Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TL Epr-Measurement For PDF
Uploaded by
Katukuri RaviOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TL Epr-Measurement For PDF
Uploaded by
Katukuri RaviCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTION MEASUREMENT OF EARTH POTENTIAL RISE (EPR) ZONE
No. EPR/A-002
No of Pages. Issue No. Issued By: Approved By: Date of Issue 06 01 T&D, Circle CGM T&D Circle 18-03-2005 NIL
Amendment No (If Any) No of Pages Issued by: Approved By: Date of Issue
Restricted use by BSNL Employees only
All efforts have been made to incorporate all relevant up to date information available, any discrepancies or need for addition or deletion is felt may please be intimated to this office for further improvement, on E-Mail Id singhai_sc2@rediffmail.com BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED (A Govt. of India Enterprise) TECHNICAL & DEVELOPMENT CIRCLE, SANCHAR VIKAS BHAWAN, RESIDENCY ROAD, JABALPUR, MP-482001
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS
Protection Power EPR/A-002
MEASUREMENT OF EARTH POTENTIAL RISE (EPR) ZONE
1 SCOPE This Engineering instruction describes the procedure for conducting the EARTH POTENTIAL RISE (EPR) test at power Sub Stations 2. GENERAL When an Earth fault occurs in a power system, some of the Fault current returns via the Earth, through the Earthing system (Eg. Earthing of towers and Sub-stations etc). This current raises the potential of Earthing system with respect to a remote Earth, for the duration of the fault. This is known as Earth Potential Rise (EPR). During such a fault, due to transfer of potential between the EPR areas and outside points by conductors of telecom circuits and other metallic structure etc., serious hazards may result to telecom personnel, installations and customers. This Earth potential rises and spreads in the surrounding areas in all directions due to the fact that the whole of fault current will not die down in the Earth mat itself, as the resistance of the Earth mat is not always O Ohms. 3. FACTORS AFFECTING EPR i. ii. iii. iv. v. Type of Power Network. Fault current level Power grounding system (earth resista- nce) Soil resistivity Local conditions.
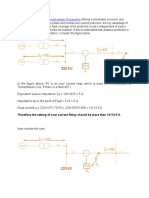
4. THEORETICAL CALCULATION OF EPR ZONE In most of the cases, the theoretical calculations of EPR zone, as calculated by the Electricity authorities, is accepted by the telecom authorities The theoretical formula for calculation of EPR zone for larger Earthing systems is given below. Ex = Emax*D/(d+D) = IR*D/(d+D), Where: Ex = Potential at radial distance d from the perimeter of Earth mat in volts I = Maximum fault current through the Earth mat in AMPS R = The measured resistance of Earth mat in Ohms D = Half the diagonal distance of Earth mat in metres. d = Distance in metres from the perimeter of the Earth mat In those cases, where the Earth mat is not essentially rectangular in shape, the value of a square, having the same area as that enclosed by the irregular Earth mat , should be taken Substituting the EPR Voltage limit for Ex, the distance d of that voltage contour from the perimeter of the Earth mat in metres can be calculated from the above formula. The limits of EPR for different types of telecom assets is given in table A
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED A Govt of India Enterprises Restricted to Telecom Staff
Page 2 of 6
Issue---------Date-----------
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS
Protection Power EPR/A-002
