Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How To Broadcast A BEx Report Through E
Uploaded by
Zaynab FadlallahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How To Broadcast A BEx Report Through E
Uploaded by
Zaynab FadlallahCopyright:
Available Formats
How to Broadcast a BEx Report through Email
How to Broadcast a BEx Report through E-mail
1) Open the BEx query in BEx Query Designer. 2) Go to Menu Query->Publish-> and Click on BEx Broadcaster 3) Internet Explorer (or any default browser) window will open with a login screen for the SAP NetWeaver Portal 4) Login using the BW login credentials of the User using which you want the BEx report to be broadcasted. 5) You will see a screen as below which shows the list of available broadcast settings for the particular query: 6) Click on Create New Setting button. 7) There will be four tabs a. Recipient(s) b. Texts c. General Precalculation d. Filter Navigation This is a step by step guide on how to broadcast a BEx report to the E-mail of specific users.
Recipients You have different options for entering recipients: User: Users in Roles: Note: If an e-mail address for a user that you have specified under User or User in Role has not been maintained in user maintenance, the user will not receive the distributed file as an e-mail. Instead the user gets a message in the Business Workplace (transaction SO01). E-Mail Addresses: Authorized User: Language: User-specific: If you schedule the broadcast setting in the background (for example for a specific time), then you can generate the document user specifically. The system generates the document for each of the specified recipients with their personal settings (date format, language) and data authorizations. Recipients that are only specified with e-mail addresses are excluded from this. For this recipient, the system generates the document with the settings for the authorized user.
Texts - Here you can make the following entries: Subject: Importance: Contents: General Precalculation o Variable Assignment: You can create values for the variables for the query that are ready for input or you can specify the Web application. The query or Web application is then precalculated with these variable values. You are able to select an existing variant for the query. The query is precalculated with the values of the variant. Filter Navigation On the Filter Navigation tab page you can specify characteristics or a control query so that the system precalculates several documents with different filter settings from the same query or Web application. These filter values provide you with a navigation option in the precalculated document. You can select the filter values using dropdown boxes in the navigation block. You can make the following settings:
No Filtering: The system precalculates an unfiltered document.
Filtering Using Selected Characteristics: The system precalculates several documents with various filter settings according to your chosen settings. Highlight the desired characteristic and specify the desired filter value using Create Filter Values. You can specify a maximum of two characteristics. Filtering Using Control Query: The system precalculates several documents with various filter settings. The filters correspond to the characteristic combinations of the control query that you specified. Specify the desired control query in the Control Query field either manually or using Selection.
8) Give a description for the broadcast setting 9) Select the Distribution type. In our case it would be Broadcast Email. 10) Select the output format. We will select XML (MS Excel) which is the Microsoft Excel Format. 11) We can enable the As ZIP file checkbox to send the file as a zipped attachment to the recipients email. 12) Recipients: Specify the email addresses of the users to whom you want the report to be broadcasted in the Email Addresses field. 13) Texts: Specify the Email Subject and the Email Contents. The subject and contents specified here will be reflected in the Subject and contents of the email delivered to the recipient.
14) General Precalculation: If the query has any input variables, you will have to create a variable assignment and assign values for the variable. The broadcasted report will be precalculated for the variable values which you assign in this tab. Select VAR_01 as shown in the below screenshot and click on Create.
You will see the variable screen where you have to assign values for the variables and click on ok. (Sample variable assignment shown below)
15) The Filter Navigation tab is used to apply filters (if any) to the query before precalculating and broadcasting the query. We can leave it blank if no filters are to be applied before broadcasting. 16) Now save the broadcast setting by giving a technical name. 17) The next step is to schedule the broadcast after specifying the recipients, the contents of the email, and the variable assignment. Click on the Schedule button. Enable the Create New Scheduling check box, and select the time to schedule the broadcast and click Transfer.
Scheduling the Broadcasts Automatically:
The scheduling of broadcasts can be automated with the help of a program and through process chains. Create a process chain and include the ABAP program RSRD_BROADCAST_BATCH. This program can be used to schedule the broadcasts in the background without any use intervention. Create a variant for this program and give the technical name of the Broadcast setting for the selection variable S_SETTNG (Broadcast Setting). Now schedule the process chain at the particular time (may be periodic) at which you want the broadcast to be sent.
Posted 7th August 2012 by SAP BI/BW
sap bi/bw
1. Feb
InfoCube Design Golden Rules
InfoCube Design Golden Rules
InfoCube
Analyze your existing SAP BW environment for potential candidates that should be redesigned by running programSAP_INFOCUBE_DESIGNS. This program takes around five minutes to run and returns a list of every table associated with every infocube grouped by infocube. Look for the dimension tables in red (which is representative of being greater than 15% of the fact tables). These are your best candidates for redesign. We highly recommend you run this program on a monthly basis to have a better handle on performance in your system. 1. Small dimension tables (more important)
o o
The smaller a dimension table is, the less time spent reading from it. Performance is much better when dimension tables remain small. 2. Few dimension tables (less important)
o o o o
table
Keep the dimension tables small (<15% the size of the fact table) Only enable time dependency if necessary Avoid Min and Max aggregation for Key Figures in large InfoCubes The most commonly used characteristics should be ordered first in a dimension
Posted 4th February by SAP BI/BW 2.
