Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ester Group
Uploaded by
Anubhav SwaroopCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ester Group
Uploaded by
Anubhav SwaroopCopyright:
Available Formats
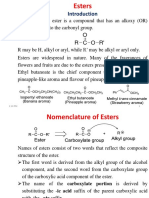
Ester group Esters are the organic compound; they have general formula as RCOOR.
They are treated as the derivatives of carboxylic acids as the hydrogen of the COOH group is replaced by an alkyl group, the alkyl group may be a saturated alkyl group, unsaturated or aromatic.lactones are the cyclkic acids , the esters are found in most of the products in nature , in fruits , nuts , glycerol , in esters of fatty acids and oils, explosive slike nitroglycerine, polysetes , plastics etc, The IUPAC name of esters ifs dine according to following scheme: The ic acid of the carboxylic acid is dropped and the suffix oate is added, following are few esters with molecular formulas a and IUPAC name written in front of them. RCOOR R = CnH2n+1 CH3-COOCH3 Methyl acetate or methyl ethanoate (IUPAC) CH3COOCH2CH2 Ethyl acetate or ethyl ethanoate (IUPAC) CH3CH2CH2-COOCH2CH3 Ethyl propanoate
Ester are the compound which are formed when OR group replaces at least one OH group organic or in organic acid, R1COOH + R2OH R1COOR2 + H2O
Inorganic esters"
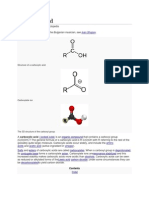
A phosphoric acid ester Ester is a general term for the product derived from the condensation of an oxo acid and an alcohol. Thus, the nomenclature extends to inorganic acids, especially phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid, and nitric acid. Cyclic esters are called lactones. The preparation of an ester is known generally as an esterification reaction. For example, triphenyl phosphate is the ester derived from phosphoric acid and phenol. Organic carbonates, such as ethylene carbonate are derived from carbonic acid and ethylene glycol. The term boronic ester is widely used but these compounds are not formally esters because they lack a B=O bond. ; they tend to be less rigid (lower melting point) and more volatile (lower boiling point) than the corresponding amides. Esters are more polar than ethers but less polar than alcohols. They participate in hydrogen bonds as hydrogen-bond acceptors, but cannot act as hydrogen-bond donors, unlike their parent alcohols. This ability to participate in hydrogen bonding confers some water-solubility. Because of their lack of hydrogen-bond-donating ability, esters do not self-associate. Consequently esters are more volatile than carboxylic acids of similar molecular weight.
[edit] Characterization and analysis
Esters are usually identified by gas chromatography, taking advantage of their volatility. IR spectra for esters feature an intense sharp band in the range 1600-1800 cm-1 assigned to C=O.
[edit] Applications and occurrence
Esters are widespread in nature and are widely used in industry. In nature, fats are generally triesters derived from glycerol and fatty acids. Esters are responsible for the aroma of many fruits, including apples, pears, bananas, pineapples, and strawberries.[2] Several billion kilograms of polyesters are produced industrially annually, important products being polyethylene terephthalate, acrylate esters, and cellulose acetate.[3] [ R1COOH + R2OH R1COOR2 + H2O
[edit] Alcoholysis of acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides
Alcohols react with acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides to give esters:
RCOCl + R'OH RCOOR' + HCl (RCO)2O + R'OH RCO2R' + RCO2H
You might also like
- Biochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingFrom EverandBiochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ether: Navigation Search AetherDocument7 pagesEther: Navigation Search AetherMuhammad Wahyu Nugraha0% (1)
- Organic Chem U-2 AlcoholDocument33 pagesOrganic Chem U-2 Alcoholsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Acyl CompoundsDocument38 pagesAcyl CompoundsAlaa Al HamedNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Nutrition and Food TechnologyFrom EverandDictionary of Nutrition and Food TechnologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- ESTERSDocument36 pagesESTERSAbdihakemNo ratings yet
- EsterificareaDocument43 pagesEsterificareaMahagney SalehNo ratings yet
- A 1Document29 pagesA 1Christopher WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Ester: For Other Uses, SeeDocument15 pagesEster: For Other Uses, SeemeritnasaNo ratings yet
- EstersDocument5 pagesEstersNevin BakrNo ratings yet
- EsterDocument2 pagesEsterCyrisse MONTANONo ratings yet
- EsterDocument13 pagesEsterdearbhupiNo ratings yet
