Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GD & T Summary
Uploaded by
fahkingmoronCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GD & T Summary
Uploaded by
fahkingmoronCopyright:
Available Formats
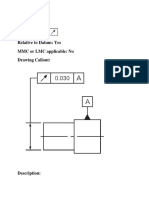
Characteristic And Symbol Flatness
Basic definition A two dimensional tolerance zone defined by two parallel planes within which the entire surface must lie.
Tolerance zone shape
Datum Refer.
Implied Condition
Allowable Modifiers
Key Points Compares to a perfect counterpoint of itself. No particular orientation Compares to a perfect counterpoint of itself. (e.g. straight line) Additive to size when applied to an axis. Compares to a perfect counterpoint of itself.
None Total width
RFS
None
A condition where an element of a surface or an axis is a straight line. Straightness Total width None RFS None
Form Tolerances
Cylindrical A condition on a surface of revolution (cylinder, cone, sphere) where all points of the surface intersected by any plane perpendicular to a common axis (cylinder, cone) or passing through a common center (sphere) are equidistant from the axis of the center. A condition on a surface of revolution in which all points of the surface are equidistant from a common axis.
Circularity
Total width tolerance zone between two concentric circles.
None
RFS
None Not additive to size or location limits. Applies over entire surface. Like wrapping flatness around cylinder Very expensive, consider using Runout
Cylindricity
Total width tolerance zone between two concentric cylinders.
None
RFS
None
Profile Tolerances
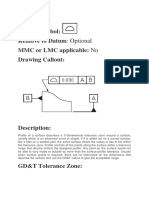
Profile of a line
A uniform two dimensional zone limited by two parallel zone lines extending along the length of a feature.
Total width: can be applied bi-directionally or uni-directionally to either side of profile.
Optional
RFS
LMC or MMC on datum ref if feature of size
The profile being controlled is defined by Basic dimensions or by equation. The profile being controlled is defined by Basic dimensions or by equation. Relation to more than one datum should be considered to stabilize the tolerance zone in more than one direction. Relation to more than one datum should be considered to stabilize the tolerance zone in more than one direction Relation to more than one datum should be considered to stabilize the tolerance zone in more than one direction
Profile of a surface
A uniform three dimensional zone contained between two envelope surfaces separated by the tolerance zone across the entire length of a surface. The distance between two parallel planes, inclined at a specified basic angle, in which the surface, axis, or center plane of the feature must lie.
Total width: can be applied bi-directionally or uni-directionally to either side of profile.
Optional
RFS
LMC or MMC on datum ref if feature of size (FOS) LMC or MMC on feature if FOS.
Angularity
Total width
Yes
RFS LMC or MMC on datum ref if FOS LMC or MMC on feature if FOS.
Orientation Tolerances
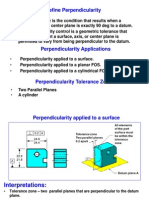
Cylindrical The condition of a surface, axis, median plane, or line which is exactly at 90 degrees with respect to a datum plane or axis.
Perpendicularity
Total width
Yes
RFS LMC or MMC on datum ref if FOS LMC or MMC on feature if FOS.
Cylindrical The condition of a surface or axis which is equidistant at all points from a datum of reference. Total width Yes RFS
Parallelism
Cylindrical
LMC or MMC on datum ref if FOS
Runout: Circular
A composite tolerance used to control the relationship of one or more features of a part to a datum axis during a full 360 degree rotation about the datum axis.
Runout
Defined by the full indicator movement (FIM) along an independant circular element when a feature is rotated 360 degrees.
Yes
RFS
None
Can be defined as the relationship between two features. Relatively inexpensive to implement. Can be defined as the relationship between two features. Relatively inexpensive to implement. Must compare axes. Very epensive to implement. Use position, profile, or runout instead if possible
Runout: Total
Each circular element of the feature/part must be within the runout tolerance.
Defined by the full indicator movement (FIM) along all circular elements across the entire feature when that feature is rotated 360 degrees.
Yes
RFS
None
Concentricity
A cylindrical tolerance zone whose axis coincides with the datum axis and within which all crosssectional axes of the feature being controlled must lie. (Note: Concentricity is very expensive and time-consuming to measure. Recommended that you try position or runout as an alternative tolerance.)
Defined by a cylindrical tolerance zone whose axis coincides with the datum axis and within which all cross-sectional axes of the feature being controlled must lie.
Location
Yes
RFS
None
A zone within which the center, axis, or center plane of a feature of size is permitted ton vary from its true (theoretically exact) position.
Position Total Width Cylindrical Yes RFS
MMC or LMC on the tolerance if the tolerance is applied to a feature of size or on a datum reference if the datum is a feature of size.
With the MMC modifier: Permits functional gage inspection. Allows additional tolerance based upon size. Relatively inexpensive to implement.
