Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Title I Termination OF Employment Art 279. Security of Tenure
Uploaded by
sweetlunacy00Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Title I Termination OF Employment Art 279. Security of Tenure
Uploaded by
sweetlunacy00Copyright:
Available Formats
TITLE I TERMINATION OF EMPLOYMENT ART 279.
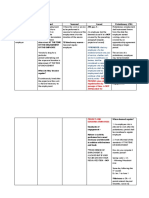
. SECURITY OF TENURE SECURITY OF TENURE is the constitutional right granted the employee, that the employer shall not terminate the services of an employee except for just cause or when authorized by law. An employee that has been dismissed illegally is entitled to: a. Reinstatement b. Backwages ART 280. REGULAR AND CASUAL EMPLOYMENT REGULAR EMPLOYMENT- One wherein an employee is engaged to perform activities which are usually necessary or desirable in the usual business or trade of the employer. TEMPORARY EMPLOYMENT-One wherein an employee is engaged to work on a specific project or undertaking which is usually necessary or desirable in the usual business or trade of the employer, the completion of which has been determined at the time of the agreement of the employee. SEASONAL EMPLOYMENT-One wherein an employee is engaged to work during a particular season on an activity that is usually necessary or desirable in the usual business or trade of the employer. PROBATIONARY PERIOD OF EMPLOYMENT - the period needed to determine the fitness for the job, i .e., the time needed to learn the job. It is period during which the employer may determine if the employee is qualified for possible inclusion in the regular force. NOTE: The standard which the probationary employee is to meet must be made known by the employer to the employee at the time of the engagement. Probationary employees may be terminated for the same causes as a regular employee, except that there is an additional ground failure to meet the standard. Is it necessary that probationary employment be for a period of 6 months? No. Provided that the following requisites concur: it is done before the lapse of 6 months;
2.employee must be advised of such extension; 3. employee must agree. EFFECT IF PROBATIONARY EMPLOYEE IS ALLOWED TO WORK BEYOND 6 MONTHS: If the probationary employee is allowed to work beyond the period of 6 months or the agreed probationary period, said employee become a regular employee by operation of law. Under the Labor Code, an employee who is allowed to work after a probationary period shall be considered a regular employee. (Art. 281.) ART. 282. TERMINATION BY EMPOYER JUST CAUSES: 1. Serious misconduct or willful disobedience by the employee of the lawful orders of his employer or representative in connection with his work; 2. Gross and habitual neglect by the employee of his duties; 3. Fraud or willful breach by the employee of the trust reposed in him by his employer or duly organized representative; 4. Commission of a crime or offense by the employee against the person of his employer or any immediate member of his family or his duly authorized representative; and 5. Other causes analogous to the following: ART. 283- 284 AUTHORIZED CAUSES OF TERMINATION BY THE EMPLOYER: 1. The installation of labor-saving devices (automation) 2. Redundancy (superfluity in the performance of a particular work) 3. Redundancy to prevent losses (there is excess of employees and employer wants to prevent financial losses) 4. The closing or cessation of operation of the establishment or undertaking UNLESS the closing is for the purpose of circumventing the provisions of the Labor Code. 5. Illness a. If illness is incurable within 6 months and is b. deleterious to his health or his co-employees. c. certification from public heath officer that illness is incurable within 6 months. STANDARDS UNDER WHICH AN EMPLOYER MAY RETRENCH: 1. Losses expected should be imminent and substantial.
