Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Encryption?: Applies To Windows 7
Uploaded by
Sibin GopOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Encryption?: Applies To Windows 7
Uploaded by
Sibin GopCopyright:
Available Formats
What is encryption?
Applies to Windows 7
Encryption is a way to enhance the security of a message or file by scrambling the contents so that it can be read only by someone who has the right encryption key to unscramble it. For example, if you purchase something from a website, the information for the transaction (such as your address, phone number, and credit card number) is usually encrypted to help keep it safe. Use encryption when you want a strong level of protection for your information.
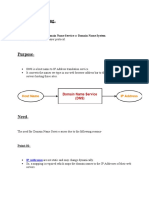
DFS allows administrators to make it easier for users to access and manage file that are physically distributed across a network. With DFS, you can make files distributed across multiple servers. It may appear for users that files actually reside in one place (computer) on the network. Benefits of DFS 1. Easily access: Users need not remember multiple locations form where they get data just by remembering one location they get access to the data. 2. Fall tolerance: For master DFS server we can have a replica (Target) on another DFS server. With the master DFS server face users can still continue accessing the data from back up DFS (Target) There is no interruption to accessing data. 3. Load balancing: If all the DFS root servers and targets are working fine it leads to load balancing. This is achieved by specifying locations for separate users. 4. Security: We can implement security by using NTFS settings. DFS Terminology: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. DFS root DFS links DFS targets Domain DFS root Stand alone DFS root
Domain DFS root: It is a server configurable in the domain and offers fall tolerance and load balancing. It is a root server, which maintains links from other file servers Requirements: DC or Member Server Stand-alone DFS root: It is configurable work group model and does not provide fall tolerance &load balancing DFS root: DFS root is the beginning of a hierarchy of DFS links that points to shared folders. DFS link: A link from a DFS root to one or more shared file or folders. Targets: The mapping destination of a DFS root or links, which corresponds to a physical folder that has been shared. Implementation of DFS Creating a DFS root: On DC Create a folder in any drive Share it Give everyone full control Use the folder name as DFS root Create 2 more folders for links Share them & everyone full control Start >p>admin tools>DFS Right click on DFS New root Select domain root Domain name Browse the server DC Next mention the root name Browse the folder to share Next finish. Implementing DFS links On DC Create 2 folders. Share them & give full control permission
On Member Server also same process On DC Start > P>Admin tools>DFS>right click on DFS New link Link name (e.g. Germany) Browse the share folder from DC Ok Create all four links two from DC & two from member server Accessing the resources (links): Either on DC or member server \\domain name\DFS root name ex: \\zoom.com\DFS root Implementing of DFS target: On Dc Open DFs Right click on DFs root Select new root target Browse server name >next Browse folder to share Next>finish Replication: After configuring the target we can configure the replication between DFS root and DFS target. And this can be scheduled. Types of replication topologies: Ring topology Hub & spoke topology Mesh topology Configuring replication between DFS root & target. On DC Open DFS Right click on the DFS root Configure replication>next Select topology Finish
You might also like
- Using Microsoft DFS For FailoverDocument10 pagesUsing Microsoft DFS For FailoverVinay Kumar ChandriNo ratings yet
- Microsoft DFS For FailoverDocument8 pagesMicrosoft DFS For FailoverBoss MassNo ratings yet
- What Is DFS?: in This SectionDocument4 pagesWhat Is DFS?: in This Sectionmyname2050No ratings yet