Feb 4
Business Objects Explorer
Business Objects Explorer
So you want to report on your data in real time instead of making canned reports for your clients? Well, business objects explorer (BOE) 4.0 is just what the doctor ordered. Imagine a world where the client can run a report on exactly what they need without the need for a front end team to create canned reports that are often restrictive in nature and dont allow the end user to fully explore data in the manner they they so often choose. No more expensive SAP BW trainingfront end and report design training courses will be needed as the traditional locked down report development landscape is becoming obsolete. Business Objects Explorer 4.0, when coupled with the Business Warehouse Accelerator make for the information powerhouse that every competitive company is seeking to obtain. Imagine running a report on your terms rather than what another team designed for you. Traditional BEx reports more than likely need updating and contain less than desirable fields. With BOE, you pick what you want to see in real time! No more making calls to Fred down on the SAP BW/BI BEx query design department as you can report on what you want when you want. Data is pulled into BOE from any source you like including existing SAP BW data warehouses. Bear in mind that if you dont have a Business Warehouse Accelerator (BWA) results will take much longer to return. BOE 4.0 allows the user to search for data at the speed of thought. Business Analysts are going to love using BOE as it unlocks so much potential for the end user and ultimately the company in the information management landscape.
Posted 4th February by SAP BI/BW 3. Feb 4
MultiProviders
MultiProviders
Why use a MultiProvider: When you need to combine multiple InfoProviders of varying types into one reportable object. Its essentially a view on InfoProvider tables which means MultiProviders store no physical data. MultiProviders do not join data. There is another BW object called an InfoSet which is a reportable object capable of joining data Common usage: Logically partitioning InfoCubes and DSOs to improve performance. Logical partitioning expedites the activation process (less data = less time to activate) as well as reporting (less time spent looking for data). Best Practices:
o o o
SAP recommends a maximum of 10 InfoProviders per MultiProvider. Set InfoProvider specific properties which force a query to point to a single InfoProvider instead of running sub-queries on all InfoProviders during query runtime. Always incorporate MultiProviders into your design when you plan on reporting off of InfoProviders like DSOs and InfoCubes. This allows you to connect reports to a single multiprovider all permitting changes to the underlying data structures without losing the report connections. Example: InfoCubes ZFIM08, ZFIM09, and ZFIM10 are logically partitioned by calendar year and built under the ZFIMMP MultiProvider umbrella. The querying user running the report only
wants to see data from 2009, however by default, the query will look for 2009 data in all three of the InfoProviders when in actuality, only one contains 2009 data. To resolve this performance issue, we can set each logically partitioned InfoCube to a static calendar year during the modeling process, so the query sees this upon execution and ignores the other two InfoCubes.
Posted 4th February by SAP BI/BW 4. Feb 4
DataStore Objects
DataStore Objects
DataStore Objects (DSO) formerly known as Operational DataStores (ODS is the old acronym) are primarily used in the BW environment to stage data and allow for another layer of data cleansing before data is moved to the InfoCube. However, you could also use a DSO to report from (although not recommended as SIDs are generated in real-time) bypassing the need for an InfoCube. Its a best practice to always include DSOs in your source to target data flow. The three containers of data within your data flow should be DataSource (source of data) > DSO (detail level data) > InfoCube (data to be reported). What makes a DSO different from an InfoCube? DataStore Objects consist of much fewer tables as data is stored at the detail level. DSOs do not utilize the Extended Star Schema and therefore it is best to not report from this type of InfoProvider. DSOs are essentially a
flat table (think of a spreadsheet) where data is dumped into. Every record is unique in a DSO thanks to technical keys which I will discuss below. When data is loaded into a DSO, it first gets sent to the New Data (40) table. The data will sit in the New Data table until it is activated, which then ships it over to the Active Data (00) table and the Change Log table (##). During the activation process, the New Data table gets wiped out, and a change record is loaded to the Change Log.
Three Types of DSOs:
o
Standard (most commonly used) When to use- Line item detail level Capable of using secondary indexes to improve read performance Secondary indexes are set within the DSO modeling screen, lower right Remember to delete data from change log regularly as it will continue to grow overtime and cause performance issues Any data no longer being used in the active table should be archived Associated tables: New Data: /BIC/Adsoname40
Active Data: /BIC/Adsoname00 Change Log: /BIC/########## (dynamically generated)
Write-Optimized (less common) When to use- When data does not need to be updated, just written Every record is written not updated so data loads quickly Uses a technical key [RequestID | DataPackage | DataRecordNumber] Uses an optional semantic key that the user defines for ordering/grouping data logically If you enable the Do Not Check Uniqueness checkbox semantic keys will become disabled data will load faster reporting will be slower Build indexes on what is accessed most often Associated tables: Active Data: /BIC/Adsoname00
Direct-Update (least used) When to use- When data is only needed in one version, active Data is written using BAPIs and Function Modules Associated tables:
Active Data: /BIC/Adsoname00
Posted 4th February by SAP BI/BW 5. Feb 4
SAP BW InfoObjects
SAP BW InfoObjects
InfoObjects are essential to the SAP business intelligence solution. InfoObjects accept and obtain information from the source, then revise and arrange the information into either a standard or unique report. The InfoObject is the smallest building block in SAP BW. It is put to use in InfoProviders (InfoCubes, DSOs, MultiProviders, Queries, etc). Picture InfoObjects as very small Lego pieces that when assorted together, make a much bigger Lego formation (InfoProvider). InfoProviders are made from InfoObjects and form something critical that permits end users to report from. You will find five different types of InfoObjects offered in the SAP BW environment. Types of InfoObjects: A) Characteristics (Employee, Customer, Material) B) Key Figures (Quantity Sold, Amount, Weight) C) Time Characteristics (Year, Month, Period, Quarter) D) Unit InfoObjects (Currency Unit, Measurement Unit) E) Technical Characteristics (Data Load Request ID, Change Run ID, Package ID)
A) Characteristics: This type of InfoObject symbolizes a business entity that you are likely going to be analyzing. Such as: material, customer, or region.
