Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Barrett Taxonomy (Task 2)
Uploaded by
Sashi KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Barrett Taxonomy (Task 2)
Uploaded by
Sashi KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
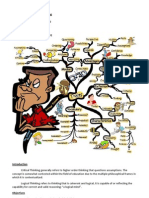
The Barrett Taxonomy (Clymer, 1968), designed originally to assist classroom teachers in developing comprehension questions and or test
questions for reading, is especially useful for classroom questioning in other content areas as well. Barrets Taxonomy is a classification of educational objectives used for developing higher level thinking skills. It classifies skills and orders them according to the degree of complexity. It consists of five categories such as literal comprehension, reorganization, inferential comprehension, evaluation and appreciation. Literal comprehension is focuses on ideas and information which are explicitly stated in the selection. A simple task in literal comprehension may be the recognition or recall of a single fact or incident. A more complex task might be the recognition or recall of a series of facts or the sequencing of incidents in a reading selection. Reorganization requires the students to analyze, synthesize, and/or organize ideas or information explicitly stated in the selection. It also used to produce the desired thought, the reader may utilize the statements of the author or he may paraphrase or translate the author's statements. Reorganization tasks are Classifying, 0utlining, Summarizing and Synthesizing. Inferential Comprehension is used to may be either convergent or divergent in nature and may be asked to verbalize the underlying rationale. It stimulated by purposes for reading which demand thinking and imagination that go beyond the printed page. There are Inferring Supporting Details, Inferring Main Ideas, Inferring Sequence, Inferring Comparisons, Inferring Cause and Effect Relationships,Inferring Character Traits, Predicting Outcomes and Interpreting Figurative Language. Evaluation requirea responses by the student which indicate that en evaluative judgment has been made. The student may compare ideas presented in the reading selection with external criteria provided by the teacher, other authorities, or written sources with internal crieteria provided by the students experiences, knowledge, or values. Evaluative thinking may be demonstrated by asking the student to make the following judgments such as reality or fantasy, fact or opinion, adequacy or validity, appropriateness and worth, desirability and acceptability. Appreciation involves all the previously cited cognitive dimensions of reading, for it deals with the psychological and aesthetic impact of the selection on the reader. Appreciation calls for the students to be emotionally and aesthetically sensitive to the work and to have a reaction to the worth of its psychological and artistic elements. Appreciation includes both the knowledge
of, and the emotional response to, literary techniques, forms, styles, and structures like Emotional Response to the Content, Identification with Characters or Incidents, Reactions to the Author's Use of Language and Imagery
You might also like
- SPIRE Draft Josie PrebbleDocument6 pagesSPIRE Draft Josie PrebbleJosieClarkNo ratings yet
- Waymark HolidayDocument2 pagesWaymark Holiday8110 KamilaNo ratings yet
- Barrett's TaxonomyDocument19 pagesBarrett's TaxonomyAlice100% (5)
- Portfolio in Prof Ed 6Document11 pagesPortfolio in Prof Ed 6Desiree Fae AllaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3Vince OjedaNo ratings yet
- Common Rail Injector Tester CR-C +S60H Multifunction Test MachineDocument3 pagesCommon Rail Injector Tester CR-C +S60H Multifunction Test MachineAlen HuangNo ratings yet