5.0 PRACTICAL MEASUREMENT OF EPR ZONE. In theoretical formula, uniform Earth resistivity is assumed. But, in practice, however, the Earth resistivity is rarely uniform. In such cases where there is ambiguity in the factors affecting the EPR and the resulting theoretical calculations, a practical measurement of EPR zone can be considered. 5.1 TEST SET UP The following are part of the set up for conducting the practical measurement of EPR zone. i. Isolation transformer that should deliver a minimum of 30 Amps constant current. ii. High Capacity dimmerstat to control the current. iii. Digital Voltmeters of very High impedance. iv. Cut out system with suitable fuses. v. Digital Ammeters. vi. Electrode of 0.5 meters length. (Galvanized iron pipe of 1 inch dia). (A remote Earth should be extended from a distance of not less than 2 kms to the test site. The remote Earth is prepared by driving a set of three numbers of 2.6 M standard earth electrodes, forming an equilateral triangle of 2.4 M, into earth. The remote Earth lead should be perpendicular to the Power line, which is chosen for the EPR test) 5.2 PROCEDURE i. Any power line originating /terminating in the Sub-station where the EPR test is being conducted may be selected taking into account that this line should be perpendicular to the remote Earth lead brought from the remote Earth.. ii. All the three phases of the power line should be looped at the Sub-station end and isolated from the Sub-station Earth mat. iii. One terminal of the secondary of power transformer should be connected to looped power line and the other terminal should be connected to Earth mat through an Ammeter. iv. The power line should be looped and Earthed at a distance of not less than 8 Kms, from the perimeter of the Earth mat, by three electrodes method, as done for the remote Earth. Tower Earth should not be used for this purpose. The input AC supply to the transformer is connected through the dimmerstat. Switch on the supply and gradually increase the current fed in to the Earth mat, ensuring that the dimmerstat is not getting heated. vi. The maximum current (not less than 16 Amps) that can be fed constantly should be noted and ensured that this current will become the constant current for all the reading to be recorded. vii. The first reading should be taken between earth mat and remote earth lead. The subsequent readings should be noted at every 50 meters interval from the perimeter of the Earth mat, by driving the electrode into earth at least 12 inches. Readings should be taken until the volt meter shows a reading corresponding to an EPR value of less than 430 Volts. (This can be ascertained by multiplying the Voltmeter reading and fault current of the substation and dividing it by the injected current). viii. After taking all the necessary readings, the readings shall be extrapolated to the maximum fault current value of the Sub-station by the method mentioned above (ie Voltmeter reading x Fault current / Injected current). The values thus obtained are plotted in a graph paper (distance verses voltage), and from the graph the EPR zone for 430V, 650V, 7KV and 10 KV or any other voltage can be found out v.
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED A Govt of India Enterprises Restricted to Telecom Staff
Page 3 of 6
Issue---------Date-----------
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS
Protection Power EPR/A-002
5.3
STRAY VOLTAGE CONSIDERATION.
Any stray voltage between the Earth electrode and remote Earth must be measured before the simulated fault current is applied. Unless this voltage is small when compared with voltage measured with fault current, the relative phase angles must be read and a correction applied. Alternatively, the current direction can be reversed and following formula applied. V12 + V2 2 - Vs2 2 Where V is the voltage due the fault current alone. Vs is the standing voltage due to stray currents. V1 is the measured voltage with current in the forward direction V2 is the measured voltage with current in the reverse direction. V= SQRT 6.0 EPR TEST OF EARTH ELECTRODE STATION OF HVDC LINE The HVDC transmission lines have only two conductors, negative and positive. In case of break fault of one of the conductors, power authorities resort to monopolar Earth return mode of working.. In this case, very High Current is drawn from the Earth mat of Earth Electrode tml station .In the case of AC Sub-stations, EPR exists only for a fraction of a second where as in the case of HVDC Earth Electrode tml station, EPR exists for the whole duration of monopolar earth return mode of working. Hence protection is to be provided in EPR zone of 60 V and above. 