Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Attainment 1
Uploaded by
api-242018367Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Attainment 1
Uploaded by
api-242018367Copyright:
Available Formats
CONCEPT ATTAINMENT LESSON PLAN
Subject Area: Science Grade Level: 2nd
Specific Content: Liquids Lengt of Le!!on: 30 minutes
In!tructional Objective"!#: The learner will state two critical attributes of liquids taking the shape of containers and taking up space. State Content Standard $ %enc &ar' $ Grade Level E(pectation: All students will measure and describe the things around us. lassif! common ob"ects and substances according to obser#able attributes$properties Long)Ter& *nit Objective: The learner will describe the critical attributes of solids% liquids% and gases and will pro#ide e&les of each state of matter. +e!terda,-! Le!!on: To&orro.-! Le!!on: ritical attributes of solids ritical attributes of gases
Prere/ui!ite 0no.ledge or %e avior! Needed: Skills: Concepts: '&perience with (categories lessons) ritical attribute or characteristic ritical attributes of solids *amiliar liquids +aising hands to contribute ideas
Behaviors:
1 , i! t e Content of Toda,-! Le!!on 2elevant for +our Student!3 States of matter is a fundamental concept in the natural sciences. States of matter compose the uni#erse. Material!: Teacher,s list of -'S$./ e&les -'S /range ./ Soda pop
Apple "uice 0ced tea 1ilk orn oil 'lmer,s 2lue Lemon "uice
ookie loaf of bread scrambled egg clouds computer plastic pitcher
Later examples for students to categorize3 4ater Soccer ball up 5ishwashing soap Where are your materials to be kept until their use during the lesson? Table in front When ill your materials be passed out? !o ill materials be passed out? oncept Attainment .$A .$A
Model of Teac ing: Procedure!
List each procedure according to stages of Concept "ttainment: 6. 2. 3. 8. 9. ;. <. Sponge acti#it! 7 ommon characteristics of a *risbee and a 5 *irst -'S and ./ e&les Second new e&les Third e&les 0ndi#idual work Ask for h!pothesis
Ask for h!pothesis
Ask for h!pothesis :artner work
2roup response to successi#e h!potheses onnection to concept from prior lesson 7 solids 5o not take the shape of their container 5efinite #olume 7 take up space.
=.
:ro#ide attributes of liquids 5o take the shape of their container
5efinite #olume 7 take up space >. 60. 66. 62. +e#iew their h!potheses to backtrack thinking ?uick re#iew of solids and liquids .ew e&les for them to categori@e '&les the! generate
#nclude each $uestion you are planning to ask students in the appropriate place in your lesson plan %& 2. 3. 8. 9. ;. < =. >. 60. Closure: 4hat do we call our guesses about categoriesA 4hat do think the categor! isA BThis is repeated throughout the lesson.C 4hat is !our h!pothesisA BThis is repeated throughout the lesson.C 4h! do !ou think this is soA BThis is repeated throughout the lesson.C 4hat do !ou think about what DDDDDD "ust saidA Attributes of solids from !esterda!,s lessonA 5o all the -'S e&les ha#e these critical attributesA .ew e&les 7 -'S or ./A 4hat were !ou first thinkingA 4hen did !ou know !our ideas were wrongA
Ticket out the door 7 4hisper a solid and a liquid as the! line up
4o. did ,ou addre!! !tudent learning !t,le! during t i! le!!on3 5e!cribe all t at appl,6 'isual +ecording successi#e e&les on the board or chart Artifacts of -'S and ./ e&les could be brought in for the lesson 5iscussion
"uditory
(inesthetic 5uring the closure of the lesson% creati#e mo#ement could be used to bring the critical attributes to life. )actile 0f artifacts are brought in% the! could be passed around .$A
*ther approaches: A!!e!!&ent Criteria:
What tangible evidence ill demonstrate your students+ learning today? group categori@ation of new e&les and groupEgenerated e&les What ill be considered $uality ork? orrect responses
*ull
,o you need a rubric to structure your assessment? .$A Will students also self-assess using this rubric? .$A