Location
You might also like
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Herbs Mooligai Uses in TamilDocument88 pagesHerbs Mooligai Uses in Tamilscribdlinus83% (6)
- Symbols in Technical Drawing and Engineering DrawingDocument10 pagesSymbols in Technical Drawing and Engineering DrawingGine AmisolaNo ratings yet
- Symbols in Technical Drawing and Engineering DrawingDocument10 pagesSymbols in Technical Drawing and Engineering Drawingshockcloud67% (3)
- GD&T PDFDocument109 pagesGD&T PDFBikash Chandra SahooNo ratings yet
- GD&T Definitions GuideDocument5 pagesGD&T Definitions GuideLokesh NarasimhaiahNo ratings yet
- Tolerance of Form & ProfileDocument73 pagesTolerance of Form & Profilermnrajan0% (1)
- Chapter 9 Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) : FPOLR-52332Document12 pagesChapter 9 Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) : FPOLR-52332Jackie HwangNo ratings yet
- GD&T GlossaryDocument4 pagesGD&T GlossarythindmanmohanNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Engineering: Based On The ASME Y14.5M-1994 Dimensioning and Tolerancing StandardDocument77 pagesDimensional Engineering: Based On The ASME Y14.5M-1994 Dimensioning and Tolerancing StandardPankaj PatilNo ratings yet
- GD&T Symbols and TermsDocument6 pagesGD&T Symbols and TermsAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- GD&T Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing ExplainedDocument63 pagesGD&T Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing ExplainedPuneet Birla100% (2)
- Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument7 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and TolerancingRamprasad T N100% (15)
- Geometric Dimensioning & TolerancingDocument67 pagesGeometric Dimensioning & TolerancingAmolPagdal100% (1)
- Control rotational variation with GD&T RunoutDocument6 pagesControl rotational variation with GD&T Runoutakash kumarNo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument33 pagesGD&TRobertrajj.s75% (4)
- GD&T Symbols and TermsDocument5 pagesGD&T Symbols and TermsMikeNo ratings yet
- GD&T GlossaryDocument22 pagesGD&T GlossaryPalani TrainerNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Differential Geometry - With the Use of Tensor CalculusFrom EverandAn Introduction to Differential Geometry - With the Use of Tensor CalculusRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- GD&T - On TolerancingDocument20 pagesGD&T - On TolerancingAkshit MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Engineering SymbolDocument3 pagesEngineering SymbollalitNo ratings yet
- GD&T Symbols ExplainedDocument5 pagesGD&T Symbols ExplainedsampathNo ratings yet
- Winncad GDT DefinitionsDocument6 pagesWinncad GDT DefinitionsVeera PandiNo ratings yet
- Inspection Training Geometrics #001Document4 pagesInspection Training Geometrics #001Curtis BellNo ratings yet
- ME232Geometric Tolerancing Classnotes: An Introduction to Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing ConceptsDocument6 pagesME232Geometric Tolerancing Classnotes: An Introduction to Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing ConceptsEngineernadeemshahidNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING - Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing - What Is The PERPENDICULARITY Tolerance?Document15 pagesMECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING - Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing - What Is The PERPENDICULARITY Tolerance?Sathya DharanNo ratings yet
- Geometric TolerancesDocument23 pagesGeometric TolerancesSameer shaikhNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing, Concentricity, Runout Tolerances, Circular Runout, Total RunoutDocument3 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing, Concentricity, Runout Tolerances, Circular Runout, Total Runoutmick.pride81No ratings yet
- Geometric Characteristic SymbolsDocument2 pagesGeometric Characteristic SymbolsAjith RoyNo ratings yet
- GD&T Glossary and Resource - GD&T Symbols and TermsDocument4 pagesGD&T Glossary and Resource - GD&T Symbols and TermsMohammed Adil100% (1)
- Goetsch ch12Document45 pagesGoetsch ch12Vijay RaghavanNo ratings yet
- GD&T Symbols GuideDocument17 pagesGD&T Symbols GuidedramiltNo ratings yet
- DIMENSIONAL ENGINEERING FORM AND ORIENTATION TOLERANCESDocument96 pagesDIMENSIONAL ENGINEERING FORM AND ORIENTATION TOLERANCESSharath Thimmegowda100% (1)
- GD&TDocument10 pagesGD&TShahed FacebookNo ratings yet
- 08 Runout & ProfileDocument22 pages08 Runout & Profilemaddy_scribdNo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument33 pagesGD&TDgreatarunNo ratings yet
- Geometric SymbolsDocument38 pagesGeometric SymbolsAdhanom G.No ratings yet
- ALVIARDocument5 pagesALVIARClaudine Luna RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document72 pagesChapter 10maddy_scribdNo ratings yet
- On SweepDocument22 pagesOn SweepPraveen CoolNo ratings yet
- GD&T Guide Symbols TermsDocument6 pagesGD&T Guide Symbols TermsvasantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5Claudine Luna RamosNo ratings yet
