Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Stainless Steel EN PDF
Uploaded by
sssf-dobojOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Stainless Steel EN PDF
Uploaded by
sssf-dobojCopyright:
Available Formats
Diamant Building
Bd. A. Reyers 80
1030 Brussels
Belgium
Phone +32 2 706 82-67
Fax -69
e-mail info@euro-inox.org
www.euro-inox.org
What is stainless steel?
Fe
Cr > 10,5%
C < 1,2%
W H A T I S S T A I N L E S S S T E E L ?
Iron alloy bearing 10,5 % chromium and
1,2 % carbon, necessary to ensure the
build-up of a self-healing surface layer
(passive layer) which provides the
corrosion resistance
Main families
Austenitic: Iron-chromium-nickel, carbon < 0,1 % (including grade 1.4301/304,
often referred to as 18/8; 18/10) , non-magnetic in the as-delivered
condition; > 65 % of world stainless use
Ferritic: Iron-chromium, carbon < 0,1%, magnetic
Martensitic: Iron-chromium, carbon > 0,1%, magnetic and hardenable
Duplex: Iron-chromium-nickel, combined austenitic-ferritic structure, magnetic
Main properties
Corrosion resistance aesthetic appeal heat resistance low life cycle cost full recyclability
biological neutrality ease of fabrication and cleaning strength-to-weight ratio
Commonly available finishes and process routes
1)
Hot rolled, heat treated, pickled
Cold rolled, heat treated, pickled,
skinpassed
Work hardened
Cold rolled, bright annealed,
may be skinpassed
1) See also: Guide to Stainless Steel Finishes (Building Series, Volume 1), L uxembourg: E uro Inox, 2005.
EN 10088-2, Stainless steels. Technical delivery conditions for sheet/plate and strip of corrosion resisting steel for general purposes, 2005
What is stainless steel ?
oxygen
passive layer
bulk stainless steel
1D
2B
2R
2H
W H A T I S S T A I N L E S S S T E E L ?
Weldability
Corrosion Resistance Mechanical Properties
+Ti 1.4541 321
Low C 1.4307 304L*
1.4306 304L*
+Ti 1.4571 316Ti
2% Mo: 1.4404 316L*
2.5% Mo: 1.4432 316L*
3% Mo: 1.4438 317L
Ni alloys
2% Mo: 1.4401 316*
2.5% Mo: 1.4436 316*
3% Mo: 317
Add Cr - Ni to
increase resistance at
high temperatures
Substitute C by N to
increase weldability,
ductility and corrosion
resistance
Increase Ni (12%)
to enhance
expansion forming
1.4315 304N
1.4311 304LN
1.4310 301
1.4318 301LN
1.4303 305
1.4828
1.4833 309(S)
1.4841 310/314
1.4845 310(S)
Designations according to EN 10088 and AISI. Please note that there is no 1:1 relationship between AISI and EN grades (*). For details about chemical composi-
tion and equivalence, please consult www.euro-inox.org/technical_tables.
Increase C to
increase mechanical
properties
(incl. cold working)
Reduce C or
add Ti to avoid
intergranular
corrosion
after welding
Add N to raise
strength, also at
low temperatures
W
e
l
d
a
b
i
l
i
t
y
M
e
c
h
a
n
i
c
a
l
P
r
o
p
e
r
t
i
e
s
Oxidation Resistance
Corrosion Resistance
304
1.4301
Fe
18% Cr
8% Ni
Add Mo to increase
corrosion resistance
How are austenitic grades interrelated?
Starting from the universal commodity grade 1.4301, the alloying content can be adapted to
modify the steels characteristics:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Add Cr, Mo, N to achieve
superior corrosion resistance
6% Mo: 1.4547
1.4529
The most popular grade is EN 1.4016 (AISI 430). Low chromium alloys can be chosen in non-
severe environments and where appearance is not a priority. Chromium and molybdenum
increase corrosion resistance. Titanium and niobium improve weldability.
What are the ferritic options?
R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
c
o
r
r
o
s
i
o
n
r
e
s
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
1.4016 430
Fe
17% Cr
1.4000 410S
1.4003
1.4521 444
Improved corrosion
resistance and weldability
+Cr
+Cr, Mo
1.4510 439
1.4520 430Ti*
Improved
weldability
1.4509 441*
Improved
weldability and
oxidation resistance
1.4113 434
Improved
corrosion
resistance
+Mo, Ti, Nb
+Ti
+Mo
1.4512 409
Improved
weldability
+Cr, Nb
* common designations
+Ti
What is stainless steel ?
