Professional Documents
Culture Documents
in Any Trapezium ABCD (Refer Figure), AB - CD, O Is The Intersection of
Uploaded by
Siddharth MaheshwariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
in Any Trapezium ABCD (Refer Figure), AB - CD, O Is The Intersection of
Uploaded by
Siddharth MaheshwariCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
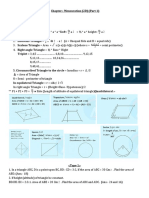
In any Trapezium ABCD (refer figure), AB || CD, O is the intersection of diagonals AD and BC then, Area of AOC = BOD
2. In any quadrilateral ABCD, with AC and BD as diagonals intersecting at O.
Let, Area of AOB = W Area of BOC = X Area of COD = Y Area of AOD = Z then, W.Y = X.Z
3. The Centroid and Incenter will always lie inside the triangle. About the other points For an acute angled triangle, the Circumcenter and the Orthocenter will lie inside the triangle. For an obtuse angled triangle, the Circumcenter and the Orthocenter will lie outside the triangle.
For a right-angled triangle, the Circumcenter will lie at the midpoint of the hypotenuse and the Orthocenter will lie at the vertex at which the angle is 90. 4. The orthocenter, centroid, and circumcenter always lie on the same line known as Euler Line. The orthocenter is twice as far from the centroid as the circumcenter is. If the triangle is Isosceles then the incenter lies on the same line.
If the triangle is equilateral, all four are the same point.
5. Appolonius Theorem {AD is the median)
AB2 + AC2 = 2 * (AD2 + BD2) 6. For cyclic quadrilaterals
Area = ?((s - a) (s - b) (s - c) (s - d)) where s is the semi perimeter s = (a + b + c + d)/2
Also, Sum of product of opposite sides = Product of diagonals ac + bd = PR * QS
7.
If a circle can be inscribed in a quadrilateral, its area is given by = (abcd) 8. In a parallelogram Sum of squares of diagonals = Sum of squares of four sides, AC2 + BD2 = AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + DA2
Trapezium Sum of the squares of the length of the diagonals = Sum of squares of lateral sides + 2 Product of bases. AC2 + BD2 = AD2 + BC2 + 2 x AB x CD If a trapezium is inscribed in a circle, it has to be an isosceles trapezium. If a circle can be inscribed in a trapezium, Sum of parallel sides = Sum of lateral sides.
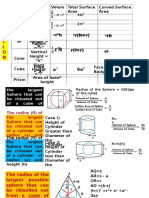
Solids - If a sphere is inscribed in a cube of side a, the radius of the sphere will be a/2. If a sphere is circumscribed about a cube of side a, the radius of the sphere will be ?3 * a/2
- If a largest possible sphere is inscribed in a cylinder of radius a and height h, its radius r will be
r = h/2 {If 2a > h}
r=a {If 2a < h}
- If a largest possible sphere is inscribed in a cone of radius r and slant height equal to 2r, then the radius of sphere = r /?3.
- If a cube is inscribed in a hemisphere of radius r, then the edge of the cube = r * ?(2/3).
On Coordinate Geometry
- The X axis divides the line joining P(x1,y1) and Q(x2,y2) in the ratio of y1 : y2
- The Y axis divides the line joining P(x1,y1) and Q(x2,y2) in the ratio of x1 : x2
- If we know three points A(x1,y1), B(x2,y2 ) and C(x3,y3) of a parallelogram, the fourth point is given by
(x1 + x3 x2, y1 + y3 y2)
You might also like
- GEOMETRY FORMULA GUIDEDocument27 pagesGEOMETRY FORMULA GUIDEMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)
- Crash Course Coordinate EnglishDocument43 pagesCrash Course Coordinate EnglishGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- Geometry & Mensuration 3Document35 pagesGeometry & Mensuration 3Neetu Jain100% (2)
- Quantitative Geometry GuideDocument76 pagesQuantitative Geometry Guidegaurav newatiaNo ratings yet
- Key Formulas MathsDocument7 pagesKey Formulas MathsAdil Ghaznavi50% (2)
- Chapter - Mensuration (2D)Document3 pagesChapter - Mensuration (2D)kunkri donNo ratings yet
- Geometry Key 2006Document2 pagesGeometry Key 2006iitforumNo ratings yet
- Circle - 1Document5 pagesCircle - 1parthdbz2005No ratings yet
- CirclesDocument11 pagesCirclesSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Term 2 Important QuestionsDocument13 pagesClass 10 Maths Term 2 Important QuestionsBhargavi JujjavarapuNo ratings yet
- Maths & Mech FormulasDocument19 pagesMaths & Mech FormulasgunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra-Mathematics Geometry Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperDocument9 pagesMaharashtra-Mathematics Geometry Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperFirdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- Key Formulas Maths PDFDocument7 pagesKey Formulas Maths PDFGeofrey100% (1)
- Angles Made by A Transverse Line:: Congruent and Similar TriangleDocument9 pagesAngles Made by A Transverse Line:: Congruent and Similar TriangleRitsikaGurramNo ratings yet
- Conic Section Muti Choice Questions: P and P and O IsDocument4 pagesConic Section Muti Choice Questions: P and P and O IsThunderswordNo ratings yet
- Formulas for triangles and circlesDocument13 pagesFormulas for triangles and circlesAtithaya Chinchalongporn100% (1)
- 05 - MensurationDocument28 pages05 - Mensurationthinkiit88% (8)
- Vector and 3d For JeeDocument7 pagesVector and 3d For JeePranavMachingalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document10 pagesChapter 10Jitesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Geometry ProblemsDocument54 pagesGeometry Problemshvphatak80% (5)
