Professional Documents
Culture Documents
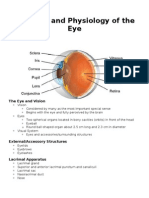
Anatomy and Embryology of Eye An Overview
Uploaded by
Kamsang Pius BeyiahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy and Embryology of Eye An Overview
Uploaded by
Kamsang Pius BeyiahCopyright:
Available Formats
Orbit and Ocular adnexa The Eye Embryology
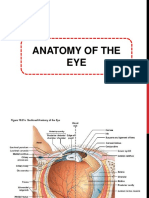
Eyeball (2.5 cm) Eyelid = lid () Eyelash () Puntum () Medial & lateral canthus () Fornix () Iris () & pupil () Cornea () (1 cm) Limbus () (Bulbar) conjunctiva () Sclera ()
Cornea () Limbus () Conjunctiva () Anterior chamber () Iris () Posterior chamber () Lens () Vitreous () Iridocorneal angle () Ciliary body ()
Retina () Choroid () Sclera () Tenons capsule (= fascial sheath)
Bony Orbit:
Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethomoidal bone Sphenoid bone Lacrimal bone Palatine bone
Medial wall: Maxilla, Sphenoid, Ethmoid, Lacrimal b.
Leteral wall: Greater wing of sphenoid Zygomiatica
Orbital floor: MaxillaPalatine Zygomatica Orbital roof: Frontal, lesser wing of sphenoid b.
Superior orbital fissure: Lesser wing of sphenoid greater wing of sphenoid
CN III CN IV CN V1 Superior ophthalmic vein
Inferior orbital fissure: sphenoidMaxilla Palatine
CN V2 Inferior ophthalmic vein
Vision: II (optic nerve) Sensation: V1 (ophthalmic nerve) Motor: III (oculomotor), IV (trochlear), VI (abducens) Pupil dilation: sympathetic Pupil constriction: parasympathetic Motor: VII (facial) not through the orbital apex -- orbicularis muscle
Frontal, lacrimal, nasocilliary
Sensory root form nasocilary branch of CN V1 Motor root form the inf. Division of CN III Sympathetic root form the internal carotid artery Parasympathetic axons form post-ganglionic fibers
(light reflex)
vision pupil constriction (parasympathetic)
(corneal) sensation orbicularis muscle blinking (motor) lacrimal tearing (parasympathetic)
1, 2 functions
Muscle
Innervation
Origin
Insertion
Primary function
Inserted Secondary Tertiary into the function function sclera distance
Intorsion Adduction 7.7mm
Superior rectus
Superior branch Annulus of Zinn of oculomotor from tendinous nerve ring Annulus of Zinn from tendinous ring
eye (anterior, superior surface)
Elevation
Inferior branch Inferior rectus of oculomotor nerve
eye (anterior, Depression Extorsion inferior surface) eye (anterior, Abduction lateral surface) eye (anterior, Adduction medial surface)
Adduction 6.5mm
Annulus of Zinn Lateral rectus Abducens nerve from tendinous ring Inferior branch Medial rectus of oculomotor nerve Annulus of Zinn from tendinous ring
6.9mm
5.5mm
Superior oblique
Annulus of Zinn via the Trochlea of superior Trochlear nerve oblique which forms a 'pulley system'.
Inferior branch of oculomotor nerve
eye (posterior, superior, lateral Intorsion surface)
Depression Abduction
Inferior oblique
Maxillary bone
eye (posterior, inferior, lateral Extorsion surface)
Elevation
Abduction
Outside to inside:
Skin Subcutaneous tissue Orbicularis oculi Orbital septum & tarsal plates M ller muscle (upper eyelid) Palpebral conjunctiva
Puntum (punta; ) Upper & lower calaniculus (canaliculi; ) Common calaniculus (90%) Lacrimal sac () Nasolacrimal duct ()
a. Lacrimal gland b. Superior lacrimal punctum c. Superior lacrimal canal d. Lacrimal sac e. Inferior lacrimal punctum f. Inferior lacrimal canal g. Nasolacrimal duct
Part Palpebral or tarsal conjunctiva
Area lines the eyelids
where the inner part of the eyelids and the eyeball meet, the palpebral conjunctiva is reflected at the superior fornix and the inferior fornix to become the bulbar conjunctiva. It is loose and flexible, Fornix conjunctiva allowing the free movement of the lids and eyeball. An ophthalmologist or optometrist can insert eye drops into the lower eyelid space. The substance works its way up the surface of the eyeball and diffuse into the internal eye.