B) Key Figures: This type of InfoObject provides numeric measures of business entities. We chose to implement these to examine characteristics by weight, quantity, price, amount, etc C) Time Characteristics: This particular type of InfoObject provides when a transaction takes place. As an option, fiscal year, month of sale, day of sale, quarter in which something sold. D) Unit InfoObjects: This kind of InfoObject provides what unit of measure a key figure is using. For instance, we might be using the metric system to gauge weights for our clients, so as a substitute for pounds we will be using kilograms. E) Technical Characteristics SAP internal InfoObjects that retain information containing automatically generated IDs that are being used for monitoring and administration of the SAP BW system. For example, every individual load into SAP BW involves a unique request ID that ties back to a exclusive load so administrators can diagnose inaccuracies or take out a bad data load. See if you are able to spot the InfoObjects that we would need to use in an effort to answer this business question
ABC Corporation is interested in finding out how much of product x shipped on date x to factory x.
0NAME (ABC Corporation), 0MATERIAL (Product x), 0DATE (Ship date x), 0LOCATION (factory location) would be our characteristics needed 0AMOUNT (Quantity shipped) would be our key figure used to measure the quantity of products shipped
We know that we would need at a minimum, an InfoProvider that incorporated the above five InfoObjects. This is important when building in BW to get the client to let you know all the pieces they are wishing to analyze (InfoObjects) so you can produce an InfoProvider containing applicable InfoObjects that will create valuable reports and in turn information for the business.
SAP delivers a plethora of InfoObjects standard. These objects are actually in the BI content (Business Content). BI content is SAPs strategy for an out of the box answer to your business requirements. These objects begin with 0 and it is not recommended to revise them. Having said that, more often than not, delivered InfoObjects will not meet your needs for development, you can effortlessly create a customized object that will meet
your requirements. You can create custom Characteristic, Key Figure, and Unit InfoObjects.
Posted 4th February by SAP BI/BW 6. Feb 4
BWA Only InfoCube Build Instructions
1. What do we do if regular loads are being added to the DSO?
You will need to set up a process chain that kicks off a DTP after you load the DSO. You need to keep the BWA only cube as recent as possible. Make sure to try and transfer the DSO delta data to the BWA only cube as frequently as possible.
2. Do we need to run DTP from the DSO to cube after every new request into DSO? Yes, the BWA only cube will only write the data to memory when the DSO to BWA only cube load is kicked off. Otherwise the BWA only cube has no idea that the DSO has new data. The DTP runs very quickly as its loading to memory so run it often.
BWA Only InfoCube Build Instructions:
Step 1: Create a new InfoCube with the DSO you want to index as the template. Select from the BWA status drop down: InfoCube only stores its data in the BWA.
Step 2: Here we can see the structure of the cube. It takes the DSOs characteristic fields and throws it all into Dimension 1. All the DSOs key figures get put into the key figures folder of the cube. Activate the InfoCube.
Step 3: In transaction RSDDB (new to 7.3, BWA transaction) we can see the index is red which means it is in the process of being created (ZBWAONLY1).
Step 4: In SM37 we can see the index activation taking place
Job Log
Step 5: RSDDB Index Info (note the F table has an Index Size of 0, as we have not run the DTP from the DSO to the BWA only InfoCube)
Step 6: Run the DTP, once complete, manage the BWA Only Cube
Step 7: When we go back to RSDDB and go to index info we can see that since the DTP completed, the F table index has 10,528 records sitting in the BWA.
Posted 4th February by SAP BI/BW 7. Feb 4
What is HANA ?
What is HANA?
The latest craze in the data warehousing industry is SAPs proprietary new database called HANA. HANA stands for High Performance Analytic Appliance and it will change the way we as an industry access data and allow for more informed decisions to be made in far less time. HANA enables the business to view data in real-time and creates a highly adaptable environment in which executives and business leaders can access data as soon as a transaction occurs. We cannot stress enough that HANA is not a replacement forBW! What is SAP HANA? HANA is a replacement for traditional disk based databases. It uses a column based storage method that allows for much faster data access and uses far less memory to store data. Its a way that all of the data a user will be seeking for their reporting needs is stored in random access memory (RAM) instead of on hard disk or flash storage. Will HANA replace the Business Warehouse Accelerator BWA? Did the Sony Playstation 3 replace the Playstation 2? In short, yes. HANA is a database that data can be either sourced from (given an ECC HANA implementation) or reported from (given a BW implementation). The BWA is an in memory appliance that sits on top of the BW application and needs to be loaded daily just like any InfoCube would in order to keep data as fresh as possible. HANA however does not need to be loaded like the BWA does. It removes the additional layer of loading up to memory because all of the data resides in memory. This is far superior to the BWA as it removes the disk based storage layer and removes the need to roll up new data into memory each time a new load comes in. HANAs memory is always up to date because of the new changes that took place with the integration of both the hardware and software. We invested a ton of money already in the BWA, can we leverage the BWA hardware to save money? Unfortunately, you would have to upgrade to new hardware in order to support HANA. SAP is a software company that is continuing to innovate faster than existing hardware can support. The HANA hardware is much more powerful What does this mean for an existing BW install? You could use the HANA database migration tool in order to migrate from a traditional disk based storage appliance to a new HANA appliance. HANA requires at a minimum BW 7.3 with service pack 6 installed. This adds a data resides on HANA appliance checkbox that
the user may check. In doing so, it would be storing all of the InfoProviders data directly in memory and not on a traditional database.