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
1.4526 436
+
+Nb
1.4513
+
+Ti
Designations according to EN 10088 and AISI
For details about chemical composition and equivalence, please consult www.euro-inox.org/technical_tables.
What are the ferritic options?
W H A T I S S T A I N L E S S S T E E L ?
Duplex stainless steels typically show higher mechanical properties and corrosion resistance than
the most common ferritic and austenitic grades. The relative differences between duplex stainless
steel grades of which EN 1.4462 is the most popular one should be viewed in this context.
And what about duplex?
1.4462 2205*
Fe
22% Cr 5% Ni 3% Mo
1.4362 2304*
1.4062 2202*
1.4162 2101*
1.4482 2001*
1.4501
1.4410 2507*
1.4507 255*
Add N to
increase strength
Add Cr, Ni, Mo, (W, Cu)
to increase
corrosion resistance
Add N to
increase strength
Add Mo, N to increase
corrosion resistance
Add N to
increase strength
Add Cr to increase
corrosion resistance
R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
c
o
r
r
o
s
i
o
n
r
e
s
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
++
++
+
+
* common designations
Designations according to EN 10088 and AISI
For details about chemical composition and equivalence, please consult www.euro-inox.org/technical_tables.
1.4662 2404*
Diamant Building
Bd. A. Reyers 80
1030 Brussels
Belgium
Phone +32 2 706 82-67
Fax -69
e-mail info@euro-inox.org
www.euro-inox.org
You might also like
- Forging - Manual of Practical Instruction in Hand Forging of Wrought Iron, Machine Steel and Tool Steel; Drop Forging; and Heat Treatment of Steel, Including Annealing, Hardening and TemperingFrom EverandForging - Manual of Practical Instruction in Hand Forging of Wrought Iron, Machine Steel and Tool Steel; Drop Forging; and Heat Treatment of Steel, Including Annealing, Hardening and TemperingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Duplex Stainless Steel 2d Edition PracticalDocument64 pagesDuplex Stainless Steel 2d Edition Practicalmahmoud_allam3No ratings yet
- Avesta Welding: How To Weld Fully Austenitic Stainless SteelsDocument0 pagesAvesta Welding: How To Weld Fully Austenitic Stainless SteelsMoosewanger01No ratings yet
- Draft Handbook On Welding TechniquesDocument77 pagesDraft Handbook On Welding Techniquessssf-doboj100% (2)
- Volkswagen Workshop Manuals - ElectricalDocument127 pagesVolkswagen Workshop Manuals - Electricalsssf-doboj100% (1)
- Gear Guide 060817Document0 pagesGear Guide 060817Anonymous oAbjbl4HNo ratings yet
- Testing of Austenitic Stainless SteelsDocument64 pagesTesting of Austenitic Stainless SteelsmirelamanteamirelaNo ratings yet
- 803 Service ManualDocument196 pages803 Service Manualвася рогов100% (1)
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- Cakes Amp Sugarcraft - April-May 2019 EditDocument45 pagesCakes Amp Sugarcraft - April-May 2019 Editapi-197110397100% (1)
- Financial Plan Checklist: Planning For EmergenciesDocument2 pagesFinancial Plan Checklist: Planning For EmergenciesInsan CornerNo ratings yet
- Ruukki Resistance Welding ManualDocument30 pagesRuukki Resistance Welding ManualRogo CatalinNo ratings yet
- Titanium Alloys and Their Machinability PDFDocument13 pagesTitanium Alloys and Their Machinability PDFznovak77No ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Five TypesDocument40 pagesStainless Steel Five Typessids82No ratings yet
- Stainless Steel 304 Product InfoDocument1 pageStainless Steel 304 Product Infoarunava001No ratings yet
- Pyrogen and Endotoxins GuideDocument13 pagesPyrogen and Endotoxins GuideAnil Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Heat-Treatment of Steel: A Comprehensive Treatise on the Hardening, Tempering, Annealing and Casehardening of Various Kinds of Steel: Including High-speed, High-Carbon, Alloy and Low Carbon Steels, Together with Chapters on Heat-Treating Furnaces and on Hardness TestingFrom EverandHeat-Treatment of Steel: A Comprehensive Treatise on the Hardening, Tempering, Annealing and Casehardening of Various Kinds of Steel: Including High-speed, High-Carbon, Alloy and Low Carbon Steels, Together with Chapters on Heat-Treating Furnaces and on Hardness TestingRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Science: PlantsDocument5 pagesGrade 3 Science: PlantsMauie Flores100% (3)
