Professional Documents
Culture Documents
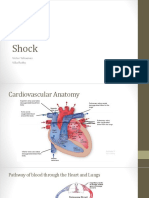
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
dukevladimirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
dukevladimirCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Subjective: Ang sakit ng ulo ko at parang barado yung ilong ko Objective: Vital Signs BP:160/100mmHg PR: 59bpm
RR: 24cpm T:36 >Paroxysmal increase in blood pressure of 160/100 >Bradycardic with pulse rate of 59 >Oliguria with urine output of 400 ml/day >Hypoactive bowel of 2 sounds in 2 minutes >Red splotches on skin and diaphoretic above the level of spinal injury >facial erythema >Presence of goose flesh and pallor
Nursing Diagnosis Autonomic Dysreflexia related to bladder/bowel distention secondary to spinal cord injury
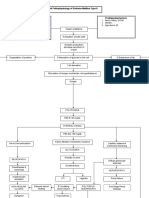
Scientific Explanation Below the t6 injury, intact peripheral sensory nerves transmit impulses that ascend in the spinothalamic and posterior columns to stimulate sympathetic neurons located in the intermediolateral gray matter of the spinal cord.. This large sympathetic outflow causes release of various neurotransmitters (norepinephrine, dopamine-bhydroxylase, and dopamine), causing piloerection, skin pallor, and severe vasoconstriction in arterial vasculature. The result is sudden elevation in blood pressure.
Planning
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
After 1 hour of Independent: nursing >Placed the patient in an intervention the upright seated position with patient will: legs down and remove constrictive clothing or 1. Be Remove devices from any stimuli that are causing the hyperactivity >After confirming a bladder of the autonomic distension, perform nervous system. immediate catheterization 2. Have a stable vital signs as evidenced by a decrease in systolic blood pressure of 20-40 mmHg and an increase in pulse rate of 60-80 bpm 3. Prevent any complication caused by an unstable condition
>Provide digital stimulation of the anus and prepare the patient for manual extraction of the feces >Carefully investigate any other stimulus such as the environmental temperature that may contribute in the condition
4. Allay restlessness >Continue to monitor the patient especially the Vital Signs every 3-5 minutes
After 1 hour of >This maneuver provokes nursing an orthostatic drop in intervention, the blood pressure by patient: allowing pooling of blood in the abdomen and lower 1. Has been extremities removed from the stimuli that >This allows the were causing emptying of urine in the the bladder that is causing the hyperactivity of stimulation of stretch the autonomic receptors that participates nervous system. in the activation of sympathetic response 2. Had a stable vital signs of >This allows the Blood pressure evacuation of the feces of 130/90 and a because of constipation pulse rate of 70 that is triggering the beats per minute exacerbation. 3. Has been >This provides a prevented from maximum possible having a serious improvement of the complications patients condition associated with unstable vital signs >To assess the effectiveness of every 4.Has been interventions being allayed from carried out restlessness
below the level of spinal injury >partial ptosis of the eyelid >restlessness >X-ray result shown fracture of the spine at the level of t6 >MRI result shown spinal cord damage at the level of t6
Vasomotor brainstem reflexes attempt to lower blood pressure by increasing parasympathetic stimulation to the heart through the vagus nerve to cause compensatory bradycardia. The inhibitory outflow above the SCI from cerebral vasomotor centers is increased, but it is unable to pass below the block of the SCI Patients commonly have a headache caused by vasodilation of pain sensitive intracranial vessels. This reflex action cannot compensate for severe
Dependent: >Adminiter medications as prescribed: >It relaxes the patient and Morphine Sulfate reduces the pain that is contributing to the spike of sympathetic response >A Calcium channel Nifedipine blocker that reduces the blood pressure >It is being administered Phentotalamine via IV if the calcium channel blocker is ineffective >This allows the blockage Lignocaine Gel of afferent input when performing painful procedures such as manual extraction of feces and catheterization
vasoconstriction, explained by the Poiseuille formula, where pressure in a tube is affected to the fourth power by change in radius (vasoconstriction) and only linearly by change in flow rate (bradycardia). Parasympathetic nerves prevail above the level of injury, which may be characterized by profuse sweating and vasodilation with skin flushing.
