Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture Notes and Guides
Uploaded by
Shahrolnizam PsasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Notes and Guides
Uploaded by
Shahrolnizam PsasCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Notes and Guides-JJ310-Strength of Materials
LECTURE 1 DATE:11/7/2010 TIME:8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 1.0 FORCES ON MATERIALS 1.1.1 Explain the effects of forces on materials. a. static b. dynamic c. impact d. fatigue and alternating loads 1.1.2 Differentiate between tensional forces, compression and shear forces. 1.1.3 Define a. tensile stress and compressive stress. b. tensile strain and compressive strain. c. modulus of elasticity (Youngs modulus).
TUTORIAL 1 DATE:14/7/2011 TIME:10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 2 DATE:18/7/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16
TOPIC: 1.0 FORCES ON MATERIALS 1.2.2 Sketch the general shape of stress versus strain to common engineering materials which is elastic and brittle when subjected to load in the tensile test. Label the points of ; a. Ratio limit b. Elasticity limit c. Yield point d. Maximum tension strength 1.2.3 Define a. the percentage of elongation and area reduction b. working stress. c. proof stress. d. factor of safety. e. Poissons ratio
1.3.1 Differentiate between single shear and double shear. 1.3.2 Define modulus of rigidity. 1.3.3 Solve problem on forces on materials, Hooke Laws, shear stress and shear strain.
TUTORIAL 2 DATE:21/7/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 3 DATE:25/7/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 2.0 THERMAL STRESSES AND COMPOSITE BARS 2.1.1 Explain the effects of temperature changes on composite bar. 2.1.2 Define the coefficient of linear expansion. 2.1.3 Calculate internal stresses developed in the material subjected to temperature changes.
2.2.1 Calculate a. Series composite bars b. Parallel composite bars
TUTORIAL 3 DATE:28/7/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 4 DATE:31/7/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 2.0 THERMAL STRESSES AND COMPOSITE BARS 2.2.2 Calculate the stress in the composite bar components which is subjected to external load. 2.2.3 Calculate stresses in composite bar due to temperature changes.
TUTORIAL 4 DATE:4/8/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 5 DATE:7/8/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 2.0 THERMAL STRESSES AND COMPOSITE BARS 2.2.4 Calculate stresses in composite bar components which are subjected to both external load and load due to temperature changes. 2.2.5 Solve problem regarding thermal stresses and composite bars.
TUTORIAL 5 DATE:11/8/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 6 DATE:14/8/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 3.0 SHEAR FORCES AND BENDING MOMENTS 3.1 Understand the types of beams 3.1.1 Explain the types of beams a. simply supported beam. b. cantilever beam. 3.2 Understand the types of beam load 3.2.1 Explain the types of beam load a. point or concentrated load b. uniformly distributed load c. couples 3.3 Understand the laws of equilibrium 3.3.1 Use the laws of equilibrium equation to determine the reaction force for the simply supported beam and cantilever beam acted upon by coplanar forces. 3.3.2 Explain shear force and symbol for shear force.
TUTORIAL 6 DATE:18/8/2011
TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 7 DATE:21/8/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 3.0 SHEAR FORCES AND BENDING MOMENTS 3.3.3 Calculate the magnitude for the shear force at the specified points on the simply supported beam and cantilever beam. 3.3.4 Sketch the diagram of shear force for beam in the simply supported beam and cantilever beam 3.3.5 Explain the standard sign for bending moment. 3.3.6 Calculate the magnitude for bending moment at the specified points of simply supported beam and cantilever beam for a given load.
TUTORIAL 7 DATE:25/8/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 8 DATE:5/9/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16
TOPIC: 3.0 SHEAR FORCES AND BENDING MOMENTS 3.3.7 Draw diagrams of bending moment for beam on the simply supported beam and cantilever beam 3.3.8 Determine the point of maximum bending moment on bending moment diagram and zero shear force point on the shear force diagram. 3.3.9 Calculate the value of maximum bending moment at the point on beam when shear force is zero. 3.3.10 Relate the point of contraflexure and the point where bending moment change sign.
