Professional Documents
Culture Documents
56544
Uploaded by
vish5610Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
56544
Uploaded by
vish5610Copyright:
Available Formats
Reinforced and Prestressed Concrete
Design
to
EC2
The
complete
process
Second edition
Eugene OBrien,
Andrew Dixon and Emma Sheils
Spon
an
Press
& Francis
imprint of Taylor
LONDON AND NEW YORK
Contents
Preface Acknowledgements
PART I
viii
x
Structural 1.
loading and qualitative design
I
3
Fundamentals of qualitative 1.1 1.2 1.3
1.4
design
The
design process
3 4 14
Structural materials Structural systems
Basic structural members
22
2.
Basic 2.1
2.2
layout of concrete
structures
30
30
Identification
of load paths in structures
41 47
Vertical load resisting systems Resistance
2.3 2.4
3.
Horizontal load resisting systems
of
structures to
incremental
collapse
56
Loads and load effects
3.1
3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7
61
61
Loads and load
effects
62
Classification of loads
61
Tributary
areas
Permanent
gravity loads on structures 67 Variable gravity loads on structures 70
Wind load
on
structures 94
77
Limit-state
design
and
PART II
Preliminary analysis
4.
design
analysis
113
107
109
Fundamentals of structural
4.1 4.2 4.3
Introduction
109
Finding moment and shear in determinate linear elastic structures Finding internal bending moment in indeterminate linear
elastic structures 117
vi
Contents 4.4 4.5 Non-linear
Finding
shear
analysis of indeterminate structures force, axial force and deflection
135
141
5.
Applications of structural analysis
5.2 5.2
to concrete structures
152
Introduction Plastic The
152
Continuous beam
moment
analysis
152 157 159
5.3 5.4
redistribution
implications of lower-bound methods 5.5 Analysis of frames 162 5.6 Analysis of slabs 173 5.7 Analysis of shear wall systems 193
6.
Preliminary sizing
6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6
of members
203
Introduction
203 204
Material grades
Preliminary sizing of beams 205 Preliminary sizing of slabs 215
Reinforcement
in
beams and slabs
221 228
Preliminary sizing
of columns and walls
7.
Case studies 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 Introduction
234
-
234
Study 1 Case Study 2 Case Study 3 Case Study 4
Case
Simple Industrial Building 234 Office Building 240 Doughnut Shaped Office Building 255
Residential Hotel
Building with Underground
Car Park
264
-
Case Study 5 Case Study 6
2 71 276
Grandstand
PART Ml
Detailed member design
8.
283
Design of reinforced concrete members for bending
8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4
285
Introduction
285
Second
Elastic
8.5 8.6 8.7 9.
285 moments of area (linear elastic) deflections and crack widths 297 Stress/strain relationships and modes of failure Ultimate moment capacity 310 Balanced design and section ductility 330 Anchorage length 336
306
Design of prestressed
9.1 9.2 Introduction
concrete
members for
bending
346
344
344
Prestressing methods and equipment
Contents 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7
vii
of design 349 Prestressing force and eccentricity 364 Losses in prestress force 375 Secondary effects of prestress 389 Ultimate moment capacity ofprestressed
Basis
concrete
397
10.
Combined axial force and 10.1 10.2 Introduction
405
bending
of reinforced
concrete
members
405
Classification of compression members (columns) 405 10.3 Design of short members for axial force 412 10.4 Design of short members for axial force and uniaxial bending 415 10.5 Design of short members for axial force and biaxial bending 424 10.6 Design of slender members for axial force and uniaxial bending 430 10.7 Design of reinforced concrete deep beams 442
11.