7.0 EPR ZONE NEAR EHT LINE TOWERS The EPR zone near any EHT line tower is negligible compared to EHT Sub-stations. The reason being that all the EHT towers carry an earth wire on top of it that returns the fault current to earth mat of the Sub-station. If any fault occurs on the tower, a negligible current flows via the tower earth system to the ground, which can create an EPR , while the earth wire will carry the maximum current to the Earth mat. A specimen copy of EPR test results is included as ANNEXURE
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED A Govt of India Enterprises Restricted to Telecom Staff
Page 4 of 6
Issue---------Date-----------
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS
Protection Power EPR/A-002
CURRENT INJECTION SET UP Power line (Three phases looped)
Dimmerstat Isolation Transformer
Primary
Secondary
AC Input
2.4M
2.4M
2.4 M
Special Earth Substation Earth mat TABLE A EPR Limits and hazard zone No Type of Telecommunication Plant 1 2 3 Terminal apparatus, manholes, pits, poles. Telephone exchanges. Cables a) Metal Sheathed. joints, cabinets, pillars, Type of Power System High reliability Other Lines lines 650V 430V 430V 650V 7 KV 430V 430V 7 KV Page 4
b) Plastic insulated and plastic sheathed, PIJF
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED A Govt of India Enterprises Restricted to Telecom Staff
Page 5 of 6
Issue---------Date-----------
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS
Protection Power EPR/A-002
ANNEXURE EARTH POTENTIAL RISE TEST RESULTS
(specimen only)
Name of Sub Station : Salem Maximum fault current of sub station : 5000 Amps No a 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Distance from the edge of Earth mat in metres b 25 75 125 175 225 275 325 375 425 475 525 575 625 675 Injected current in Amps c 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 Measured value in Volts d 56.2 45.7 37.3 31.3 25.0 18.3 14.4 10.7 8.4 6.2 4.6 3.8 2.6 1.6 Date : 09 - 08 - 03
EPR in volts (d/c) x 5000 11235 9135 7452 6250 4998 3653 2876 2137 1675 1237 926 756 513 312
12000
10000
8000
EPR in Volts
6000
4000
2000
0 1 50 2 100 3 150 4 200 5 250 6 300 7 350 8 400 9 10 50011 550 12 60013 650 14 700 450 Distance from the edge of Earth Mat in metres
Page 5
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED A Govt of India Enterprises Restricted to Telecom Staff
Page 6 of 6
Issue---------Date-----------
You might also like
- Protective Relays in Substations: Types and ApplicationsDocument46 pagesProtective Relays in Substations: Types and ApplicationsLee Boon HongNo ratings yet
- SIP5 7UT85-86-87 V09.20 Manual C094-1 en PDFDocument2,406 pagesSIP5 7UT85-86-87 V09.20 Manual C094-1 en PDFDanilo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Directional Over Current Relay - Maximum Torque AngleDocument19 pagesDirectional Over Current Relay - Maximum Torque AngleTamjid KabirNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar Protection: External FaultsDocument4 pagesBus Bar Protection: External FaultsChanderSinghWarkadeNo ratings yet
- XS2 - Negative Sequence Relay: Original Technical Manual XS2 (Revision B)Document20 pagesXS2 - Negative Sequence Relay: Original Technical Manual XS2 (Revision B)Catrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- REPORT ON TRANSFORMER PRE-COMMISSIONING TEST RESULTSDocument2 pagesREPORT ON TRANSFORMER PRE-COMMISSIONING TEST RESULTSmohan babuNo ratings yet
- Sepam 10 Seped307026en Int PDFDocument22 pagesSepam 10 Seped307026en Int PDFJeffrey Reynaldo RidwanNo ratings yet
- Neelum Jhelum Switchyard Comissioning & Testing PDFDocument16 pagesNeelum Jhelum Switchyard Comissioning & Testing PDFRaza312No ratings yet
- N6166 E05 F871 TR Diff Relay 7UT613Document6 pagesN6166 E05 F871 TR Diff Relay 7UT613মোঃ মহসিনNo ratings yet
- Setings Calculation New HavenDocument6 pagesSetings Calculation New HavenWilfred AsonmwonririNo ratings yet
