place and thus cannot change shape. The only movement is a slight vibration where the ions return to their original place afterwards.
As a result, they do not conduct electricity as solids because the ions are held in place and cannot conduct.
However, when melted, they will conduct electricity because the strong forces within the ionic lattice have been broken, and the ions can move around in any direction.
Ionic substances have high melting points and high boiling points. An ionic bond is defined as the electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive and negative ions.
You might also like
- Solution Manual - Chemistry-4th Ed. (McMurry)Document546 pagesSolution Manual - Chemistry-4th Ed. (McMurry)Abdullah Raza Khan82% (17)
- SACE Stage 1 - Psychology Revision NotesDocument9 pagesSACE Stage 1 - Psychology Revision NotesNhi Hin100% (1)
- Solid State Physics - Structure and Properties of Materials - M. A. WahabDocument147 pagesSolid State Physics - Structure and Properties of Materials - M. A. WahabSukhjot Brar67% (3)
- SACE Stage 1 Chemistry - Materials and Their AtomsDocument1 pageSACE Stage 1 Chemistry - Materials and Their AtomsMarcusNo ratings yet
- Pixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017Document27 pagesPixl Knowledge Test Powerpoint - Aqa c1 Core Science - Legacy 2016 and 2017api-342297566No ratings yet
- HalogenoalkanesDocument3 pagesHalogenoalkanesapi-504683923No ratings yet
- SACE Stage 1 Biology Test Revision/Summary QuestionsDocument1 pageSACE Stage 1 Biology Test Revision/Summary QuestionsNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Practice Questions: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding - Practice Questions: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionJemina R. B. Espedillon100% (1)
- c3 Revision WorksheetsDocument5 pagesc3 Revision Worksheetsapi-236179294No ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry: Topic 3 PeriodicityDocument90 pagesIb Chemistry: Topic 3 Periodicitynoob masterNo ratings yet
- GCSE C2 Revision + Exam Questions (1) - Chemi-BondingDocument35 pagesGCSE C2 Revision + Exam Questions (1) - Chemi-BondingPrincess KimNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Notes: Practical ActivitiesDocument24 pagesTeacher's Notes: Practical ActivitieshafsatutuNo ratings yet
- ch03 SM Chemistry2eDocument36 pagesch03 SM Chemistry2eLLL0% (1)
- Pauli Exclusion PrincipleDocument66 pagesPauli Exclusion PrincipleAtul SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding-NotesDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding-NotesHimanshu Meena100% (3)
- Everything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandEverything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Gcesoln 2Document3 pagesGcesoln 2api-3734333100% (1)
- Chemistry Pre Test - Before Starting Yr 12Document8 pagesChemistry Pre Test - Before Starting Yr 12Nhi HinNo ratings yet
- Science Report Template and ScaffoldDocument6 pagesScience Report Template and ScaffoldAndrewNo ratings yet
- Unit-8 D - and F - Block ElementsDocument2 pagesUnit-8 D - and F - Block ElementsSaurabhNo ratings yet
- 10 - Lab - Properties of Ionic Compounds 2017f With Answer Sheet 3Document4 pages10 - Lab - Properties of Ionic Compounds 2017f With Answer Sheet 3api-2920004480% (1)
- Naming Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesNaming Covalent Compoundsapi-296446442No ratings yet
- Dot Structures Practice PacketDocument6 pagesDot Structures Practice Packetgoogley71No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH08 D and F Block Elements 02Document8 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH08 D and F Block Elements 02srivathson7No ratings yet
- 01 Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstanceDocument39 pages01 Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstanceNandi100% (1)
- AS Level Chemistry - Unit 1 Revision GuideDocument16 pagesAS Level Chemistry - Unit 1 Revision GuideJoel Biffin100% (1)
- Chemistry Periodic Trends ActivityDocument6 pagesChemistry Periodic Trends ActivityocNo ratings yet
- PeriodicityDocument6 pagesPeriodicityHadi AlnaherNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Unit 2 NotesDocument26 pagesAs Chemistry Unit 2 Notesizzy 12100% (1)
- CHEMISTRY Grade 10 End of Term 3 2021Document4 pagesCHEMISTRY Grade 10 End of Term 3 2021Marthalaurent Zulu100% (1)