TUTORIAL 8 DATE: 8/9/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 9 DATE:12/9/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 4.0 BENDING STRESSES 4.1 Understand the bending stresses 4.1.1 Name the quantity represented by each letter in the general bending formula;
4.1.2 Explain the bending stress changes at the section of the beam in bending. Formula. 4.1.3 Show by sketch, the meaning of radius of curvature for the beam in bending.
TUTORIAL 9 DATE: 15/9/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 10 DATE: 18/9/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 4.0 BENDING STRESSES 4.1.4 Calculate the following, for the given standard section: a. the position of neutral axis, NA b. second moment of area, I 4.1.5 Use the table of characteristics in standard section.
TUTORIAL 10 DATE: 21/9/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 11 DATE: 2/10/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 4.0 BENDING STRESSES 4.1.6 Use relation in bending formula to solve problems involving the strength and bending of simply supported beam and cantilever beam.
TUTORIAL 11 DATE: 29/9/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 12 DATE: 9/10/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 5.0 BEAM DEFLECTION 5.1 Understand beam deflections 5.1.1 Explain Double Integration Method 5.1.2 Define each quantity illustrated in the given formula
State the boundary condition for simply support and cantilever beam.
TUTORIAL 12 DATE: 6/10/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 13 DATE: 16/10/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 5.0 BEAM DEFLECTION 5.1.4 Determine by using double integration method the deflection and slope at every specify points on simply support and cantilever beam in every loaded situation as below: a. Simply support, with concentrated load at center of the beam. b. Simply support with evenly distributed load.
TUTORIAL 13 DATE: 13/10/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 14 DATE: 17/10/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16
TOPIC: 5.0 BEAM DEFLECTION c. Cantilever beam with single concentrated load at edge end of the beam. d. Cantilever beam with evenly distributed load. e. Cantilever beam with concentrated load at center of the beam.
TUTORIAL 14 DATE: 20/10/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3 TOPIC:
LECTURE 15 DATE: 24/10/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 6.0 TORSION 6.1 Understand Torsion 6.1.1 Explain the terms represented by each letter in the general equation for the torsion of circular cross-section shafts:
6.1.2 Define the polar moment of inertia. 6.1.3 Show by diagram the torsional shear stress changes/varies with the sectional radius for shafts subjected to torque. 6.1.4 Sketch the angle of twist of a shaft subjected to torque. 6.1.5 Calculate the polar moments of inertia for solid shaft, hollow shaft and circular shaft. 6.1.6 Use the table of section characteristic to determine the polar moments of inertia.
TUTORIAL 15 DATE: 27/10/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
LECTURE 16 DATE: 31/10/2011 TIME: 8-10 PG/E16 TOPIC: 6.0 TORSION 6.1.7 Use the relationship in general equation to solve problem related to solid shaft or hollow circular shaft subjected to torque. 6.1.8 Use the relationship in 6.1.1 to solve problems on simple parallel and series composite shafts. 6.1.9 Calculate the power transmitted by the shaft using the following formula
TUTORIAL 16 DATE: 3/11/2011 TIME: 10-11PG/BJM3
You might also like
- Analysis of Additional Load and Fatigue Life of Preloaded BoltsDocument20 pagesAnalysis of Additional Load and Fatigue Life of Preloaded BoltsSang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Roll No: (To Be Filled in by The Candidate) : ALL FourDocument2 pagesRoll No: (To Be Filled in by The Candidate) : ALL FourRAJANo ratings yet
- Continuous Beam Design With Moment Redistribution (CSA A23.3-14) PDFDocument35 pagesContinuous Beam Design With Moment Redistribution (CSA A23.3-14) PDFtimNo ratings yet