Gender or cultural concern! &a, affect ,our in!tructional or a!!e!!&ent c oice! in t i! le!!on6 If appropriate7 identif, t e!e and de!cribe o. ,ou .ill addre!! t e&6 Students will work in partners during the lesson. Table groupings are alread! made with a heterogeneous culture$gender mi&. 'SL student will ha#e a bilingual student or paraprofessional translate e&les into nati#e language as needed. In!tructional Modification! 8 5e!cribe a !tudent in ,our cla!! . o a! !pecial need!6 Con!ider o. ,ou &ig t &odif, ,our in!truction and $ or a!!e!!&ent for t i! !tudent during t i! 5irect In!truction le!!on6 Traditional print7 Internet and NETS re!ource! can a!!i!t ,ou6 1icrophone s!stem in use b! teacher for the benefit of all students. /ne student is a lip reader. Fe is seated in the front of the room. Teacher remains forward when speaking. She does not speak when she is writing on the board. *requent #isual checks and questions will be used to assess his understanding during the lesson. Tec nolog, 8 1 at tec nolog, &ig t en ance t i! le!!on or t i! unit at !o&e point3 Traditional print7 Internet and NETS re!ource! can a!!i!t ,ou6 2ander Academ! website has multiple acti#ities to learn and re#iew solids% liquids% and gases. http3$$www.cdli.ca$ 0T'$matter.htm 4o. .ill ,ou provide practice for t i! objective3
Fomework about famil!,s use of liquids enter acti#ities making collages of pictures of states of matter 4eb resources School building search for use of states of matter 4orksheets $ pu@@les Bcrosswords% word searches% etc.C
You might also like
- Elementary Science Experiments: Analyzing Data to Make PredictionsFrom EverandElementary Science Experiments: Analyzing Data to Make PredictionsNo ratings yet
- Mi Plantilla Plan Unidad Final 1 Correcteddoc 1Document10 pagesMi Plantilla Plan Unidad Final 1 Correcteddoc 1api-257838720No ratings yet
- Week 2 Lesson 4Document6 pagesWeek 2 Lesson 4api-252835803No ratings yet
- 6-10 Day Unit Lesson PlanDocument18 pages6-10 Day Unit Lesson Planapi-252173413No ratings yet
- Unit Plan Lesson 5 FinalDocument3 pagesUnit Plan Lesson 5 Finalapi-242412350No ratings yet
- Science Unit - PlantsDocument31 pagesScience Unit - Plantsapi-242215249No ratings yet
- Unit PlanDocument4 pagesUnit Planapi-249889728No ratings yet
- Week 2 Lesson 3Document5 pagesWeek 2 Lesson 3api-252835803No ratings yet
- 3-4 1 Lesson Plan - Monday - ScienceDocument3 pages3-4 1 Lesson Plan - Monday - Scienceapi-203262811No ratings yet
- Ubd 3 Jae Hee Kim With Comments 3-22-14Document35 pagesUbd 3 Jae Hee Kim With Comments 3-22-14api-253754657No ratings yet
- Las Expectativas de Español IV CPDocument5 pagesLas Expectativas de Español IV CPlevanshhsNo ratings yet
- La LP 4-21-25Document13 pagesLa LP 4-21-25api-254017867No ratings yet
- 2 1 LessonDocument3 pages2 1 Lessonapi-252482926No ratings yet
- Stepp3 111Document6 pagesStepp3 111api-253593723No ratings yet
- EDUC2220, Assignment 12,13 - Technology Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesEDUC2220, Assignment 12,13 - Technology Lesson PlanknapkejNo ratings yet
- 7 1 LessonDocument3 pages7 1 Lessonapi-252482926No ratings yet
- Guia de InglesDocument24 pagesGuia de Inglesveroelizabeth13No ratings yet
- Las Expectativas de Español II AvanzadoDocument5 pagesLas Expectativas de Español II AvanzadolevanshhsNo ratings yet
- Guia 1 InglesDocument24 pagesGuia 1 Inglesveroelizabeth13No ratings yet
- Summary Lesson Plan 3Document10 pagesSummary Lesson Plan 3syazaNo ratings yet
- Job Search E1 - L2 Tutor NotesDocument46 pagesJob Search E1 - L2 Tutor NotesNeil RobertsNo ratings yet
- Thames Dakota DsDocument3 pagesThames Dakota Dsapi-253020739No ratings yet
- 3 1 Learning GoalsDocument4 pages3 1 Learning Goalsapi-254453201No ratings yet
- 476 Lessonplan 2Document4 pages476 Lessonplan 2api-240341792No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan EdtDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Edtapi-263788822No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson Planapi-237191226No ratings yet
- Text Research 02Document5 pagesText Research 02api-239648283No ratings yet
