Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BSS Interfaces
Uploaded by
Sherif KamalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BSS Interfaces
Uploaded by
Sherif KamalCopyright:
Available Formats
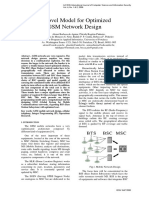
BSS interfaces
Image of the GSM network, showing the BSS interfaces to the MS, NSS and GPRS Core Network Um The air interface between the mobile station (MS) and the BTS. This interface uses LAPDm protocol for signaling, to conduct call control, measurement reporting, handover, power control, authentication, authorization, location update and so on. Traffic and signaling are sent in bursts of 0.577 ms at intervals of 4.615 ms, to form data blocks each 20 ms. Abis The interface between the BTS and BSC. Generally carried by a DS-1, ES-1, or E1 TDM circuit. Uses TDM sub channels for traffic (TCH), LAPD protocol for BTS supervision and telecom signaling, and carries synchronization from the BSC to the BTS and MS. A The interface between the BSC and MSC. It is used for carrying traffic channels and the BSSAP user part of the SS7 stack. Although there are usually transcoding units between BSC and MSC, the signaling communication takes place between these two ending points and the transcoder unit doesn't touch the SS7 information, only the voice or CS data are transcoded or rate adapted. Ater The interface between the BSC and transcoder. It is a proprietary interface whose name depends on the vendor (for example Ater by Nokia), it carries the A interface information from the BSC leaving it untouched. Gb Connects the BSS to the SGSN in the GPRS core network.
GSM Interfaces ALL
The Air interface is the wireless medium for carrying the user voice & data from MS to BTS, hence it has to be an open interface to be able to support MS produced by various manufacturers. The Abis interface is generally a wireless (microwave) or a wired (Copper/fiber optic) medium between BTS to BSC, the type of medium to be used depends on the capacity (Mbps) the link has to carry and also considering future expansion of the network. It is a proprietary interface i.e. the BTS & BSC should be from the same manufacturer to be able to understand the signalling as well as traffic that is to be routed. The next is the Ater interface between BSC to TCSM which is again proprietary as the BSC & the Transcoder should be compatible to each other to be able to understand each other. Generally the medium is a high capacity Fiber optic link using SDH Technology. The A interface is between TCSM & MSC which again is an open interface, as the individual user info is to be converted to PSTN compatible 64Kbps rate. As for a large number of users there would be a large number of cables required between TCSM & MSC hence to minimize the cabling cost the TCSM is kept at the MSC.
You might also like
- BSS Interfaces: Edit Source EditDocument1 pageBSS Interfaces: Edit Source EditUpendra TiwariNo ratings yet
- Base Station SubsystemDocument65 pagesBase Station SubsystemRicardo Ngeng PitpituNo ratings yet
- Base Station SubsystemDocument72 pagesBase Station SubsystemDivya GoelNo ratings yet
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- WCN Unit III - Wireless Data Services Dec-11Document56 pagesWCN Unit III - Wireless Data Services Dec-11Atluri Sri Harsha100% (1)
- Base Station SubsystemDocument4 pagesBase Station SubsystemDaniyal AliNo ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Communication System Lecture 6-2 PDFDocument9 pagesCommunication System Lecture 6-2 PDFmiro jasimNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabFrom EverandSimulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- GSM OverviewDocument8 pagesGSM OverviewAnuj ThakurNo ratings yet
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- BSC Configuration Bss OverviewDocument17 pagesBSC Configuration Bss OverviewJesus Percival BarattaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Data ServicesDocument40 pagesWireless Data ServicesbhavanimaddulaNo ratings yet
- IP in MNDocument8 pagesIP in MNMashhood NasirNo ratings yet
- Base Station Subsystem1Document4 pagesBase Station Subsystem1ajune30No ratings yet
- Abis Link SignallingDocument7 pagesAbis Link Signallingsrikanth.2335528No ratings yet
- Protocol FamilyDocument120 pagesProtocol FamilyHà Tài ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Art1-Understanding GSM TechnologyDocument7 pagesArt1-Understanding GSM TechnologyJoseph NajaNo ratings yet
- GSM ProtocolsDocument12 pagesGSM ProtocolsraymondushrayNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On GSM ArchitectureDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On GSM Architecturenodahydomut2100% (1)
- My Seminar 222Document18 pagesMy Seminar 222Rajat NegiNo ratings yet
- GsmOverview Qasim, ShahzebDocument94 pagesGsmOverview Qasim, ShahzebQasimBajwaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document37 pagesUnit 3Vaibhav HolkarNo ratings yet