- Low Frequency Stator Earth Fault Protection SetupDocument6 pagesLow Frequency Stator Earth Fault Protection SetupAmaresh NayakNo ratings yet
- Lec-3 Effect of Fault Resistance and Pre-Fault Power Flow On The Performance of Distance RelayDocument5 pagesLec-3 Effect of Fault Resistance and Pre-Fault Power Flow On The Performance of Distance RelayTamjidNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Voltage Transforme1Document4 pagesCapacitance Voltage Transforme1ayushNo ratings yet
- Harmonics Transformer de RatingDocument6 pagesHarmonics Transformer de RatingFabricio Dias CoimbraNo ratings yet
- Typical Limiting Values of SubStation Equipments.Document10 pagesTypical Limiting Values of SubStation Equipments.Jeya KannanNo ratings yet
- MJT 315 - or Rev 1-1 PDFDocument32 pagesMJT 315 - or Rev 1-1 PDFashish_muley100% (1)
- Final ProjectDocument57 pagesFinal ProjectKumar JiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 1 19bee069 Date: 20/01/2022 Aim: To Determine Magnetization Characteristics of A Given Current TransformerDocument11 pagesExperiment No: 1 19bee069 Date: 20/01/2022 Aim: To Determine Magnetization Characteristics of A Given Current TransformerR.D Sutariya100% (1)
- k0 CalculationDocument1 pagek0 CalculationLRHENGNo ratings yet
- Non-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 ADocument6 pagesNon-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 AyethweNo ratings yet
- Busbar Differential ProtectionDocument19 pagesBusbar Differential ProtectionVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- DTS 2687 - 132kV GIS Method Statement For HV Test & Partial Discharge Measurement - Rev.CDocument38 pagesDTS 2687 - 132kV GIS Method Statement For HV Test & Partial Discharge Measurement - Rev.Cমোঃ মহসিনNo ratings yet
- VAMP 300F/M: Protection IEDDocument374 pagesVAMP 300F/M: Protection IEDdiyanNo ratings yet
- Distance Teleprotection Methods PDFDocument15 pagesDistance Teleprotection Methods PDFaeanteNo ratings yet
- Micom - 211 Motor Protection Relay Used For 275kwDocument8 pagesMicom - 211 Motor Protection Relay Used For 275kwShrikant KajaleNo ratings yet
- Application of Digital Relay Protection On APUA.....Document50 pagesApplication of Digital Relay Protection On APUA.....Sharmaine MeranoNo ratings yet
- Proposal Setting Gi Tanjung BungaDocument20 pagesProposal Setting Gi Tanjung Bungawandy RJ100% (1)
- 7SR242 - Duobias Technical Manual Chapter 07 Applications GuideDocument56 pages7SR242 - Duobias Technical Manual Chapter 07 Applications GuideVishwanath TodurkarNo ratings yet
- National Grid: Checklist For Commissioning of Oil-Immersed Power TransformerDocument8 pagesNational Grid: Checklist For Commissioning of Oil-Immersed Power TransformerSanthosh Kumar VinayagamNo ratings yet
- Relay For Transformer Backup ProtectionDocument6 pagesRelay For Transformer Backup ProtectionOmar Chayña VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection (Distance) RelaysDocument6 pagesPower System Protection (Distance) RelaysAisamuddin SubaniNo ratings yet
- ADR219 CMDocument133 pagesADR219 CMRajiv ChandranNo ratings yet
- SIP5 6MD85-86 V07.50 Manual C015-9 en PDFDocument1,216 pagesSIP5 6MD85-86 V07.50 Manual C015-9 en PDFandreabautista1982No ratings yet
- MVAXDocument24 pagesMVAXkedsoi2No ratings yet
- Sect 02 Power System ProtectionDocument25 pagesSect 02 Power System Protectionnirmalb21No ratings yet
- Transformer Protection SchemesDocument5 pagesTransformer Protection SchemesIppiNo ratings yet
- Ground Distance Relays-Residual Compensation JVDocument33 pagesGround Distance Relays-Residual Compensation JVmatthijsvisser174100% (1)
- Connections and applications of overcurrent and earth fault relaysDocument4 pagesConnections and applications of overcurrent and earth fault relaysMahmoud AlshairNo ratings yet
- Transformer stability test for differential and REF protectionDocument2 pagesTransformer stability test for differential and REF protectionykh92167No ratings yet