- How DFS Works - Remote File SystemsDocument55 pagesHow DFS Works - Remote File SystemsDayakar MeruguNo ratings yet
- DFCDocument6 pagesDFCBhupendra Kumar DadsenaNo ratings yet
- DFS in Simple TermsDocument13 pagesDFS in Simple Termssudhi12345No ratings yet
- Distributed File SystemDocument5 pagesDistributed File SystemHarsh NebhwaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture13 15319 MHH 27feb 2012Document30 pagesLecture13 15319 MHH 27feb 2012Anthony Yueh Grsy CaNo ratings yet
- Can DFS Replication Communicate With FRSDocument29 pagesCan DFS Replication Communicate With FRSBhupendra Kumar DadsenaNo ratings yet
- 2distributed File System DfsDocument21 pages2distributed File System DfsNUREDIN KEDIRNo ratings yet
- Step-By-Step Guide To Distributed File System (DFS) : Top of PageDocument7 pagesStep-By-Step Guide To Distributed File System (DFS) : Top of Pageapi-26365311No ratings yet
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 - Administration: File Services and EncryptionDocument69 pagesMicrosoft Windows Server 2012 R2 - Administration: File Services and EncryptionAnonymous NeRBrZyAUbNo ratings yet
- How To Install An Linux or UnixDocument8 pagesHow To Install An Linux or UnixSimranjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Distributed File SystemDocument12 pagesUnit 3: Distributed File SystemLakshya RuhelaNo ratings yet
- Staging Folders and Conflict and Deleted FoldersDocument2 pagesStaging Folders and Conflict and Deleted FoldersVijeth RaiNo ratings yet
- Distributed File Systems-2Document4 pagesDistributed File Systems-2onele mabhenaNo ratings yet
- Can I Change/redefine The Attributes? 2003 Security FesturesDocument7 pagesCan I Change/redefine The Attributes? 2003 Security FesturesSiddaraju RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Network File System (NFS) : Tom Rhodes Bill SwingleDocument5 pagesNetwork File System (NFS) : Tom Rhodes Bill SwingleAbul HayatNo ratings yet
- Distributed File SystemsDocument107 pagesDistributed File SystemsSudha PatelNo ratings yet
- DFS BasicsDocument3 pagesDFS BasicsRaja Mohammed ANo ratings yet
- Topik 4Document71 pagesTopik 4Anita SupramaniamNo ratings yet
- DFS Solution in Microsoft Windows Server 2003 R2Document9 pagesDFS Solution in Microsoft Windows Server 2003 R2ragmynNo ratings yet
- 8 06072873 Sec Real DFSDocument6 pages8 06072873 Sec Real DFSvikasbhowateNo ratings yet
- Interview QuesionsDocument47 pagesInterview Quesionsapi-3716933No ratings yet
- DS UNIT-4 Saqs Laqs (Completed)Document14 pagesDS UNIT-4 Saqs Laqs (Completed)siddumudavath93No ratings yet
- Hadoop Administration Interview Questions and Answers For 2022Document6 pagesHadoop Administration Interview Questions and Answers For 2022sahil naghateNo ratings yet
- Distributed File SystemsDocument46 pagesDistributed File SystemsFrank OyugiNo ratings yet
- Protocols-Domain Name System (DNS)Document22 pagesProtocols-Domain Name System (DNS)Ali AbdNo ratings yet
- What Is A Distributed File System?: Dfs Has Two Important GoalsDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Distributed File System?: Dfs Has Two Important GoalsWeeb Coder 404No ratings yet
- DFS, HDFS, Architecture, Scaling ProblemDocument32 pagesDFS, HDFS, Architecture, Scaling Problemsaif salahNo ratings yet
- DC EXP8-1Document5 pagesDC EXP8-1anooja wadeNo ratings yet
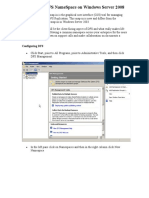
- Configure A Dfs Namespace On Windows Server 2008Document12 pagesConfigure A Dfs Namespace On Windows Server 2008Cristian StanNo ratings yet
- Distributed File SystemsDocument8 pagesDistributed File SystemsE KARANINo ratings yet
- Unit-V: Dns-Domain Name SpaceDocument33 pagesUnit-V: Dns-Domain Name SpaceMr.T.Vijayakumar Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- DFS Technical RefferenceDocument59 pagesDFS Technical Refferenceapi-3716933No ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Frs-SonarDocument83 pagesTroubleshooting Frs-SonartubaidadaNo ratings yet
- Distributed File System ImplementationDocument30 pagesDistributed File System ImplementationRajat Aggarwal100% (1)