- Intercostal Drainage and Its ManagementDocument36 pagesIntercostal Drainage and Its ManagementAnusha Verghese67% (3)
- Worship Aid - May Crowning 2020Document5 pagesWorship Aid - May Crowning 2020Kevin RyanNo ratings yet
- Eating From One Pot: The Dynamics of Survival in Poor South African HouseholdsDocument38 pagesEating From One Pot: The Dynamics of Survival in Poor South African HouseholdsLittleWhiteBakkie0% (1)
- Inc Eddy 2011Document14 pagesInc Eddy 2011hendriek hasan100% (1)
- Workforce ManagementDocument39 pagesWorkforce ManagementWahyu Arya PutraNo ratings yet
- Metacognitive Awareness of Reading Strategies and Critical ReadingDocument11 pagesMetacognitive Awareness of Reading Strategies and Critical ReadingLG SinanesNo ratings yet
- Levels of ReadingDocument2 pagesLevels of ReadingKyle bryan AbutalNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature Reading ComprehensionDocument8 pagesReview of Related Literature Reading ComprehensionSiza SorupiaNo ratings yet
- Using Bloom's Taxonomy in Teaching Reading SkillDocument8 pagesUsing Bloom's Taxonomy in Teaching Reading SkillHa To100% (1)
- Faculy Convention Workshop 2013Document3 pagesFaculy Convention Workshop 2013api-246726823No ratings yet
- Teachers' Guide Manual For Formulating Reading Comprehension QuestionsDocument135 pagesTeachers' Guide Manual For Formulating Reading Comprehension QuestionsPuvaneswari PuvaNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking and Other Higher-Order Thinking Skills-SLACDocument13 pagesCritical Thinking and Other Higher-Order Thinking Skills-SLACJG D MenesesNo ratings yet
- Cognitive (Thinking), Affective (Emotions or Feeling) and Psychomotor (Physical or Kinesthetic) To BeDocument2 pagesCognitive (Thinking), Affective (Emotions or Feeling) and Psychomotor (Physical or Kinesthetic) To BeBenedict NicolasNo ratings yet
- Poetry and Exile Thesis DefenseDocument21 pagesPoetry and Exile Thesis DefenseROMERO, AIRA JOY M.No ratings yet
- Critical ReadingDocument4 pagesCritical Readingsardar NabeelNo ratings yet
- What Is A Simple Definition of Critical ThinkingDocument23 pagesWhat Is A Simple Definition of Critical ThinkingTanzeela BashirNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Assessment in The Affective DomainDocument46 pagesLesson 4 - Assessment in The Affective DomainMila GamidoNo ratings yet
- Barrett's Taxonomy: Take ActionDocument2 pagesBarrett's Taxonomy: Take ActionKhoirul NurNo ratings yet
- Affective Learning Competencies: Prepared By: Jolina Arandia Sharie Mae H. JecielDocument54 pagesAffective Learning Competencies: Prepared By: Jolina Arandia Sharie Mae H. JecielSharie Mae JecielNo ratings yet
- SOFTDocument9 pagesSOFTMr. MagrataNo ratings yet
- BloomsDocument6 pagesBloomsmjacquinetNo ratings yet
- Significance of Assessment and Evaluation of Learning inDocument45 pagesSignificance of Assessment and Evaluation of Learning inAna Marie D. BorjaNo ratings yet
- How Should Critical Thinking Be Conceptualized?Document10 pagesHow Should Critical Thinking Be Conceptualized?Azher BeboNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Assessment in Learning 2Document22 pagesGroup 4 Assessment in Learning 2Angelique Nicole CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Student Level of Critical Thinking-3745Document11 pagesStudent Level of Critical Thinking-3745Maria Christina ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Amir Reza Nemat TabriziDocument7 pagesAmir Reza Nemat TabriziKatia MulikNo ratings yet
- Designing Lesson Plan Based On Critical Thinking For Language ClassesDocument15 pagesDesigning Lesson Plan Based On Critical Thinking For Language ClassesShaniya Margaretha SitumorangNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2-WPS OfficeDocument11 pagesUNIT 2-WPS OfficeLady Carmelle AbreaNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy of Educational Objectives OutlineDocument9 pagesTaxonomy of Educational Objectives OutlineRexonChanNo ratings yet
