Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fuel System Engine Control System Hydraulic sYSTEM
Uploaded by
lamborghini1991Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fuel System Engine Control System Hydraulic sYSTEM
Uploaded by
lamborghini1991Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 8 Engine Control System 1. What are the three main aspects of engine control?
Fuel flow to allow varying engine speeds to be demanded and to allow the engine to be handled without damage by limiting rotating assembly speeds, rates of acceleration and temperatures. Air flow to allow the engine to be operated efficiently throughout the aircraft flight envelope and with adequate safety margins. Exhaust gas flow by burning the exhaust gases and varying the exhaust nozzle area to provide additional thrust.
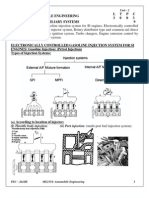
2. What are the typical inputs and outputs of an engine control system? INPUT Throttle Position-thrust demand air data Total temp Engine speed engine temp Nozzle Position Fuel Flow Pressure ratio OUTPUT Fuel flow control Air flow control 3. Describe the functions of fuel control unit (FCU) of jet engines. connected to electronic control to allow precise & continous automatic control of fuel flow, in response to throttle. 4. Draw a schematic diagram to show the basic inputs and outputs of an engine control system. 5. Draw a schematic diagram to illustrate a full authority engine control system with electrical throttle signaling. 6. Describe a typical way of engine speed measurement using a schematic diagram, including how the engine speed is calculated. Gearbox mounted speed probe Exhaust gas temp, by means of thermocouples. Present to pilot as analogue readings in cockpit 7. Describe two ways of engine operating temperature measurement. Chapter 9 Fuel System 1. List typical aircraft fuel system modes of operation.
2. What are the major components of aircraft fuel system and their functions? Fuel pumps o Booster pumps used to pump fuel to engine o Transfer pump, used to transferring fuel between a/c fuel tanks Fuel valves, level sensors, measure level in particular tanks, prevent over filing Guaging probes, measure fuel quantity on board a/c 3. Discuss advantages and disadvantages of AC and DC fuel quantity management systems.
In an AC system the tank unit information is conveyed by means of an AC voltage modulated by the
measured tank capacitance and therefore fuel quantity. The problem with the AC signaling technique is that there is a greater risk of electromagnetic interference (EMI) so that coaxial cables and connectors are required, making the installation more complex, expensive and difficult to maintain. In the DC system the probes are fed by a constant voltage/frequency probe drive and utilize automatic fuel probe diode temperature compensation. Fuel probe signals are rectified by the diodes and the resulting signal proportional to fuel contents returned to the processor as a DC analogue signal A disadvantage of a DC system is the need for additional components with the fuel tank.
4. Discuss the two common in-flight refueling methods. Probe and Drougue Method o Multiple a/c cab be refuelled o basket has greater history of causing damage to a.c o lower fuel flow Flying Boomb method o higher fuel flow o only one a/c at a time Chapter 10 Hydraulic System 1. Discuss the major advantages of aircraft hydraulic actuation in comparison with electrical motors. Electric motor cant match power to weight ratio of gydrualic actuator, particually above 3kW Hydraulics meets low weight, low volume, low inital cost, high reliability, low maintainence 2. What are the main components of an aircraft hydraulic system? Explain their functions. Reservoir-ensures sufficient fluid is aviable under all conditions Heat exchanger filter pump cause a flow of fluid at certain pressure gearbox-connected to hydraulic pump, primary source of power actuator accumulator demand signals 3. Describe the operation of principle of hydraulic pumps. sense outlet pressure and feed back this signal to play carrying reciprocating pistons 4. Discuss the design procedure of hydraulic piping.