- Guide Lines For DCD414 RelaysDocument3 pagesGuide Lines For DCD414 RelaysPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Abdul Fareh Khan 2k19Document5 pagesMuhammad Abdul Fareh Khan 2k19Fareh KhanNo ratings yet
- Power Supply To Plot P18 at Zayed Military City D108337 SWH38A1Document2 pagesPower Supply To Plot P18 at Zayed Military City D108337 SWH38A1Jayaprakash M PNo ratings yet
- Grounding Resistance MeasurementsDocument13 pagesGrounding Resistance MeasurementskishansaiNo ratings yet
- RX DiagramDocument14 pagesRX DiagrambalaelectNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker Timing Test ResultsDocument2 pagesCircuit Breaker Timing Test ResultsAhmed FathyNo ratings yet
- Protection Relay StandardDocument3 pagesProtection Relay StandardThirumalNo ratings yet
- CVT Test Report FormatDocument3 pagesCVT Test Report FormatsamarbtechNo ratings yet
- Uitm-Fkestudent - Handbook. - Final Edited Version - 13 Dis. 2011-EditDocument99 pagesUitm-Fkestudent - Handbook. - Final Edited Version - 13 Dis. 2011-EditsilentsioNo ratings yet
- Study of Short Circuit Faults-Case Study Sudanese National GridDocument75 pagesStudy of Short Circuit Faults-Case Study Sudanese National GridYousra Daya0% (1)
- Upgrading The ProtectionDocument4 pagesUpgrading The ProtectionMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Feeder Protection Relay SpecificationDocument4 pagesFeeder Protection Relay SpecificationMeghavahinaNo ratings yet
- EPR ZoneDocument5 pagesEPR ZonedgrsriNo ratings yet
- earthingFAQ PDFDocument7 pagesearthingFAQ PDFAsif Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Design of Earthing System For HVDocument22 pagesDesign of Earthing System For HVAshwani Dogra100% (1)
- Engineering Encyclopedia: Ground System TestingDocument31 pagesEngineering Encyclopedia: Ground System TestingAhmed OusamaNo ratings yet
- Ground System TestingDocument31 pagesGround System TestingJellyn BaseNo ratings yet
- Ground TestingDocument31 pagesGround TestingabdulkadhirNo ratings yet
- BallastsDocument4 pagesBallastsradhashyamsunderNo ratings yet
- Volume 7 Issue 4 June 2003: Home About Us Newsroom PublicationsDocument1 pageVolume 7 Issue 4 June 2003: Home About Us Newsroom PublicationsKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- List of First Aid Kit: Due Date Jan Feb Mar Apr May JunDocument1 pageList of First Aid Kit: Due Date Jan Feb Mar Apr May JunKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- Megha Engineering and Infrastructure - LTD: 220 KV Sikka To Lilo Form Jam-Jetpur LineDocument4 pagesMegha Engineering and Infrastructure - LTD: 220 KV Sikka To Lilo Form Jam-Jetpur LineKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- Earthing Measurement SheetDocument4 pagesEarthing Measurement SheetKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- Hardware & Accesoris QTY SheetsDocument2 pagesHardware & Accesoris QTY SheetsKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- Material QtyDocument3 pagesMaterial QtyKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- 12 SwitchyardErectionRev07Document91 pages12 SwitchyardErectionRev07Rajesh Sirigirisetty SNo ratings yet
- Material StatementDocument6 pagesMaterial StatementKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- Transmission Tower Foundation DesignDocument26 pagesTransmission Tower Foundation DesignSara Nuon86% (7)
- 4hpi PC Scanned BomDocument1 page4hpi PC Scanned BomKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- MEASURING EARTH POTENTIAL RISEDocument6 pagesMEASURING EARTH POTENTIAL RISEKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- Transmission LineDocument2 pagesTransmission LineakiferindrariskyNo ratings yet
- Motor Starting Basics ChapterDocument25 pagesMotor Starting Basics ChapterMaintenance Circle100% (2)
- SPDCL Sub-Engineer Recruitment NotificationDocument15 pagesSPDCL Sub-Engineer Recruitment NotificationSwathi ReddyNo ratings yet
- 4HPI-PC-Scanned DWGDocument1 page4HPI-PC-Scanned DWGKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- Reactor ProtectionDocument25 pagesReactor Protectiongkpalepu90% (10)