- EsterDocument5 pagesEsterRonNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydeDocument62 pagesModule 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydePrincess NavarroNo ratings yet
- Siml Geometric Presentation by SlidesgoDocument62 pagesSiml Geometric Presentation by SlidesgobltrnNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups: Naming of EstersDocument6 pagesFunctional Groups: Naming of EsterspappadakunduNo ratings yet
- Science Ester Info 1Document10 pagesScience Ester Info 1Albert AntonioNo ratings yet
- Bautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)Document4 pagesBautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)2g8vdspqm5No ratings yet
- LayoutDocument55 pagesLayoutHenok Moges KassahunNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document9 pagesExp 10ChantalDanaNo ratings yet
- L4 - Acids, Esters and Its DerivativesDocument48 pagesL4 - Acids, Esters and Its DerivativesAlexNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives ExplainedDocument12 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Derivatives ExplainedÏt's RîçkgãrçīäNo ratings yet
- Are A Class of Organic Compounds That Have An OxygenDocument6 pagesAre A Class of Organic Compounds That Have An OxygenArianne MontañoNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.inggris HerlisyaDocument3 pagesTugas B.inggris HerlisyatrisnadewiNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument7 pagesNotesAmahNo ratings yet
- 5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Document28 pages5 Hydrocarbon Derivatives 2Marivic TayabanNo ratings yet
- A. Experiment Title: The Making of N-Butyl Acetate B. Experiment Started Date: Wednesday, March 4Document21 pagesA. Experiment Title: The Making of N-Butyl Acetate B. Experiment Started Date: Wednesday, March 4Era MelaniaNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument34 pages9.1 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesgoverotaropafadzwaNo ratings yet
- ALDEHYDES & KETONES GUIDEDocument40 pagesALDEHYDES & KETONES GUIDEMGoyalNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EpoxidesDocument134 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EpoxidesStudent 365100% (1)
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument26 pagesAldehydes and KetonesVoteone Enhypen100% (1)
- Chem Notes No6Document31 pagesChem Notes No6AnyhaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid: "COOH" Redirects Here. For The Bulgarian Musician, SeeDocument9 pagesCarboxylic Acid: "COOH" Redirects Here. For The Bulgarian Musician, SeeFighter_ace_97No ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Lesson 7 Organic Chemistry and Functional Groups 1Document71 pagesQuarter 2 Lesson 7 Organic Chemistry and Functional Groups 1Lhyn DE Leon DumayaNo ratings yet
- Esters Fats and Oils Pupil NotesDocument19 pagesEsters Fats and Oils Pupil NotesMasumNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Structure and PropertiesDocument11 pagesCarboxylic Acid Structure and PropertiesDipti BagdeNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument6 pagesCarboxylic AcidVishu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Structure of A Carboxylic AcidDocument7 pagesStructure of A Carboxylic AcidKajal SinghNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument16 pagesIntroductionAkhtar RazaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Study of Structure, Properties & ReactionsDocument42 pagesOrganic Chemistry Study of Structure, Properties & ReactionsAlisha KhanNo ratings yet
- EthersDocument16 pagesEthersPriskoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes - PPTMDocument40 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes - PPTMandrew.mooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Functional GroupsDocument81 pagesChapter 23 Functional GroupsYudi PermanaNo ratings yet
- EsterificationDocument3 pagesEsterificationKhris Sy-HandumonNo ratings yet
- EtherDocument23 pagesEtherOng Kok LeongNo ratings yet
- 4.1.3 Carboxylic Acids & EstersDocument5 pages4.1.3 Carboxylic Acids & EstersFin BrickmanNo ratings yet
- Esterification: An IntroductionDocument16 pagesEsterification: An IntroductionSudiv GullaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and EtherDocument29 pagesAlcohol and Etherapi-276904981No ratings yet
- I. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument10 pagesI. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidLaily SafitriNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument15 pagesCarboxylic Acidsmadhu bonamNo ratings yet
- Cac Bo EngliDocument4 pagesCac Bo EngliLinh ĐồngNo ratings yet