2.It must be reasonably necessary and likely to effectively prevent the expected losses 3. Alleged losses if already incurred, and the expected imminent losses sought to be forestalled, must be proved by sufficient and convincing evidence. ART. 285. TERMINATION BY EMPLOYEE TERMINATION BY THE EMPLOYEE An employee may terminate WITHOUT JUST CAUSE the employeeemployer relationship by serving a WRITTEN NOTICE on the employer at least one month in advance. . The employer upon whom no such notice was served may hold the employee liable for damages. An employee may put an end to establish WITHOUT SERVING ANY NOTICE on the employer for any of the following just causes: 1. Serious insult by the employer or his representative on the hour and person of the employee; 2. Inhuman and unbearable treatment accorded the employee by the employer or his representative; 3. Commission of a crime or offense by the employer or his representative against the person of the employee or any of the immediate members of his family; and 4. Other causes analogous to any of the foregoing. SEPARATION PAY In case of termination due to a) THE INSTALLATION OF LABOR-SAVING DEVICES OF b) REDUNDANCY, - the worker affected thereby shall be entitled to a separation pay equivalent to at least one (1) month pay or to at least one (1) month pay for every year of service, whichever is higher. c) RETRENCHMENT TO PREVENT LOSSES and CLOSURES OR CESSATION OF OPERATIONS (NOT due to serious business losses or financial reverses) - The separation pay shall be equivalent to one (1) month pay or at least month pay for every year of service, whichever is higher. d) In the case of ILLNESS - separation pay equivalent to at least one month salary or to month salary for every year of service, whichever is greater, a fraction of at least 6 months shall be considered one (1) whole year. NOTE: If CLOSURE is due to severe financial losses, it is still debatable whether or not separation pay should be given.
I f you are able to prove that such portion of capital (10%) investment has been impaired, the employer should be exempt for the payment of separation pay.
GUIDELINES TO DETERMINE THE VALIDITY OF TERMINATION: 1. Gravity of the offence 2. Position occupied by the employee 3. Degree of damage to the employer 4. Previous infractions of the same offense 5. Length of service ART 287. RETIREMENT RETIREMENT AGE -The age of retirement is that specified in the CBA or in the employment contract. If it is not specified, 1. 60-65 -retirement is optional but the employee must have served at least 5 years ; 2. 65-compulsory retirement age (no need for 5 years of service)
BENEFITSA retiree is entitled to a retirement pay equivalent at least month salary for every year of service, a fraction of at least six (6) months being considered as one whole year. Unless the parties provide for broader inclusions, the term one half (1/2) month salary shall mean: 15 days plus 1/12 of the 13th month pay and the cash equivalent of NOT more than 5 days of service incentive leaves. (22.5 days per year of service) NOTE: Exempted from the payment of retirement pay are retail, service and agricultural establishments or operations employing NOT more than ten (10) employees or workers. BOOK SEVEN TRANSITORY AND FINAL PROVISIONS TITLE II PRESCRIPTION OF OFFENSES AND CLAIMS ART. 291. MONEY CLAIMS PERIODS OF PRESCRIPTION
A. MONEY CLAIMS-The prescriptive period is 3 years from the accrual of the cause of action. B. ULP -The prescriptive period of filing a case for ULP is 1 year from the accrual of the cause of action. ILLEGAL DISMISSAL The prescriptive period of filing a case for illegal dismissal is 4 years from the accrual of the cause of action. (Art. 1146) NOTE: The period of prescription mentioned under Article 281, now Article 292, of the Labor Code, refers to and is limited to money claims, all other cases of injury to rights of a workingman being governed by the Civil Code. Hence, reinstatement prescribes in 4 years. POST- EMPLOYMENT FORMS OF REINSTATEMENT: 1. ACTUAL OR PHYSICAL REINSTATEMENT -the employee shall be admitted back to work; 2. PAYROLL REINSTATEMENT - the employee is merely reinstated in the payroll.
PERIOD COVERED BY THE PAYMENT OF BACKWAGES: Backwages shall cover the period from the date of dismissal of the employee up to the date of actual reinstatement. SECURITY OF TENURE: An employer CANNOT terminate the services of an employee EXCEPT for a just cause or when authorized by law. REQUIREMENTS OF DUE PROCESS BEFORE AN EMPLOYEE CAN BE REMOVED: 1. written notice to apprise the employee of the particular acts or omission for which his dismissal is sought and is hereby considered as the proper charge; 2. ample opportunity to be employee to be heard and if the employee so decides, with the assistance of counsel; and 3. written notice informing the employee of the employers decision to dismiss him. Under the so-called WENPHIL DOCTRINE if just or authorized cause exist but the affected employees right to due process has been violated, the dismissal is valid but the employee is entitled to damages by way of indemnification for the violation of the right.