You might also like
- Approach To ShockDocument40 pagesApproach To ShockDivesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- ICP Head InjuryDocument57 pagesICP Head InjuryWengel RedkissNo ratings yet
- NCP For HypertensionDocument4 pagesNCP For HypertensionCiariz Charisse83% (6)
- .SHOCK, Alice - 1704638750000Document12 pages.SHOCK, Alice - 1704638750000Nakintu AliceNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Madi, Krister: Salvador, Ma. Grace BSN-4ADocument36 pagesPrepared By: Madi, Krister: Salvador, Ma. Grace BSN-4ATap Tap100% (2)
- Azmi SyncopeDocument50 pagesAzmi Syncopezakiyyatul aflakhaNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia & Intensive Care: Short Answer QuestionsDocument53 pagesAnaesthesia & Intensive Care: Short Answer QuestionsPaola FgmNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument9 pagesCardioVirgilio Reyes ManuelNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis & Treament: ShockDocument52 pagesDiagnosis & Treament: ShockasepNo ratings yet
- ReferatDocument50 pagesReferatvnNo ratings yet
- Shock: DR Vishwabharathi TDocument51 pagesShock: DR Vishwabharathi TSumaNo ratings yet
- Stroke by Dr. Amit RoyDocument32 pagesStroke by Dr. Amit RoyDr Sutanwi DasNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With Acute Biologic CrisisDocument72 pagesCare of Patients With Acute Biologic CrisisJames QuilingNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument53 pagesShockHassan Ahmed100% (3)
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument32 pagesCoronary Artery DiseasecjissamNo ratings yet
- Shock: Departemen Anestesiologi Dan Reanimasi Fakultas Kedokteran USUDocument54 pagesShock: Departemen Anestesiologi Dan Reanimasi Fakultas Kedokteran USURuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP) : Dr. IsazadehfarDocument20 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure (ICP) : Dr. Isazadehfarجهاد جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- KP 2.5.5.4 112036 - Shock AlfanDocument52 pagesKP 2.5.5.4 112036 - Shock Alfannurul ramadhiniNo ratings yet
- Artery Bypass GraftDocument3 pagesArtery Bypass GraftJasmine ChuaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Acute Pain, Ineffective Airway Clearance, and Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plans for Acute Pain, Ineffective Airway Clearance, and Impaired Gas ExchangeAgronaSlaughter0% (1)
- Intracranial SurgeryDocument40 pagesIntracranial Surgerynur muizzah afifah hussinNo ratings yet
- Management of Hypertensive EmergencyDocument35 pagesManagement of Hypertensive EmergencyRaditya Indah TofaniNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Bagent 1-9 BWAKANANG SHETDocument5 pagesMrs. Bagent 1-9 BWAKANANG SHETaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary: 1. BackgroundDocument3 pagesPreliminary: 1. BackgroundPriskaCliquersNo ratings yet
- Methylergonovine Maleate Route & Dosage IM/IV: 0.2 MG q2-4hr PRN Not To Exceed 5 Doses Oral: 0.2-0.4 MG q6-8hr PRN For 2-7 Days ClassificationDocument2 pagesMethylergonovine Maleate Route & Dosage IM/IV: 0.2 MG q2-4hr PRN Not To Exceed 5 Doses Oral: 0.2-0.4 MG q6-8hr PRN For 2-7 Days ClassificationPatricia Anne Nicole CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support GuideDocument44 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life Support GuideDeborah Anasthasia PakpahanNo ratings yet
- 13.shock and Electrolytic ImbalanceDocument4 pages13.shock and Electrolytic ImbalanceBhaveshNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Dysreflexia-Part OneDocument3 pagesAutonomic Dysreflexia-Part OneManuel BucurNo ratings yet
- SIrs Sepsis Septic Shock MODSDocument7 pagesSIrs Sepsis Septic Shock MODSAndrea Norton100% (5)
- PHEOCHROMOCYTOMADocument37 pagesPHEOCHROMOCYTOMAYosi OktarinaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Shock: Dr. Refli Hasan SPPD, SPJP (K) FihaDocument37 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Shock: Dr. Refli Hasan SPPD, SPJP (K) FihaWinson ChitraNo ratings yet
