Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microbiology Charts
Uploaded by
clower112Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microbiology Charts
Uploaded by
clower112Copyright:
Available Formats
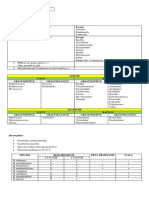
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24.
25. 26. 27. 28.
Sheep Blood agar Bacteroides Bile-esculin agar Bile esculin agar Brucella base agar Blood with kanamycin and vancomycin Phenylethyl alcohol agar (aerobic and anaerobic) Bordet-gengou Blood agar Buffered charcoal-yeast extract agar Burkholderia cepacia selective agar Campylobacter blood agar Cefsulodin-Irgansan-Novobiovin agar Chococlate agar Chromagars Simmons Citrate agar Columbia agar with antibiotics CTA sugars Egg Yolk Agar Eosin Methylene Blue Agar Hektoen Enteric Agar Lowenstein-Jensen medium Macconkey agar Macconkey sorbitol agar Mannitol salt agar Modified Thayer Martin agar Mueller Hinton agar Mueller hinton agar with 4% NaCl and 6 ug Oxacillin New York City Medium Pseudomonas cepacia agar
29. Regan-Lowe medium 30. Salmonella-Shigella agar 31. Thiogylcolate broth 32. Thiosulfate citrate bile salts sucrose agar 33. Tinsdale agar 34. Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) 35.KligersIronAgar(KIA) 36. Trypticase Soy Agar 37. Urea Broth 38. Urea Agar 39. Xylose-Lysine-Desoxycholate Agar 40. Vaginalis Agar
Type Enriched, Nonselective, and Differential (Detection of hemolysis) Selective and Differential Selective and Differential Nonselective nutrient medium Enriched and Selective Selective Enriched. May be made selective by adding antibiotics Nonselective and Enriched Selective and Differential Selective Selective and Differential Enriched and Nonselective Nonselective and Differential Differential Nonselective Differential Nonselective and Differential Selective and Differential Selective and Differential Nonselective Selective and Differential Selective Selective and Differential Selective Nonselective Nonselective Selective Selective
Selective Selective and Differential Nonselective Selective and Differential Selective and Differential Differential Differential Nonselective Selective Differential Selective and Differential Nonselective and Differential
Organisms That Will Grow Fastidious/Nonfastidious organisms. Ex: Staph, Strep, GPR, Most Neisseria species, etc. Isolation and Presumptive ID of Bacteroides fragilis group Isolation of Enterococcus species Cultivaton of many organisms Isolation of obligately anaerobic organisms Isolation of gram (+) organisms. Inhibition of gram (-) organisms Isolation of Bordetella pertussis and B. parapertussis Isolation of Legionella. Will also support the growth of Bordetella, Brucella, and Francisella tularensis Isolation of B. cepacia Isolation of Campylobacter jejuni subspecies jejuni and C. coli Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica, which ferments mannitol and forms bullseye colonies. Also used to isolate Aeromonas from stool specimens Cultivation of fastidious organisms, including Haemophilus, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Brucella Isolation of MRSA Gram (-) bacteria ability to utilize citrate Cultivation of many organisms Determines if organisms can ferment various carbs: maltose, lactose, sucrose. Differentiates Neisseria and Moraxella species Identifiation of certain anaerobic isolates Isolation of nonfastidious GNR. Inhibition of gram (+) organisms. E. coli (Strong lactose fermenter), Shigella and Salmonella (Non-lactose fermenters) Isolation of Salmonella and Shigella. Inhibition of gram (+) organisms and some gram (-). Cultivation of Mycobacteria Inhibition of Gram (+) organisms. Isolation of many nonfastidious GNR, Ex. Enterics. Isolation of E. coli H0157:H7 Isolation of S. aureus, which uses mannitol and turns medium yellow. Inhibition of most gram (-) and many gram (+) organisms. Isolation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests Isolation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Isolation of Neisseria species Isolation of Burkholderia cepacia (Previously known as Pseudomonas cepacia)
Isolation of Bordetella pertussis and B. parapertussis Isolation of Salmonella and Shigella. Inhibition of gram (+) organisms and some gram (-). Supports the growth of aerobes, anaerobes, and facultatives Isolation of Vibrio. Inhibition of many gram (+) and gram (-) organisms. Isolation of Corynebacterium diphtheriae Contains lactoe, sucrose, and glucose. Differentiates enteric organisms. Differentiates gram (-) enteric bacilli. Cultivation of fastidious and nonfastidious organisms. May be used as base for blood agar Tests for the presence of the enzyme urease Differentiates members of the Enterobacteriaceae group Isolation of Salmonella and Shigella. Inhibition of gram (+) organisms and some gram (-). Isolation of Gardnerella vaginalis, which is B-hemolytic on human blood.
