Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Robin Grayson Gold Recovery Method02
Uploaded by
oskar0706Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Robin Grayson Gold Recovery Method02
Uploaded by
oskar0706Copyright:
Available Formats
World Placer Journal 2007, Volume 7, pages 66-161.
2: Cyanide chemical leaching of gold
www.mine.mn
Operation
The sodium cyanide (NaCN) is either in a dry solid or liquid form, sourced from specialised manufacturers. 1st stage leaching gold into solution A weak cyanide solution is prepared, usually 0.020.05%, and must be kept strongly alkaline (pH 10-11). Cyanide leaching can be by different methods:
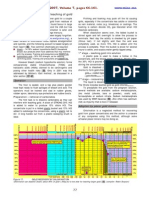
A Chinese operation near Zuunkharaa in north Mongolia, leaching fine gold from mercury-laden tailings of edge mills. (photo: Jrgen Hartwig of Projekt-Consult)
Figure 15.
CYANIDE LEACHING
Cyanide leaching has been used to recover gold since the 1890s but only since the 1960s with the advent of heap leaching has cyanide become the method-of-choice for leaching gold from milled hardrock, and has potential for leaching gold from placer concentrates. Cyanidation uses a very weak cyanide solution to dissolve (leach) fine gold into solution, and then precipitates it as easy-to-recover gold. It leaches gold that due to flatness, small size or attached quartz is lost by simple gravitational devices or mercury. Cyanide has risks if handled carelessly or gains access to streams or wells. The cyanide solution must be kept strongly alkaline to prevent the generation of highly toxic hydrogen cyanide gas. A problem is cyanide vapour rising from ponds. Such concerns have triggered the gold industry to seek cost-effective alternatives [32] Coarse gold typical of most placers takes too long to leach. Marcello Veiga noted that for a 0.21mm gold particle to dissolve in cyanide took over 60 hours!
percolation leaching very weak cyanide solution percolates down through a vat of concentrate. Commonly used for ground hardrock ore, but also successful in tests on placer gold concentrates in Alaska by Cleland Conwell [33]; agitated leaching very weak cyanide solution is added to vats that are agitated by paddles or by blowing in compressed air to keep the material in suspension; and heap leaching very weak cyanide solution percolates down through crushed/milled ore heaped in a heap basin lined with leach-proof materials e.g. clay, asphalt or tarpaulin.
2nd stage recovering gold from solution Having leached the gold and dissolved it into solution as gold cyanide complexaqueous, the solid gold is recovered by a choice of methods, such as traditional methods tested on placer gold concentrates in Alaska [33]:
absorption by activated carbon 99.85% Au recovery; absorption by ion-exchange resin 96.31% Au recovery; or precipitation by zinc dust 99% recovery.
The zinc dust method, as typified by the Merill-Crowe process, first removes oxygen from the cyanide solution and then mixes in a fine zinc powder and recovers the fine gold precipitate (<50) on a precoat filter.
Adoption by placer gold miners
The author is unaware of the cyanide leaching being used at large-scale placer gold mines. Yet for small-scale and artisanal mining, cyanide leaching is now widespread for hardrock ores and difficult lateritic ores in Peru, Ecuador, Columbia, Brazil, Philippines and China.
Figure 16.
GOLD RECOVERY BY CYANIDE LEACHING
Cyanide can dissolve (leach) >90% of very fine gold, but is too slow for leaching larger gold. [22] (compiler: Robin Grayson)
76
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Orch Johnstone WHSquire Tarantella ORCH CELLODocument8 pagesOrch Johnstone WHSquire Tarantella ORCH CELLOoskar0706No ratings yet
- Robin Grayson Gold Recovery Method06Document1 pageRobin Grayson Gold Recovery Method06oskar0706No ratings yet
- 695-714 - Rumpold Recycling of Platinum Group Metals From Automotive Catalysts by An Acidic Leaching ProcessDocument20 pages695-714 - Rumpold Recycling of Platinum Group Metals From Automotive Catalysts by An Acidic Leaching Processoskar0706No ratings yet
- Met - 52!2!267 - 270 - Saternus Possible Ways of Refining Precious Group Metals (PGM) Obtained From Recycling of The Used Auto Catalytic ConvertersDocument4 pagesMet - 52!2!267 - 270 - Saternus Possible Ways of Refining Precious Group Metals (PGM) Obtained From Recycling of The Used Auto Catalytic Convertersoskar0706No ratings yet
- Bromine Leaching GoldDocument1 pageBromine Leaching GoldSteven TremolNo ratings yet
- Robin Grayson Gold Recovery Method07Document1 pageRobin Grayson Gold Recovery Method07oskar0706No ratings yet
- Continuous Extrusion of Recovered Ultra-HighDocument6 pagesContinuous Extrusion of Recovered Ultra-Highoskar0706No ratings yet
- Robin Grayson Gold Recovery Method03Document1 pageRobin Grayson Gold Recovery Method03oskar0706No ratings yet