- Lab Manual DK 5th Edition 2022Document51 pagesLab Manual DK 5th Edition 2022Insyirah NazriNo ratings yet
- 3 - Gravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water - S PDFDocument6 pages3 - Gravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water - S PDFJon CranNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6Document148 pagesEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6AbdulRahman MustafaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chemistry Final Exam Review SheetDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Chemistry Final Exam Review SheetAshleyNo ratings yet
- 15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsDocument16 pages15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsGiselle PeachNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NSW Prelim Summary (New Syllabus)Document20 pagesChemistry NSW Prelim Summary (New Syllabus)Bella PurserNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding NotesDocument1 pageCovalent Bonding Noteschongkee56100% (1)
- Caie A2 Chemistry 9701 Theory v3Document33 pagesCaie A2 Chemistry 9701 Theory v3Aditya DroliaNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 8 Transition ChemistryDocument17 pagesNotes Chapter 8 Transition ChemistryGauravRajNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Review Worksheet 22Document2 pagesPeriodic Table Review Worksheet 22Citra YohannaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument26 pagesUnit 2 NotesRameez Mazhar Siddiqi100% (1)
- Ch2 Atoms&Molecules MolesDocument23 pagesCh2 Atoms&Molecules MolesFlorinel BaietelNo ratings yet
- Flametest PDFDocument2 pagesFlametest PDFChecaina RistonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesWorksheet 1 - Chemical BondingFahd KhanNo ratings yet
- U3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT WatermarkDocument45 pagesU3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT Watermarkapi-125934329No ratings yet
- Shapes of Molecules and Ions PDFDocument9 pagesShapes of Molecules and Ions PDFMagenta SparklegemNo ratings yet
- Sec 3e Chem My 09 p2 (Ans)Document14 pagesSec 3e Chem My 09 p2 (Ans)martynchekycNo ratings yet
- 12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSDocument6 pages12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSLydia LamNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE BiologyDocument350 pagesCambridge IGCSE BiologyDelfina Alvarez RoccoNo ratings yet
- Photochemical ReactionDocument16 pagesPhotochemical ReactionChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 3 Student GuideDocument28 pagesChemistry Unit 3 Student GuideApollo WongNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument4 pagesMolecular PolarityTea RadicNo ratings yet
- ChemLab - Techniques - TitrationDocument4 pagesChemLab - Techniques - TitrationdynamicqNo ratings yet
- AP ChemistryDocument24 pagesAP Chemistrykshen2001No ratings yet
- Organic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristicDocument8 pagesOrganic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristictasneemNo ratings yet
- Charles Law PDFDocument3 pagesCharles Law PDFIvan BayonaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 - Chemical BondingArshad Ansari100% (1)
- IAL Chemistry SB2 Answers Topic17Document6 pagesIAL Chemistry SB2 Answers Topic17salmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Document4 pagesChemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Lama DebanaNo ratings yet
- Practice Atomic TheoryDocument10 pagesPractice Atomic Theoryveethu23No ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces HandoutDocument1 pageIntermolecular Forces Handoutanurag yadavNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding AnsDocument251 pagesStructure and Bonding Ansgkawsar22No ratings yet
- Unit 12 6Document130 pagesUnit 12 6Lai BryanNo ratings yet
- O Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9From EverandO Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SACE2 Chem Sample Chapter From Essentials TextbookDocument15 pagesSACE2 Chem Sample Chapter From Essentials TextbookNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Summary of Organic ChemDocument1 pageSummary of Organic ChemNhi HinNo ratings yet