Posted 4th February by SAP BI/BW 8. Feb 4
Layers of SAP NetWeaver BW
The SAP Business Warehouse has different layers that are responsible for reliable data acquisition and information processing along with robust analytical capabilities. Based on the functions and applications in the solution, the different layers in SAP BW are:
A) Extraction layer B) Staging layer C) Transformation layer D) Loading layer
E) Reporting and analysis layer The extraction layer is the collection of data from source systems. It aims to guarantee the integrity of data while eliminating reporting burdens on the source systems. Data can be extracted from an array of different sources. A) Extraction layer: SAP NetWeaver BW offers predefined, customizable extractors for application data from the entire SAP Suite. You can also design extractors for customized SAP applications. Most extractors for SAP application transaction data are delta-enabled, which means that transactions can be written to a delta queue at the time of posting. They are then extracted from this delta queue into SAP BW. Direct extraction from databases based on table or view definitions using DB Connect and UD Connect extraction interfaces. DB Connect (Database Connection) permits the extraction from and direct access to data lying in tables or views of database management systems. This feature is available only for some specific databases. UD Connect (Universal Data Connect) permits the extraction from and direct access to both relational and multidimensional data. Web services allow you to push data to the SAP BW system with external control. Flat file interface enables extraction from flat files in ASCII and CSV format. Staging BAPIs (Staging Business Application Programming Interfaces) are open interfaces from which third-party tools can extract data from older systems. The data transfer can be triggered by a request from the SAP BW system or by a third-party tool. Data is acquired from SAP BW using a pull mode, through objects called InfoPackages. Parameters for the data acquisition can be set in the InfoPackage.
B) Staging layer: Extracted data is received and temporarily stored in the staging layer of SAP NetWeaver BW. The data staging layer stores source data from different operational sources. When data is inside of the staging layer all needed transformations can then occur without interfering with the operations in the source systems. Data is also preprocessed for cleansing before calculation and/or aggregation based on business requirements. This layer is mostly represented by the persistent staging area (PSA), where data is stored in SAP BW after its extracted. The technical structure of a PSA depends on the structure of the DataSource. C) Transformation layer: The transformation layer of SAP BW facilitates the consolidation, cleaning, and integration of data into the warehouse. Data gets converted from the source format into the desired destination data format. Data transformation can involve data mapping and formulas. D) Loading layer:
The actual process of pushing data through the transformation layer into the data targets. A data transformation process (DTP) transforms the data based on the parameters defined between the DataSource and the data target. E) Reporting and Analysis layer: Within the reporting and analysis layer, reports and dashboards are created to display data in a format where analysis can be done. The components that represent the reporting and analysis layer are grouped together in the SAP business explorer (BEx) toolset and more recently the Business Objects toolset.
Posted 4th February by SAP BI/BW 9. Jan 31
sap wide information
http://sapdocs.info/?cat=92 Posted 31st January by SAP BI/BW 10. Jan 31
SD Configuration
Enterprise Structure: 1 Edit, Copy, Delete, Check Company Code(T001) Company is created by FI Consultant. The company code is an organizational unit used in accounting. It is used to structure the business organization from a financial accounting perspective. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Definition -> Financial Accounting -> Define, copy, delete, check Company Code
2 Define Credit Control Area(T014) Company is created by FI Consultant. The credit control area is an organizational unit that specifies and checks a credit limit for customers.A credit control area can include one or more company codes. It is not possible to assign a company code to more than one control area. Within a credit control area, the credit limits must be specified in the same currency. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Definition -> Financial Accounting-> Define Credit Control Area 3. Maintaining Sales Organization(TVKO) Sales Organization is an organizational unit responsible for the sale of certain products or services. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Definition -> Sales and Distribution -> Define, copy, delete, check Sales organization 4. Assigning Sales Organization to Company Code(TVKO~BUKRS) This assignment ensures all the sales made through this Sales Organization are accounted for in the assigned Company Code (Company Code is created by FI Consultant). IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Assignment -> Sales and Distribution -> Assign Sales Organziation to Company Code 5. Maintaining Distribution Channel(TVTW) Distribution Channel is the way, in which Products or Services reach Customers. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Definition -> Sales and Distribution -> Define, copy, delete, check distribution channel 6. Assigning Distribution Channel to Sales Organization(TVKOV) This assignment ensures, a Sales Organization can supply Materials to Customers through this Distribution Channel. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Assignment -> Sales and Distribution > Assign distribution channel to sales organization 7. Maintaining Division(TSPA) Division is a way of grouping materials, products, or services. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Definition -> Logistics General -> Define, copy, delete, check division 8. Assigning Division to Sales Organization(TVKOS) IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Assignment -> Sales and Distribution -> Assign division to sales organization 9. Setting up Sales Area(TVTA) All the sales are made from a particular sales Area. For creating a Sales Order Sales Area is compulsory. IMG ->Enterprise Structure -> Assignment -> Sales and Distribution -> Set up sales area 10 Maintain sales office(TVBUR) you define the sales offices in your company. The definition of sales offices is optional. For each sales office, you can determine the printer for output based on the sales documents in different ways IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Definition -> Sales and Distribution -> Maintain Sales Office