- Past Present and Future of The Duplex Stainless SteelsDocument10 pagesPast Present and Future of The Duplex Stainless SteelsbayumahardikaNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical and Physical Properties of the British Standard EN Steels (B.S. 970 - 1955): EN 21 to EN 39From EverandThe Mechanical and Physical Properties of the British Standard EN Steels (B.S. 970 - 1955): EN 21 to EN 39Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Material Selection and Corrosion Resistant AlloysDocument4 pagesMaterial Selection and Corrosion Resistant Alloysعزت عبد المنعمNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steels Guide - Properties, Applications & GradesDocument16 pagesStainless Steels Guide - Properties, Applications & GradesAndika RizalNo ratings yet
- Control and Analysis in Iron and SteelmakingFrom EverandControl and Analysis in Iron and SteelmakingRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Materials Selection For Corrosion PreventionDocument61 pagesMaterials Selection For Corrosion PreventionJeremy Coleman100% (1)
- Sexton's Pocket-Book for Boiler-Makers and Steam Users: Comprising a Variety of Useful Information for Employer and Workmen, Government Inspectors, Board of Trade Surveyors, Engineers in Charge of Works and Ships, Foreman of Manufactories, and the General Steam-Using PublicFrom EverandSexton's Pocket-Book for Boiler-Makers and Steam Users: Comprising a Variety of Useful Information for Employer and Workmen, Government Inspectors, Board of Trade Surveyors, Engineers in Charge of Works and Ships, Foreman of Manufactories, and the General Steam-Using PublicNo ratings yet
- Duplex Stainless Steel Guide - Strengths, Uses & LimitationsDocument7 pagesDuplex Stainless Steel Guide - Strengths, Uses & LimitationsRizalzi BachtiarNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Installation of Vertical Steel Pressure ShaftDocument23 pagesFabrication and Installation of Vertical Steel Pressure ShaftPasan RajasingheNo ratings yet
- En 1.4301Document1 pageEn 1.4301sheinilaNo ratings yet
- FEB09SSIDocument24 pagesFEB09SSILouHew100% (2)
- PunchMan 85Document245 pagesPunchMan 85sssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Trabeculectomy Complications: Characteristics and ManagementDocument31 pagesTrabeculectomy Complications: Characteristics and ManagementalfarizyjefryNo ratings yet
- Lincoln Stainless Welding GuideDocument40 pagesLincoln Stainless Welding GuideAnonymous yQ7SQr100% (1)
- Concept of Health and IllnessDocument24 pagesConcept of Health and IllnessHydra Olivar - Pantilgan100% (1)
- Burns SeminarDocument66 pagesBurns SeminarPratibha Thakur100% (1)
- Ce Este Inox-UlDocument6 pagesCe Este Inox-UlIulian OlaruNo ratings yet
- FormingPotential EN PDFDocument28 pagesFormingPotential EN PDFNhan LeNo ratings yet
- The Role Stainless Steel in Industrial Heat ExchangersDocument46 pagesThe Role Stainless Steel in Industrial Heat ExchangerswholenumberNo ratings yet
- Born From Fire, Made To Endure: Stainless SteelDocument12 pagesBorn From Fire, Made To Endure: Stainless Steelqnetomid55No ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Duplex Stainless SteelsDocument4 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Duplex Stainless SteelsAndy PhoenixNo ratings yet
- European Steel and Alloy Grades: X6Crniti18-10 (1.4541)Document3 pagesEuropean Steel and Alloy Grades: X6Crniti18-10 (1.4541)farshid KarpasandNo ratings yet
- TylekI MechanicalProperties PDFDocument22 pagesTylekI MechanicalProperties PDFAldin AlicNo ratings yet
- Austenitic Standard GradesDocument6 pagesAustenitic Standard Gradesfierro44No ratings yet
- Welding Consumables For Lean Duplex Stainless SteelDocument2 pagesWelding Consumables For Lean Duplex Stainless SteelMohamed FaragNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials Selection GuideDocument6 pagesEngineering Materials Selection Guidesilent spritsNo ratings yet
- SS - LincolnDocument40 pagesSS - LincolnLuis DuarteNo ratings yet