Bulbar or ocular conjunctiva covers the eyeball, over the sclera. This region of the conjunctiva is bound tightly and moves with the eyeball movements.
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
Limbus Bulbar conjunctiva Forniceal conjunctiva Tarsal conjunctiva punctum
Anterior chamber: 250 L Posterior chamber: 60 L Vitreous cavity: 4~6 mL
Lens () Aperture
Pupil Cornea Lens ()
Film
Retina
Dark room
Sclera, choroid
Iris sphincter (parasym): Iris dilator (sympathetic)
Superficial oily layer
Predominantly by meibomian glands
Middle aqueous layer
Main and accessory lacrimal glands
Deep mucin layer
Conjunctival goblet cells
Contribute most refractive power: 43D Central cornea is thinner (0.5 mm) than periphery (0.7 mm)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Epithelium Bowmans layer Stroma Descemets membrane Endothelium
Cover the posterior 4/5 of the surface of the globe Anterior opening: cornea Posterior opening: optic nerve
Thinnest (0.3mm): just behind the insertions of rectus muscles Thickest (1.0mm): posterior pole around the optic nerve head
Conjunctiva and limbal palisades Tenons capsule Episclera Corneoscleral stroma Aqueous outflow apparatus
Anterior border: cornea Posterior border: iris diaphragm of the pupil
Ciliary process: zonule (lens suspension) Ciliary epithelium: aqueous secretion (Trabecular meshwork: absorption) Ciliary muscle: lens thickening (accommodation; near vision) Ciliary vessels: nutrition
Anterior chamber Posterior chamber Vitreous
Iridocorneal angle Trabecular meshwork
Ciliary epithelium
Biconvex structure Contribute 20D of focusing power Accommodation ability: deceased by aging
Adolescents: 12-16D Age 50: 2D
Lacks vasculature and innervations Hardens by aging: senile cataract
2 functions:
As a transparent gel occupying the major volume of the globe As a route of nutrition to lens
98% of water and 0.15% macromolecules
2 major components: collagen and hyaluronan
Progressive liquefaction with age
Cup / Disc 10 layers
1 2 3
Foveola Fovea (centralis)
5 6 7 8 9 10
Macula (lutea)
Phtoreceptors:
Rods + 3 types of cones
Bipolar cells:
Rod on bipolars Cone on- and offbipolars
Interneurons
Horizontal and amacrine cells
Ganglion cells
Forming optic nerve
Macula lutea (yellow spot)
Major element: Zeaxanthin and lutein
Fovea is a concave central retinal depression approximately 1.5 mm in diameter
Only cones in fovea
3 parts:
Iris Ciliary body (located in the anterior uvea) Choroid ( located in the posterior uvea)
Firmly attached to 3 sites:
Scleral spur Vortex veins Optic nerve
Sphincter muscle
Parasympathetic innervation
Dilator muscle Posterior pigmented layer
Sympathetic 1-adrenergic stimulation Continuous with the non-pigmented epithelium of ciliary body
Ciliary epithelium and stroma
Pars plana Pars plicata Inner non-pigmented epithelium Pigmented epithelium
Ciliary muscle
Longitudinal Radial Circular
3 layers
Choriocapillaries (innermost) Small vessels (middle) Large vessels (outer)
Nourish the outer portion of retina
Regional Differences in the Optic Nerve
Segment Intraocular Optic disc Pre-laminar Laminar Intraorbital Intracanalicular Length (mm) 1.0 Diameter (mm) Blood Supply Retinal arterioles 1.5X1.75
Branches of posterior ciliary arteries
25 4-10
3-4
Intraneural branches of central retinal artery; pial branches from CRA and choroid Ophthalmic artery
Intracranial
10
4-7
Branches of internal carotid and ophthalmic artery
Internal carotic artery Ophthalmic artery 7 anterior ciliary a. (ACA) (4 rectus m., anterior segment) 20 short posterior ciliary a. (SPCA) (choroid, outer 1/3 retina, anterior segment) 2 long posterior ciliary a. (LPCA) (the same as above) 1 central retinal a. 4 branches (inner 2/3 retina)
Optic Optic Optic Optic
sulcus pit vesicle cup
Lens placode Lens vesicle
Derivatives of Embryonic Tissues
Neuroectoderm
