Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antibiotic 1 PDF
Uploaded by
micheal1960Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antibiotic 1 PDF
Uploaded by
micheal1960Copyright:
Available Formats
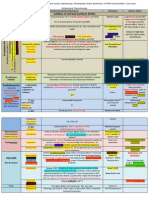
Chemotherapy
(Antimicribial) Antibiotic Antiviral Antifungal Antihlmintic Antiprotozoal Anticancer
----------------Antibiotic---------------A) Classification according to MOA: no. 1 2
MOA
Inhibit cell wall synthesis
Inhibit plasma membrane
Inhibit nucleic acid synthesis A) inhibit DNA:
FQ
Drugs
A) -lactam group 1- polymyxin
1234penicillin cephalosporin carbapenem monobactam
2- deptomycin
B) glycopeptide
1- vancomycin 2- teicoplanin
B) Inhibit RNA:
-
(on 30S / 50S ribosomal subunit) 1- AG (on 30S) 2- Tetracycline(on 30S) 3- Macrolide(on 50S) 4- Chloramphenicol(on 50S) 5- Clindamycin(on 50S)
Inhibit protein synthesis
Inhibit metabolic pathway
1- Sulfonamide 2- trimethoprim
rifampicin
B) Classification according to the effect: A) bacteriocidal 1,2,3 NOTE: Macrolide in high kill organism without need for immune system dosecidal B) bacteriostatic 4,5 Combination of stop growth of organism SO, need immune system Sulfonamide+ trimethoprim "co-trimoxazole"cidal for eradication C) Classification according antibacterial spectrum: rd th "FQ"New g. (3 , 4 ) broad spectrum A. G-ve o Polymyxin AG not active against anaerobe o FQ monobactam not active against anaerobe o AG o monobactam vancomycin use in C.difficle"G+ve" B. G+ve o Glycopeptides infection o Deptomycin clindamycin use in anaerobe o clindamycin Macrolide less effective against G-ve C. Broad (+ve & -ve) o Penicillin sulfonamide not active against anaerobe o Cephalosporin carbapenem use in anaerobe o carbapenem tetracycline, macrolide, chloramphenicol, o rifampicin FQ: have Atypical action o tetracycline o macrolide Atypicals o chloramphenicol (Mycoplasma, Legionella, Chlamydia) o sulfonamide o trimethoprim
Clinical points: G+ve Streptococcus spp. Enterococcus spp. Staphylococcus spp. Listeria monocytogenis E coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa Klebsiella spp. Serratia spp. Enterobacter spp. G-ve Proteus spp. Haemophilus influenzae Moraxella catrarrhalis Neisseria meningitides
most suspected organism in the following cases: E.Coli UTI Klebsiella DM=UTI E.Coli, proteus mirabilis ,s.aureus Acut prostatits Prosthatic valve endocarditis S.epidermis S. pneumonae Pregnant with pneumonia pseudomonous , klebsilla Nosocomial pneumonia anaerobe ,-ve bacteria Intra abdomen infection H. influenza meningitis
In case of penicillin allergy: Type-1 hypersensitivity>>> give monobactam (only from -lactam group) , or other groups "macrolide,.." Type-2 hypersensitivity (skin rash)>>> give cephalosporin In case of immunodeficiency patient(AIDS) give bacteriocidal antibiotic bcz it's doesnt need immune system In case of drug combination>>> the 2 drugs should be act on different MOA NB: Bactericidal + Bactericidal = Synergism. Bacteristatic + Bacteristatic = Addition.