- Material For Rolling StocksDocument82 pagesMaterial For Rolling Stockskr_ananthNo ratings yet
- AN ISO 9001: 2000: ProductsDocument2 pagesAN ISO 9001: 2000: ProductsKamlesh DalavadiNo ratings yet
- Stainless Tubing in BiotechDocument14 pagesStainless Tubing in BiotechClaudia MmsNo ratings yet
- Martensitic Stainless SteelDocument2 pagesMartensitic Stainless SteelEdgar Apaza HuallpaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stainless Steel Welded Joints A Comparison Between Destructive and Non-Destructive TechniquesDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Stainless Steel Welded Joints A Comparison Between Destructive and Non-Destructive TechniquesKhalid M. HafezNo ratings yet
- Stell 2011specificDocument7 pagesStell 2011specificninatenaNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel I1i1 enDocument6 pagesStainless Steel I1i1 ensacalaseniNo ratings yet
- 410S Data BulletinDocument4 pages410S Data BulletinkatchaniNo ratings yet
- Plasma Nitriding Process - DataDocument11 pagesPlasma Nitriding Process - Datayadu kumar singhNo ratings yet
- CS098 Corrosion of LeadDocument24 pagesCS098 Corrosion of LeadFrancisco José Ager VázquezNo ratings yet
- S&T Stainless CatalogueDocument66 pagesS&T Stainless CatalogueAnonymous jbvNLNANLINo ratings yet
- Ferrous Metals and Alloys: (26 Marks)Document10 pagesFerrous Metals and Alloys: (26 Marks)Abhinav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aalco Datasheet ST ST SpecificationsDocument5 pagesAalco Datasheet ST ST SpecificationsAmer Y KNo ratings yet
- Background: Table 1. Some Standard Designations For Duplex Stainless SteelalloysDocument3 pagesBackground: Table 1. Some Standard Designations For Duplex Stainless SteelalloysBharat TailorNo ratings yet
- 304 304L Data Sheets 1 28 13 PDFDocument12 pages304 304L Data Sheets 1 28 13 PDFneerajtrvNo ratings yet
- Metal Alloys Guide: Properties and Applications of Aluminum, Copper, Nickel, Titanium and Their AlloysDocument31 pagesMetal Alloys Guide: Properties and Applications of Aluminum, Copper, Nickel, Titanium and Their AlloysAsyiqotul UlyaNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Reinforcement BenefitsDocument21 pagesStainless Steel Reinforcement BenefitsAnket PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ce 3003 Steel Kac Lecture Notes - 2020-2021 - AnnotatedDocument109 pagesCe 3003 Steel Kac Lecture Notes - 2020-2021 - AnnotatedMannyNo ratings yet
- Materials QuestionsDocument30 pagesMaterials QuestionsMatheus SouzaNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Material Properties NewDocument71 pagesOrthodontic Material Properties NewHiba AbdullahNo ratings yet
- High Temperature Corrosion: Fundamentals and EngineeringFrom EverandHigh Temperature Corrosion: Fundamentals and EngineeringNo ratings yet
- DV03PUB18 Study GuideDocument5 pagesDV03PUB18 Study Guidesssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Resetting Windows PasswordDocument8 pagesResetting Windows Passwordsssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Cr4 Technical GuideDocument3 pagesCr4 Technical Guidesssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Morse Band CatDocument36 pagesMorse Band Catsssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- D1Document1 pageD1sssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Accessories eDocument2 pagesAccessories esssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Gas Strut Force CalculationDocument1 pageGas Strut Force Calculationsssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- D1Document1 pageD1sssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- AluminumDocument5 pagesAluminumsssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- CNC Cutter Diameter Compensation GuideDocument12 pagesCNC Cutter Diameter Compensation GuideSankaralingam ShankarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Formulas 2Document1 pageElectrical Formulas 2Ranjit RjtNo ratings yet
- Emboss Continuous Bead: Tool Code BTDocument1 pageEmboss Continuous Bead: Tool Code BTsssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of SpringsDocument8 pagesManufacture of Springssssf-dobojNo ratings yet