On Jan. 27, 2000, the SC in the case of SERRANO vs. ISETANN et. al. Disregarded this WENPHIL DOCTRINE and ruled that if the employees right to due process is violated, his dismissal becomes illegal regardless of the existence of a just and authorized cause. REINSTATEMENT - Restoration of the employee to state from which one has been removed or separated without loss of seniority rights and other privileges. WHAT HAPPENS IF THERE IS AN ORDER OF REINSTATEMENT BUT THE POSITION IS NO LONGER AVAILABLE? If the position previously occupied by the employee is no longer available at the time of reinstatement, he should be given a substantially equivalent position. If THERE IS NO SUBSTANTIALLY EQUIVALENT POSITION: If no substantially equivalent position is available, reinstatement should not be ordered because that would in effect compel the employer to do the impossible. In such a situation, the employee should merely be given separation pay of the one month salary for every year of service (1:1). CIRCUMSTANCES WHEN COMPANY MAY NOT REINSTATE DESPITE ORDER OF REINSTATEMENT 1. Transfer of business ownership;There is no law requiring a purchasing corporation to absorb the employees of the selling corporation. A fortiori, reinstatement of unjustly dismissed employees CANNOT be enforced against the new owner UNLESS there is an express agreement on the assumption of liabilities by the purchasing corporation. 2. When reinstatement is rendered impossible due to the abolition of the position; 3. When the business has closed down; 4. Physical incapacity of employee 5. Doctrine of Strained Relations-When the employer can no longer trust the employee and vice-versa, reinstatement could not effectively serve as a remedy. Applies only to positions which require trust and confidence; or Under the circumstances where the employment relationship has become so strained to preclude a harmonious working relationship, and that all hopes at reconciliation are nil after reinstatement, it would be more beneficial to accord the employee backwages and separation pay. BACKWAGES-Relief given to an employee to compensate him for lost earnings during the period of his dismissal. How computed: Under existing law, backwages is computed from the time of the illegal dismissal up to time of actual reinstatement.
WHAT ARE INCLUDED IN THE COMPUTATION OF BACKWAGES 1. transportation and emergency allowances 2. vacation or service incentive leave and sick leave 3. 13th month pay. However, facilities such as uniforms, shoes, helmets and ponchos should NOT be included in the computation of backwages. REASON: said items are given free, to be used only during official tour of duty not for private or personal use. CIRCUMSTANCES THAT PREVENT AWARD OF BACKWAGES: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. death of the employee physical and mental incapacity business reverses closure of business reinstatement of dismissed employee confinement in jail
You might also like
- S V MAKUA 1993 1 SACR 160 TDocument4 pagesS V MAKUA 1993 1 SACR 160 TLuvashen Gounden64% (42)
- Gad'S Justice: Lead, Empower, and Achieve Through Data-Driven DecisionsDocument45 pagesGad'S Justice: Lead, Empower, and Achieve Through Data-Driven DecisionsANNA MARIE LARGADAS MALULANNo ratings yet
- The Four Fold TestDocument4 pagesThe Four Fold TestGeneva Bejasa Arellano100% (3)
- PFR Assignment Parental AuthorityDocument14 pagesPFR Assignment Parental AuthorityAnnabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Cancellation of Mortgage or EncumbranceDocument24 pagesCancellation of Mortgage or EncumbranceRommel Tottoc100% (3)