Special Comments Nutritional base Inhibitors: Gentamicin and Bile Bile salts and Esculin Nutrients (Blood may be added) Inhibits gram (+) organisms Inhibitor: Phenylethyl alcohol Glycerol, potato infusion, and blood. Nutrients. Also inactivate toxic substances. Charcoal: Removes toxic substances. Nutrients: Yeast etract, cysteine, iron salts, and alpha-ketoglutarate Isolated from respiratory secretions Nutrient base, inhibitors: antimicrobial agents, blood may be added Inhibitors: Cefsulodin, irgasan, novobiocin, bile salts, crystal violet. Carb: Mannitol Nonfastidious organisms will also grow. Nutritional base, heated RBCs or other supplements None None Nutrient, blood/antibiotics may be added None None Inhibitors and pH indicators. Contains carbohydrate: lactose. Inhibitor: Bile salts. pH indicators: Acid fuchsin and bromthymol blue. Carbs: Lactose, sucrose, salicin. H2S system. Eggs, Malachite green Inhibitors: Bile salts and crystal violet. pH indicator: Neutral red. Carb: Lactose. None Inhibitor: 7.5% salt. pH indicator: Phenol red. Mannitol None Supplements may be added: Salt, cations (broth), sheep or lysed horse blood None None Contains antimicrobial agents
None Inhibitors: Bile salts, citrate, and brilliant green. pH indicator: Neutral red. Carb: Lactose. H2S system. Reducing agents: Thioglycollate, cystine, sodium sulfite. Agar: Reduces O2 diffusion. Inhibitors: Citrate, bile, and high pH. pH indicator: Bromthymol blue. Carb: Sucrose. H2S system. Tellurite: inhibitors many organisms None None Contains: Digested soybeans and casein None None Inhibitor: Bile salts. pH indicator: Phenol red. Carbs: Lactose, sucrose, xylose. Lysine. H2S system Contains: Nutrients, human blood
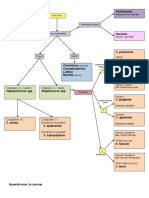
Bacitracin susceptibility CAMP test Hippurate Hydrolysis PYR hydrolysis Optichin susceptibility Bile esculin hydrolysis Salt-Tolerance Test X and V Factor Requirement Oxidase Spot Indol Catalase Coagulase Hydrogen sulfide production Urease Motility Vibriotstatic compound, O/129 disc test ONPG Deoxycholate Cefinase
Purpose/Principle Some organisms are suseptible to 0.04 units of bacitracin. Inoculate agar for confluent growth; add disk. Measure GBS make CAMP factor. S aureus makes B-lysin. Hemolysis enhanced when CAMP factor meets B-lysin. Test organ Hippurate ---(Hippuricase)---> Sodium benzoate + glycine. Detect either benzoate or glycine. Benzoate + Ferric chlo Chemical reaction - detects B-naphthylamine Inoculate agar plate for confluent growth with isolate. Place disk onto inoculate area. Incubate plate; measure zon 40% bile inhibits many organisms. Esculin ---> Esculetin + Glucose. Esculetin + Ferric ions --> Black 6.5% salt inhibits many organisms. Inoculate broth with organism Test organism inoculated onto trypticase soy agar or Mueller-Hinton agar, which lack X and V factors. Paper disk w Chemical Reaction - Detects indophenol Rub organism onto reagent-impregnated filter paper. Place organism on slide and add drop of H2O2. Detect bubbles Prepare saline suspension, mix in drop of plasma H2S + Iron or lead ----> Black Medium becomes alkaline as ammonia is produced Stab organism into semisolid agar deep Inoculate agar for confluent growth, add disks, incubate plate and measure zone Chemical reaction - Yellow color change in positive reaction Added to agar in order, visible pitting in the agar -- positive reaction Beta-lactamase detection