Design for shear and torsion
22.2 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7
11.8
450
Introduction
450
Types of cracking 453 Types of shear failure 458 Shear strength of members without shear reinforcement 463 Shear strength of members with shear reinforcement 471 Design of slabs for punching shear 480
Torsional stresses in uncracked members 491
499
Design of members for torsion in accordance with EC2
A:
Stiffness of structural members and associated bending diagrams Appendix B: Reactions and bending moment diagrams due to applied load Appendix C: Tributary lengths Appendix D: Formulae for analysis of continuous beams (from Reynolds and Appendix
moment
504 506
508
Steedman 1988)
511
moment
Appendix equations design Appendix F: General notation for chapters 8-11 References
Index
E: Slab
515 516 520 522
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- SPE Paper ReferencesDocument4 pagesSPE Paper ReferencesjamartiNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Bolted Beam Column ConnectionsDocument16 pagesBolted Beam Column Connectionssgopalkn7559No ratings yet
- Roads & BridgesDocument66 pagesRoads & BridgesvivekranjanjamNo ratings yet
- Roads & BridgesDocument66 pagesRoads & BridgesvivekranjanjamNo ratings yet
- AASHTO Standard Specifications For Highway Bridges 17th - TOCDocument84 pagesAASHTO Standard Specifications For Highway Bridges 17th - TOCGeorge Christodoulidis71% (7)
- Design of Truck Chassis Frame With Various Cross SectionDocument23 pagesDesign of Truck Chassis Frame With Various Cross SectionZAKIURREHAMAN MUJAWARNo ratings yet
- Technical Note Torsional Analysis of Steel SectionsDocument7 pagesTechnical Note Torsional Analysis of Steel SectionskidseismicNo ratings yet
- Bridge Foundation On RockDocument12 pagesBridge Foundation On RockBipin PadhyNo ratings yet
- ETABS ExampleDocument65 pagesETABS Examplevish5610100% (2)
- Beam Splice Connection Calculation - (Bolted)Document9 pagesBeam Splice Connection Calculation - (Bolted)Naresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis 0809 - Colin CapraniDocument92 pagesPlastic Analysis 0809 - Colin CapraniSourabhAdikeNo ratings yet
- Intze Water Tank Based On K. RajuDocument49 pagesIntze Water Tank Based On K. RajuRamachandra SahuNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Liquid Storage TanksDocument112 pagesSeismic Design of Liquid Storage TanksMunna Bhai100% (1)
- Seismic Design of Liquid Storage TanksDocument112 pagesSeismic Design of Liquid Storage TanksMunna Bhai100% (1)
- Design Concept For Jib CraneDocument12 pagesDesign Concept For Jib Cranevish5610100% (3)
- NCCI - Design of Portal Frame Apex ConnectionsDocument9 pagesNCCI - Design of Portal Frame Apex ConnectionsAdham OunahNo ratings yet
- Elevated Intz Tank 279Document23 pagesElevated Intz Tank 279Navasivayam Sankar100% (2)
- Offcon DNV Zorro SkidDocument7 pagesOffcon DNV Zorro SkidRAMSINGH CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- DNV CN 32.2 Container SecuringDocument39 pagesDNV CN 32.2 Container Securingdamnaged100% (2)
- Mackenzie PVP2017 Stress Linearization Concepts and Restrictions in Elastic Design by AnalysisDocument8 pagesMackenzie PVP2017 Stress Linearization Concepts and Restrictions in Elastic Design by Analysissvk_ntNo ratings yet
- Castellated Beam Design Conformation and ExamplesDocument24 pagesCastellated Beam Design Conformation and ExamplesAlexandru Stefan Both88% (8)
- Seismic Design of Gravity Retaining WallDocument160 pagesSeismic Design of Gravity Retaining Wallอภิรักษ์ มานะกิจศิริสุทธิ100% (1)
- Engine Workshop-Left - Final 16.12.16Document144 pagesEngine Workshop-Left - Final 16.12.16vish5610No ratings yet
- Load CombiDocument2 pagesLoad Combivish5610No ratings yet
- Bonds and CrystalsDocument37 pagesBonds and Crystalsvish5610No ratings yet
- Connections in Steel StructureDocument17 pagesConnections in Steel Structurevish5610No ratings yet
- Staad Examples2Document40 pagesStaad Examples2Suman SahaNo ratings yet
- Load CombiDocument1 pageLoad Combivish5610No ratings yet
- Wind ExampleDocument8 pagesWind ExampleKyle ForemanNo ratings yet