separate pipes to avoid common mode failures as result of accidental damage measure lengths of pipe to calculate flow rate in each section press drop of less than 25% selected, this may be divided between pressure pipes, return pipes 5. Discuss aircraft hydraulic system fluid conditioning. Fluid needs cooling and cleaning Heat exchange is sued for cooling, provided when a/c is in flight Servo-valves with fine clearances emphasize need fo clean fluids Filter elements and wire mesh are able to withstand pressure
You might also like
- Fuel InjectionDocument4 pagesFuel InjectionWeyih ReganNo ratings yet
- Multi Port Fuel Injection SystemDocument4 pagesMulti Port Fuel Injection SystemVarsha SreekumarNo ratings yet
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- SheronDocument20 pagesSheronSheron ThomasNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideFrom EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Mixture Preparation SIDocument42 pagesMixture Preparation SIMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Engine Structure and ComponentsDocument14 pagesEngine Structure and ComponentsMarco OlivettoNo ratings yet
- Explain Function of Mass Air Flow Sensor.: The Leaner FuelDocument15 pagesExplain Function of Mass Air Flow Sensor.: The Leaner FuelAbubaker MuzayinNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine ManagementDocument56 pagesDiesel Engine Managementbravo6dNo ratings yet
- Lecture-9-Electronic Engine Management SystemDocument102 pagesLecture-9-Electronic Engine Management SystemPiyush BidwaiNo ratings yet
- Performance of a Gasoline Engine at Partial LoadDocument5 pagesPerformance of a Gasoline Engine at Partial LoadGritz Kay Labucay MarforiNo ratings yet
- OBD-InsightsDocument52 pagesOBD-Insightsjayasundar100% (1)
- MR SolomonDocument6 pagesMR SolomonMarcusNo ratings yet
- Section 2 EngineDocument14 pagesSection 2 EngineCarlosNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection in VehiclesDocument38 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection in VehiclesKelvin WairiNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection System Bosch AfcDocument28 pagesFuel Injection System Bosch AfcShivam TandonNo ratings yet
- Paper 17Document9 pagesPaper 17Faitar CatalinNo ratings yet
- General Layout of Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument34 pagesGeneral Layout of Diesel Engine Power PlantMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Injection Systems and Their Control9Document13 pagesAdvanced Injection Systems and Their Control9Musa TandiarrangNo ratings yet
- Report-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiDocument19 pagesReport-Multi Point Fuel Injection-MpfiHemant PatraNo ratings yet
- Common Rail Diesel Diagnostics in Shropshire & Mid Wales: CR Diesel Engine RepairDocument8 pagesCommon Rail Diesel Diagnostics in Shropshire & Mid Wales: CR Diesel Engine RepairMügïshá ÆlfieNo ratings yet
- Common Rail Diesel Diagnostics in Shropshire & Mid Wales: CR Diesel Engine RepairDocument8 pagesCommon Rail Diesel Diagnostics in Shropshire & Mid Wales: CR Diesel Engine RepairMügïshá ÆlfieNo ratings yet
- Automotive ElectronicsDocument44 pagesAutomotive ElectronicsRohit Kumar100% (1)
- Electronic Fuel Management in I.C Engines G Nagarajan Professor Department of Mechanical Engg. Anna University Chennai 60025Document5 pagesElectronic Fuel Management in I.C Engines G Nagarajan Professor Department of Mechanical Engg. Anna University Chennai 60025alagarg137691No ratings yet
- Weber Injection-Ignition SystemDocument27 pagesWeber Injection-Ignition SystemjohnvandurenNo ratings yet
- MPFI Vs Carburetor Technology For Multi Cylinder EnginesDocument14 pagesMPFI Vs Carburetor Technology For Multi Cylinder EnginesDipak Kumar100% (1)
- Multi Point Fuel Injection SystemDocument12 pagesMulti Point Fuel Injection Systemashwini yewaleNo ratings yet
- PropulsãoDocument144 pagesPropulsãoANTONIONo ratings yet
- The Use of Onboard Real-Time Models For Jet Engine ControlDocument27 pagesThe Use of Onboard Real-Time Models For Jet Engine ControljoukendNo ratings yet
- International Service Information SolutionsDocument7 pagesInternational Service Information SolutionsTuấn NeoNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About MPFI SystemsDocument16 pagesEverything You Need to Know About MPFI SystemsIshan Rastogi100% (4)
- How To Calibrate ECU and Engine - SAEDocument42 pagesHow To Calibrate ECU and Engine - SAEVishwanathanPulugandi100% (2)
- Engine Management MechatronicsDocument18 pagesEngine Management MechatronicsTanuj Kumar67% (3)