Pos. Rxn Susceptible: Any zone Enhanced hemolysis Benzoate: Precipitate, Glycine: Blue Red Susceptible: Zone > Cutoff Black Turbidity or acid pH Growth around disk Dark purple or Blue-black Blue-green Bubbles Cell clumping Black Red/pink Diffuse haze of growth throughout Any zone Yellow Pitting in agar Yellow to Red color change
Pos. Organism Micrococcus, GAS GBS GBS, Listeria, C. jejuni GAS, Enterococcus, Other gram (+) bacteria S. pneumoniae Enterococcus, GDS, Listeria Enterococci X only: H. ducreyi, V only: H. parainflu and H parahaemo., X and V: H. influ and H. haemo. Neisseria, Moraxella, Pseudomonas, B. cepacia, Vibrio, Aeromonas, and others E coli, P vulgaris, Morganella, Vibrio, Aeronomas, Plesiomonas, and others Staph, Micrococcus, Corynebacterium, Many Bacillus, and others S aureus Edwardsiella, Salmonella, Proteus K pneumoniae, Proteus, Morganella, Most Brucella, H pylori, and others Vibrio and Campylobacter (Darting), Bacillus, Many enterics, Aeromonas, and others Susceptible: Plesiomonas, Most V. cholerae E coli, Citrobacter, K pneumoniae, Enterobacter, S marcescens Enterics N gonorrhoeae, H influenzae, M catarrhalis, Enterococcus, Staph, Anaerobic bacteria
Neg. Rxn Resistant: No zone No enhanced hemolysis Benzoate: No precipitate, Glycine: No color No color change Resistant: No zone No color No turbidity or pH change No growth around disk No color change No color No bubbles No clumping No color Yellow Growth only near stab line No zone Colorless No pitting in agar No color change
Neg. Organism Staph, Stomatococcus, GBS, Other B-strep Groups A, C, D, F, and G Strep, Enterococci Groups A, C, F, and G Strep, Enterococci, Helicobacter Other Strep Other Strep Other Strep GDS not enterococci, Other Strep All other bacteria Enterics, S. maltophilia, Acinetobacter, Gardnerella Salmonella, K pneuoniae, Enterobacter, and others Clostridium, Fusobacterium, and others S saprophyticus, S epidermidis, Many other Staph species, Micrococcus E coli, Shigella, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia E coli, Shigella, Salmonella, S marcescens, P multocida Corynebacterium, Lactobacillus, Shigella, Klebsiella, Brucella, and others Resistant: Aeromonas Salmonella, Proteus, Providencia, Morganella Gram positive bacteria Non-B-lactamase bacteria
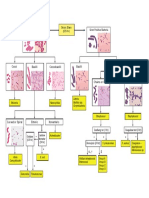
Urinary tract GenitalsandSTDs Upper Respiratory Tract Lower Respiratory Tract Ocular Skin and Soft Tissue (what about bone?) Gastrointestinal + Agents of possible food poisoning Central Nervous System Circulatory (blood)
Pathogens E coli, Other Enterobacteriaceae, S saprophyticus, P aeruginosa N gonorrhoeae, C trachomatis, T pallidum, H ducreyi S pyogenes, H influenzae S pneumoniae, H influenzae, S aureus, M tuberculosis S aureus, N gonorrhoeae, C trachomatis B burgdorferi, R ricketsii V cholerae, Salmonella, C jejuni, Shigella, C difficile, S aureus C botulinum, C tetanus, N meningitidis S pyogenes
Disease Associated UTI, Pyelonephritis Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, Syphillis, Chancroid Strep throat, Influenza Pneumonia, Tuberculosis Conjunctivitis (Infectious and Neonatal), Trachoma Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Cholera, Salmonella food poisoning Botulism, Tetanus, Meningitis Sepsis, Endocarditis
Areas Affected Bladder, Ureters, Kidneys Genitals Throat, Lungs Lungs Eyes Skin GI Tract CNS Heart, Blood Vessels
You might also like
- Board Exam Topic ChecklistDocument3 pagesBoard Exam Topic ChecklistVianney Angeli LorenzanaNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Staph and Strep SummaryDocument24 pagesStaph and Strep SummaryJihrus Mendoza100% (1)