- SPA - Authority To ProsecuteDocument2 pagesSPA - Authority To Prosecutesweetlunacy00100% (1)
- Unfair Labor PracticeDocument6 pagesUnfair Labor PracticeVance CeballosNo ratings yet
- Format Civpro Case DigestDocument5 pagesFormat Civpro Case DigestPrincess Cruz MacalingaNo ratings yet
- Marcelo Labor 1 Reviewer PDFDocument37 pagesMarcelo Labor 1 Reviewer PDF8LYN LAW100% (1)
- Labor Code Articles 106, 107 and 109 Joint and Several LiabilityDocument3 pagesLabor Code Articles 106, 107 and 109 Joint and Several LiabilityEgo sum pulcher100% (1)
- Labor Law Module 1Document8 pagesLabor Law Module 1ALYSSA NOELLE ARCALAS100% (1)
- Proxy FormDocument1 pageProxy Formsweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Module 02 - Recruitment and Placement of Workers PDFDocument87 pagesModule 02 - Recruitment and Placement of Workers PDFKatharina CantaNo ratings yet
- CCV NOTES FOR THE 2019 Labor Relations: Ia. Employer-Employee RelationshipDocument200 pagesCCV NOTES FOR THE 2019 Labor Relations: Ia. Employer-Employee RelationshipJay Mark Albis SantosNo ratings yet
- Nature and Classes of Corporations 1Document4 pagesNature and Classes of Corporations 1Emyrose Capones CalgoNo ratings yet
- Complaint for Malicious MischiefDocument4 pagesComplaint for Malicious Mischiefsweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- The Doctrine of Qualified Political AgencyDocument2 pagesThe Doctrine of Qualified Political AgencyPatrick TanNo ratings yet
- Obli 1356-1390 PDFDocument10 pagesObli 1356-1390 PDFCMLNo ratings yet
- 1376 1377Document2 pages1376 1377Huricane SkyNo ratings yet
- People V MontenegroDocument6 pagesPeople V MontenegroAiko EleniNo ratings yet
- Christology: YeshuaDocument6 pagesChristology: Yeshuasweetlunacy0067% (3)
- PartnershipDocument20 pagesPartnershipLm RicasioNo ratings yet
- Sources of Labor LawsDocument3 pagesSources of Labor LawsFarhan Jumdain100% (2)
- Jurisdiction of Labor ArbitersDocument6 pagesJurisdiction of Labor Arbiterstwenty19 law100% (1)
- Deed of Indemnity For GLA PropertiesDocument1 pageDeed of Indemnity For GLA PropertiesEmeka NkemNo ratings yet
- Camitan vs. FidelityDocument2 pagesCamitan vs. FidelityPMV50% (2)
- Art277 and Up Azucena Notes On Labor RelationsDocument15 pagesArt277 and Up Azucena Notes On Labor Relationsmc.rockz14100% (1)
- List of Violations CRM PosDocument3 pagesList of Violations CRM PosAxel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Unfair Labor Practices of Labor OrganizationsDocument14 pagesUnfair Labor Practices of Labor OrganizationsJica GulaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle and CiceroDocument28 pagesAristotle and CiceroJed MendozaNo ratings yet
- KINDS OF EMPLOYEES AND STRIKESDocument16 pagesKINDS OF EMPLOYEES AND STRIKESDennie Vieve IdeaNo ratings yet
- Ncm-120-Week-14-Topic 8 (F-P) - Nov 8 To 13, 2021Document45 pagesNcm-120-Week-14-Topic 8 (F-P) - Nov 8 To 13, 2021Shaf Abubakar100% (1)
- Obligations of The AgentDocument5 pagesObligations of The Agentjovelyn davoNo ratings yet
- Management PrerogativesDocument3 pagesManagement PrerogativesJFANo ratings yet
- Labor Code of The PhilippinesDocument115 pagesLabor Code of The PhilippinesToto EpantoNo ratings yet
- Deed of Donation FormsDocument5 pagesDeed of Donation FormsJecky Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Deed of Donation FormsDocument5 pagesDeed of Donation FormsJecky Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Deed of Donation FormsDocument5 pagesDeed of Donation FormsJecky Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Labor laws and contractsDocument3 pagesLabor laws and contractsJaneen ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Rule 39 - DayanghirangDocument16 pagesRule 39 - DayanghirangAnna Marie DayanghirangNo ratings yet