- Community Health Final Exam ReviewDocument4 pagesCommunity Health Final Exam ReviewkcharmaigneNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock: Dr. Sherwin BuluranDocument8 pagesHypovolemic Shock: Dr. Sherwin BuluranChristian UretaNo ratings yet
- 1324autonomicdysfunc 180617164555Document83 pages1324autonomicdysfunc 180617164555Minaz PatelNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial InfarctionDocument44 pagesCoronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial Infarctionalejandrino_leoaugustoNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument3 pagesCardiogenic Shockmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Problems of The Adult ClientDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Problems of The Adult ClientMarylle AntonioNo ratings yet
- Stroke ManagementDocument18 pagesStroke ManagementAETCM Emergency medicineNo ratings yet
- NCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityDocument4 pagesNCM 118L/ 119L (Related Learning Experience) Day 3-ActivityNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- SCORPION STING: CARDIOVASCULAR TOXICITY AND MANAGEMENTDocument23 pagesSCORPION STING: CARDIOVASCULAR TOXICITY AND MANAGEMENTSiva Narendra Naidu RangumudriNo ratings yet
- B.inggris Laporan Pendahuluan Hipertensi-1-DikonversiDocument13 pagesB.inggris Laporan Pendahuluan Hipertensi-1-DikonversiTia AmandaNo ratings yet
- Shock 19Document7 pagesShock 19Teema UmarNo ratings yet
- Vasovagal Reflex SyndromeDocument19 pagesVasovagal Reflex SyndromeJalalludin AnNo ratings yet
- Shock Tugas Anestesi ViliaDocument81 pagesShock Tugas Anestesi ViliaviliaNo ratings yet
- Icp NewDocument50 pagesIcp Newanon_411736789No ratings yet
- Causes and Management of Syncope in DentistryDocument27 pagesCauses and Management of Syncope in DentistrySelvarathi KandhaswamyNo ratings yet
- Nclex Study Content - UseDocument65 pagesNclex Study Content - Usesbrooks6914100% (22)
- 8.syncope & PresyncopeDocument11 pages8.syncope & PresyncopeIbrahim RamizNo ratings yet
- SHOCK GUIDEDDocument70 pagesSHOCK GUIDEDrajevikramNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan UC 4 Batch Feb 2017Document770 pagesPembahasan UC 4 Batch Feb 2017Tommy LiuNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Intracranial PressureDocument29 pagesPaediatric Intracranial PressuredratiqurNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Nursing Guide to Shock and Multi-Organ DysfunctionDocument63 pagesCritical Care Nursing Guide to Shock and Multi-Organ DysfunctiontikoNo ratings yet
- SHOCKDocument60 pagesSHOCKJoseph John K PothanikatNo ratings yet
- Spinal Chord InjuryDocument11 pagesSpinal Chord InjuryFitri FebriandaniNo ratings yet
- Understanding Strokes: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Strokes: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentValerie BarrNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument17 pagesCongestive Heart FailureLyana StarkNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for AMI ClientDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan for AMI ClientChic Dian UsmanNo ratings yet
- Shock ManagementDocument26 pagesShock ManagementMuhammad Irfanuddin Bin IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medications GuideDocument7 pagesEmergency Medications Guidejohn72decNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationdukevladimirNo ratings yet
- Quebec Lifeline Assessment FormDocument5 pagesQuebec Lifeline Assessment FormdukevladimirNo ratings yet
- How To Choose Your Perfect Soloticas Color Contact Lenses For Dark Brown or Dark EyesDocument6 pagesHow To Choose Your Perfect Soloticas Color Contact Lenses For Dark Brown or Dark EyesdukevladimirNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document7 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jnrue_aerith96% (28)
- Antm Cycle20 EligibilityDocument4 pagesAntm Cycle20 EligibilitydukevladimirNo ratings yet
- Leslie Arceo DocumentsDocument5 pagesLeslie Arceo DocumentsdukevladimirNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 10 The Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 10 The Nervous SystemKiyotaka AyanokoujiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System and Reflex Arc (GCSE)Document35 pagesThe Nervous System and Reflex Arc (GCSE)Raja UsamaNo ratings yet