- Bacterial ID FlowchartDocument6 pagesBacterial ID FlowchartTom Tsou50% (2)
- Gram Negative RodsDocument8 pagesGram Negative RodsRuel Maddawin100% (1)
- High Yield - Bacteriology ChartsDocument54 pagesHigh Yield - Bacteriology Chartsadom09100% (1)
- Mecha World Compendium Playbooks BWDocument12 pagesMecha World Compendium Playbooks BWRobson Alves MacielNo ratings yet
- Bacte TestDocument10 pagesBacte TestRiondalionNo ratings yet
- D&D 5.0 Combat Reference Sheet Move Action: Interact With One Object Do Other Simple ActivtiesDocument2 pagesD&D 5.0 Combat Reference Sheet Move Action: Interact With One Object Do Other Simple ActivtiesJason ParsonsNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry NotesDocument24 pagesClinical Chemistry Notesclower112100% (3)
- CC Conversion-FactorsDocument1 pageCC Conversion-FactorsAndrei Tumarong AngoluanNo ratings yet
- CHALLENGE QUESTIONS (Write Your Answer/s Here For Practice)Document2 pagesCHALLENGE QUESTIONS (Write Your Answer/s Here For Practice)Roma Ann ManahanNo ratings yet
- Simulated No.1 General Rule:: ExceptDocument29 pagesSimulated No.1 General Rule:: ExceptJie FuentesNo ratings yet
- CSMLS Exam Guide Notes (Referrence Range)Document4 pagesCSMLS Exam Guide Notes (Referrence Range)software4us.2023No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument10 pagesClinical ChemistryChristina AtefNo ratings yet
- Gram +ve BacteriaDocument58 pagesGram +ve BacteriaGx NavinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry ReviewDocument6 pagesClinical Chemistry Reviewclower112100% (1)
- 2Document8 pages2Eduardo Antonio Comaru Gouveia75% (4)
- Microbiology Memorization SheetDocument5 pagesMicrobiology Memorization Sheetalobrien100% (1)
- Bacte Day 2Document24 pagesBacte Day 2Jadey InfanteNo ratings yet
- Coagulation NotesDocument14 pagesCoagulation NotesthrowawyNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Exam 01 - RBC, WBC, BacteriaDocument30 pagesMicroscopic Exam 01 - RBC, WBC, BacteriaBrent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Mega Micro para Table 1 (1) (PDF - Io)Document81 pagesMega Micro para Table 1 (1) (PDF - Io)CheryldaneBaculiNo ratings yet
- Agglutination, Complement, Neutralization, and Inhibition: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 4From EverandAgglutination, Complement, Neutralization, and Inhibition: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 4No ratings yet
- Streptococcus, Entrococcus and Other Catalayse Negative GramDocument15 pagesStreptococcus, Entrococcus and Other Catalayse Negative GramKeen ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Spp. Gram Positive. ClusteredDocument15 pagesStaphylococcus Spp. Gram Positive. ClusteredIvy NNo ratings yet
- Microbiology, Bailey - S and Scotts Chapter 28, Moraxella and Related Orgs. by MT1232Document3 pagesMicrobiology, Bailey - S and Scotts Chapter 28, Moraxella and Related Orgs. by MT1232Aisle Malibiran PalerNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lab CSFDocument6 pagesAubf Lab CSFAndrei Tumarong AngoluanNo ratings yet
- Pass Ascp 2020 LatestDocument6 pagesPass Ascp 2020 LatestLorelie ChenNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart of Gram Negative OrganismsDocument1 pageFlow Chart of Gram Negative OrganismsKristine Marie PateñoNo ratings yet
- Incorrectly: CorrectlyDocument25 pagesIncorrectly: CorrectlypikachuNo ratings yet