- LAB 4 - Forces in Trusses 1 v1Document11 pagesLAB 4 - Forces in Trusses 1 v1fauzaniNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 - Strut-Buckling (Revised July 2010)Document7 pagesExp 4 - Strut-Buckling (Revised July 2010)Darker SoraNo ratings yet
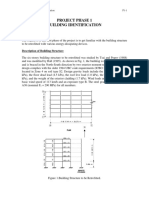
- SID-Project Phase 1 - Spring 2015Document5 pagesSID-Project Phase 1 - Spring 2015fernando CanizaresNo ratings yet
- Determination of Moment Capacity Mp for Rectangular Reinforced Concrete ColumnsDocument20 pagesDetermination of Moment Capacity Mp for Rectangular Reinforced Concrete ColumnsRatul RanjanNo ratings yet
- Lab2 Forces in TrussDocument14 pagesLab2 Forces in TrussAlif EmirNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesFrom EverandStrength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Andrew Pytel, Ferdinand L. Singer - Strength of Materials (1987, Harpercollins College Div) - Libgen - LiDocument606 pagesAndrew Pytel, Ferdinand L. Singer - Strength of Materials (1987, Harpercollins College Div) - Libgen - LiMoshi ULNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07-Unit 04 - Design of Continous Beam For Flexure PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 07-Unit 04 - Design of Continous Beam For Flexure PDFabdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07-Unit 04 - Design of Continous Beam For FlexureDocument14 pagesChapter 07-Unit 04 - Design of Continous Beam For FlexureabdullahNo ratings yet
- Buckling of StrutsDocument9 pagesBuckling of StrutsMARVINNo ratings yet
- Shear Force in A Beam (Edited) 1Document20 pagesShear Force in A Beam (Edited) 1Ana Jannah80% (5)
- Software Verification - Plane Frame Beam Span Loads AnalysisDocument3 pagesSoftware Verification - Plane Frame Beam Span Loads AnalysisErRajivAmieNo ratings yet
- ME231 Strength of MaterialsDocument5 pagesME231 Strength of MaterialsVedant GavhaneNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTINUOUS BEAMS)Document26 pagesUnit 6 (DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTINUOUS BEAMS)Zara Nabilah90% (30)
- CE297 Ch7Document8 pagesCE297 Ch7madhes4everNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Truss Forces Lab ReportDocument8 pagesEngineering Mechanics Truss Forces Lab ReportzaimNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Truss Forces Lab ReportDocument8 pagesEngineering Mechanics Truss Forces Lab ReportzaimNo ratings yet
- Combined Bending & TorsionDocument12 pagesCombined Bending & TorsiongilbertllhNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Optimization of Shaft Design Under Fatigue Loading Using Goodman MethodDocument5 pagesResearch Paper Optimization of Shaft Design Under Fatigue Loading Using Goodman MethodIshwar PatilNo ratings yet
- SKM WorkDocument22 pagesSKM WorkLmedinaluisNo ratings yet
- Buckling of StrutsDocument11 pagesBuckling of StrutsIkhwan Z.91% (68)
- Syllibus cc601Document9 pagesSyllibus cc601Adron LimNo ratings yet
- LAB 4 - Forces in Trusses 1Document8 pagesLAB 4 - Forces in Trusses 1zaim100% (1)
- Optimization of Connecting Rod Parameters Using CAE Tools: Student, Mechanical Engineering GJUS&T, HisarDocument7 pagesOptimization of Connecting Rod Parameters Using CAE Tools: Student, Mechanical Engineering GJUS&T, HisarMahesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test Properties from Stress-Strain CurvesDocument9 pagesTensile Test Properties from Stress-Strain CurveszaimNo ratings yet
- Measure bending moment with loadsDocument9 pagesMeasure bending moment with loadsOmar Arabi0% (1)
- Section: R Assignment No. Date of Assignment - /9/2015 Date of Submission - /9/2015Document3 pagesSection: R Assignment No. Date of Assignment - /9/2015 Date of Submission - /9/2015Bharat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nottingham Concrete Beam TestingDocument8 pagesNottingham Concrete Beam TestingYaasiin OozeerNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Shear Force and Bending Moment DiagramsDocument29 pagesStructural Analysis Shear Force and Bending Moment DiagramsCt Kamariah Md SaatNo ratings yet