You might also like
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Clinical Pharmacology - Rationale Behind Antibiotics PrescriptionDocument12 pagesClinical Pharmacology - Rationale Behind Antibiotics PrescriptionhalesNo ratings yet
- 2011 PK-PD AntibiotikDocument88 pages2011 PK-PD AntibiotikUniatimelindaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument6 pagesAntibioticsCyrus100% (1)
- Antibiotics IN Maxillofacial Surgery: Presenter: Dr. Venu G.RDocument92 pagesAntibiotics IN Maxillofacial Surgery: Presenter: Dr. Venu G.RkatnevNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics F MCP 1Document37 pagesAntibiotics F MCP 1Mohamed ElraiyNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of ResistanceDocument75 pagesMechanisms of ResistancedewantarisaputriNo ratings yet
- 2 Beta Lactum 2020Document25 pages2 Beta Lactum 2020Sparks Francis EzikaNo ratings yet
- First Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsDocument23 pagesFirst Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsLaura Lopez RocaNo ratings yet
- 1.sulfonamide FinalDocument31 pages1.sulfonamide FinalPrasad SangishettyNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Table BasicDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial Table BasicPAschoolstuffNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics - Pathogen ChartDocument3 pagesAntibiotics - Pathogen ChartYanling LiNo ratings yet
- Drug of Choices PDFDocument10 pagesDrug of Choices PDFRavi Amin100% (1)
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument3 pagesAntimicrobial AgentsErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (2)
- Pharma LMRDocument21 pagesPharma LMRAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- 14 Antibiotik Dan Antiseptik Untuk IskDocument40 pages14 Antibiotik Dan Antiseptik Untuk IskSintaKleoNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument7 pagesAntibioticsRahmania Eka SagitaNo ratings yet
- Year Two Drugs: Proneuduction)Document4 pagesYear Two Drugs: Proneuduction)Caine ReganNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobials: Mode of Action Mechanism of Resistance Origin of Resistance Spectrum of Activity Classic Side EffectsDocument43 pagesAntimicrobials: Mode of Action Mechanism of Resistance Origin of Resistance Spectrum of Activity Classic Side Effectssupermanofearth27No ratings yet
- Pharmacology-Antibiotic 2021Document52 pagesPharmacology-Antibiotic 2021Ngọc VânNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy: BY Professor Dr. Ahmed KhalilDocument29 pagesChemotherapy: BY Professor Dr. Ahmed KhalilSAYED ZAKINo ratings yet
- General Principles - AdditionsDocument3 pagesGeneral Principles - AdditionsMoe KebabNo ratings yet
- First Generation Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) : Cell Wall SynthesisDocument17 pagesFirst Generation Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) : Cell Wall SynthesisVAnh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Part II. Antimycobacteria Agents.Document69 pagesAntibiotics Part II. Antimycobacteria Agents.inaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of ENT InfectionsDocument86 pagesPharmacotherapy of ENT InfectionsHoque Mohammed Newaz ShorifulNo ratings yet
- Microbiology, Infections, and Antibiotic Therapy: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 22, 2000Document86 pagesMicrobiology, Infections, and Antibiotic Therapy: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 22, 2000skmvicky1483No ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Microbial Control Antimicrobial AgentsDocument25 pagesAntibiotics: Microbial Control Antimicrobial AgentsMohammed Moutasim AyoubNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Inhibitors - Pharmacology 3 - Frank SsengoobaDocument16 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors - Pharmacology 3 - Frank SsengoobaVhugala AudreyNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics ClassificationDocument7 pagesAntibiotics ClassificationTabarcea Dorin100% (1)
- AntibioticsDocument9 pagesAntibioticsprince1500100% (1)
- Anti Infection AgentsDocument18 pagesAnti Infection AgentsRawabi SalehNo ratings yet
- Print Antibiotics ReviewDocument6 pagesPrint Antibiotics ReviewtiuwangNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: by Dr. Jihad AnadDocument89 pagesAntibiotics: by Dr. Jihad AnadJihad AnadNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Eti Nurwening SholikhahDocument50 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Eti Nurwening SholikhahYogi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument253 pagesChemotherapyalmskein100% (1)