- Kamal Roop Class Ix - CDocument15 pagesKamal Roop Class Ix - CPuneet SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Sample Booklet (Study Material + Model Paper) For SA-2 Class 10Document32 pagesSample Booklet (Study Material + Model Paper) For SA-2 Class 10Apex Institute88% (8)
- (Rise Up) - Straight Lines - Sep 1Document238 pages(Rise Up) - Straight Lines - Sep 1prakhar100% (1)
- Math HelpDocument8 pagesMath Helpatiggy05100% (1)
- Given: Chord length = 2/3 radiusLet the central angle be θUsing the theorem: Chord length = 2r sin(θ/2)2/3r = 2r sin(θ/2)1/3 = sin(θ/2)θ = 2 * sin^-1(1/3) = 39.9°The central angle is 39.9 degreesDocument51 pagesGiven: Chord length = 2/3 radiusLet the central angle be θUsing the theorem: Chord length = 2r sin(θ/2)2/3r = 2r sin(θ/2)1/3 = sin(θ/2)θ = 2 * sin^-1(1/3) = 39.9°The central angle is 39.9 degreesFree student100% (1)
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer KeyDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer Keygeetha100% (1)
- Geometry FormulasDocument5 pagesGeometry FormulasAlyzza Rose Pampliega LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Sample Paper CBSE 2015 XDocument12 pagesMathematics Sample Paper CBSE 2015 Xvv1234567No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Co-Ordinarte GeometryDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 7 Co-Ordinarte GeometryJannatNo ratings yet
- Math 23Document34 pagesMath 23Sajed RahmanNo ratings yet
- Marko Radovanovic Complex Numbers in GeometryDocument53 pagesMarko Radovanovic Complex Numbers in Geometrymaraujo68No ratings yet
- Geometry FundamentalsDocument10 pagesGeometry FundamentalsAshrithNo ratings yet
- Formulas for Pre-Olympiad Math CompetitionsDocument11 pagesFormulas for Pre-Olympiad Math Competitionsjehovisti100% (1)
- Formulas Pre OlympiadDocument11 pagesFormulas Pre Olympiadbus9No ratings yet
- Circles RevisionDocument31 pagesCircles RevisionTuition MastersNo ratings yet
- Banyan International SchoolDocument10 pagesBanyan International SchoolVyoum MahajanNo ratings yet
- Important Theorems of Geometry by Abhishek Jain Very Important For All SSC ExamsDocument22 pagesImportant Theorems of Geometry by Abhishek Jain Very Important For All SSC ExamsStudy IQ92% (38)
- 330 MensurationDocument27 pages330 MensurationK V Aditya Prakash100% (1)
- Introduction To Conic Sections and Circles (PT in Precal and Etech)Document8 pagesIntroduction To Conic Sections and Circles (PT in Precal and Etech)Stephanie TitularNo ratings yet
- Solutions to Mathematics Questions from Class XI & XII O-Caps -3Document12 pagesSolutions to Mathematics Questions from Class XI & XII O-Caps -3Honey ChunduruNo ratings yet
- Straight Line NIEDocument35 pagesStraight Line NIESubramaniam RajendramNo ratings yet
- Rice MathDocument60 pagesRice MathHarikrishna ShenoyNo ratings yet
- The SphereDocument9 pagesThe SpherePast Buanget100% (1)
- Geometry: 3. Solid BodiesDocument40 pagesGeometry: 3. Solid BodiesEduardo Tello del PinoNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument8 pagesCircleShirjak ThokarNo ratings yet
- Geometry Practice Quiz For High School StudentsDocument3 pagesGeometry Practice Quiz For High School StudentsGyermie Ross CarpesoNo ratings yet
- 330 MensurationDocument27 pages330 MensurationK V Aditya Prakash100% (1)
- And VolumesDocument31 pagesAnd Volumesdev mittalNo ratings yet
- 16.co Ordinate GeometryDocument8 pages16.co Ordinate GeometrykeerthanasubramaniNo ratings yet
- In Euclidean GeometryDocument32 pagesIn Euclidean GeometryGilar JatisundaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions on Circles from Class IX Mathematics Assignments (Term 2Document25 pagesImportant Questions on Circles from Class IX Mathematics Assignments (Term 2sshoeburrahman100% (1)
- ConicsDocument9 pagesConicsniranjankumar79No ratings yet
- Snap It With SCMHRD: Formulae For Quantitative and Data Interpretation Sections AlgebraDocument20 pagesSnap It With SCMHRD: Formulae For Quantitative and Data Interpretation Sections AlgebraAditya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 07 GemoetryDocument11 pages07 GemoetryKomanduri Murali SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Circles and Squares Problems For TCSDocument4 pagesCircles and Squares Problems For TCSAnonymous ZVbwfcNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Case in PointDocument185 pagesCase in PointSiddharth Maheshwari100% (1)
- Zs Case Study 11Document52 pagesZs Case Study 11Siddharth Maheshwari67% (9)
- 1000 Sentence Correction QuestionsDocument239 pages1000 Sentence Correction QuestionsSiddharth MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- in Any Trapezium ABCD (Refer Figure), AB - CD, O Is The Intersection ofDocument6 pagesin Any Trapezium ABCD (Refer Figure), AB - CD, O Is The Intersection ofSiddharth Maheshwari100% (1)
- Total Gadha-Number System PDFDocument85 pagesTotal Gadha-Number System PDFChandramauli GovindNo ratings yet
- Economic Development and Patenting BehaviourDocument8 pagesEconomic Development and Patenting BehaviourSiddharth MaheshwariNo ratings yet