Neurosensary retina Retinal pigment epithelium Pigmented ciliary epithelium Non-pigmented ciliary epithelium Sphincter and dilator muscles of iris Optic nerve, axons and glia Vitreous Corneal stroma and endothelium Sclera Trabecular meshwork Sheaths and tendons of extraocular muscles Connective tissues of iris Ciliary muscles Choroidal stroma Melanocytes (uveal and epithelial) Meningeal sheaths of the optic nerve Schwann cells of cliary nerves Ciliary ganglion Cartilage Connective tissues of orbit
Surface Ectoderm
Epithelium, glands, cilia of skin of eyelids and carnucle Conjunctival epithelium Lens Lacrimal gland Lacrimal drainage system Vitreous
Neural Crest Cells
Mesoderm
Fibers of extraocular muscles Endothelial lining of all orbital and ocular blood vessels Temporal portion of sclera Vitreous
You might also like
- Visual and Lacrimal AppratusDocument45 pagesVisual and Lacrimal AppratusAzman Bin KadirNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology V Eye Anatomy and FunctionDocument45 pagesOphthalmology V Eye Anatomy and FunctionEndale AschenakiNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 2Document235 pagesOphthalmology 2yididiyagirma30No ratings yet
- Yoga & Eye - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument73 pagesYoga & Eye - Anatomy and Physiologysachi sharma0% (1)
- ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF THE EYEDocument70 pagesANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF THE EYEArif MohammadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument73 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeMea ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Kuliah RO - Basic Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument76 pagesKuliah RO - Basic Anatomy & PhysiologySi LynNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeBalkos 61No ratings yet
- Ocular Anatomy OverviewDocument89 pagesOcular Anatomy OverviewFikri M Asgar SNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument48 pagesThe Eyezyrine jhen100% (1)
- Gross Eye AnatomyDocument48 pagesGross Eye AnatomyAzizan Hanny100% (1)
- 1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesDocument124 pages1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesSMEY204100% (1)
- Introduction To Ophthalmology: by DR - Bakhtiar Q. JafDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Ophthalmology: by DR - Bakhtiar Q. JafChristian JaraNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: INNER EYEDocument71 pagesANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: INNER EYEGermanyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument72 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeYerke NurlybekNo ratings yet
- Full Anatomy CoassDocument74 pagesFull Anatomy CoassKartikaSariNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 3 Classes Objects 1. Master The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2. Relationship With Clinical DiseasesDocument181 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 3 Classes Objects 1. Master The Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2. Relationship With Clinical DiseasessanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sashwat Ray IsmDocument98 pagesDr. Sashwat Ray IsmCastleKGNo ratings yet
- Eyes and Vision AnatomyDocument50 pagesEyes and Vision AnatomyNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Eyes and Vision PresentationDocument142 pagesEyes and Vision Presentationrhimineecat71100% (1)
- Physiology of The Eye: Bagian Ilmu Kesehatan Mata FK UnhasDocument59 pagesPhysiology of The Eye: Bagian Ilmu Kesehatan Mata FK UnhasimelNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Part 2 (Eye)Document64 pagesSpecial Senses Part 2 (Eye)rizwanbasNo ratings yet
- Glossary of termsDocument6 pagesGlossary of termsAlberto Ybañez CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 1 PENGINDRAAN C2Document113 pagesPemicu 1 PENGINDRAAN C2CcNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument28 pagesEmbryologyKamleshwari RenganathanNo ratings yet
