Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Chapter 10-Refraction and Dispersion of Light
Uploaded by
Sam Wing HongOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Chapter 10-Refraction and Dispersion of Light
Uploaded by
Sam Wing HongCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Chapter 10: Refraction and Dispersion of Light 1.
The phenomenon where light rays change their directions as they travel from a transparent medium to another transparent medium is known as __________________. 2. Draw a schematic diagram to illustrate the refraction of light.
3. The medium with greater speed of light is called the ___________________________ while the one with lower speed of light is called the ____________________________. 4. What are the effects of refraction?
5. When the angle of refraction in the optically less dense medium is 90, the angle of incidence in the optically denser medium is called the _______________________. 6. When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, all the light will be totally internally reflected, this is called ___________________________________. 7. What are the applications of total internal reflection?
8. Indicate whether total internal reflection will occur in the following situations: a. Light travelling from oil to water b. Light travelling from glass to air c. Light travelling from air to oil d. Light travelling from water to glass 9. The two types of lenses are _____________________ and __________________________.
10. Draw the following lenses: a. Converging lens b. Diverging lens
11. The _____________________ joins the centres of curvature of two spherical surfaces of the lens. 12. In a convex lens, parallel light converge to a point called ________________________. 13. The distance from focal point to the optical centre is called ____________________. 14. Try Exercise 10.3 Question 2. 15. Construct a ray diagram having a convex lens of 5cm focal length with an object placed 7cm from the lens.
16. Construct a ray diagram having a concave lens of 8cm focal length with an object placed 5cm from the lens.
17. Construct a ray diagram having a convex lens of 7cm focal length with an object placed 3cm from the lens.
18. Construct a ray diagram having a concave lens of 5cm focal length with an object placed 8cm from the lens.
19. A real image is always ____________; a virtual image is always ________________. 20. A concave lens can only produce ___________, _______________ and _____________ image. 21. Write down the lens formula.
22. The focal length of a convex lens is ______________; the focal length of a concave lens is _______________. 23. Explain magnifying power and write out the formula.
24. The focal length of a convex lens is 40cm. An object 5cm high is placed 30cm in front of the convex lens. Calculate its image distance, magnifying power and image height.
25. The focal length of a concave lens in 5cm. If an object is placed 8cm from the screen, where is the image?
26. An object of 6cm tall is placed 10cm in front of a diverging lens of 15cm focal length. Find the image distance and the height of the image produced. Is the image real or virtual?
27. An object placed 20cm in front of a lens produces a real image 5cm away from the lens. Find the focal length of the lens. What type of lens is it?
28. The series of coloured patches is called a _____________. 29. List down the order of the colours of spectrum.
30. _______________ of light shows that white light is not a single-coloured light but is made up of several light colours. 31. In the dispersion of white light, _______________ is deviated the least; _______________ light is deviated the most.