- Robin Grayson Gold Recovery Method01Document1 pageRobin Grayson Gold Recovery Method01oskar0706No ratings yet
- WPJ3 2 Cutting Costs in Placer Gold MiningDocument4 pagesWPJ3 2 Cutting Costs in Placer Gold Miningoskar0706No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Plate Tectonics LessonDocument3 pagesPlate Tectonics LessonChristy P. Adalim100% (2)
- Industrial/Organi Zational Psychology: Alday, Angeli Camille M. - 2P2Document51 pagesIndustrial/Organi Zational Psychology: Alday, Angeli Camille M. - 2P2SteffanyNo ratings yet
- To Be African or Not To Be: An Autoethnographic Content Analysis of The Works of Dr. Asa Grant Hilliard, III (Nana Baffour Amankwatia, II) - by Qiana M. CuttsDocument283 pagesTo Be African or Not To Be: An Autoethnographic Content Analysis of The Works of Dr. Asa Grant Hilliard, III (Nana Baffour Amankwatia, II) - by Qiana M. Cutts☥ The Drop Squad Public Library ☥100% (1)
- Wilo Mather and Platt Pumps Pvt. LTD.: Technical DatasheetDocument2 pagesWilo Mather and Platt Pumps Pvt. LTD.: Technical DatasheetTrung Trần MinhNo ratings yet
- Hireena Essay AnsDocument2 pagesHireena Essay AnsTasniiem ChandraaNo ratings yet
- MRP Format MbaDocument6 pagesMRP Format Mbasankshep panchalNo ratings yet
- Public Speaking Skills for Career SuccessDocument7 pagesPublic Speaking Skills for Career SuccessAnish John100% (1)
- 4PW16741-1 B EKBT - Bufftertank - Installation Manuals - EnglishDocument6 pages4PW16741-1 B EKBT - Bufftertank - Installation Manuals - EnglishBernard GaterNo ratings yet
- JNTUA Mechanical Engineering (R09) Syllabus BookDocument147 pagesJNTUA Mechanical Engineering (R09) Syllabus Bookslv_prasaad0% (1)
- G10 - Math - Q1 - Module 7 Grade 10Document12 pagesG10 - Math - Q1 - Module 7 Grade 10Shua HongNo ratings yet
- Advisory Circular: Aircraft Maintenance Engineer Licence - Examination Subject 2 Aircraft Engineering KnowledgeDocument44 pagesAdvisory Circular: Aircraft Maintenance Engineer Licence - Examination Subject 2 Aircraft Engineering KnowledgejashkahhNo ratings yet
- Advancements in Organic Rankine Cycle System Optimisation For Combined Heat and Power Applications Components Sizing and Thermoeconomic ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesAdvancements in Organic Rankine Cycle System Optimisation For Combined Heat and Power Applications Components Sizing and Thermoeconomic ConsiderationsGuadalupe Abigail Rueda AguileraNo ratings yet
- Land Equivalent Ratio, Growth, Yield and Yield Components Response of Mono-Cropped vs. Inter-Cropped Common Bean and Maize With and Without Compost ApplicationDocument10 pagesLand Equivalent Ratio, Growth, Yield and Yield Components Response of Mono-Cropped vs. Inter-Cropped Common Bean and Maize With and Without Compost ApplicationsardinetaNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The LearnerDocument23 pagesThe Teacher and The LearnerUnique Alegarbes Labra-SajolNo ratings yet
- X32 Digital Mixer: Quick Start GuideDocument28 pagesX32 Digital Mixer: Quick Start GuideJordán AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Hci01 HumanComputerInteraction OverviewDocument140 pagesHci01 HumanComputerInteraction OverviewAlexSpiridonNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Manifesting Money Blueprint by Sonia RicottiDocument34 pagesThe Ultimate Manifesting Money Blueprint by Sonia RicottiViolet VioletNo ratings yet
- Inbound 8511313797200267098Document10 pagesInbound 8511313797200267098phan42No ratings yet
- Bronchogenic CarcinomaDocument13 pagesBronchogenic Carcinomaloresita_rebongNo ratings yet
- BH Tif03Document21 pagesBH Tif03Andres R. OlguinNo ratings yet
- 4439 Chap01Document28 pages4439 Chap01bouthaina otNo ratings yet
- MarasiNews Issue 12Document47 pagesMarasiNews Issue 12Sunil Kumar P GNo ratings yet
- Captive Screws - Cap Head: Hex. SocketDocument5 pagesCaptive Screws - Cap Head: Hex. SocketvikeshmNo ratings yet
- Ti 1000 0200 - enDocument2 pagesTi 1000 0200 - enJamil AhmedNo ratings yet
- MIL (Second Quarter)Document13 pagesMIL (Second Quarter)Menma ChanNo ratings yet
- NotesTransl 108 (1985) Larsen, Who Is This GenerationDocument20 pagesNotesTransl 108 (1985) Larsen, Who Is This GenerationluzuNo ratings yet
- Female and Male Hacker Conferences Attendees: Their Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) Scores and Self-Reported Adulthood ExperiencesDocument25 pagesFemale and Male Hacker Conferences Attendees: Their Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) Scores and Self-Reported Adulthood Experiencesanon_9874302No ratings yet
- Black BeautyDocument70 pagesBlack BeautyMeryem DevirgenNo ratings yet
- Cave Rescue ActivityDocument6 pagesCave Rescue Activityshweta bambuwalaNo ratings yet
- Estimating PSCC for Electrical InstallationsDocument2 pagesEstimating PSCC for Electrical InstallationsgmuitaNo ratings yet