- Lac 10&11 PPTDocument16 pagesLac 10&11 PPTRaghdaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobials Complete by DR - Mayur Sayta M 91 PDFDocument86 pagesAntimicrobials Complete by DR - Mayur Sayta M 91 PDFRuthvi Jain100% (1)
- AntibioticsDocument4 pagesAntibioticsVladimir GurjanovNo ratings yet
- Step 1 DrugsDocument46 pagesStep 1 DrugsZebram ZeeNo ratings yet
- Inhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus ComboDocument12 pagesInhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus Comboflomax23100% (1)
- DR - Saleh-26 March 2013-Farmakologi (Anti Jamur, Anti Virus, Anti Parasit, DLL)Document72 pagesDR - Saleh-26 March 2013-Farmakologi (Anti Jamur, Anti Virus, Anti Parasit, DLL)jeinpratpong100% (4)
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Laboratory of Microbiology Medical Faculty Brawijaya UniversityDocument38 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Laboratory of Microbiology Medical Faculty Brawijaya UniversityYuu Ayu'k LifestarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology, Infection and Antibiotic TherapyDocument86 pagesMicrobiology, Infection and Antibiotic TherapyRahul100% (1)
- 1 AntibioticsDocument16 pages1 AntibioticsNashat SaadiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract MicrobiologyDocument68 pagesRespiratory Tract Microbiologysultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For Antibiotics-2Document10 pagesMnemonics For Antibiotics-2totallyfakeusernameNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: General ConsiderationDocument50 pagesAntibiotics: General ConsiderationAyush ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Antibiotic TherapyDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Antibiotic TherapyVicviclookThekingNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapeutic DrugsDocument122 pagesChemotherapeutic Drugsdex7reme100% (1)
- Bugs and Drugs: ST ND RD TH THDocument2 pagesBugs and Drugs: ST ND RD TH THNora A. AlkhudairNo ratings yet
- MonoklonalDocument6 pagesMonoklonalNandar Rahmad - KUNE PROJECTNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Antiviral: Husnul Khotimah Dept. Pharmacology Medical Faculty University of BrawijayaDocument69 pagesAntibiotics Antiviral: Husnul Khotimah Dept. Pharmacology Medical Faculty University of BrawijayaDya Yda'sNo ratings yet
- A. Chemical StructureDocument34 pagesA. Chemical StructureAmit GaurNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Mechanism of Action & Resistance: R. Lia Iswara, DR, MS, SPMK Dept. of Microbiology FK UsuDocument16 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Mechanism of Action & Resistance: R. Lia Iswara, DR, MS, SPMK Dept. of Microbiology FK UsuDivika ShilvanaNo ratings yet
- Piocianic EsblDocument15 pagesPiocianic EsblMari FereNo ratings yet
- Overview of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesOverview of AntibioticsakshahinbdNo ratings yet
- List of AntibioticsDocument10 pagesList of AntibioticsAia JavierNo ratings yet
- 4 C 566 A 70 Da 279 BCFDocument8 pages4 C 566 A 70 Da 279 BCFMazin AlmaziniNo ratings yet
- Nursing 3703 Pharmacology: Antimicrobials by Linda SelfDocument78 pagesNursing 3703 Pharmacology: Antimicrobials by Linda Selfdon yenNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: 4 Medical Year PharmacologyDocument30 pagesDrug Treatment of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: 4 Medical Year PharmacologyRuchi KholiyaNo ratings yet
- Lipid Lowering With Statin Is Better Than Adding Other AgentDocument1 pageLipid Lowering With Statin Is Better Than Adding Other Agentmicheal1960No ratings yet
- Taylors.10 Minute - Diagnosis.manual - Symptoms.and - Signs.in - The.time Limited - Encounter.Document656 pagesTaylors.10 Minute - Diagnosis.manual - Symptoms.and - Signs.in - The.time Limited - Encounter.micheal1960No ratings yet
- Simple Depression Anxiety 2 Simple Screenin QuestionsDocument2 pagesSimple Depression Anxiety 2 Simple Screenin Questionsmicheal1960No ratings yet
- ABX Common Effects of Antibiotics On Other Drugs MMDocument3 pagesABX Common Effects of Antibiotics On Other Drugs MMmicheal1960No ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Which Tests Distinguish Community-Acquired From Healthcare-Associated Infection?Document3 pagesPneumonia: Which Tests Distinguish Community-Acquired From Healthcare-Associated Infection?micheal1960100% (1)