- SACE2 Chemistry Test Exam Pack Sample PagesDocument6 pagesSACE2 Chemistry Test Exam Pack Sample PagesNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Core Knowledge Chemistry 2012 SAMPLEDocument6 pagesCore Knowledge Chemistry 2012 SAMPLENhi HinNo ratings yet
- UMATE 2012 Sample UMAT QuestionsDocument10 pagesUMATE 2012 Sample UMAT QuestionsNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Microscope Skills Year 11 WorksheetDocument1 pageMicroscope Skills Year 11 WorksheetNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Quadratics and Other Polynomials Test RevisionDocument7 pagesQuadratics and Other Polynomials Test RevisionNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Revision Biology Midyear Exam 2011 - Stage 1 SACEDocument2 pagesRevision Biology Midyear Exam 2011 - Stage 1 SACENhi HinNo ratings yet
- 2012 Cancer Assignment Stage 1 BiologyDocument2 pages2012 Cancer Assignment Stage 1 BiologyNhi HinNo ratings yet
- Ib PPT 3 SL PDFDocument24 pagesIb PPT 3 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Topic Guide Energetics Energy and EntropyDocument21 pagesChemistry Topic Guide Energetics Energy and EntropyGazar100% (1)
- Chemistry (Syllabus 9729) : Singapore-Cambridge General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Higher 2 (2022)Document59 pagesChemistry (Syllabus 9729) : Singapore-Cambridge General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Higher 2 (2022)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument274 pagesChemical BondingSafwan AliNo ratings yet
- Together: I of BindDocument15 pagesTogether: I of BindShreyas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- STEM 006 Day 2Document13 pagesSTEM 006 Day 2Caryl Ann C. SernadillaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding ChemistryDocument101 pagesChemical Bonding ChemistryYoshitha Kuntumalla100% (2)
- Naming CompoundsDocument21 pagesNaming CompoundsSir JoshNo ratings yet
- Compounds of Carbon: (I) Per, Nonocarhonic Acid, (Ii) Perdicarbonic AcidDocument72 pagesCompounds of Carbon: (I) Per, Nonocarhonic Acid, (Ii) Perdicarbonic Acidsant venkatakrishnanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocument16 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- Worksheet IGCSE Match Key Words For Revision 2Document2 pagesWorksheet IGCSE Match Key Words For Revision 2oscarbecNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Term 1 MCQ 2021Document29 pagesChemistry Term 1 MCQ 2021manish dagarNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Reactivity of Metals MSDocument21 pages4.1 Reactivity of Metals MSRoqaya BadawyNo ratings yet
- 1 Periodic TableDocument50 pages1 Periodic TableHimanshu GoyalNo ratings yet
- 2019 SS FunctionalMatNanoMat 01Document230 pages2019 SS FunctionalMatNanoMat 01Varisa RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Iv. Chemical BondingDocument27 pagesIv. Chemical BondingReovhenz BeronesNo ratings yet
- Honors Chemistry WKSHT Periodic Table IA ANSWERSDocument10 pagesHonors Chemistry WKSHT Periodic Table IA ANSWERSKaleb HuttoNo ratings yet
- 001145Document50 pages001145purvahattekar100% (1)
- ME 2203 Engineering Materials: Dr. Kazi MD ShorowordiDocument24 pagesME 2203 Engineering Materials: Dr. Kazi MD ShorowordiTahmim AlamNo ratings yet
- Chem Super Secret Syllabus of OlevDocument20 pagesChem Super Secret Syllabus of OlevnooneparticularNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study CardsDocument84 pagesChemistry Study Cardskf8rdNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 13th by TortoraDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 13th by Tortorahieugiaoau0mNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Science Fair Projects Using French Fries, Gumdrops, Soap, and Other Organic Stuff PDFDocument129 pagesChemistry Science Fair Projects Using French Fries, Gumdrops, Soap, and Other Organic Stuff PDFale_neiraNo ratings yet
- Born Haber PDFDocument13 pagesBorn Haber PDFsaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Journal of Physical and Chemistry of SolidsDocument27 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Journal of Physical and Chemistry of SolidsJay Bee SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Board Level Assignment: 1. Which of The Following Has Maximum Bond Angle? HDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding Board Level Assignment: 1. Which of The Following Has Maximum Bond Angle? HLightNo ratings yet