- SPDCL Sub-Engineer Recruitment NotificationDocument15 pagesSPDCL Sub-Engineer Recruitment NotificationSwathi ReddyNo ratings yet
- J B WaybillDocument1 pageJ B WaybillKatukuri RaviNo ratings yet
- Survey On FaultDocument13 pagesSurvey On Faultfaridkhoucha0% (1)
- HVE 2022 MidpaperDocument2 pagesHVE 2022 MidpaperVishalNo ratings yet
- List of IEEE StandardsDocument224 pagesList of IEEE StandardsAbhay Kumar50% (2)
- Application Note - Electric Arc Furnace Modeling and ValidationDocument2 pagesApplication Note - Electric Arc Furnace Modeling and Validationqais652002No ratings yet
- Testing Requirements for High Voltage Cable SystemsDocument28 pagesTesting Requirements for High Voltage Cable SystemsGualadrake100% (2)
- Solid State Transformer-TechnologyReviewDocument5 pagesSolid State Transformer-TechnologyReviewvshalshethNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Energy HarvestingDocument8 pagesElectrostatic Energy HarvestingSpam MeeNo ratings yet
- GMPC Enables Energy Transmission Over Interconnected SAPP GridDocument8 pagesGMPC Enables Energy Transmission Over Interconnected SAPP GridNhacaNo ratings yet
- POWER Power June 2022 IntlDocument49 pagesPOWER Power June 2022 IntlNelson NavaNo ratings yet
- Company Profile PT LSA Cable Indonesia - 211214 - 182836Document6 pagesCompany Profile PT LSA Cable Indonesia - 211214 - 182836ikhsan firdausNo ratings yet
- Development of Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) and Fast Prototyping Tool (FPT) Using OPAL-RTDocument18 pagesDevelopment of Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) and Fast Prototyping Tool (FPT) Using OPAL-RTaboofazilNo ratings yet
- Abb Goes OffshoreDocument12 pagesAbb Goes OffshoreНемања КатићNo ratings yet
- On Control and Balancing of Rigid Bipolar MMC-HVDC Links Enabling Subsystem-Independent Power TransferDocument8 pagesOn Control and Balancing of Rigid Bipolar MMC-HVDC Links Enabling Subsystem-Independent Power TransferM8ow6fNo ratings yet
- BSTP en HVDC Psse Training, Day 1 - TheoryDocument107 pagesBSTP en HVDC Psse Training, Day 1 - TheoryEngr Mohsin Saleem100% (1)
- AR09Document50 pagesAR09LuckyStripeNo ratings yet
- UTP Bulletins 300 3Document52 pagesUTP Bulletins 300 3Lucho Dom100% (1)
- Modified Newton-Raphson Load Flow Analysis For Integrated Ac/Dc Power SystemsDocument5 pagesModified Newton-Raphson Load Flow Analysis For Integrated Ac/Dc Power SystemsZuneid AlamNo ratings yet
- HVDC Cables Market to Surpass $4B by 2027Document19 pagesHVDC Cables Market to Surpass $4B by 2027A. HassanNo ratings yet
- CleanLinePt2 Appendix 10 JDocument233 pagesCleanLinePt2 Appendix 10 JChristos ApostolopoulosNo ratings yet
- Icsd 2013 PDFDocument4 pagesIcsd 2013 PDFAnonymous rAFSAGDAEJNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - EEE - IvyearDocument38 pagesSyllabus - EEE - IvyearSIETDOC100% (1)
- IEEE Press Series On Power Engineering: Series Editor: M. E. El Hawary, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova ScotiaDocument7 pagesIEEE Press Series On Power Engineering: Series Editor: M. E. El Hawary, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova ScotiaAnders AguilarNo ratings yet
- HVDC StationDocument26 pagesHVDC StationmeraatNo ratings yet
- Final Report Hokkaido Blackout Summarized PDFDocument36 pagesFinal Report Hokkaido Blackout Summarized PDFaaaaaaa aaaaNo ratings yet
- Ilsas 2013Document70 pagesIlsas 2013Amirul RasyidNo ratings yet
- Reqno Jrc60700 Ldna24583enc PDFDocument8 pagesReqno Jrc60700 Ldna24583enc PDFelsayedNo ratings yet
- EEE 306 Project Presentation Group 2Document81 pagesEEE 306 Project Presentation Group 2Sabbir BejoyNo ratings yet
- Order in Pet No 277 of 2009 (5.4.2010)Document12 pagesOrder in Pet No 277 of 2009 (5.4.2010)BijuNo ratings yet
- HVDC - Lecture 1Document17 pagesHVDC - Lecture 1yesmuraliNo ratings yet
- Energies: AC Transmission Emulation Control Strategies For The BTB VSC HVDC System in The Metropolitan Area of SeoulDocument15 pagesEnergies: AC Transmission Emulation Control Strategies For The BTB VSC HVDC System in The Metropolitan Area of Seoulnikon reddyNo ratings yet