- Capacity Design of Earthquake Resistant Reinforced Concrete WallsDocument244 pagesCapacity Design of Earthquake Resistant Reinforced Concrete Wallsvish5610100% (1)
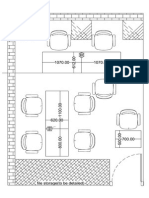
- Room PlanDocument1 pageRoom Planvish5610No ratings yet
- Brushbond TGP: Crystalline Capillary Waterproofing System For Cementitious Substrates Instructions For UseDocument2 pagesBrushbond TGP: Crystalline Capillary Waterproofing System For Cementitious Substrates Instructions For Usevish5610No ratings yet
- CEP-Construction of Railway Overbridge by Ishan KaushalDocument45 pagesCEP-Construction of Railway Overbridge by Ishan KaushalreniguntaswethareddyNo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis ProcedureDocument24 pagesSeismic Analysis Procedurevish5610No ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete PavementDocument13 pagesReinforced Concrete Pavementvish5610100% (1)
- Coastal Protection Aspects of Intake OutfallStructuresDocument12 pagesCoastal Protection Aspects of Intake OutfallStructuresvish5610No ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument5 pagesPile DesignAnonymous nwByj9LNo ratings yet
- General Arrangement of Elevated Water TankDocument1 pageGeneral Arrangement of Elevated Water Tankvish5610No ratings yet
- ANSYS - Method of AnalysisDocument6 pagesANSYS - Method of AnalysisTee Bun PinNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2: Derivation of Shear Stress Produced in A Circular Shaftsubjected To TorsionDocument13 pagesUnit - 2: Derivation of Shear Stress Produced in A Circular Shaftsubjected To TorsionKomalaselvan VNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6.0 - Analysis and Design For TorsionDocument22 pagesLecture 6.0 - Analysis and Design For TorsionRonnie BarreraNo ratings yet
- RCD-Lecture 2Document61 pagesRCD-Lecture 2SALMANNo ratings yet
- CE2155 - Stability of Compression MembersDocument20 pagesCE2155 - Stability of Compression MembersJuliaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Mechanical Engineering & Mechatronics MCQsDocument36 pagesFundamental of Mechanical Engineering & Mechatronics MCQsAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- Designing Hollow-Core Slabs For ContinuityDocument10 pagesDesigning Hollow-Core Slabs For ContinuityRiblocrete Floor systemNo ratings yet
- Plates and Shells: Instructor's Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesPlates and Shells: Instructor's Solutions Manualehab elsawyNo ratings yet
- ARC 615 Advanced Building Structures Lesson 2 Introduction To Longspan Building Structures 160424hDocument53 pagesARC 615 Advanced Building Structures Lesson 2 Introduction To Longspan Building Structures 160424hAsif Ahmed100% (1)
- 002JTGT B02-01-2008-EnDocument75 pages002JTGT B02-01-2008-Enziming liNo ratings yet
- A Study of The Various Structural Framing Systems Subjected To Seismic LoadsDocument8 pagesA Study of The Various Structural Framing Systems Subjected To Seismic LoadsJashwin UllalNo ratings yet
- Module 1bDocument10 pagesModule 1bLhee Ann GarboNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Reinforced ConcreteDocument9 pagesBamboo Reinforced ConcreteE.m. Karishma E MNo ratings yet
- AdSec8.2 ManualDocument120 pagesAdSec8.2 ManualJonathan WardropNo ratings yet
- Forming Notes PDFDocument4 pagesForming Notes PDFMuthuKumarNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of RC Frames UsingDocument22 pagesNonlinear Dynamic Analysis of RC Frames UsingDeybi TtNo ratings yet
- Select The Correct Answer by Encircling The Letter Ofyour Choice. Stricly No ErasuresDocument10 pagesSelect The Correct Answer by Encircling The Letter Ofyour Choice. Stricly No ErasuresJenesis de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Steel Fiber PDFDocument224 pagesSteel Fiber PDFJoseAngelFernandezOrtegaNo ratings yet
- CEMDEF40 Module 1 - Introduction To Mechnanics of MaterialsDocument29 pagesCEMDEF40 Module 1 - Introduction To Mechnanics of MaterialsengrrrrNo ratings yet
- Holeyman-Whenham2017 - Article - CriticalReviewOfTheHypervib1MoDocument19 pagesHoleyman-Whenham2017 - Article - CriticalReviewOfTheHypervib1MoJúlia Hein MazuttiNo ratings yet