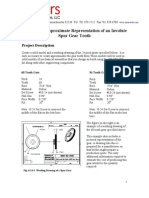
- Basic Spur Gear GeometryDocument3 pagesBasic Spur Gear Geometrysssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Draw A GearDocument4 pagesDraw A GearVasukiparashar MavathurNo ratings yet
- Montgomery Plate Roll MachineDocument48 pagesMontgomery Plate Roll Machinesssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Joseph MillerDocument175 pagesJoseph MillerAlberto DanNo ratings yet
- Fastener FactsDocument6 pagesFastener FactsPieter van der WaltNo ratings yet
- Title Lager RuDocument10 pagesTitle Lager Russsf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Technical Data - IP Protection Classification IEC 529Document1 pageTechnical Data - IP Protection Classification IEC 529sssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Band Saw Blade TerminologyDocument2 pagesGlossary of Band Saw Blade Terminologysssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of SpringsDocument8 pagesManufacture of Springssssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Measuring Boxes For Street LightingDocument1 pageMeasuring Boxes For Street Lightingsssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Distributive TransformersDocument4 pagesDistributive Transformerssssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Metal Boxes For Half Indirect and Indirect Metering of EEDocument1 pageMetal Boxes For Half Indirect and Indirect Metering of EEsssf-dobojNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Burn & BleedingDocument2 pagesMind Map Burn & BleedingUlfia KhoirinnissaNo ratings yet
- D 2144 - 01 - RdixndqDocument4 pagesD 2144 - 01 - RdixndqjayakumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ManojDocument4 pagesChapter 2 ManojBro FistoNo ratings yet
- HLF Sharing Fitness Business CooperationDocument17 pagesHLF Sharing Fitness Business Cooperationbhardwajharsh2706No ratings yet
- 1644 CV Europass Daniel MatosDocument2 pages1644 CV Europass Daniel MatosDaniel MatosNo ratings yet
- Chem For Engineering Material by Pup BuddiesDocument46 pagesChem For Engineering Material by Pup BuddiesJedidiah MondaresNo ratings yet
- Análisis de Estabilidad de TaludesDocument4 pagesAnálisis de Estabilidad de TaludesJosue Acosta EspinozaNo ratings yet
- CEU - Catalytic ReactorsDocument3 pagesCEU - Catalytic ReactorsPong VongNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - SOP ON DispensingDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Word - SOP ON DispensingPalawan Baptist HospitalNo ratings yet
- Final ESIA On Construction Materials - Tamiru BultoDocument110 pagesFinal ESIA On Construction Materials - Tamiru BultoKayo Shankulie100% (1)
- Research Journal DNA PolymeraseDocument12 pagesResearch Journal DNA PolymeraseMauhibahYumnaNo ratings yet
- Ethics Zoo EssayDocument2 pagesEthics Zoo EssayChanel SalinasNo ratings yet
- WILLIEEMS TIBLANI - NURS10 Student Copy Module 15 Part1Document32 pagesWILLIEEMS TIBLANI - NURS10 Student Copy Module 15 Part1Toyour EternityNo ratings yet
- Causes & Prevention of Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument41 pagesCauses & Prevention of Coronary Artery DiseaseeenagpurcongNo ratings yet
- Schedule Examination 2010 2011Document5 pagesSchedule Examination 2010 2011pawan15588rediffmailNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Abnormality by Dr. Kanwal QadeerDocument7 pagesDefinitions of Abnormality by Dr. Kanwal QadeerHaya EishaNo ratings yet
- Evonik-BREAK THRU Brochure Microbials EN Asset 2214205Document5 pagesEvonik-BREAK THRU Brochure Microbials EN Asset 2214205李雷No ratings yet
- Eye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiaDocument22 pagesEye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiawellawalalasithNo ratings yet
- Cottonhill - Red Collection PDFDocument33 pagesCottonhill - Red Collection PDFVioricaNo ratings yet
- SEAS Scoliosis Course NYC Feb 2018Document4 pagesSEAS Scoliosis Course NYC Feb 2018BorislavNo ratings yet
- Airtel's Africa Growth: Surviving CompetitionDocument9 pagesAirtel's Africa Growth: Surviving CompetitionSagar RiazNo ratings yet