- Rules on marriage between competitors analyzedDocument3 pagesRules on marriage between competitors analyzednew covenant churchNo ratings yet
- EXTRAJUDICIAL SETTLEMENT AND PARTITION - SampleDocument4 pagesEXTRAJUDICIAL SETTLEMENT AND PARTITION - Samplesweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- EXTRAJUDICIAL SETTLEMENT AND PARTITION - SampleDocument4 pagesEXTRAJUDICIAL SETTLEMENT AND PARTITION - Samplesweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Employee-Employer Relationship Who Is An Employee?Document6 pagesEmployee-Employer Relationship Who Is An Employee?Johanne LariosaNo ratings yet
- People of The Phils Vs JUMARANGDocument3 pagesPeople of The Phils Vs JUMARANGEpalan Justine AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Backend Outsourcing Agreement For Administrative ServicesDocument6 pagesBackend Outsourcing Agreement For Administrative ServicesReuel JacintoNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement DraftDocument1 pageAcknowledgement Draftsweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- AZUCENA'S GUIDE TO EMPLOYMENT CLASSIFICATIONDocument3 pagesAZUCENA'S GUIDE TO EMPLOYMENT CLASSIFICATIONRoma Flores100% (1)
- Labor Relations NotesDocument52 pagesLabor Relations NotesBilog Ang Mundo100% (1)
- Explain The Difference Between Ordinary Assets and Capital Assets?Document1 pageExplain The Difference Between Ordinary Assets and Capital Assets?JeromeNo ratings yet
- Affidavit Repainting Vehicle Color ChangeDocument2 pagesAffidavit Repainting Vehicle Color Changesweetlunacy00100% (2)
- Constitutional Law II Exam - ClarionDocument10 pagesConstitutional Law II Exam - ClarionManny Carl ClarionNo ratings yet
- The Law On PartnershipDocument4 pagesThe Law On Partnership123445No ratings yet
- Effect of new debtor's insolvency or non-fulfillment in delegacionDocument2 pagesEffect of new debtor's insolvency or non-fulfillment in delegacionAnn Go100% (1)
- Collective Bargaining Units ExplainedDocument32 pagesCollective Bargaining Units ExplainedHarold Garcia0% (1)
- Philippines Taxation Scope and ReformsDocument4 pagesPhilippines Taxation Scope and ReformsAngie Olpos Boreros BaritugoNo ratings yet
- Labor 1 - Laws - 091015Document8 pagesLabor 1 - Laws - 091015Karla BeeNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. L-15363 (Links To An External Site.)Document2 pagesG.R. No. L-15363 (Links To An External Site.)glaide lojeroNo ratings yet
- Research Consultation: Bs Psychology 4ADocument62 pagesResearch Consultation: Bs Psychology 4ARyan Estonio100% (1)
- Palmeria vs. NLRC, G.R. Nos. 113290-91, 3 Aug. 1995, 247 SCRA 57Document10 pagesPalmeria vs. NLRC, G.R. Nos. 113290-91, 3 Aug. 1995, 247 SCRA 57Novie AmorNo ratings yet
- Part II - On Strikes and Lock OutsDocument53 pagesPart II - On Strikes and Lock OutsJenifer PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Security of TenureDocument2 pagesSecurity of TenureAyme SoNo ratings yet
- ILLEGAL RECRUITMENT ELEMENTSDocument6 pagesILLEGAL RECRUITMENT ELEMENTSLenie Ricardo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Law On Agency - Reflection Paper - TiongsonDocument2 pagesLaw On Agency - Reflection Paper - TiongsonAbby Gail TiongsonNo ratings yet
- M2u Classification Individual Taxation P1Document30 pagesM2u Classification Individual Taxation P1Xehdrickke FernandezNo ratings yet
- Article 1216 and 1217, Civil CodeDocument2 pagesArticle 1216 and 1217, Civil CodeDindo Roxas100% (1)