- Transcoder FunctionsDocument1 pageTranscoder Functionsbuban8888No ratings yet
- Apis Training GSM System Overview - Base Station SystemDocument6 pagesApis Training GSM System Overview - Base Station SystemKhaja MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- What Are LAPD and LAPD ?: Time Diversity Is Used in Digital Communication Systems To Combat That The TransmissionsDocument8 pagesWhat Are LAPD and LAPD ?: Time Diversity Is Used in Digital Communication Systems To Combat That The TransmissionsVikas MishraNo ratings yet
- Mobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #13Document17 pagesMobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #13Student Lecture Notes75% (4)
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS) : CH 1: GSM (Global System For Mobile)Document4 pagesBase Station Subsystem (BSS) : CH 1: GSM (Global System For Mobile)Qahwagi MochaNo ratings yet
- Smds Ieee 802.6Document6 pagesSmds Ieee 802.6Girija VaniNo ratings yet
- Numbers: Previous Chapter First Page Previous PageDocument26 pagesNumbers: Previous Chapter First Page Previous Pageh2amdh2No ratings yet
- Interview Question On GSM Cdma WcdmaDocument17 pagesInterview Question On GSM Cdma WcdmaAnimesh Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- MTRCDocument16 pagesMTRCPrapti AlokNo ratings yet
- GSM Word FileDocument11 pagesGSM Word FileevilanubhavNo ratings yet
- 2.1 GPRS Network Coverage Area: Information & Communications TechnologyDocument20 pages2.1 GPRS Network Coverage Area: Information & Communications TechnologyultimoridigNo ratings yet
- RF QuestionsDocument31 pagesRF QuestionsShashank PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Adsl Tutorial: Home Wide Area Network (WAN)Document13 pagesAdsl Tutorial: Home Wide Area Network (WAN)Mircea BujorNo ratings yet
- Past Exams IoTDocument9 pagesPast Exams IoTandreaNo ratings yet
- 7 GSM Network Connectivity RDocument5 pages7 GSM Network Connectivity RJayan KulathoorNo ratings yet
- A Radio Over Fiber Based Wireless Access Network Architecture For Rural AreasDocument5 pagesA Radio Over Fiber Based Wireless Access Network Architecture For Rural AreasBernard NarhNo ratings yet
- A Novel Model For Optimized GSM Network DesignDocument6 pagesA Novel Model For Optimized GSM Network Designinfluemento agborNo ratings yet
- GSMDocument11 pagesGSMLinduxNo ratings yet
- OVERVIEWDocument79 pagesOVERVIEWseth_awuah100% (1)
- Generations of MobileDocument28 pagesGenerations of MobileIqra YasmeenNo ratings yet
- GSM Signaling System: Course ObjectivesDocument31 pagesGSM Signaling System: Course ObjectivesBsskkd KkdNo ratings yet
- 4 Bss Interfaces: GSM Basics, Version 2.2 T.O.P. Businessinteractive GMBH Page 1 of 34Document34 pages4 Bss Interfaces: GSM Basics, Version 2.2 T.O.P. Businessinteractive GMBH Page 1 of 34kamertonNo ratings yet
- General Fill in The Blanks' Questions (: May Have Some Duplicates)Document4 pagesGeneral Fill in The Blanks' Questions (: May Have Some Duplicates)Larry Et AlNo ratings yet
- Base Transceiver Station: Figure 1 Subsystems of GSMDocument21 pagesBase Transceiver Station: Figure 1 Subsystems of GSMPravin GaretaNo ratings yet
- Reseaux GSM Et UmtsDocument4 pagesReseaux GSM Et UmtsadjadNo ratings yet
- NOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Document10 pagesNOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Ramesh MattaparthiNo ratings yet
- Roupe Pecial Obile: Page 1 of 17Document17 pagesRoupe Pecial Obile: Page 1 of 17shwetaecNo ratings yet
- Wan - Wide Area Networking: Wan-Pdf Page 1 of 8Document8 pagesWan - Wide Area Networking: Wan-Pdf Page 1 of 8suneelsohalNo ratings yet
- What Is Cell Site: The Radio Network Controller (Or RNC) Is A Governing Element in The UMTSDocument10 pagesWhat Is Cell Site: The Radio Network Controller (Or RNC) Is A Governing Element in The UMTSshripalNo ratings yet
- Kimmo K. Saarela Tampere University of Technology Telecommunication Laboratory P.O. Box 553, 33101 Tampere, Finland Kks@cs - Tut. February 17, 1995Document20 pagesKimmo K. Saarela Tampere University of Technology Telecommunication Laboratory P.O. Box 553, 33101 Tampere, Finland Kks@cs - Tut. February 17, 1995José AranibarNo ratings yet
- Television Et TransmissionDocument4 pagesTelevision Et TransmissionadjadNo ratings yet
- Telecoms ModernesDocument4 pagesTelecoms ModernesadjadNo ratings yet
- A On Summer Vocational Training: Bharat Sanchar Nigam LimitedDocument20 pagesA On Summer Vocational Training: Bharat Sanchar Nigam LimitedMohammad ShoebNo ratings yet
- Elite - VES - Elan - Rs-ADocument2 pagesElite - VES - Elan - Rs-Ashreeket3953No ratings yet
- A High Performance Blockchain Platform For Intelligent DevicesDocument2 pagesA High Performance Blockchain Platform For Intelligent DevicesAfriza MeigiNo ratings yet
- Intro To MA5300 Command HelpDocument28 pagesIntro To MA5300 Command HelpMohamad AshrafiNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions - Jacob SchwegmanDocument3 pages1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions - Jacob Schwegmanberniemonkeyzor20% (5)