11 Assign sales office to sales area(TVKBZ) IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Assignment -> Sales and Distribution -> Assign sales Office to Sales Area 12 Maintain sales Group(TVKGR) company. The definition of sales groups is optional. You can use the SD system without creating sales groups. 13 Assign sales group to sales office(TVBVK) you can assign as many sales groups as desired to the sales offices. Any one sales group can belong to several sales offices. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Assignment -> Sales and Distribution -> Assign sales group to sales office 14. Define Shipping Points(TVST) Shipping Point is the Organizational element, which is responsible for shipping the Materials to the Customers. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Definition -> Logistics Execution -> Define, copy, delete, check shipping point 15 Define, copy, delete, check plant(T001W) Plant is created by MM Consultant. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Definition -> Logistics General -> Define, copy, delete, check plant 16 Assigning Shipping Point to Plant(TVSWZ) This assignment ensures that goods from different Plant can be dispatched from different Shipping Points. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Assignment -> Logistics Execution -> Assign shipping point to plant 17. Assigning Sales Organization- Distribution Channel- Plant(TVKWZ) Plant is created ny MM Consultant. IMG -> Enterprise Structure -> Assignment -> Sales and Distribution -> Assign sales organization distribution channel plant Note: Ensure to do the undermentioned configuration also though it is not in Customizing node of Enterprise Structure. 18. Defining Common Distribution Channels for Master Data(TVKOV-VKWKO TVKOV~VTWKU) Use The purpose of this activity is to define distribution channels which have common master data.. Procedure Access the activity using one of the following navigation options: IMG Menu -> Sales and Distribution -> Master Data -> Define Common Distribution Channels Transaction Code: VOR1 19. Defining Common Divisions for Master Data(TVKOS-SPAKO TVKOS~SPAKU) Use The purpose of this activity is to define distribution channels which have common master data..
Procedure Access the activity using one of the following navigation options: IMG Menu -> Sales and Distribution -> Master Data -> Define Common Division Transaction Code: VOR2 Pricing ProcedureIn SD, Pricing Procedure is determined based on Sales Area (Sales Organization + Distribution Centre + Division) + Customer Pricing Procedure + Document Pricing Procedure. Sales Area is determined in Sales Order Header Level. Customer Pricing Procedure is determined from Customer Master. Document Pricing Procedure is determined from Sales Document Type / Billing Type (if configured). Once the pricing procedure is determined, Condition records are fetched. If appropriate condition records are found, the price is determined. If Mandatory pricing condition is missing, system will through an error message. In SD, the steps to configure Pricing procedure are as under: Step 1: Condition table: If existing condition table meets the requirement, we need not create a new condition table. Considering the requirement for new condition table, the configuration will be done in spro as follows: IMG -> Basic Function -> Condition Table (select the required fields combination, which will store condition record). Step 2: Access Sequence: If existing access sequence meets the requirement, we need not create a new access sequence. Considering the requirement for new sequence, the configuration will be done in spro as follows: IMG -> Basic Function -> Access Sequence (Access sequence is made up of Accesses (Tables) & the order of priority in which it is to be accessed. Here we assign the condition table to access sequence. Step 3: Condition Type: If existing condition type meets the requirement, we need not create a new condition type. Considering the requirement for new condition type, the configuration will be done in spro as follows: IMG -> Basic Function -> Condition Type. It is always recommended to copy an existing similar condition type & make the neccessary changes. Here we assign Access sequence to Condition type. Step 4: a. Pricing Procedure: It is recommended to copy a similar pricing procedure & make the neccesary changes in new pricing procedure. Pricing Procedure is a set of condition type & arranged in the sequence in which it has to perform the calculation. Considering the requirement for new Pricing Procedure, the configuration will be done in spro as follows: IMG -> Basic Function -> Pricing Procedure > Maintain Pricing Procedure. b. Pricing Procedure: After maintaining the pricing procedure the next step will be determination of pricing procedure. Configuration for determining pricing procedure in SPRO is as follows: IMG -> Basic Function -> Pricing Procedure > Determine Pricing Procedure. 5. Condition record: Condition record is a master data, which is required to be maintained by Core team / person responsible from the client. During new implementation, the condition records can be uploaded using tools like SCAT, LSMW, etc. Normal Sales Order Cycle:Step 1: Sales Document Type IMG > Sales and Distribution > Sales > Sales Documents > Sales Document Header: 1. Sales Document Type:The sales document types represent the different business transactions, such as Inquiry, Quotation, Sales Order, etc. To create new sales order type, always copy as with reference to similar sales order. If possible use standard sales order.