- Lect 1-Efi Petrol 3HRSDocument50 pagesLect 1-Efi Petrol 3HRSHodge LorneNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection SystemDocument9 pagesFuel Injection SystemJM PraveenNo ratings yet
- MPFI System ExplainedDocument15 pagesMPFI System Explainedಶಿವರಾಜ್ ಎನ್No ratings yet
- Engine Management: Subject: Mechatronics System Design Submitted To: Engr. Zubair Submitted byDocument6 pagesEngine Management: Subject: Mechatronics System Design Submitted To: Engr. Zubair Submitted byqazi_mohsin87100% (1)
- Cummins ISX Fuel System 02-05Document18 pagesCummins ISX Fuel System 02-05g665013100% (21)
- IntelligentDocument7 pagesIntelligentfahad19aNo ratings yet
- FuelDocument30 pagesFuelrakhikishoreNo ratings yet
- Electronically Controlled Diesel EngineDocument50 pagesElectronically Controlled Diesel EngineVictorIjadunminiyi100% (2)
- AUTOTRONICADocument3 pagesAUTOTRONICAJhon Arreaga AguilarNo ratings yet
- Paper 17Document8 pagesPaper 17Faitar CatalinNo ratings yet
- Improving industrial productivity through energy efficient VSDsDocument4 pagesImproving industrial productivity through energy efficient VSDssayed2846No ratings yet
- Fig. 1: Completed - The First Commercial ME EngineDocument4 pagesFig. 1: Completed - The First Commercial ME EngineAshutosh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- MPFI System: How It Works and Its ComponentsDocument6 pagesMPFI System: How It Works and Its Componentsalan kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment 2Document5 pagesElectronic Assignment 2MarcusNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Automobile Engine SystemsDocument34 pagesUnit 2 Automobile Engine SystemschezhianbabuNo ratings yet
- QSM11 Engine Components and StructureDocument14 pagesQSM11 Engine Components and StructureTaha RdmanNo ratings yet
- 4-Cylinder Engine EMS ExplainedDocument27 pages4-Cylinder Engine EMS ExplainedGabriel BalcazarNo ratings yet
- GloriasDocument4 pagesGloriastimNo ratings yet
- Novel Configuration For Air Flow Rationalization and Turbo Lag Reduction in CRDI EngineDocument4 pagesNovel Configuration For Air Flow Rationalization and Turbo Lag Reduction in CRDI Engineyash1239No ratings yet
- Aircraft Systems and IntegrationDocument21 pagesAircraft Systems and IntegrationGanesh Bashyal Pittals100% (1)
- Hybrid 06Document0 pagesHybrid 06Jorge Eduardo Diaz ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Cat c6 6 Troubleshooting Manual PDFDocument10 pagesCat c6 6 Troubleshooting Manual PDFAlexendra100% (2)
- ME 6I 22655 UNIT 1 Shaikh Sir NotesDocument21 pagesME 6I 22655 UNIT 1 Shaikh Sir Notesharshaldhangar999No ratings yet
- FUEL SYSTEM OF C18 and C6.6Document135 pagesFUEL SYSTEM OF C18 and C6.6Sahr, Cyprian Fillie100% (2)
- Cantilever Beam FinalDocument8 pagesCantilever Beam Finallamborghini19910% (1)
- Aircraft Performance Problem Solution Range MachDocument1 pageAircraft Performance Problem Solution Range Machlamborghini1991No ratings yet
- Linearization Notes Online 2Document29 pagesLinearization Notes Online 2lamborghini1991No ratings yet
- 441 Lecture 10Document19 pages441 Lecture 10nanduslns07No ratings yet
- Cantiliever Beam LabDocument4 pagesCantiliever Beam Lablamborghini1991No ratings yet
- Fatigue Failure AnalysisDocument42 pagesFatigue Failure Analysislamborghini1991No ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3lamborghini1991No ratings yet
- Aeroelasticity Homework ProblemsDocument1 pageAeroelasticity Homework Problemslamborghini1991No ratings yet
- Avionics Ch4.Document4 pagesAvionics Ch4.lamborghini1991No ratings yet
- Avionics Ch4.Document4 pagesAvionics Ch4.lamborghini1991No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Environmental Control SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Environmental Control Systemlamborghini1991No ratings yet
- SPH3U: Vector Diagrams Name:: A B D E A B D EDocument2 pagesSPH3U: Vector Diagrams Name:: A B D E A B D Elamborghini1991No ratings yet
- Marley PRG 11B L PDFDocument64 pagesMarley PRG 11B L PDFIlkuNo ratings yet
- Air Operated Double Diaphragm Pump: Service & Operating ManualDocument12 pagesAir Operated Double Diaphragm Pump: Service & Operating ManualLuiz AraujoNo ratings yet
- 45 Series E Frame 100cc, 130cc, 147cc Parts Manual (520L0584)Document48 pages45 Series E Frame 100cc, 130cc, 147cc Parts Manual (520L0584)Sasko Dimitrov100% (4)
- Dat Gv180tiDocument2 pagesDat Gv180tiThomasRudyNo ratings yet
- Comments Resolution Sheet Against Comments Given by Bureau Veritas - GEC ReplyDocument2 pagesComments Resolution Sheet Against Comments Given by Bureau Veritas - GEC ReplybecpavanNo ratings yet