- L5 Affective AssessmentDocument34 pagesL5 Affective Assessmentbyunbacooon456No ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning Ii: Textbook and ReviewerDocument13 pagesAssessment of Learning Ii: Textbook and ReviewerWAFA SAGALANo ratings yet
- Assessing Affective Learning OutcomesDocument5 pagesAssessing Affective Learning OutcomesHanna RanetNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Authentic Assessment in Affective Domain PDFDocument13 pagesModule 3 Authentic Assessment in Affective Domain PDFMae Asperin100% (2)
- Bloom TaxonomyDocument7 pagesBloom TaxonomyBenjamin HaganNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Learning Targets For Performance AssessmentDocument12 pagesLesson 2 Learning Targets For Performance AssessmentKATE VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Taxonomies of E-Wps OfficeDocument26 pagesTaxonomies of E-Wps OfficeAmado RegoyaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Literal ComprehensionDocument10 pages1.0 Literal ComprehensionJocelynt TabaosaresNo ratings yet
- Full Paper Endang Kusrini RevisedDocument10 pagesFull Paper Endang Kusrini Revisedfaiz nuha ilmawanNo ratings yet
- Questioning The LectureDocument10 pagesQuestioning The Lecturecrab849No ratings yet
- Topic 2.what To AssessDocument19 pagesTopic 2.what To AssesssiaukenNo ratings yet
- Assessing Students' Critical Thinking Performance: Urging For Measurements Using Multi-Response FormatDocument7 pagesAssessing Students' Critical Thinking Performance: Urging For Measurements Using Multi-Response FormatJenitalNo ratings yet
- BloomsDocument31 pagesBloomsMaira AnoshNo ratings yet
- Researchhhhhhh Group 8Document18 pagesResearchhhhhhh Group 8Hezel Palmero0% (1)
- Submitted By: Leticia S. Ong: Title: Logical and Critical ThinkingDocument3 pagesSubmitted By: Leticia S. Ong: Title: Logical and Critical ThinkingDanille Ivan OngNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Problem Solving in The Information Age: Lesson 1 - New Learning Skills 2Document8 pagesIntroduction To Problem Solving in The Information Age: Lesson 1 - New Learning Skills 2hayleykhoNo ratings yet
- Ed 586762Document14 pagesEd 586762Eugelly RiveraNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 MentahDocument4 pagesBab 2 MentahKeeganNo ratings yet
- Assessment PP TDocument31 pagesAssessment PP TJohncedrick S. PunzalNo ratings yet
- Concept of AssessmentDocument8 pagesConcept of AssessmentSANA SAFDARNo ratings yet
- The Function of Measurement and Evaluation in Improving InstructionDocument3 pagesThe Function of Measurement and Evaluation in Improving InstructionDenny AriswanNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy Questioning: Discussion StrategiesDocument13 pagesBloom's Taxonomy Questioning: Discussion Strategiesmgar10No ratings yet
- Developmental Reading HandoutDocument23 pagesDevelopmental Reading HandoutCharina May Nolan85% (13)
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain: KnowledgeDocument2 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain: KnowledgeKlara Alexandra JuraNo ratings yet
- Remedios Beran ReportDocument22 pagesRemedios Beran ReportKhyla Mae Bassig CondeNo ratings yet
- Reading First Teacher Education Network (RFTEN) : Teaching Teachers Strategies For Reading SuccessDocument19 pagesReading First Teacher Education Network (RFTEN) : Teaching Teachers Strategies For Reading SuccessmkanwarsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2, Topic 2Document12 pagesLesson 2, Topic 2Janaica lace pitpitNo ratings yet
- The Use of Pre-Questioning in Reading ComprehensionDocument5 pagesThe Use of Pre-Questioning in Reading ComprehensionAnnisa LatifaNo ratings yet
- Bibliografi ThivakarDocument1 pageBibliografi ThivakarSashi KumarNo ratings yet