- Name Server Operations Guide For: Release 4.9.3 Releases From 4.9Document29 pagesName Server Operations Guide For: Release 4.9.3 Releases From 4.9Donny ArieffianNo ratings yet
- Active Directory: FMSO RolesDocument12 pagesActive Directory: FMSO Rolessmile2me2012No ratings yet
- Network Solution ProposalDocument10 pagesNetwork Solution ProposalInfiniziNo ratings yet
- Distributed File SystemDocument6 pagesDistributed File SystemDimitrov GudipudiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document104 pagesUnit 4nosopa5904No ratings yet
- AD Interview QuestionsDocument16 pagesAD Interview QuestionsMohammed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Windows Server 2003 Active Directory and Security Questions: February 3, 2010Document28 pagesWindows Server 2003 Active Directory and Security Questions: February 3, 2010Mohammed RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Rohini 65577954848Document7 pagesRohini 65577954848nareshkushwahaNo ratings yet
- Active DirectoryDocument7 pagesActive DirectoryGauriNo ratings yet
- 70-411 R2 Test Bank Lesson 04Document12 pages70-411 R2 Test Bank Lesson 04Mazaher MohamedaliNo ratings yet
- NfsDocument15 pagesNfsmohamad amin Rastgoo100% (2)
- DFS Configuration GuideDocument9 pagesDFS Configuration Guideprabhakar prabhaNo ratings yet
- DNS in NetworkingDocument45 pagesDNS in NetworkingzekariasNo ratings yet
- Windows Admin InterviewDocument24 pagesWindows Admin Interviewsagarika Mane100% (1)
- M.C.I.T.P L2 InterView QuestionsDocument8 pagesM.C.I.T.P L2 InterView QuestionsShaik Ashwaq JavedNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM (DNS) Part 1Document22 pagesLecture2 DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM (DNS) Part 1Kas7W 5kNo ratings yet
- ClouddafinalDocument8 pagesClouddafinalRahithya AmbarapuNo ratings yet
- ClouddaDocument8 pagesClouddaRahithya AmbarapuNo ratings yet
- DfsDocument5 pagesDfsasegunloluNo ratings yet
- BIND 9 Administrator Reference Manual: November 4, 2005Document79 pagesBIND 9 Administrator Reference Manual: November 4, 2005Eric Cofré SánchezNo ratings yet
- 1) Discuss The Design of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and Concept in DetailDocument11 pages1) Discuss The Design of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and Concept in DetailMudit KumarNo ratings yet
- Distributed File SystemDocument43 pagesDistributed File SystemDefendersNo ratings yet
- Week1 QuizDocument7 pagesWeek1 QuizKrishna EelaNo ratings yet
- Thermo Sample ProblemsDocument5 pagesThermo Sample ProblemsDeniel AndalNo ratings yet
- 036 Siga-UmDocument6 pages036 Siga-UmzezohomeNo ratings yet
- The Refining Industry in IraqDocument29 pagesThe Refining Industry in Iraqanwar alamNo ratings yet
- Power Xpert Power Quality Meters: Product FocusDocument20 pagesPower Xpert Power Quality Meters: Product FocusMike MendozaNo ratings yet
- HDSD may cắt hàn màng nhiệtDocument20 pagesHDSD may cắt hàn màng nhiệtsetavietnamNo ratings yet
- Casagrande Lecture Recommended Practice For Soft Ground Site Characterization Ladd and de GrootDocument60 pagesCasagrande Lecture Recommended Practice For Soft Ground Site Characterization Ladd and de GrootPavlos VardoulakisNo ratings yet
- Assembly Language 8086 Exercise Solution (Marut) PDFDocument58 pagesAssembly Language 8086 Exercise Solution (Marut) PDFShaibal Ahmed56% (9)
- Open Channel FlowDocument14 pagesOpen Channel FlowHijab Renjana100% (1)
- Damco Cambodia Corporate BrochureDocument9 pagesDamco Cambodia Corporate BrochureSok HengNo ratings yet
- Dimethylamine PDFDocument2 pagesDimethylamine PDFangelofgloryNo ratings yet
- TR5010 1Document2 pagesTR5010 1Yellow FalconNo ratings yet
- BMW HUD Factory SchematicDocument4 pagesBMW HUD Factory SchematicGreg Wade100% (1)
- Territory ManagementDocument52 pagesTerritory ManagementAjay Tyagi100% (1)
- Hydro Static Interlocks and Pins in Lifeboat Hook SystemsDocument2 pagesHydro Static Interlocks and Pins in Lifeboat Hook Systemsdwad82No ratings yet