2. Define Number Ranges For Sales Documents: Maintain number range with discussion with core team. 3. Assign Sales Area To Sales Document Types: A. Combine sales organizations / Combine distribution channels / Combine divisions: Ensure to maintain these, else Sales Order creation will give error. B. Assign sales order types permitted for sales areas: Assign only required Sales Order Types to required Sales Area. This will minimize selection of Sales Order Type as per sales area. Sales Document Item: 1. Define Item Categories: If possible use Standard Item Category. Incase if required to create new, copy as from standard & maintain New. 2. Assign Item Categories: If possible, use standard. Formula for deriving item category: Sales Document Type + Item Category Group + Usage + Higher Level Item Category = Item Category Schedule Line: 1. Define Schedule Line Categories: If possible use Standard Schedule Lines. Incase if required to create new, copy as from standard & maintain New. 2. Assign Schedule Line Categories: If possible, use standard. Formula for deriving Schedule Line: Item Category + MRP Type / No MRP Type. Step 2: IMG > Logistic Execution > Shipping > Deliveries > 1. Define Delivery Types: If possible use Standard Delivery Type. Incase if required to create new, copy as from standard & maintain New. 2. Define Item Categories for Deliveries: If possible use Standard Item Categories for Delivery Type. Incase if required to create new, copy as from standard & maintain New. 3. Define Number Ranges for Deliveries: Ensure to maintain number range. Step 3: IMG > Sales and Distribution > Billing > 1. Define Billing Types: If possible use Standard Billing Type. Incase if required to create new, copy as from standard & maintain New. 2. Define Number Range For Billing Documents : Ensure to maintain number range. 3. Maintain Copying Control For Billing Documents: Maintain relevant copy controls such as Sales Order to Billing, Deliver to Billing, etc. The configuration differs from scenario to scenario & requirement of the client.
Posted 31st January by SAP BI/BW Loading Send feedback
ads not by this site
You might also like
- Exploring Advanced Features of Oracle BI PublisherDocument113 pagesExploring Advanced Features of Oracle BI PublisherPaul Dfouni100% (1)
- MIPI DPI Specification v2Document34 pagesMIPI DPI Specification v2Dileep ChanduNo ratings yet
- As PDF Best Wayfinding Design (Vol .1 Office - Culture) by HI-DESIGN INTERNATIONAL PUBLISHING (HK) CO., LTD PDFDocument162 pagesAs PDF Best Wayfinding Design (Vol .1 Office - Culture) by HI-DESIGN INTERNATIONAL PUBLISHING (HK) CO., LTD PDFBuliga Alexandra ElenaNo ratings yet
- How To Broadcast A BEx Report Through E-MailDocument13 pagesHow To Broadcast A BEx Report Through E-Mailswati phadatareNo ratings yet
- DOC-25391 - How To Broadcast A BEx Report Through E-Mail PDFDocument9 pagesDOC-25391 - How To Broadcast A BEx Report Through E-Mail PDFeltonheNo ratings yet
- Bi Certi Bw305Document62 pagesBi Certi Bw305Albert FranquesaNo ratings yet
- NW Portals 2007 Broadcaster Berg v5Document61 pagesNW Portals 2007 Broadcaster Berg v5NarendraNo ratings yet
- Create Custom Analytical ReportsDocument55 pagesCreate Custom Analytical ReportsBhousonNo ratings yet
- CRN Report OptimizationDocument183 pagesCRN Report OptimizationGiridhar PodishettyNo ratings yet
- New Dimensions For Reporting: Applies ToDocument13 pagesNew Dimensions For Reporting: Applies ToZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- SAP Business Objects Interview Questions With AnswersDocument6 pagesSAP Business Objects Interview Questions With Answersscholarmaster0% (1)
- Interview CognosDocument9 pagesInterview Cognosraj.bl111No ratings yet
- Project Report On Daily Expense Tracking SystemDocument37 pagesProject Report On Daily Expense Tracking SystemDrashti RaichuraNo ratings yet
- Birst Trial - Getting Started Exercise 3 DashboardDocument11 pagesBirst Trial - Getting Started Exercise 3 DashboardAvinNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With Oracle BI Publisher 11gDocument76 pagesGetting Started With Oracle BI Publisher 11greturnasapNo ratings yet
- BO QuestionsDocument94 pagesBO QuestionssatyalipuNo ratings yet
- BO Interview Ques 4Document2 pagesBO Interview Ques 4Abhilasha ModekarNo ratings yet
- IBM® Tivoli® Software: Document Version 4Document50 pagesIBM® Tivoli® Software: Document Version 4RajMohenNo ratings yet
- Obiee 11g Bi PublisherDocument85 pagesObiee 11g Bi PublisherPriyanka GargNo ratings yet
- Cognos Interview Q&A: Reports, Scheduling, Drill-ThroughDocument5 pagesCognos Interview Q&A: Reports, Scheduling, Drill-Throughabdul87sNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure of Creating Workbook Using Bex AnalyzerDocument16 pagesStep by Step Procedure of Creating Workbook Using Bex Analyzerrohith_teja2426No ratings yet
- 10 Tips Optimize Web Intelligence Reports PerformanceDocument69 pages10 Tips Optimize Web Intelligence Reports PerformancekksrisriNo ratings yet
- Query PerformanceDocument6 pagesQuery PerformancemngtrajeshNo ratings yet
- Petrol Info SysDocument108 pagesPetrol Info Sysvinay999100% (1)
- Interview - Oracle BI Publisher2Document4 pagesInterview - Oracle BI Publisher2mohammed almoorNo ratings yet