- Methods of Studying Fungi: Dr. Alice Alma C. BungayDocument74 pagesMethods of Studying Fungi: Dr. Alice Alma C. BungayKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination of UrineDocument4 pagesMicroscopic Examination of UrineGlaiza Erika Baes GudaNo ratings yet
- Correctly: IncorrectlyDocument70 pagesCorrectly: IncorrectlyDjdjjd Siisus100% (1)
- GeneralDocument31 pagesGeneralpikachu100% (1)
- Bergy's Manual Identification Flow ChartDocument8 pagesBergy's Manual Identification Flow ChartOmid Nilchi Zadeh RahbarNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Gram Negative Rods Flowchart 508Document1 pageAerobic Gram Negative Rods Flowchart 508Issa AlejoNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Classification FlowchartDocument1 pageBacteria Classification FlowchartLindsayNo ratings yet
- ASCP Certification SOP PDFDocument2 pagesASCP Certification SOP PDFDeanne LambanNo ratings yet
- Practical 4 Staphylococci PresentationDocument24 pagesPractical 4 Staphylococci PresentationPatrisha BuanNo ratings yet
- CompilationDocument3 pagesCompilationBelle Cherlette FelipeNo ratings yet
- Project Quality Plan (JFJS-788)Document18 pagesProject Quality Plan (JFJS-788)mominNo ratings yet
- Hema AscpDocument5 pagesHema AscpDyne SabijonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Bacteriology ReviewerDocument17 pagesClinical Bacteriology Reviewer99noname100% (1)
- ENZYMOLOGYDocument2 pagesENZYMOLOGYCarla Lagar FloresNo ratings yet
- Microbiology CaseDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Caseclower112100% (2)
- Laboratory # 3 Biochemical Differentiation of Some Medically ImportantDocument34 pagesLaboratory # 3 Biochemical Differentiation of Some Medically ImportantSirine AjourNo ratings yet
- Blood SmearsDocument4 pagesBlood SmearsAmor KourdouliNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci Flow ChartDocument2 pagesGram Positive Cocci Flow ChartNgMinhHai0% (1)
- Recall 1Document4 pagesRecall 1pikachuNo ratings yet
- Anaerobe of Clinical ImportanceDocument43 pagesAnaerobe of Clinical ImportanceDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Microscopy: Definition and Volume Disease and Cause PolyuriaDocument5 pagesClinical Microscopy: Definition and Volume Disease and Cause PolyuriaJovanni andesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry IDocument8 pagesClinical Chemistry IMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Reagent Strip TestsDocument8 pagesSummary of Reagent Strip TestsDarla YsavelNo ratings yet
- MedtechDocument7 pagesMedtechLyudmyla GillegoNo ratings yet
- HemaDocument59 pagesHemaSteph VeeNo ratings yet
- (Bacteriology) Chapter 8: Use of Colonial Morphology For The Presumptive Identification of MicroorganismsDocument6 pages(Bacteriology) Chapter 8: Use of Colonial Morphology For The Presumptive Identification of MicroorganismsJean BelciñaNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument4 pagesCulture MediaHabibur RahamanNo ratings yet
- BOC Study Guide: The MostDocument17 pagesBOC Study Guide: The MostDeanne LambanNo ratings yet
- Immuno Serology ReviewDocument16 pagesImmuno Serology ReviewM CNo ratings yet
- Drummelsmith - Laboratory Diagnosis and Bacterial Identification - Study GuideDocument19 pagesDrummelsmith - Laboratory Diagnosis and Bacterial Identification - Study GuideTom TsouNo ratings yet
- Presentation DocumentDocument3 pagesPresentation Documentclower112No ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry NotesDocument1 pageClinical Chemistry Notesclower112No ratings yet