- Lawrence Syllabus 2014-2015Document4 pagesLawrence Syllabus 2014-2015api-264385633No ratings yet
- Coordinates Cover SheetDocument2 pagesCoordinates Cover Sheetapi-244738679No ratings yet
- Djones PnwtribelessonDocument5 pagesDjones Pnwtribelessonapi-244738679No ratings yet
- Frog Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFrog Lesson Planapi-266473625No ratings yet
- Read Aloud 10-15Document5 pagesRead Aloud 10-15api-239432668No ratings yet
- Lesson5 PilgrimsDocument4 pagesLesson5 Pilgrimsapi-240589503No ratings yet
- Weingart Nature Investigation - The Physical Prop of Water 2014Document4 pagesWeingart Nature Investigation - The Physical Prop of Water 2014api-251848378No ratings yet
- Science Lesson Plan 2Document4 pagesScience Lesson Plan 2api-251798124No ratings yet
- Latin 1 Course Expectations 2013-2014Document8 pagesLatin 1 Course Expectations 2013-2014levanshhsNo ratings yet
- JMJ Narrative Topic 1Document22 pagesJMJ Narrative Topic 1Jeffrey MacalinoNo ratings yet
- N S C Teacher Preparation Program Lesson Plan Format: Description of ClassroomDocument4 pagesN S C Teacher Preparation Program Lesson Plan Format: Description of ClassroomknstraderNo ratings yet
- 3 Eppt TN Unit 5 Readng SBHDocument6 pages3 Eppt TN Unit 5 Readng SBHCecil EnsemNo ratings yet
- Literature Unit 2014 1Document30 pagesLiterature Unit 2014 1api-267275160No ratings yet
- Lessonplan 2Document2 pagesLessonplan 2api-251124395No ratings yet
- Instructional Design Education 429Document17 pagesInstructional Design Education 429api-122660687No ratings yet
- Read Aloud Lesson 5213Document7 pagesRead Aloud Lesson 5213api-239432668No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - IctDocument4 pagesLesson Plan - Ictapi-249422779No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan/: Investigating Materials: States of MatterDocument3 pagesLesson Plan/: Investigating Materials: States of MatterU.s. MaaranNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On TextureDocument7 pagesLesson Plan On Textureapi-264368749No ratings yet
- Own Lesson 2Document10 pagesOwn Lesson 2api-254041206No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Class SecondaryDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Class Secondaryapi-263455625No ratings yet
- 4 1 LessonDocument3 pages4 1 Lessonapi-252482926No ratings yet
- Class SyllabusDocument3 pagesClass Syllabusapi-262489611No ratings yet
- Lesson Planning Form For Accessible Instruction - Calvin College Education ProgramDocument3 pagesLesson Planning Form For Accessible Instruction - Calvin College Education Programapi-252008448No ratings yet
- Plan Sarah Plain and TallDocument13 pagesPlan Sarah Plain and Tallapi-242129716No ratings yet
- Day 1 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesDay 1 Lesson Planapi-252721756No ratings yet
- Domain 1 Lesson - Ss Unit 2 - Communities Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDomain 1 Lesson - Ss Unit 2 - Communities Lesson Planapi-267230750No ratings yet
- Elp021 Syllabus Spring 2014Document5 pagesElp021 Syllabus Spring 2014api-219891906No ratings yet
- Final Unit PlanDocument8 pagesFinal Unit Planapi-258725022No ratings yet
- Unit Plan TemplateDocument14 pagesUnit Plan Templateapi-245791329No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PressureDocument9 pagesLesson Plan PressureMohamad Rizal MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Opal Lee and What It Means to Be Free Educator's Guide: The True Story of the Grandmother of JuneteenthFrom EverandOpal Lee and What It Means to Be Free Educator's Guide: The True Story of the Grandmother of JuneteenthRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Problem Based Learning Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesProblem Based Learning Lesson Planapi-242018367100% (3)
- Lecture-Discussion Model Lesson 2Document3 pagesLecture-Discussion Model Lesson 2api-242018367No ratings yet
- Electronic NB - Jigsaw Lesson 1Document3 pagesElectronic NB - Jigsaw Lesson 1api-313394680No ratings yet