- BO 5.0 Repository Create/maintain 50 Tables, They Are Distributed As FollowsDocument32 pagesBO 5.0 Repository Create/maintain 50 Tables, They Are Distributed As FollowsvenkatakishoreBLNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Report Development in CognosDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Report Development in CognosArpit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Cog 1Document24 pagesCog 1pavanm84No ratings yet
- SAP BO Admin QuestionsDocument4 pagesSAP BO Admin QuestionsKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Online Fast Food Django - SynopsisDocument18 pagesOnline Fast Food Django - SynopsisGauri vanveNo ratings yet
- 1-Getting Started With Oracle BI PublisherDocument93 pages1-Getting Started With Oracle BI PublisherMostafa TahaNo ratings yet
- Logging In: Accessing Business Intelligence Publisher EnterpriseDocument23 pagesLogging In: Accessing Business Intelligence Publisher EnterpriselionelpippoNo ratings yet
- Creating ODS Objects: Prerequisites ProcedureDocument4 pagesCreating ODS Objects: Prerequisites ProcedurebuddydavisNo ratings yet
- E-Billing & Invoice System - SynopsisDocument21 pagesE-Billing & Invoice System - SynopsisUmesh Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Optimize Cognos Query Performance with Best PracticesDocument11 pagesOptimize Cognos Query Performance with Best PracticesPreethy SenthilNo ratings yet
- SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)Document52 pagesSQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)ChillagattaAdarshNo ratings yet
- Sending Alerts Using Oracle Business Intelligence DeliversDocument70 pagesSending Alerts Using Oracle Business Intelligence DeliversSreenivas KalluriNo ratings yet
- Main Report Online Tour TravelsDocument49 pagesMain Report Online Tour Travelsjfdj_898jgkgfNo ratings yet
- PS/nVision: Build Reports in Excel from PeopleSoft DataDocument41 pagesPS/nVision: Build Reports in Excel from PeopleSoft Datavivek0% (1)
- SAP BO Auditor ConfigurationDocument11 pagesSAP BO Auditor ConfigurationRajeshNo ratings yet
- How To Broadcast A BI Report To A Directory On The Enterprise Portal ServerDocument15 pagesHow To Broadcast A BI Report To A Directory On The Enterprise Portal ServerPiedone64No ratings yet
- Business Objects QuestionsDocument71 pagesBusiness Objects QuestionsNagamalleswara_3492No ratings yet
- Calculated Key Figures and Restricted Key FiguresDocument20 pagesCalculated Key Figures and Restricted Key FiguresVamsi Kiran100% (1)
- BPC 410 NotesDocument47 pagesBPC 410 NotesGaurav TipnisNo ratings yet
- PS Nvision HandbookDocument80 pagesPS Nvision HandbooknetsriNo ratings yet
- Redy ReportDocument42 pagesRedy ReportArati chavanNo ratings yet
- SAP BusinessObjects Planning and ConsolidationDocument209 pagesSAP BusinessObjects Planning and Consolidationharikishore660% (1)
- ABAP Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesABAP Interview Questions and Answersvenkat_vantipalliNo ratings yet
- Arun Project ReportDocument6 pagesArun Project ReportRiya VijayvargiyaNo ratings yet
- Expenditure Account AbstractDocument2 pagesExpenditure Account AbstractThe Futura LabsNo ratings yet
- How to execute the plsql procedure from the report by clicking with mouseDocument2 pagesHow to execute the plsql procedure from the report by clicking with mouseAbhilasha ModekarNo ratings yet
- Multidimensional AnalysisDocument6 pagesMultidimensional AnalysisR SreenuNo ratings yet
- The Data Detective's Toolkit: Cutting-Edge Techniques and SAS Macros to Clean, Prepare, and Manage DataFrom EverandThe Data Detective's Toolkit: Cutting-Edge Techniques and SAS Macros to Clean, Prepare, and Manage DataNo ratings yet
- SharePoint 2010 Issue Tracking System Design, Create, and ManageFrom EverandSharePoint 2010 Issue Tracking System Design, Create, and ManageRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Microsoft Dynamics GP 2013 Reporting, Second EditionFrom EverandMicrosoft Dynamics GP 2013 Reporting, Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Bi 7 Training Manual 2Document32 pagesBi 7 Training Manual 2Zaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Asug Ohio v3Document67 pagesAsug Ohio v3Zaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- BW Training 7 BW Reporting BEx 1Document19 pagesBW Training 7 BW Reporting BEx 1Zaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Oracle Data Integrator SAP ABAPDocument79 pagesOracle Data Integrator SAP ABAPlulawarNo ratings yet
- 086 LeseprobeDocument12 pages086 LeseprobeZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Bi 7 Training Manual 2Document32 pagesBi 7 Training Manual 2Zaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Understanding BEx Query Designer - Part-3 Calculated Key Figures and Restricted Key FiguresDocument20 pagesUnderstanding BEx Query Designer - Part-3 Calculated Key Figures and Restricted Key FiguresZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Understanding BEx Query Designer - Part-5 Query Element PropertiesDocument21 pagesUnderstanding BEx Query Designer - Part-5 Query Element PropertiesZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Understanding BEx Query Designer - Part-4 Conditions & ExceptionsDocument22 pagesUnderstanding BEx Query Designer - Part-4 Conditions & ExceptionsZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Process ChainDocument6 pagesProcess ChainNoopur PahalNo ratings yet
- Intro BWGuideDocument56 pagesIntro BWGuideromooscNo ratings yet
