Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tenses English
Uploaded by
julioorozcoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tenses English
Uploaded by
julioorozcoCopyright:
Available Formats
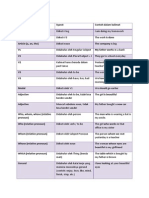
tense
Affirmative/Negative/Question
Use
Habits, repeated actions. Facts S added to the verb in 3 person Auxiliaries: do / does Actions taking place permanently. (in contrast with present progressive)
rd
Signal Words
always, every , never, normally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually
Simple Present
A: He speaks. N: He does not speak. Q: Does he speak?
Simple Past
A: He spoke. N: He did not speak. Q: Did he speak?
Action that started and finished in the past. Used for specific time in the past. Auxiliary verb did. It is not a time reference to another action.
yesterday, 2 minutes ago, in 1990, the other day, last Friday
Future Simple
A: He will speak. N: He will not speak. Q: Will he speak?
Action that will start and finish in the future. Offer to help. spontaneous decision Predictions. Auxiliary verb: will Action that will start and finish in the future. Plans. Predictions. Auxiliary verb: going to Action taking place in the moment of speaking. action taking place only for a limited period of time (in contrast with simple present)
in a year, next , tomorrow
(will)
Future Simple (going to)
A: He is going to speak. N: He is not going to speak. Q: Is he going to speak?
in one year, next week, tomorrow
Present Progressive
A: He is speaking. N: He is not speaking. Q: Is he speaking?
Right now, at the moment, just, just now, now.
Past Progressive
A: He was speaking. N: He was not speaking. Q: Was he speaking?
Action taking place at a specific period of time in the past. actions taking place at the same time (using while + past progressive) action in the past that is interrupted by another action (using when) used as a time reference to other actions. Action that will take place at a specific period of time in the future. 2 actions that will take place at the same time in the future (using while). Action in the future that will be interrupted by another action (using when + simple present)
when, while, as long as
Future Progressive
A: He will be speaking. N: He will not be speaking. Q: Will he be speaking?
in one year, next week, tomorrow
Present Perfect Simple A: He has spoken. N: He has not spoken. Q: Has he spoken? Experiences. Action that starts in the past and continues to the future (using since or for) already, ever, just, never, not yet, so far, till now, up to now
Past Perfect Simple
A: He had spoken. N: He had not spoken. Q: Had he spoken?
Action taking place before another one in the past. (connect with when, before or by the time) Sometimes interchangeable with past perfect progressive
already, just, never, not yet, once, until that day if sentence type III (If I had talked, )
Future perfect Simple
A: He will have spoken. N: He will not have spoken. Q: Will he have spoken?
Action that will take place before another one in the future. (connect with when, before or by the time)
by Monday, in a week
Present Perfect Progressive
A: He has been speaking. N: He has not been speaking. Q: Has he been speaking?
Continuously happens from the past to the present.
all day, for 4 years, since 1993, how long?, the whole week for, since, the whole day, all day for , the last couple of hours, all day long if sentences type II (If I were you, I would go home.)
Past Perfect Progressive Future perfect Progressive Conditional Simple
A: He had been speaking. N: He had not been speaking. Q: Had he been speaking?
Same as past perfect
A: He will have been speaking. N: He will not have been speaking. Q: Will he have been speaking? A: He would speak. N: He would not speak. Q: Would he speak?
Same as future perfect
action that might take place
Conditional Progressive
A: He would be speaking. N: He would not be speaking. Q: Would he be speaking?
action that might take place putting emphasis on the course / duration of the action if sentences type action that might have taken III place in the past (If I had seen that, I would have helped.) action that might have taken place in the past puts emphasis on the course / duration of the action
Conditional Simple
A: He would have spoken. N: He would not have spoken. Q: Would he have spoken?
Conditional Progressive
A: He would have been speaking. N: He would not have been speaking. Q: Would he have been speaking?