- K5 - Disorders of Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument47 pagesK5 - Disorders of Autonomic Nervous Systemengkiii100% (1)
- AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: PRECISION REGULATION WHAT TO LOOK FOR Babette RothschildDocument1 pageAUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: PRECISION REGULATION WHAT TO LOOK FOR Babette Rothschildest54No ratings yet
- Waterbury Diet PDFDocument26 pagesWaterbury Diet PDFrobert allenNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Martini Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Martini Solutions Manualscarletba4cc100% (32)
- Kundalini GlandDocument4 pagesKundalini Glandvijender AtriNo ratings yet
- Khartoum University - Faculty of Dentistry Enterance Examinations McqsDocument24 pagesKhartoum University - Faculty of Dentistry Enterance Examinations McqsHazim Rhman AliNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Psychology A Concise Introduction 5th Edition Griggs Test Bank PDFDocument11 pagesDwnload Full Psychology A Concise Introduction 5th Edition Griggs Test Bank PDFcoosjepurutn100% (7)
- Official Lab 01 SBF3033Document14 pagesOfficial Lab 01 SBF3033Foster Van VossenNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System & Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesPeripheral Nervous System & Autonomic Nervous Systemobsgynunair januari18No ratings yet
- Nervous System PowerpointDocument39 pagesNervous System PowerpointManveer SidhuNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Test IiDocument44 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Test IiNOslipperyslopeNo ratings yet
- Ms - Angeline M.SC (N) Previous Year Psychiatric Nursing Choithram College of NursingDocument79 pagesMs - Angeline M.SC (N) Previous Year Psychiatric Nursing Choithram College of NursingPankaj TirkeyNo ratings yet
- Hyperactivation of Sympathetic Nerves Drives Depletion of Melanocyte Stem CellsDocument23 pagesHyperactivation of Sympathetic Nerves Drives Depletion of Melanocyte Stem CellsFrancisco Ciaffaroni MNo ratings yet
- Where Is The LesionDocument12 pagesWhere Is The LesionHo Yong WaiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument570 pagesPDFEshaal FatimaNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of IBS - A Physician Answers Your Questions About Irritable Bowel Syndrome (A Johns Hopkins Press Health Book) (PDFDrive)Document320 pagesMaking Sense of IBS - A Physician Answers Your Questions About Irritable Bowel Syndrome (A Johns Hopkins Press Health Book) (PDFDrive)Huỳnh TúNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 14 AnswersdanielNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemAnonymous kQuaT9arl5No ratings yet
- Respiration:: Mcqs PhysiologyDocument96 pagesRespiration:: Mcqs PhysiologyAhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 15 Review Questionsjoeyseo00No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-NotesDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-NotesAkirah Jewelle JaenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ryodoraku TreatmentDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Ryodoraku Treatmentcarlosbuzo57No ratings yet
- Absorption Distribution Metabolism Elimination (ADMEDocument7 pagesAbsorption Distribution Metabolism Elimination (ADMETsukikage12No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of Behavior: Presented By: Dr. Saima ShaheenDocument31 pagesBiological Basis of Behavior: Presented By: Dr. Saima ShaheenSana FatimaNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument35 pagesBlood Pressure Regulationبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument1 pagePeripheral Nervous SystemChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Syllab bscct1819-24102018Document65 pagesSyllab bscct1819-24102018vasanthNo ratings yet
- Coronary Circulation PhysiologyDocument25 pagesCoronary Circulation PhysiologyDerrick Ezra Ng100% (1)