32. The separation of light into its different colour components is known as _____________. 33. The colour of a ______________ object is determined by the colour of light which it transmits when illuminated by white light. 34. The colour of an _______________ object is determined by the colour of the light reflected by it. 35. ______________ objects absorb all colours of light; _______________ reflects all colours of light.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Equipment CapabilitesDocument19 pagesEquipment Capabilitesapi-1975359897% (194)
- Concrete Pipe Installation Guide-CPMDocument17 pagesConcrete Pipe Installation Guide-CPMSankar CdmNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Instruction Manual STR 155 RL-1Document24 pagesInstruction Manual STR 155 RL-1VENDI100% (3)
- Hot Water Supply (Apprentice) M2 U10Document39 pagesHot Water Supply (Apprentice) M2 U10Sam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- TAIL Project NewsletterDocument9 pagesTAIL Project NewsletterAbdul R. MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in Oil and Gas Industry A Perspective On Corrosion InhibitorsDocument1 pageCorrosion in Oil and Gas Industry A Perspective On Corrosion InhibitorsAsma Sed100% (1)
- Pyrochem Operation ManualDocument82 pagesPyrochem Operation ManualSam Wing Hong100% (2)
- Cat 120H, 12H, 140H, 143H, 160H, 163H TransmisiónDocument8 pagesCat 120H, 12H, 140H, 143H, 160H, 163H TransmisiónJefferson Maldonado.No ratings yet
- Lateral Earth Pressure TheoryDocument45 pagesLateral Earth Pressure TheoryAdel JamalNo ratings yet
- ESD 18-91-067 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 305Document208 pagesESD 18-91-067 - Instruction Manual and Parts List - Ed. 305Centrifugal SeparatorNo ratings yet
- Domestic Hot Water RecirculationDocument2 pagesDomestic Hot Water RecirculationSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Examples of Fire Safety Engineering Calculations.Document18 pagesExamples of Fire Safety Engineering Calculations.Sam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- HVAC Handbook HVAC Design Brief (Singapore)Document26 pagesHVAC Handbook HVAC Design Brief (Singapore)Sam Wing Hong50% (2)
- Cag I Air Compressor HPDocument24 pagesCag I Air Compressor HPcamenitaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cost EstimationDocument49 pagesPlant Cost EstimationAlpianto100% (1)
- Strategic Supply Chain Management and LogisticsDocument16 pagesStrategic Supply Chain Management and LogisticsNalaka Manawadu67% (3)
- Lift Traffic Design Spreadsheet - All PeaksDocument8 pagesLift Traffic Design Spreadsheet - All PeaksSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
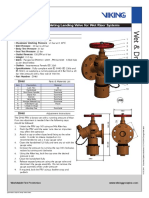
- PRV High Pressure Regulating Landing Valve Wet Riser SystemsDocument1 pagePRV High Pressure Regulating Landing Valve Wet Riser Systemskan_chan_01No ratings yet
- REA2015 REG2015 (Final) PDFDocument92 pagesREA2015 REG2015 (Final) PDFAuYongTheanSengNo ratings yet
- Quality NBR Insulation Thickness Guide for Condensation ControlDocument8 pagesQuality NBR Insulation Thickness Guide for Condensation ControlSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Board of Engineers Malaysia Code of ConductDocument12 pagesBoard of Engineers Malaysia Code of ConductJude FrancisNo ratings yet
- Bomba UBBL 1984 (Amendment 2012) HighlightDocument11 pagesBomba UBBL 1984 (Amendment 2012) HighlightSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Duct Pressure Loss CalculationDocument24 pagesDuct Pressure Loss CalculationbernardsilvanoNo ratings yet
- Room Aircon Heat Load Estimate FormDocument3 pagesRoom Aircon Heat Load Estimate FormMena G. El NimrNo ratings yet
- Draft SCA Guidance On Smoke Control in Apartment BuildingsDocument67 pagesDraft SCA Guidance On Smoke Control in Apartment BuildingsSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Designing Your Compressed Air System - KAESER Compressor PDFDocument8 pagesDesigning Your Compressed Air System - KAESER Compressor PDFhugoNo ratings yet