- நீதிகதைDocument4 pagesநீதிகதைSashi KumarNo ratings yet
- Institut Pendidikan Guru Kampus Tengku Ampuan Afzan, Kuala Lipis, PahangDocument2 pagesInstitut Pendidikan Guru Kampus Tengku Ampuan Afzan, Kuala Lipis, PahangSashi KumarNo ratings yet
- RujukanDocument1 pageRujukanSashi KumarNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0008 JgyguyDocument1 pageIMG - 0008 JgyguySashi KumarNo ratings yet
- 5 FDX DFXDFXX DXDFX DFX DFXD XDFX DFXDF XDFDocument1 page5 FDX DFXDFXX DXDFX DFX DFXD XDFX DFXDF XDFSashi KumarNo ratings yet
- Round-Off Sample N: Finding ToDocument1 pageRound-Off Sample N: Finding ToSashi KumarNo ratings yet
- 7 ZSF ZSDZ SDDocument1 page7 ZSF ZSDZ SDSashi KumarNo ratings yet
- Inferential ComprehensionDocument4 pagesInferential ComprehensionSashi KumarNo ratings yet
- Pro Con ChartDocument3 pagesPro Con Chartapi-461614875No ratings yet
- Library SectionsDocument4 pagesLibrary SectionsGello Sotnuiq100% (4)
- Philippines and Singapore Trade Relations and Agreements: 1. What Leads To Said Agreement?Document11 pagesPhilippines and Singapore Trade Relations and Agreements: 1. What Leads To Said Agreement?Ayrah Erica JaimeNo ratings yet
- Gender Inequality and Its Impact On Mental HealthDocument20 pagesGender Inequality and Its Impact On Mental Healthbanipreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Empowerment TechnologyDocument2 pagesEmpowerment TechnologyRegina Mambaje Alferez100% (1)
- EL2 - Raise Organic Small RuminantsDocument62 pagesEL2 - Raise Organic Small RuminantsButch Demayo100% (1)
- 0 - Danica Joy v. RallecaDocument2 pages0 - Danica Joy v. RallecaRandy Jake Calizo BaluscangNo ratings yet
- Sabre V8Document16 pagesSabre V8stefan.vince536No ratings yet
- The Duty To Warn in Products Liability: Contours and CriticismDocument115 pagesThe Duty To Warn in Products Liability: Contours and CriticismArun HiroNo ratings yet
- Ask NasaDocument68 pagesAsk Nasacavaco2008No ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document7 pagesCase Study 2api-561058683No ratings yet
- HimediaDocument2 pagesHimediaWiwit MarianaNo ratings yet
- 3250-008 Foundations of Data Science Course Outline - Spring 2018Document6 pages3250-008 Foundations of Data Science Course Outline - Spring 2018vaneetNo ratings yet
- CE - 441 - Environmental Engineering II Lecture # 11 11-Nov-106, IEER, UET LahoreDocument8 pagesCE - 441 - Environmental Engineering II Lecture # 11 11-Nov-106, IEER, UET LahoreWasif RiazNo ratings yet
- Assignment Brief - Starting A Business and Fundamental of MarketingDocument7 pagesAssignment Brief - Starting A Business and Fundamental of Marketingmd rahimNo ratings yet
- Sagan WaltzDocument14 pagesSagan WaltzKathleen RoseNo ratings yet
- C MukulDocument1 pageC Mukulharishkumar kakraniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Integration Testing PDFDocument74 pagesChapter 7 Integration Testing PDFebrgsrtNo ratings yet
- PostmanPat Activity PackDocument5 pagesPostmanPat Activity PackCorto Maltese100% (1)
- Rights of An Accused Under Custodial InvestigationDocument17 pagesRights of An Accused Under Custodial Investigationadrianfrancis9100% (1)
- Tasha Giles: WebsiteDocument1 pageTasha Giles: Websiteapi-395325861No ratings yet
- Omran WalidDocument196 pagesOmran WalidDébora AmougouNo ratings yet
- The Mutant Epoch Mature Adult Content Mutations v1Document4 pagesThe Mutant Epoch Mature Adult Content Mutations v1Joshua GibsonNo ratings yet
- Concept of ConstitutionDocument32 pagesConcept of ConstitutionDorepe Icon0% (1)
- AWANA Handbook 2010-2011Document8 pagesAWANA Handbook 2010-2011carriepratchard100% (1)
- JamPlay 30 Minute Guitar Pratice TemplateDocument23 pagesJamPlay 30 Minute Guitar Pratice TemplateSunkilr Sönny100% (4)
- Compact Switch: Series 96201, 96211, 96221Document2 pagesCompact Switch: Series 96201, 96211, 96221Sales DIGIHU100% (1)