- Long-Term Targets Addressed (Based On Nysp12 Ela CCLS)Document5 pagesLong-Term Targets Addressed (Based On Nysp12 Ela CCLS)api-242018367No ratings yet
- TeradyneDocument4 pagesTeradyneZeus KhanNo ratings yet
- Theme Analysis RubricDocument2 pagesTheme Analysis Rubricapi-181156496No ratings yet
- Final Examination in Empowerment Technologies SY 2019 - 2020Document5 pagesFinal Examination in Empowerment Technologies SY 2019 - 2020Reyboy TagsipNo ratings yet
- The Association Kunsthalle Marcel Duchamp, Cully, SwitzerlandDocument3 pagesThe Association Kunsthalle Marcel Duchamp, Cully, Switzerlandapi-25895744No ratings yet
- Personal Succes Program - Self-Scoring Aptitude Test - Joseph SpeicherDocument14 pagesPersonal Succes Program - Self-Scoring Aptitude Test - Joseph SpeicherAndreea VirtejNo ratings yet
- 50+ Language Topics To Keep The Conversation FlowingDocument14 pages50+ Language Topics To Keep The Conversation Flowingpeter.mireckiNo ratings yet
- Deterritorializing The New German CinemaDocument216 pagesDeterritorializing The New German Cinemaleretsantu100% (3)
- DLL For CSSDocument3 pagesDLL For CSSAriel CancinoNo ratings yet
- Instant Download First Course in Probability 10th Edition Ross Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument32 pagesInstant Download First Course in Probability 10th Edition Ross Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterGailLarsennqfb100% (9)
- Portfolio Reflection FormDocument4 pagesPortfolio Reflection Formapi-270549230No ratings yet
- Global Warming ProjectDocument5 pagesGlobal Warming Projectperfectglorious0% (2)
- Acr Inset 17Document4 pagesAcr Inset 17Eddah Dahan50% (2)
- Introduction To Management - Understanding Groups and Managing Work TeamsDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Management - Understanding Groups and Managing Work TeamsDhanis ParamaguruNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Portfolio Based On Deped-1Document51 pagesWork Immersion Portfolio Based On Deped-1funelasrhiza4No ratings yet
- Neuron Lesson LoebleinDocument2 pagesNeuron Lesson LoebleinCoacytTucumanNo ratings yet
- 2015-Noble III v. AilesDocument5 pages2015-Noble III v. AilesCeresjudicataNo ratings yet
- Modalexercises PDFDocument1 pageModalexercises PDFGergadroAlmib0% (1)
- PAF 4OF/M Course Outline: Grade 12 Personal FitnessDocument3 pagesPAF 4OF/M Course Outline: Grade 12 Personal FitnessKarusan PuvanesanNo ratings yet
- All The Heaps of Suffering Add Up To Kama Kilesa PDFDocument16 pagesAll The Heaps of Suffering Add Up To Kama Kilesa PDFrhvenkatNo ratings yet
- DLL Level 3 - 4th Quarter WEEK-1Document3 pagesDLL Level 3 - 4th Quarter WEEK-1Johaira AcotNo ratings yet
- Intercultural Communication Globalization and Social Justice (Kathryn Sorrells)Document444 pagesIntercultural Communication Globalization and Social Justice (Kathryn Sorrells)Omar Leon IñiguezNo ratings yet
- English Notes by Liveenglish 12Document102 pagesEnglish Notes by Liveenglish 12sumit100% (2)
- The War Within Islam-FinalDocument206 pagesThe War Within Islam-Finalsarfaraz_niazi100% (1)
- Literacy Mini LessonDocument4 pagesLiteracy Mini LessonSteffaneyNo ratings yet
- Your Journey: I.Pre-TestDocument14 pagesYour Journey: I.Pre-TestmikkaellaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Curriculum DevelopmentDocument17 pagesFoundations of Curriculum DevelopmentNikki Mae ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Relationship Between Sport and AggressionDocument16 pagesA Study On The Relationship Between Sport and AggressionNur SyuhadahNo ratings yet
- Prospectus: FOR Short Term Educational CoursesDocument15 pagesProspectus: FOR Short Term Educational CoursesShabbir AnjumNo ratings yet
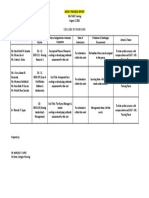
- CONSOLIDATED STATUS REPORT As of August 2Document1 pageCONSOLIDATED STATUS REPORT As of August 2Xander BancaleNo ratings yet
- 3rd International Conference On Filipino As Global Language - Call For PapersDocument2 pages3rd International Conference On Filipino As Global Language - Call For PapersDavid Michael San JuanNo ratings yet