- Civil Code Provisions Related To Labor CodeDocument9 pagesCivil Code Provisions Related To Labor CodeNoel GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Labor Law Protections for Home and Night WorkersDocument23 pagesLabor Law Protections for Home and Night WorkersAnonymous r1cRm7FNo ratings yet
- Legal Opinion, Regular Seasonal EmployeesDocument4 pagesLegal Opinion, Regular Seasonal EmployeesJo Tr Avelard DvNo ratings yet
- Governance, Business Ethics, Risk Management and Control: GGSRDocument15 pagesGovernance, Business Ethics, Risk Management and Control: GGSRLysss EpssssNo ratings yet
- KINDS OF OBLIGATIONS: SIMPLE, COMPOUND, ALTERNATIVE, FACULTATIVE, JOINT AND SOLIDARYDocument4 pagesKINDS OF OBLIGATIONS: SIMPLE, COMPOUND, ALTERNATIVE, FACULTATIVE, JOINT AND SOLIDARYDino AbieraNo ratings yet
- ABI v. SMCDocument10 pagesABI v. SMCAndrea IvanneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document20 pagesLecture 3Grim 1118No ratings yet
- EMPLOYER-EMPLOYEE RELATIONSHIP TESTSDocument3 pagesEMPLOYER-EMPLOYEE RELATIONSHIP TESTSElaine Belle OgayonNo ratings yet
- Article 1174Document1 pageArticle 1174paula rose dumaopNo ratings yet
- Defective Contracts Reviewer: Rescissible, Voidable, Unenforceable, VoidDocument1 pageDefective Contracts Reviewer: Rescissible, Voidable, Unenforceable, VoidEmi SicatNo ratings yet
- Strikes, Picketing and Lock-Outs ProceduresDocument23 pagesStrikes, Picketing and Lock-Outs ProceduresMaChere ReyesNo ratings yet
- PSBA-QC Business Law QuizDocument4 pagesPSBA-QC Business Law Quizkath gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Law on Obligation and Contracts Module 4 RecapDocument38 pagesLaw on Obligation and Contracts Module 4 Recapyna kyleneNo ratings yet
- Security of Tenure To The Employee. E.g., If The Employee Work For That Company For About 10yrs Don'tDocument8 pagesSecurity of Tenure To The Employee. E.g., If The Employee Work For That Company For About 10yrs Don'tYsabel JaoNo ratings yet
- Book6, Title 1 Termination of Employment Art. 278. CoverageDocument27 pagesBook6, Title 1 Termination of Employment Art. 278. Coveragericohizon99No ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 6715Document15 pagesRepublic Act No. 6715gennady18No ratings yet
- Affidavit of Buyer and SellerDocument1 pageAffidavit of Buyer and Sellersweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Affidavit of Closure of BusinessDocument1 pageAffidavit of Closure of Businesssweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- SPA PermitsDocument3 pagesSPA Permitssweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Know All Men by These Presents:: Special Power of AttorneyDocument4 pagesKnow All Men by These Presents:: Special Power of Attorneysweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Know All Men by These Presents:: General Power of AttorneyDocument2 pagesKnow All Men by These Presents:: General Power of Attorneysweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Special Power of AttorneyDocument2 pagesSpecial Power of Attorneysweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- 2018 Citizens Charter As of 20180723Document290 pages2018 Citizens Charter As of 20180723jeszamaeferrerNo ratings yet
- Requirements For Petition For AnnulmentDocument1 pageRequirements For Petition For Annulmentsweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- RR 2-2013 PDFDocument23 pagesRR 2-2013 PDFnaldsdomingoNo ratings yet
- READMEDocument4 pagesREADMEzetteNo ratings yet