- DM 2015 Jcjd591 - ProofDocument3 pagesDM 2015 Jcjd591 - Proofmicheal1960No ratings yet
- Nail Diseases, Hand in Diagnosis, Terry's NailDocument35 pagesNail Diseases, Hand in Diagnosis, Terry's Nailmicheal1960No ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesDocument25 pagesOral Manifestations of Systemic Diseasesmicheal1960No ratings yet
- Facial InjuriesDocument6 pagesFacial Injuriesmicheal1960No ratings yet
- Fluids SummaryDocument3 pagesFluids Summarymicheal1960No ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 03-Volume II-A The MIPS64 Instruction Set (MD00087)Document793 pages03-Volume II-A The MIPS64 Instruction Set (MD00087)miguel gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Student Management System - Full DocumentDocument46 pagesStudent Management System - Full DocumentI NoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Award Sheet Government College University, FaisalabadDocument1 pageDetailed Award Sheet Government College University, FaisalabadAnayat KhetranNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To Society, Community and EducationDocument29 pages1 Intro To Society, Community and EducationMaria Michelle A. Helar100% (1)
- Self Authoring SuiteDocument10 pagesSelf Authoring SuiteTanish Arora100% (3)
- أثر البحث والتطوير على النمو الاقتصادي - دراسة قياسية لحالة الجزائر (1990 -2014)Document17 pagesأثر البحث والتطوير على النمو الاقتصادي - دراسة قياسية لحالة الجزائر (1990 -2014)Star FleurNo ratings yet
- CASE: Distributor Sales Force Performance ManagementDocument3 pagesCASE: Distributor Sales Force Performance ManagementArjun NandaNo ratings yet
- The Civil Mutinies of Romeo and Juliet: Glenn ClarkDocument21 pagesThe Civil Mutinies of Romeo and Juliet: Glenn ClarkmilcahNo ratings yet
- Modul9 VPNDocument34 pagesModul9 VPNDadang AbdurochmanNo ratings yet
- How To Use The ActionDocument3 pagesHow To Use The Actioncizgiaz cizgiNo ratings yet
- Solution Document For Link LoadBalancerDocument10 pagesSolution Document For Link LoadBalanceraralNo ratings yet
- Indiabix PDFDocument273 pagesIndiabix PDFMehedi Hasan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- TG - Health 3 - Q3Document29 pagesTG - Health 3 - Q3LouieNo ratings yet
- Soal Pas Myob Kelas Xii GanjilDocument4 pagesSoal Pas Myob Kelas Xii GanjilLank BpNo ratings yet
- Fireware EssentialsDocument499 pagesFireware EssentialsEmmanuel RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Interview QuestionsDocument19 pagesCivil Engineering Interview QuestionsSrivardhanSrbNo ratings yet
- Google Chrome OSDocument47 pagesGoogle Chrome OSnitin07sharmaNo ratings yet
- Odisha Block Summary - NUAGAONDocument8 pagesOdisha Block Summary - NUAGAONRohith B.NNo ratings yet
- Total ChangeDocument9 pagesTotal ChangeaurennosNo ratings yet
- Army War College PDFDocument282 pagesArmy War College PDFWill100% (1)
- 2-Emotional Abuse, Bullying and Forgiveness Among AdolescentsDocument17 pages2-Emotional Abuse, Bullying and Forgiveness Among AdolescentsClinical and Counselling Psychology ReviewNo ratings yet
- Isolated Foundation PDFDocument6 pagesIsolated Foundation PDFsoroware100% (1)
- Facilities Strategic Asset Management Plan TemplateDocument85 pagesFacilities Strategic Asset Management Plan Templateoli mohamedNo ratings yet
- Types of Vegetation in Western EuropeDocument12 pagesTypes of Vegetation in Western EuropeChemutai EzekielNo ratings yet
- Pre-Boarding Announcement Skill Focus: ListeningDocument5 pagesPre-Boarding Announcement Skill Focus: ListeningJony SPdNo ratings yet
- Ham (Son of Noah) - WikipediaDocument3 pagesHam (Son of Noah) - Wikipediamike bNo ratings yet
- Lunch Hour Meetings: Kiwanis Mission:: - Officers & Directors, 2018-2019Document2 pagesLunch Hour Meetings: Kiwanis Mission:: - Officers & Directors, 2018-2019Kiwanis Club of WaycrossNo ratings yet
- Accountancy Service Requirements of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises in The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesAccountancy Service Requirements of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises in The PhilippinesJEROME ORILLOSANo ratings yet
- EFL Listeners' Strategy Development and Listening Problems: A Process-Based StudyDocument22 pagesEFL Listeners' Strategy Development and Listening Problems: A Process-Based StudyCom DigfulNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1.COMMUNICATION PROCESSES, PRINCIPLES, AND ETHICS - Ver 2Document24 pagesLECTURE 1.COMMUNICATION PROCESSES, PRINCIPLES, AND ETHICS - Ver 2Trixia Nicole De LeonNo ratings yet