- How To Broadcast A BEx Report Through EDocument22 pagesHow To Broadcast A BEx Report Through EZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- BW Training 7 BW Reporting BEx 1Document19 pagesBW Training 7 BW Reporting BEx 1Zaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- 086 LeseprobeDocument12 pages086 LeseprobeZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Usgae of ABAP in BIDocument32 pagesUsgae of ABAP in BIZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- 7 BIPUWorkshop BEx Query DesignerDocument32 pages7 BIPUWorkshop BEx Query DesignerZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- ABAP Programming in BWDocument14 pagesABAP Programming in BWZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Process ChainDocument6 pagesProcess ChainNoopur PahalNo ratings yet
- 593 Abap Debugging GuideDocument7 pages593 Abap Debugging GuideZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- 20 Uses For ABAP On BW ProjectsDocument10 pages20 Uses For ABAP On BW ProjectsZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Beginner's Guide To BI ABAPDocument19 pagesBeginner's Guide To BI ABAPZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- 4 Ways To Use ABAP On Your SAP NetWeaver BW ProjectDocument2 pages4 Ways To Use ABAP On Your SAP NetWeaver BW ProjectZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Oops ABAPDocument53 pagesOops ABAPkrameshkrNo ratings yet
- ABAP Programming in BWDocument14 pagesABAP Programming in BWZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Five Ways To Enhance SAP BI Backend Functionality Using ABAPDocument72 pagesFive Ways To Enhance SAP BI Backend Functionality Using ABAPZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- 593 Abap Debugging GuideDocument7 pages593 Abap Debugging GuideZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ABAP: Hyderabad February 24-26th 2009 Instructor: Subhas KatikalaDocument69 pagesObject Oriented ABAP: Hyderabad February 24-26th 2009 Instructor: Subhas KatikalaZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- 4 Ways To Use ABAP On Your SAP NetWeaver BW ProjectDocument2 pages4 Ways To Use ABAP On Your SAP NetWeaver BW ProjectZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- 593 Abap Debugging GuideDocument7 pages593 Abap Debugging GuideZaynab FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Process ChainDocument6 pagesProcess ChainNoopur PahalNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument30 pagesSeminar Reportshashank_gowda_7No ratings yet
- Ecec 621 Syllabus f2010Document2 pagesEcec 621 Syllabus f2010wiznickNo ratings yet
- FdupesDocument4 pagesFdupesschmiddy101No ratings yet
- Brochure SpeedCastDocument16 pagesBrochure SpeedCastAmirul Syakilla AONo ratings yet
- STMP3410: Integrated Mixed-Signal SolutionsDocument213 pagesSTMP3410: Integrated Mixed-Signal SolutionsvetchboyNo ratings yet
- h14963 Unity Hybrid Family DC SsDocument9 pagesh14963 Unity Hybrid Family DC SsSABIRNo ratings yet
- Password Recovery Procedure For The Cisco 2600 and 2800 Series Routers - Cisco SystemsDocument7 pagesPassword Recovery Procedure For The Cisco 2600 and 2800 Series Routers - Cisco SystemsWahyu_Satyaneg_7453No ratings yet
- Embeded PU ComputerDocument188 pagesEmbeded PU ComputerLoknath RegmiNo ratings yet
- Live Agent Developer GuideDocument54 pagesLive Agent Developer GuideHeatherNo ratings yet
- 133 VPN Interview Questions Answers GuideDocument6 pages133 VPN Interview Questions Answers GuideAshish SharmaNo ratings yet
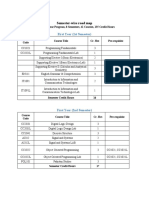
- Semester-Wise Road Map: First Year (1st Semester)Document4 pagesSemester-Wise Road Map: First Year (1st Semester)Hashim AliNo ratings yet
- KEHIDUPAN EKONOMI MASYARAKAT KERAJAAN KUTAIDocument4 pagesKEHIDUPAN EKONOMI MASYARAKAT KERAJAAN KUTAIVeevaaNo ratings yet
- Calculate Hexadecimal DHCPDocument4 pagesCalculate Hexadecimal DHCPTiago SoaresNo ratings yet
- How Orchard Works Orchard Foundations: Love This PDF? Add It To Your Reading List!Document8 pagesHow Orchard Works Orchard Foundations: Love This PDF? Add It To Your Reading List!Amanda HarveyNo ratings yet
- HTTP SssssssDocument3 pagesHTTP SssssssZahoor AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ase Sag 1 PDFDocument376 pagesAse Sag 1 PDFZack HastleNo ratings yet
- IBM Director Planning, Installation, and Configuration GuideDocument448 pagesIBM Director Planning, Installation, and Configuration GuideshektaNo ratings yet
- GSM Gprs Based Automatic Rain Station Kws 033 2 Pcatalog1 128Document2 pagesGSM Gprs Based Automatic Rain Station Kws 033 2 Pcatalog1 128AP1979123No ratings yet
- Software Acceptance FormDocument1 pageSoftware Acceptance FormArnel John Mabalot NayraNo ratings yet
- 03 Nfs PDFDocument48 pages03 Nfs PDFKaran Deep SinghNo ratings yet
- hw2 AnsDocument5 pageshw2 AnsJIBRAN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Eng TELE-satellite 1207Document324 pagesEng TELE-satellite 1207Alexander WieseNo ratings yet
- Analysis of IMS Based Communication Services in The 5G NetworkDocument97 pagesAnalysis of IMS Based Communication Services in The 5G NetworkDương HàNo ratings yet
- Basic Mpls VPN LabDocument2 pagesBasic Mpls VPN LabcarolatuNo ratings yet
- Protocol Document For OT10 (OBDII) ITL FW Version V3.5 2017-03-23Document85 pagesProtocol Document For OT10 (OBDII) ITL FW Version V3.5 2017-03-23Isyar HarunNo ratings yet
- Examining Data Runs of A Fragmented File in NTFSDocument15 pagesExamining Data Runs of A Fragmented File in NTFSCarlos CajigasNo ratings yet
- TCL Vs VXMLDocument3 pagesTCL Vs VXMLaravindant11No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Test BankDocument50 pagesChapter 8 - Test Bankjuan100% (1)