- Monitoring System For Intelligent Transportation System Based in ZigbeeDocument6 pagesMonitoring System For Intelligent Transportation System Based in ZigbeeGabriel DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Form AuthenticationDocument5 pagesForm Authenticationaimt_rajivNo ratings yet
- 19 - PXG80-N - BACnet Router For LON, Ethernet IPDocument10 pages19 - PXG80-N - BACnet Router For LON, Ethernet IPAsh FakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14. ONT WEB Management (Router, Nat, Pppoe)Document26 pagesChapter 14. ONT WEB Management (Router, Nat, Pppoe)CarlosNo ratings yet
- OpenScape Business V1 Administrator DocumentationDocument1,407 pagesOpenScape Business V1 Administrator Documentationsorin birou100% (2)
- Final Seminar JobyDocument30 pagesFinal Seminar JobyJoby ThattilNo ratings yet
- Polycom Admin Guide UCS v3 3 0Document440 pagesPolycom Admin Guide UCS v3 3 0chamaco_calienteNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument127 pagesFormula SheetvishaltpadhyaNo ratings yet
- f77 f55 User ManualDocument36 pagesf77 f55 User ManualGabi GabrielNo ratings yet
- Internet and The World Wide WebDocument14 pagesInternet and The World Wide WebOloka George OkwirNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I (Introduction To Networks)Document19 pagesUNIT - I (Introduction To Networks)kondraguntajbNo ratings yet
- LTE and SchedulingDocument25 pagesLTE and SchedulingKrunoslav IvesicNo ratings yet
- UBNT New PresentationDocument20 pagesUBNT New PresentationJohn Seth Toribio SalazarNo ratings yet
- 1Document13 pages1Anoop JamadagniNo ratings yet
- White Paper - FSODocument7 pagesWhite Paper - FSOS. MagidiNo ratings yet
- Ericsson - LTE Architecture, KPIs and Troubleshooting - AircomDocument54 pagesEricsson - LTE Architecture, KPIs and Troubleshooting - Aircomvishalkavi18100% (2)
- Qos Troubleshooting For RETAINABILITYDocument20 pagesQos Troubleshooting For RETAINABILITYleandre vanieNo ratings yet
- 6500 Switch DifferenceDocument51 pages6500 Switch DifferencemailchNo ratings yet
- Huawei hg8240h KKDocument2 pagesHuawei hg8240h KKMihaela CaciumarciucNo ratings yet
- Asterisk SIP Channels - Voip-InfoDocument8 pagesAsterisk SIP Channels - Voip-InfoSammy Manuel DominguezNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications in The 21st CenturyDocument13 pagesWireless Communications in The 21st CenturycastrojpNo ratings yet
- VRRPDocument20 pagesVRRPTanveer AkramNo ratings yet
- LTRT-65415 MP-11x and MP-124 SIP User's Manual Ver 6.2Document504 pagesLTRT-65415 MP-11x and MP-124 SIP User's Manual Ver 6.2Alex RamNo ratings yet
- ECO Report 03Document96 pagesECO Report 03ahmedshah512No ratings yet
- Lte Zte Base StationDocument58 pagesLte Zte Base Stationnkapnangluther3099No ratings yet
- CCNA ProjectDocument54 pagesCCNA ProjectManan33% (3)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityFrom EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldFrom EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (55)
- Chaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyFrom EverandChaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (111)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyFrom EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Cyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItFrom EverandCyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (66)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (228)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderFrom EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (398)
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyFrom EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNo ratings yet
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldFrom EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (107)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldFrom EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveFrom EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNo ratings yet
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyFrom EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessFrom EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNo ratings yet
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeFrom EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (99)
- Broken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterFrom EverandBroken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Solutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesFrom EverandSolutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesNo ratings yet
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andFrom EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (709)
- Four Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandFour Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)