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Grammar Test 1Document3 pagesGrammar Test 1Abi AndaNo ratings yet
- NHA2 - Derivational and Inflectional ParadigmsDocument14 pagesNHA2 - Derivational and Inflectional Paradigms08AV2D100% (3)
- 13 Linking Words 1Document6 pages13 Linking Words 1Lucie Cetkovic50% (2)
- Indirect QuestionsDocument4 pagesIndirect QuestionsAndres Portillo0% (1)
- Basic TensesDocument11 pagesBasic Tensesm.arunNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test For - Common-CoreDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test For - Common-CoreAbdelqoudous BenezhaNo ratings yet
- Explanations: All Roads To The North Have Been Blocked by SnowDocument3 pagesExplanations: All Roads To The North Have Been Blocked by Snowzarathusta_1234No ratings yet
- Singular Plural Nom. Obl. Nom. OblDocument4 pagesSingular Plural Nom. Obl. Nom. ObltrapezundNo ratings yet
- Course Planner As Level SpanishDocument11 pagesCourse Planner As Level SpanishAnonymous eynRrXPNo ratings yet
- ЛекцииDocument22 pagesЛекцииPintican Alex AndreiNo ratings yet
- Serbo-Croatian Basic Course - Volume 1 - Student TextDocument642 pagesSerbo-Croatian Basic Course - Volume 1 - Student TextGizem Alever67% (3)
- AoristDocument234 pagesAoristsemanoesisNo ratings yet
- Exhibit B of Mortgage AffidavitDocument5 pagesExhibit B of Mortgage AffidavitpuretrustNo ratings yet
- XXZXDocument7 pagesXXZXmavekcx1112No ratings yet
- Elementary Unit 9aDocument2 pagesElementary Unit 9amau_fumarolo5337No ratings yet
- A Research On Reliability of Umpire Decision Review System in Cricket PDFDocument3 pagesA Research On Reliability of Umpire Decision Review System in Cricket PDFDhruv ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Malachi - A Handbook On The Hebrew Text - Terry W. EddingerDocument169 pagesMalachi - A Handbook On The Hebrew Text - Terry W. EddingerJohnny Hanna100% (4)
- Selting Turn Construction Interplay Syntax ProsodyDocument32 pagesSelting Turn Construction Interplay Syntax ProsodyidschunNo ratings yet
- Comparative SDocument11 pagesComparative SEgealfa NetsNo ratings yet
- Tabel Error RecognitionDocument4 pagesTabel Error RecognitionNurPiter ThiodorisNo ratings yet
- Important Spanish Verb ListDocument9 pagesImportant Spanish Verb Listglenn_smith_11100% (1)
- The Rover - Part 5 Melchester Rovers 2016/17 SeasonDocument24 pagesThe Rover - Part 5 Melchester Rovers 2016/17 SeasonCyril "Storky" KnightNo ratings yet
- Week / Date Grammar (Monday) Listening & Speaking (Tuesday) Reading (Wednesday) Writing (Thrusday) Vocabulary (Friday)Document3 pagesWeek / Date Grammar (Monday) Listening & Speaking (Tuesday) Reading (Wednesday) Writing (Thrusday) Vocabulary (Friday)Rajen RajNo ratings yet
- Past ContinousDocument17 pagesPast ContinousAlex Choong100% (1)
- 7 Patterns of Sentence StructureDocument20 pages7 Patterns of Sentence StructureCikgu Ambuyun Jr.No ratings yet
- Shortcuts Tenses: Present Continous Üvey Evlat! Ancak İşaret Verildiğinde Güven!Document13 pagesShortcuts Tenses: Present Continous Üvey Evlat! Ancak İşaret Verildiğinde Güven!IntegraBy Semih PalaNo ratings yet
- Naiki of ChandaDocument33 pagesNaiki of Chandacha072No ratings yet
- Cause & Effect Conjuncti Ns Exercises: - Go To TheDocument5 pagesCause & Effect Conjuncti Ns Exercises: - Go To TheJean CabingatanNo ratings yet
- Participle ClausesDocument10 pagesParticiple ClausesMoka VimerNo ratings yet
- 10th Sem MemorialDocument22 pages10th Sem Memorialmunmun kadamNo ratings yet