- HR T&CDocument29 pagesHR T&CSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Daikin Download Link (070915)Document6 pagesDaikin Download Link (070915)Sam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- TOLCO Pipe HangersDocument26 pagesTOLCO Pipe HangersPaulo VeríssimoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Sump Design Guide PDFDocument8 pagesEngineering Sump Design Guide PDFHaimwant DhanieNo ratings yet
- Papaya Pipe HangerDocument2 pagesPapaya Pipe HangerSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Typical SMATV For Condo-ApartmentDocument3 pagesTypical SMATV For Condo-ApartmentSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Quality NBR Insulation Thickness Guide for Condensation ControlDocument8 pagesQuality NBR Insulation Thickness Guide for Condensation ControlSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Paper-on-Swimming Pool Circulation-Systems PDFDocument5 pagesPaper-on-Swimming Pool Circulation-Systems PDFIlyas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Quality NBR Insulation Thickness Guide for Condensation ControlDocument8 pagesQuality NBR Insulation Thickness Guide for Condensation ControlSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Choosing Soft Starter or Variable Frequency DriveDocument4 pagesChoosing Soft Starter or Variable Frequency Drivesiva_nagesh_2No ratings yet
- Typical MSW SchematicDocument9 pagesTypical MSW SchematicSam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Soil Pipe (Timplas)Document9 pagesSoil Pipe (Timplas)Sam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Surge ControlDocument14 pagesSurge Control31jamesNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Calculation On Sizing of Surge VesselDocument3 pagesPreliminary Calculation On Sizing of Surge VesselSam Wing Hong100% (3)
- Single and Multiphase CFD Simulations For Designing Cavitating VenturiDocument12 pagesSingle and Multiphase CFD Simulations For Designing Cavitating VenturiCarlos GamarraNo ratings yet
- 1,3,3-Trinitroazetidine (TNAZ) - Part I. Syntheses and PropertiesDocument23 pages1,3,3-Trinitroazetidine (TNAZ) - Part I. Syntheses and PropertiesThanh XomNo ratings yet
- PX 9 enDocument532 pagesPX 9 enjjccmmaaNo ratings yet
- Bluskies Engineering PVT LTD: Acp Panel Inpection ReportDocument7 pagesBluskies Engineering PVT LTD: Acp Panel Inpection ReportRavi Shankar KolluruNo ratings yet
- Process Level ChartDocument2 pagesProcess Level ChartzaidinNo ratings yet
- Extrusion-Spheronization Process Variables and CharacterizationDocument57 pagesExtrusion-Spheronization Process Variables and CharacterizationKhanh Le0% (1)
- 06 - 1 Cutting Tools - 2013 - LRDocument17 pages06 - 1 Cutting Tools - 2013 - LRBaggerkingNo ratings yet
- Ma-Mscmt-10 J16Document5 pagesMa-Mscmt-10 J16Dilip BhatiNo ratings yet
- Control Valve and Steam Line PDFDocument19 pagesControl Valve and Steam Line PDFRofi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Linthwaite: Conservatio N AreaDocument26 pagesLinthwaite: Conservatio N Areabill baileyNo ratings yet
- Measurement & Calculation of Vehicle Center of Gravity Using Portable Wheel ScalesDocument11 pagesMeasurement & Calculation of Vehicle Center of Gravity Using Portable Wheel ScalesVedant KodagiNo ratings yet
- Physicaltestingofrubberrogerbrown2006 Book 150514103634 Lva1 App6892Document389 pagesPhysicaltestingofrubberrogerbrown2006 Book 150514103634 Lva1 App6892AbdelhamidHarratNo ratings yet
- Nitobond EP 0608Document2 pagesNitobond EP 0608James PittsNo ratings yet
- Zw3d2022 Lite Vs Cadbro 2022Document4 pagesZw3d2022 Lite Vs Cadbro 2022Carlos LimaNo ratings yet
- TSB 1106 - MFY Starter Solenoid - ChangeDocument1 pageTSB 1106 - MFY Starter Solenoid - ChangeChrisMNo ratings yet
- Torque Specifications: Service Specifications - Ra60F Manual TransmissionDocument1 pageTorque Specifications: Service Specifications - Ra60F Manual TransmissionPedro Javier Castro SanchezNo ratings yet
- BPO2-Module 9 PROJECT PLANDocument16 pagesBPO2-Module 9 PROJECT PLANJudame Charo ZozobradoNo ratings yet
- Revit Domoty 1Document1 pageRevit Domoty 1SAN RAKSANo ratings yet
- TASK 1 Physics Class XI: (Do Always Any Five Numerical Problems Related To The Chapter)Document3 pagesTASK 1 Physics Class XI: (Do Always Any Five Numerical Problems Related To The Chapter)frank 101No ratings yet
- Psib 20150212Document10 pagesPsib 20150212Léandre Ettekri NdriNo ratings yet