- Reactions and Uses of EstersDocument14 pagesReactions and Uses of Estersdela2No ratings yet
- EsterDocument16 pagesEsterBk CmNo ratings yet
- 2019 Ch104 Organic AcidsDocument111 pages2019 Ch104 Organic Acidsgenesis gengerNo ratings yet
- CARBOXYLIC ACIDS: KEY PROPERTIESDocument7 pagesCARBOXYLIC ACIDS: KEY PROPERTIESAntonia GhitaNo ratings yet
- Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument6 pagesAlehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidYoNo ratings yet
- ESTERS: Derivatives of Carboxylic AcidsDocument13 pagesESTERS: Derivatives of Carboxylic AcidsMohd NazriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Naming and Drawing of Carboxylic Acids and EsterDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Naming and Drawing of Carboxylic Acids and Esterkartika.pranotoNo ratings yet
- Ester FormationDocument6 pagesEster Formationkriss WongNo ratings yet
- 13 08 Divergence THMDocument6 pages13 08 Divergence THMAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Proofs For The EllipseDocument4 pagesProofs For The EllipseAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Post AP 2014 Drug Dosage ProblemsDocument6 pagesPost AP 2014 Drug Dosage ProblemsAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Important MathsDocument161 pagesImportant MathsAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- 17trek Precalculus - Piecewise FunctionsDocument2 pages17trek Precalculus - Piecewise FunctionsAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Algebra II (Day-5, Content Test-1)Document4 pagesAlgebra II (Day-5, Content Test-1)Anubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Formal definitions of limits and examplesDocument11 pagesFormal definitions of limits and examplesAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- 'S Concept ListDocument80 pages'S Concept ListMegan O'DonnellNo ratings yet
- Set1Day1 AnswersDocument4 pagesSet1Day1 AnswersAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Application Definite IntegrationDocument16 pagesApplication Definite IntegrationAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- T I 84 Calculus CommandsDocument7 pagesT I 84 Calculus CommandsAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Education CalculatorDocument1 pageEducation CalculatorAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Natural Forces - ClimaticDocument8 pagesNatural Forces - ClimaticAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Summary of Statistics FormulasDocument2 pagesSummary of Statistics FormulasAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- How Can We Determine The Effectiveness of Commercial Antacids?Document4 pagesHow Can We Determine The Effectiveness of Commercial Antacids?Anubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Physics ISC SyllabusDocument12 pagesPhysics ISC SyllabusAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Factor Each Expression. If It Cannot Be Factored, Write "In Simplest Form." 1. 2Document2 pagesFactor Each Expression. If It Cannot Be Factored, Write "In Simplest Form." 1. 2Anubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Nucleophile StrengthDocument1 pageNucleophile StrengthAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Test 1 (Algebra II)Document1 pageTest 1 (Algebra II)Anubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Trapez SimpsonDocument4 pagesTrapez SimpsonAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SyllabusDocument11 pagesChemistry SyllabusAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Basic Ideas in ChemistryDocument16 pagesBasic Ideas in ChemistryLucianaAcostaNo ratings yet
- Common Math ErrorsDocument38 pagesCommon Math Errorsmsahin1955No ratings yet
- The Theory of GamesDocument4 pagesThe Theory of GamesAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel Short ArticleDocument1 pageFossil Fuel Short ArticleAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Heats of Solution and ReactionDocument3 pagesHeats of Solution and ReactionAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- The Power Plant Is The Starting Point For Producing Electrical EnergyDocument1 pageThe Power Plant Is The Starting Point For Producing Electrical EnergyAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- ApplDefiniteIntegralVolume PDFDocument17 pagesApplDefiniteIntegralVolume PDFAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and PrecisionDocumentPhysics PDFDocument6 pagesAccuracy and PrecisionDocumentPhysics PDFAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Apd032p47p48varforce Springs PDFDocument11 pagesApd032p47p48varforce Springs PDFAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet