Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EAS450 Lab1 Gravity
Uploaded by
ammar303Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EAS450 Lab1 Gravity
Uploaded by
ammar303Copyright:
Available Formats
EAS-450 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth Lab exercise - Gravity
Objective: Understand the concepts of gravitation and gravity and quantify some of the major contributions to the Earths gravity field. The graphs for problems 7, and 8 should be done on a computer using !icrosoft E"cel, !atlab, or any other suitable soft#are you may $no#%. &roblem ' is easier on a computer too but it #ont comment the results(%. ). *alculate the mass and density of the Earth, assuming it is a non+rotating sphere of radius ',7) $m. ,. The mass of -upiter is about .// times larger than the Earth. 0o#ever, gravity on the surface of -upiter is only . times larger than on the surface of the Earth. E"plain #hy. .. 0o# much smaller #ould your #eight be on the !oon !oon mass 1 7.2x)/,, $g, radius 1 )7.8 $m%3 45ou dont even need to $no# your mass67 2. 8hat should the length of the day be so that gravity is 9ero at the equator3 :. ; geostationary also called geosynchronous% satellite is a satellite located on an orbit such that it remains above the same point on the Earths surface. 8hat is the angular velocity of such a satellite3 8hat is the altitude of such a satellite3 '. *omplete the table belo# and briefly comment your results.
<ocation ?orth &ole >ey$javi$ &aris !id+;tlantic ocean *hamoni" =rench ;lps% Aan =rancisco !orovia Equator -a$arta !elbourne <at. @/? '2? 2@? 2'? 2'? .8? '? / 'A .8A !easured g m.s+,% @.8.,2: @.8,,7 @.8/@2 @.8/278, @.8/..,@ @.7@@' @.78)' @.78/. @.78)8 @.7@@@ Earths gravitation only *entrifugal acceleration only =lattening only Total gravity >esidual gravity
7. Bra# a graph #ith latitude along the "+a"is from C@/ to @/% and the value of gravity at the surface of the Earth in the three follo#ing hypothesisD The Earth is a non+rotating sphere The Earth is a rotating sphere The Earth is rotating and flattened at the pole &lot the observed values from the Table above on the same graph. *omment your results. 8. *onsider a spherical volume near the Earths surface or radius R 1 )// m, at a depth h 1 ,// m, #ith a density 1 .,/// $g.m+.. 8e discussed in class the contribution of this mass on the gravity field at the Earths surface directly above it. Berive the formula that gives the contribution of this mass to gravity on the Earth surface as a function of distance x along the Earths surface ;s if you #ere traveling on the Earths surface to#ard the heterogeneity and a#ay from it, Aee figure belo#%. 40intD #rite gsE #e need to determine the vertical component of gravity gz, so #rite gz as a function of gsE then use simple trigonometric relations to get rid of and plug in h and x7. &lot the value of the contribution of this mass to gravity on the Earth surface as a function of x. Fn the same graph but in a different color or #ith a different type of line% plot the contribution of the same mass if it #as located at a depth of :// m and ) /// m.
0 gs h r
x0
gz
m,
Earth
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Lesson Plan in Science 6 - Forms of Energy and Their Uses.Document5 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6 - Forms of Energy and Their Uses.Mike Casañas87% (39)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Types of Pulses Minimum PhaseDocument1 pageTypes of Pulses Minimum Phaseammar303No ratings yet
- Important Surface WaveDocument1 pageImportant Surface Waveammar303No ratings yet
- ML 101600151Document4 pagesML 101600151ammar303No ratings yet
- Earthquake Hazards 201 - Technical Q&ADocument7 pagesEarthquake Hazards 201 - Technical Q&Aammar303No ratings yet
- Surface Wave ReferencesDocument6 pagesSurface Wave Referencesammar303100% (1)
- ExcelExercise PDFDocument10 pagesExcelExercise PDFammar303No ratings yet
- Geophysics 224 D: Magnetic Exploration Methods - Summary D1: Basic of GeomagnetismDocument2 pagesGeophysics 224 D: Magnetic Exploration Methods - Summary D1: Basic of Geomagnetismammar303No ratings yet
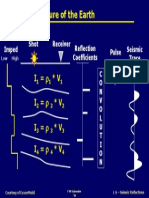
- Acoustic Structure of The Earth: I V I V I VDocument1 pageAcoustic Structure of The Earth: I V I V I Vammar303No ratings yet
- 3 - Petroleum Exploration MethodsDocument4 pages3 - Petroleum Exploration MethodsSameer Goran NoamanNo ratings yet
- Xia 99 04 PDFDocument10 pagesXia 99 04 PDFammar303No ratings yet
- Shot Receiver Seismic Record: Impedance Velocity DensityDocument1 pageShot Receiver Seismic Record: Impedance Velocity Densityammar303No ratings yet
- Important Surface WaveDocument1 pageImportant Surface Waveammar303No ratings yet
- Ideal Seismic Response for Resolving Thin BedsDocument1 pageIdeal Seismic Response for Resolving Thin Bedsammar303No ratings yet
- Designing 3D Seismic SurveysDocument7 pagesDesigning 3D Seismic Surveysammar303No ratings yet
- Xia 02 02 PDFDocument15 pagesXia 02 02 PDFammar303No ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity Shear WaveDocument17 pagesBearing Capacity Shear WaveMaan GalangNo ratings yet
- Articolo 9bDocument1 pageArticolo 9bammar303No ratings yet
- seismics - bj - - rklinge - 2008 مهم جدا رفراكشن تفسيرDocument5 pagesseismics - bj - - rklinge - 2008 مهم جدا رفراكشن تفسيرammar303No ratings yet
- Estimating G-Max & Field CBR of Soil Subgrade Using A Seismic MethodDocument10 pagesEstimating G-Max & Field CBR of Soil Subgrade Using A Seismic Methodammar303No ratings yet
- 234 241Document8 pages234 241Carlos BelmarNo ratings yet
- MASW Equipment for Seismic SurveyingDocument2 pagesMASW Equipment for Seismic Surveyingammar303No ratings yet
- Engineering Properties of MaterialsDocument6 pagesEngineering Properties of Materialspapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Seismic Velocities Contain Information About Depth, Lithology, Fluid Content, and MicrostructureDocument18 pagesSeismic Velocities Contain Information About Depth, Lithology, Fluid Content, and Microstructureammar303No ratings yet
- Evaluation of Seismic Design Methodologies in TurkeyDocument1 pageEvaluation of Seismic Design Methodologies in Turkeyammar303No ratings yet
- Sezen StructDesignofTallBldDocument14 pagesSezen StructDesignofTallBldammar303No ratings yet
- Politecnico Di Torino - Information SheetDocument2 pagesPolitecnico Di Torino - Information Sheetammar303No ratings yet
- BlvdstudentDocument1 pageBlvdstudentAndrew BredobNo ratings yet
- Us International Code ChartDocument2 pagesUs International Code ChartAmit TawdeNo ratings yet
- The Management of Student AccommodationDocument2 pagesThe Management of Student Accommodationammar303No ratings yet
- Earth's Timeline (Earth & Life ScienceDocument4 pagesEarth's Timeline (Earth & Life ScienceRUTH DEBORAH PECIONo ratings yet
- Urban Climate Mapping For Supporting Urban Planning in Chennai, IndiaDocument5 pagesUrban Climate Mapping For Supporting Urban Planning in Chennai, Indiaanil horrisonNo ratings yet
- Proof of Life - How Would We Recognize An Alien If We Saw One - Reader ViewDocument3 pagesProof of Life - How Would We Recognize An Alien If We Saw One - Reader ViewBlazing BooksNo ratings yet
- Pearson Ib Chemistry Text Book AnswersDocument99 pagesPearson Ib Chemistry Text Book Answersmohammad abdurehmanNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Modern Periodic Law and The Present Form of The PeriodicDocument22 pages3.3 Modern Periodic Law and The Present Form of The PeriodicAbijithGamer123No ratings yet
- First Semester Examination Class: VII Geography Marks: 40 / Pgs. 3 Date: 06.10.2021 Time: 1 HRDocument3 pagesFirst Semester Examination Class: VII Geography Marks: 40 / Pgs. 3 Date: 06.10.2021 Time: 1 HRश्रवण कुमारNo ratings yet
- Delhi's Air Pollution Crisis & SolutionsDocument22 pagesDelhi's Air Pollution Crisis & SolutionsRati SindhwaniNo ratings yet
- Properties of Saturated and Superheated SteamDocument42 pagesProperties of Saturated and Superheated Steamscha_shaaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Q2 - Week2 - Melc 5Document10 pagesScience 9 - Q2 - Week2 - Melc 5Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: Oscar P.R. Van Vliet, André P.C. Faaij, Wim C. TurkenburgDocument22 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: Oscar P.R. Van Vliet, André P.C. Faaij, Wim C. TurkenburgElliNo ratings yet
- Rock Classification and Formation ProcessesDocument6 pagesRock Classification and Formation ProcessesYogendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities of Sustainable UrbanizationDocument18 pagesChallenges and Opportunities of Sustainable UrbanizationAniket gajanan shinde shindeNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesModule 7: Solved Problemscaptainhass67% (6)
- Code No: 45005Document4 pagesCode No: 45005SRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- CH 26Document9 pagesCH 26Marilyn UrreaNo ratings yet
- Condensor AKMDocument14 pagesCondensor AKMSharmin SumiNo ratings yet
- MID 17-40KTL3-X User ManualDocument30 pagesMID 17-40KTL3-X User ManualRizaldy AhmadNo ratings yet
- 10 - Hazardous Wastes PDFDocument30 pages10 - Hazardous Wastes PDFEruvin Ike SumisuNo ratings yet
- Room 11 12 13 Turangawaewae PlanningDocument19 pagesRoom 11 12 13 Turangawaewae Planningapi-541161082No ratings yet
- Evelyn Canonce LAS WK 3Document8 pagesEvelyn Canonce LAS WK 3malouNo ratings yet
- On-Grid Inverter with Energy Storage Solution GuideDocument2 pagesOn-Grid Inverter with Energy Storage Solution GuideMohd NB MultiSolarNo ratings yet
- RE-REFINING OF USED LUBRICATING OILSDocument23 pagesRE-REFINING OF USED LUBRICATING OILSJaydeep TayadeNo ratings yet
- Biology Project on Transpiration in PlantsDocument29 pagesBiology Project on Transpiration in PlantsDhanush PSNo ratings yet
- AMOC Weakening May Be Delayed by Warming Indian OceanDocument4 pagesAMOC Weakening May Be Delayed by Warming Indian Oceanmojo xoxoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Matter: Material Pure Substance or Mixture Element, Compound, Homogeneous, HeterogeneousDocument2 pagesClassification of Matter: Material Pure Substance or Mixture Element, Compound, Homogeneous, HeterogeneousKira YoshikageNo ratings yet
- Sewage Sludge and The Circular Economy - Final ReportDocument138 pagesSewage Sludge and The Circular Economy - Final ReportvzgscribdNo ratings yet
- UHVE 2.0 Class Notes Part 3 of 4Document37 pagesUHVE 2.0 Class Notes Part 3 of 4Jayaprabakar JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Composites Today January 2023 PDFDocument36 pagesComposites Today January 2023 PDFGautamNo ratings yet