- Organon Visuum: Tri Indah Winarni, MD, PHD Anatomy Dept. Faculty of Medicine Diponegoro UniversityDocument46 pagesOrganon Visuum: Tri Indah Winarni, MD, PHD Anatomy Dept. Faculty of Medicine Diponegoro UniversityLailatuz ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Organon Visuum: Tri Indah Winarni, MD, PHD Anatomy Dept. Faculty of Medicine Diponegoro UniversityDocument46 pagesOrganon Visuum: Tri Indah Winarni, MD, PHD Anatomy Dept. Faculty of Medicine Diponegoro UniversityLailatuz ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Full Anatomy CoassDocument74 pagesFull Anatomy CoassAuliaRusdiAllmuttaqienNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear HistologyDocument96 pagesEye and Ear HistologyErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (1)
- ORGAN OF VISION. Clinical Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture by M. Bezugly MD, PH.D.)Document9 pagesORGAN OF VISION. Clinical Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture by M. Bezugly MD, PH.D.)Azra AzmunaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the EyeDocument37 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the EyeRajakannan60% (5)
- Anatomy&Physiology.eye สอน นศพ. 2Document77 pagesAnatomy&Physiology.eye สอน นศพ. 2ณัช เกษมNo ratings yet
- Anatomi dan Fisiologi MataDocument91 pagesAnatomi dan Fisiologi Mataanacay87100% (1)
- EyeballDocument14 pagesEyeballMirko BelanNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument32 pagesHuman Eyekaruparthi sripravallikaNo ratings yet
- Examination of The EyeDocument16 pagesExamination of The EyeRoxana SurliuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeBryan Espanol100% (1)
- Anatomy of The EyeDocument15 pagesAnatomy of The EyeZeljko TomicNo ratings yet
- EyeDocument50 pagesEyedavid100% (1)
- On EyeDocument19 pagesOn Eyesazzad suvroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Visual System April 2014Document41 pagesAnatomy Physiology Visual System April 2014levianaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-physiology Eyeball 2023Document75 pagesAnatomy-physiology Eyeball 2023debdeepbhattacharya411No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahDocument36 pagesAnatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahRida ShahNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Embriologi Mata: Setia PepetDocument31 pagesAnatomi Dan Embriologi Mata: Setia PepetDi Hati Alonelly SetiaPepetNo ratings yet
- Faal PenglihatanDocument87 pagesFaal PenglihatanObet Agung 天No ratings yet
- K1 Anatomi Mata - 2017Document63 pagesK1 Anatomi Mata - 2017akuNo ratings yet
- 2014 16.visual OrganDocument28 pages2014 16.visual OrganPascal TurksonNo ratings yet
- PhotopicDocument10 pagesPhotopicVivian AmosNo ratings yet
- Special Sense EYEDocument74 pagesSpecial Sense EYEprekshya shresthaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Human EyeDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Human EyeMaryy Basilio100% (2)
- Anatomy of External EyeDocument39 pagesAnatomy of External EyeUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- FK Unissula 2010: Feat. Anatomy LaboratoryDocument48 pagesFK Unissula 2010: Feat. Anatomy LaboratoryTeguh PambudiNo ratings yet
- Embryo EyeDocument25 pagesEmbryo EyeMarera DomnicNo ratings yet
- B & C, Vol-12 PDFDocument4 pagesB & C, Vol-12 PDFKiran RmvNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Optic Nerve: B.Optometry, Maharajgunj Medical Campus, Institute of Medicine, T.U. NepalDocument84 pagesAnatomy of Optic Nerve: B.Optometry, Maharajgunj Medical Campus, Institute of Medicine, T.U. Nepalsafasayed100% (1)
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- Suprachoroidal Space InterventionsFrom EverandSuprachoroidal Space InterventionsShohista SaidkasimovaNo ratings yet