- Booster Pump CalculationDocument11 pagesBooster Pump CalculationSuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Universal Engines Fast Moving Parts ListsDocument21 pagesUniversal Engines Fast Moving Parts Liststarek ali ahmedNo ratings yet
- Bstway Filter Pump Owner's ManualDocument68 pagesBstway Filter Pump Owner's ManualtomusimundoNo ratings yet
- COPPUS Steam Turbines PRODUCT GUIDEDocument6 pagesCOPPUS Steam Turbines PRODUCT GUIDEaminardakaniNo ratings yet
- Lorentz Sunswitch Manual en en PDFDocument3 pagesLorentz Sunswitch Manual en en PDFLuis RolaNo ratings yet
- Diesel Fuels and Diesel Fuel Systems (LEBW4976-07)Document64 pagesDiesel Fuels and Diesel Fuel Systems (LEBW4976-07)Mormor OmertaNo ratings yet
- SPE-23429 A Simple Method of Predicting The Performance of Sucker Rod Pumping SystemDocument10 pagesSPE-23429 A Simple Method of Predicting The Performance of Sucker Rod Pumping SystemOsmund MwangupiliNo ratings yet
- Causes and Prevention of Pump Cavitation DamageDocument2 pagesCauses and Prevention of Pump Cavitation DamageJJNo ratings yet
- KITS Bomba Combustível FUEL CAT C0375A 01.21 Int enDocument216 pagesKITS Bomba Combustível FUEL CAT C0375A 01.21 Int enAndre FilipeNo ratings yet
- Vats Introduction PresentationDocument19 pagesVats Introduction PresentationAMOLNo ratings yet
- RIELO RL - 70mDocument52 pagesRIELO RL - 70mspace recycling levanteNo ratings yet
- Cat AXCATDocument80 pagesCat AXCATgazwang478No ratings yet
- Utility - Fire Water SystemDocument17 pagesUtility - Fire Water SystemGloria HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Story of Seasons Pioneers of Olive TownDocument74 pagesStory of Seasons Pioneers of Olive TownBeatrizNo ratings yet
- Considering The Effect of Crude Oil Viscosity On Pumping Requirements - Campbell Tip of The MonthDocument6 pagesConsidering The Effect of Crude Oil Viscosity On Pumping Requirements - Campbell Tip of The MonthalexescNo ratings yet
- CEMS GuidlinesDocument94 pagesCEMS GuidlinesBiohm ConsultareNo ratings yet
- Air Toxics LTD Sampling GuideDocument27 pagesAir Toxics LTD Sampling Guideatykirana5562No ratings yet
- Troubleshooting The Hydraulic CircuitDocument3 pagesTroubleshooting The Hydraulic CircuitalexanderNo ratings yet
- Exxon IP 10-4-1 Reciprocating Process CompressorsDocument9 pagesExxon IP 10-4-1 Reciprocating Process CompressorsGilvan SilvaNo ratings yet
- Cummins Onan MDKDS DT DU Parts ManualDocument94 pagesCummins Onan MDKDS DT DU Parts ManualAsep Shaifurrahman0% (1)
- Centrifugal Pumps for Water Applications in Stainless Steel and Cast IronDocument176 pagesCentrifugal Pumps for Water Applications in Stainless Steel and Cast IronFotis Petropoulos100% (1)
- Cargas para BoquillasDocument7 pagesCargas para Boquillasnikoonz2528No ratings yet
- Jacto 300 500 OperatorsmanualDocument4 pagesJacto 300 500 OperatorsmanualOhTenThickeNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts For Peougeot 306 Comm. Part No. Part NameDocument189 pagesSpare Parts For Peougeot 306 Comm. Part No. Part NameMarco D'AndreaNo ratings yet
- Preview E102-17Document17 pagesPreview E102-17acount checkNo ratings yet
- The Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureFrom EverandThe Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (48)
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemFrom EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresFrom EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsFrom EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesFrom EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyFrom EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesFrom EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionFrom EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentFrom EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridFrom EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualFrom EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryFrom EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNo ratings yet
- Inherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachFrom EverandInherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- OFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyFrom EverandOFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyNo ratings yet
- The Way Home: Tales from a life without technologyFrom EverandThe Way Home: Tales from a life without technologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesFrom EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)