- Parallelism GD & TDocument2 pagesParallelism GD & Tath-harNo ratings yet
- Geometric DimensioningDocument3 pagesGeometric DimensioningAhmedNo ratings yet
- Angularity, cylindricity, flatness, perpendicularity, straightness, tolerance zones in under 40Document3 pagesAngularity, cylindricity, flatness, perpendicularity, straightness, tolerance zones in under 40kevinjaisNo ratings yet
- Concentricity GD & TDocument3 pagesConcentricity GD & Tath-harNo ratings yet
- Profile ControlDocument9 pagesProfile ControlSahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Flatness and SquarenessDocument25 pagesFlatness and SquarenessPradeshKumar100% (1)
- 11 RunoutDocument14 pages11 RunoutImranNo ratings yet
- Common Terms and Definitions: Basic DimensionDocument9 pagesCommon Terms and Definitions: Basic Dimensionswap dNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Alignment: Martha Leni Siregar DTSL - FtuiDocument21 pagesHorizontal Alignment: Martha Leni Siregar DTSL - FtuiRadifan HalifNo ratings yet
- 05 Orientation TolerancesDocument16 pages05 Orientation Tolerancesmaddy_scribdNo ratings yet
- Angularity: GD&T Symbol: Relative To Datum: Yes MMC or LMC Applicable: Yes (Uncommon) Drawing CalloutDocument5 pagesAngularity: GD&T Symbol: Relative To Datum: Yes MMC or LMC Applicable: Yes (Uncommon) Drawing CalloutrahulNo ratings yet
- Multilinear Functions Of Direction And Their Uses In Differential GeometryFrom EverandMultilinear Functions Of Direction And Their Uses In Differential GeometryNo ratings yet
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)From EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)No ratings yet
- Chinese TraditionalDocument1 pageChinese Traditionalsqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Chinese Tradition BoysDocument1 pageChinese Tradition Boyssqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Chinese KidsDocument1 pageChinese Kidssqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- CH TR by GLDocument1 pageCH TR by GLsqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Black Belt BrochureDocument2 pagesBlack Belt Brochuresqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Casio Alarm Clock Dql-110j-7jfDocument3 pagesCasio Alarm Clock Dql-110j-7jfsqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Residential Plot / Land For Sale in Tambaram East, Chennai 28.8 LakhsDocument2 pagesResidential Plot / Land For Sale in Tambaram East, Chennai 28.8 Lakhssqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide for SanDisk SecureAccessDocument21 pagesQuick Start Guide for SanDisk SecureAccessbijan034567No ratings yet
- TellTale SymbologyDocument1 pageTellTale Symbologysqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document1 pagePresentation 2sqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Ocean Retreat BrochureDocument15 pagesOcean Retreat Brochuresqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- ModifiersDocument1 pageModifierssqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Tamil MeasuresDocument1 pageTamil Measuressqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- 10ways To Remember ThingsDocument1 page10ways To Remember Thingssqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Window of OpportunityDocument1 pageWindow of Opportunitysqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- How To Be ProductiveDocument1 pageHow To Be Productivesqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Key Figures Before Investing in StocksDocument5 pagesKey Figures Before Investing in Stockssqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Window of OpportunityDocument1 pageWindow of Opportunitysqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- I R F Educational Trust Chennai ContactDocument1 pageI R F Educational Trust Chennai Contactsqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Madhuchandan, A Software Engineer From US Is Making Farmers Richer! - RediffDocument15 pagesMadhuchandan, A Software Engineer From US Is Making Farmers Richer! - Rediffsqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Daily FoodsDocument1 pageDaily Foodssqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Team-BHP PDI ChecklistDocument3 pagesTeam-BHP PDI Checklistsqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Samsung Galaxy Note 2 N7100Document6 pagesSamsung Galaxy Note 2 N7100sqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Slaughtering (Halal)Document2 pagesSlaughtering (Halal)sqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Sl. No. Name of The Programme Faculty of Civil EngineeringDocument2 pagesSl. No. Name of The Programme Faculty of Civil EngineeringVidyarthiplus IndiaNo ratings yet
- Villas On The ECR - Coimbatore - The HinduDocument1 pageVillas On The ECR - Coimbatore - The Hindusqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Electro Spanish Village 2BHK Villas Chennai NorthDocument3 pagesElectro Spanish Village 2BHK Villas Chennai Northsqaiba_gNo ratings yet
- Car DrivingDocument3 pagesCar Drivingsqaiba_g100% (1)
- Read MeDocument1 pageRead Mesqaiba_gNo ratings yet