- The 2011 NLRC Rules of ProcedureDocument1 pageThe 2011 NLRC Rules of Proceduresweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Afffidavit of LossDocument1 pageAfffidavit of Losssweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Sec-Ogc Opinion No. 09-15Document8 pagesSec-Ogc Opinion No. 09-15sweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Affidavit of ServiceDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Servicesweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Remedies NLRC LADocument1 pageRemedies NLRC LAsweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Conserve WaterDocument2 pagesConserve Watersweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Albenson Enterprises V CA: Elements: (1) There's A Legal Right or Duty (2) Exercised in BadDocument1 pageAlbenson Enterprises V CA: Elements: (1) There's A Legal Right or Duty (2) Exercised in Badsweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Afffidavit of LossDocument1 pageAfffidavit of Losssweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Roldan V PH Veterans Board: Juridical Person: A Being of Legal Existence Susceptible ofDocument2 pagesRoldan V PH Veterans Board: Juridical Person: A Being of Legal Existence Susceptible ofsweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Villanueva vs. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 143286 April 14, 2004 FactsDocument8 pagesVillanueva vs. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 143286 April 14, 2004 FactsClark Vincent PonlaNo ratings yet
- Emata v. IAC, G.R. No. L-72714, June 29, 1989Document4 pagesEmata v. IAC, G.R. No. L-72714, June 29, 1989Alan Vincent FontanosaNo ratings yet
- Partition Dispute Leads to Contempt CaseDocument9 pagesPartition Dispute Leads to Contempt CaseFrances Angelica Domini KoNo ratings yet
- Resume of 9/11 Commission Staffer Barbara GreweDocument3 pagesResume of 9/11 Commission Staffer Barbara Grewe9/11 Document ArchiveNo ratings yet
- ROTC-NOT-MANDATORY - Revised1Document6 pagesROTC-NOT-MANDATORY - Revised1Krystine GodalleNo ratings yet
- Non-Creamy Layer ApplicationDocument4 pagesNon-Creamy Layer ApplicationHanamant BhanseNo ratings yet
- Sec'y April-21-11Document10 pagesSec'y April-21-11brownrob4732No ratings yet
- Indian Penal Code Project Report On: Section 377Document16 pagesIndian Penal Code Project Report On: Section 377muskaanNo ratings yet
- DigestNotes Mitigating CircumstancesDocument9 pagesDigestNotes Mitigating CircumstancesAllen SoNo ratings yet
- Agrarian ReformDocument7 pagesAgrarian ReformRaffy San AntonioNo ratings yet
- News Item GamesDocument35 pagesNews Item GamesUmi KuswariNo ratings yet
- SPL Undertaking Letter PDFDocument3 pagesSPL Undertaking Letter PDFSuttonFakesNo ratings yet
- Rabor vs CSC - Retirement age extension disputeDocument2 pagesRabor vs CSC - Retirement age extension disputeGladys Bustria OrlinoNo ratings yet
- Petition to Annul Sandiganbayan Ruling on Preliminary Attachment Against Philippine GeneralDocument14 pagesPetition to Annul Sandiganbayan Ruling on Preliminary Attachment Against Philippine GeneralAurora Pelagio VallejosNo ratings yet
- National Association of Barbados Organizations, Inc.Document2 pagesNational Association of Barbados Organizations, Inc.api-22426418No ratings yet
- Transfer of Property With TitleDocument10 pagesTransfer of Property With TitleHarris AdamNo ratings yet
- Legislative DepartmentDocument39 pagesLegislative DepartmentLianne DarauayNo ratings yet
- Uy Vs CA G.R. No. 120465Document8 pagesUy Vs CA G.R. No. 120465Maria Fiona Duran MerquitaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LawDocument15 pagesIntroduction To LawCheliette JaritoNo ratings yet