- Hematology Study GuideDocument2 pagesHematology Study Guideclower112No ratings yet
- Slide ReticsDocument1 pageSlide Reticsclower112No ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry NotesDocument1 pageClinical Chemistry Notesclower112No ratings yet
- Lab 3,4,5Document2 pagesLab 3,4,5clower112No ratings yet
- Lab AboDocument5 pagesLab Aboclower112No ratings yet
- Applying For A Job: Pre-ReadingDocument5 pagesApplying For A Job: Pre-ReadingDianitta MaciasNo ratings yet
- ..Product CatalogueDocument56 pages..Product Catalogue950 911No ratings yet
- Total Physical Response (G4)Document3 pagesTotal Physical Response (G4)Aq Nadzrul LarhNo ratings yet
- 25 Middlegame Concepts Every Chess Player Must KnowDocument2 pages25 Middlegame Concepts Every Chess Player Must KnowKasparicoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Project 4º Eso Beauty Canons 2015-16 DefinitivoDocument2 pages2nd Term Project 4º Eso Beauty Canons 2015-16 DefinitivopasferacosNo ratings yet
- Shri Naina Devi Aarti English 167Document5 pagesShri Naina Devi Aarti English 167ratt182No ratings yet
- Math F112Document3 pagesMath F112ritik12041998No ratings yet
- Imabalacat DocuDocument114 pagesImabalacat DocuJänrëýMåmårìlSälängsàngNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument40 pagesPDFAndi NursinarNo ratings yet
- Industrial ExperienceDocument30 pagesIndustrial ExperienceThe GridLockNo ratings yet
- Been There, Done That, Wrote The Blog: The Choices and Challenges of Supporting Adolescents and Young Adults With CancerDocument8 pagesBeen There, Done That, Wrote The Blog: The Choices and Challenges of Supporting Adolescents and Young Adults With CancerNanis DimmitrisNo ratings yet
- (20836104 - Artificial Satellites) Investigation of The Accuracy of Google Earth Elevation DataDocument9 pages(20836104 - Artificial Satellites) Investigation of The Accuracy of Google Earth Elevation DataSunidhi VermaNo ratings yet
- Lady in The House, Her Responsibilities & Ambitions: Amrita DuhanDocument7 pagesLady in The House, Her Responsibilities & Ambitions: Amrita DuhanFitness FableNo ratings yet
- ICMApprovedCentres - Ghana PDFDocument8 pagesICMApprovedCentres - Ghana PDFPrince Kelly100% (2)
- A P P E N D I X Powers of Ten and Scientific NotationDocument5 pagesA P P E N D I X Powers of Ten and Scientific NotationAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Img 20150510 0001Document2 pagesImg 20150510 0001api-284663984No ratings yet
- CURRICULUM PharmasubDocument10 pagesCURRICULUM PharmasubZE Mart DanmarkNo ratings yet
- Img 20201010 0005Document1 pageImg 20201010 0005Tarek SalehNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document18 pagesSession 1Akash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Alaba Adeyemi AdediwuraDocument12 pagesAlaba Adeyemi AdediwuraSchahyda ArleyNo ratings yet
- AISOY1 KiK User ManualDocument28 pagesAISOY1 KiK User ManualLums TalyerNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic QuestionsDocument2 pagesArithmetic QuestionsAmir KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EthicsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To EthicsMarielle Guerra04No ratings yet
- Sale Counter List JuneDocument9 pagesSale Counter List Junep6a4nduNo ratings yet
- 40 Sink and FloatDocument38 pages40 Sink and Floatleandro hualverdeNo ratings yet
- Studies On Drying Kinetics of Solids in A Rotary DryerDocument6 pagesStudies On Drying Kinetics of Solids in A Rotary DryerVinh Do ThanhNo ratings yet