- EIA/TIA 568A Wiring Standard EIA/TIA 568B Wiring StandardDocument3 pagesEIA/TIA 568A Wiring Standard EIA/TIA 568B Wiring Standardavnish100No ratings yet
- The Chengdu Jian-20Document20 pagesThe Chengdu Jian-20Cat CrysisNo ratings yet
- Inventory Database - All Parts Inc (8/20/20)Document2,835 pagesInventory Database - All Parts Inc (8/20/20)All Parts Inc.No ratings yet
- Hana UpgradeDocument10 pagesHana Upgradevasu srinuNo ratings yet
- Signaling in RE AreaDocument30 pagesSignaling in RE AreaVikas Srivastav93% (15)
- CONTENTSDocument9 pagesCONTENTSESRANo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani Practice School Division Session 2018 PSI Assignment HandoutDocument3 pagesBirla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani Practice School Division Session 2018 PSI Assignment Handouttarun chauhanNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Retaining WallsDocument38 pagesDesign and Analysis of Retaining WallsMohamed MuayidNo ratings yet
- HVAC Dampers Installation Method StatementDocument3 pagesHVAC Dampers Installation Method StatementDong VanraNo ratings yet
- 3M Festool Catalog - 60-4402-7925-9Document25 pages3M Festool Catalog - 60-4402-7925-9Kaled VásquezNo ratings yet
- C Library Math.h Functions - GeeksforGeeksDocument11 pagesC Library Math.h Functions - GeeksforGeeksSoumadip Banerjee100% (1)
- Primavera Manual PDFDocument445 pagesPrimavera Manual PDFsajeevNo ratings yet
- Allpile ManualDocument103 pagesAllpile ManualKang Mas WiralodraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Placement Chemistry: 1991 Free Response QuestionsDocument15 pagesAdvanced Placement Chemistry: 1991 Free Response QuestionsManasNo ratings yet
- Alternative Binder Systems For Lower Carbon Concrete Code of PracticeDocument8 pagesAlternative Binder Systems For Lower Carbon Concrete Code of Practicezaidiamna9No ratings yet
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsFrom EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleFrom EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Dark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersFrom EverandDark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Fusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureFrom EverandFusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureNo ratings yet
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsFrom EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Kali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionFrom EverandKali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Starting Database Administration: Oracle DBAFrom EverandStarting Database Administration: Oracle DBARating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- RHCSA Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (EX200), Third EditionFrom EverandRHCSA Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (EX200), Third EditionNo ratings yet
- Optimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesFrom EverandOptimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesNo ratings yet
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]From EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLFrom EverandSQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- Linux For Beginners: The Comprehensive Guide To Learning Linux Operating System And Mastering Linux Command Line Like A ProFrom EverandLinux For Beginners: The Comprehensive Guide To Learning Linux Operating System And Mastering Linux Command Line Like A ProNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveFrom EverandBusiness Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Excel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1From EverandExcel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Hacking : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Ethical HackingFrom EverandHacking : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Ethical HackingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)






































































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1714829744?v=1)