- On The Influence of Additional Axial and Bending Loads On Fatigue Life of Preloaded BoltsDocument36 pagesOn The Influence of Additional Axial and Bending Loads On Fatigue Life of Preloaded BoltsWojciechNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump 2009Document8 pagesCentrifugal Pump 2009juan diazNo ratings yet
- MSI02 Bending Moment in A BeamDocument6 pagesMSI02 Bending Moment in A BeamLutfi AminNo ratings yet
- CCIA EnglezaDocument22 pagesCCIA EnglezaJohnNo ratings yet
- Bolted Joints Analysis Methods and EvaluationDocument9 pagesBolted Joints Analysis Methods and EvaluationIJMERNo ratings yet
- 2019 Test 2Document4 pages2019 Test 2Tefelo TsimaneNo ratings yet
- FEA Lifting Device Det SupDocument13 pagesFEA Lifting Device Det SupAus AlisterNo ratings yet
- I Jeter 129112021Document5 pagesI Jeter 129112021WARSE JournalsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Slope and Deflection Strength of Materials - Part 1Document14 pagesChapter 8 Slope and Deflection Strength of Materials - Part 1Abhijith ShettyNo ratings yet
- Bolts TheoryDocument12 pagesBolts TheorybovingNo ratings yet
- Ansys Analysis-Trolley Beam 3T1Document13 pagesAnsys Analysis-Trolley Beam 3T1Ye Wint ThuNo ratings yet
- School of Mechanical Engineering Laboratory ManualDocument19 pagesSchool of Mechanical Engineering Laboratory ManualShubham TyagiNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Strut ReportDocument9 pagesBuckling of Strut ReportYamada Takeshi80% (5)
- Static Caracteristics BellowsDocument56 pagesStatic Caracteristics BellowsDiana SoareNo ratings yet
- JNTU World Structural Analysis NotesDocument11 pagesJNTU World Structural Analysis NotesMuhammed MuktarNo ratings yet
- Report Fatigue TestDocument20 pagesReport Fatigue TestCherif Chokeir75% (4)
- CIE4160 Textbook February 2019Document371 pagesCIE4160 Textbook February 2019Manank ShahNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiments Tensile Testing: July 2019Document25 pagesLaboratory Experiments Tensile Testing: July 2019Salih MohayaddinNo ratings yet
- 3.strength of MaterialsDocument6 pages3.strength of MaterialsNandhini NallasamyNo ratings yet
- Assignment I DME I Aug-Dec 2019Document4 pagesAssignment I DME I Aug-Dec 2019Vajrangi BharadwajNo ratings yet
- M.Tech Exam Advanced Mechanics of SolidsDocument2 pagesM.Tech Exam Advanced Mechanics of SolidsRaghuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Strength and Applied ElasticityDocument280 pagesAdvanced Strength and Applied Elasticityvipulugale67% (3)
- Mechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave Dispersion: Instrumentation and Experiment InterpretationFrom EverandMechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave Dispersion: Instrumentation and Experiment InterpretationYvon ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- Construction Rules For Shear Force and Bending Moment DiagramsDocument2 pagesConstruction Rules For Shear Force and Bending Moment DiagramsArash KamaliNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure WorksheetAryan Agrawal50% (2)
- CLASS 11 Vacation Assignment CHEMISTRY PDFDocument12 pagesCLASS 11 Vacation Assignment CHEMISTRY PDFGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Iso Plate Bending StiffnessDocument29 pagesIso Plate Bending StiffnesslapuNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Calculation of The Efficiency Limit For Solar CellsDocument30 pagesTheoretical Calculation of The Efficiency Limit For Solar CellsVianney TyzeNo ratings yet
- John Titor TIME MACHINEDocument21 pagesJohn Titor TIME MACHINEKevin Carey100% (1)
- Boyle's Law: Inverse Relationship of Gas Volume and PressureDocument12 pagesBoyle's Law: Inverse Relationship of Gas Volume and PressureLex PabustanNo ratings yet
- Is 11954 1987 Guide For Colour Coding of Electrical Mimic Diagrams PDFDocument10 pagesIs 11954 1987 Guide For Colour Coding of Electrical Mimic Diagrams PDFchandrakant patelNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of FluidsDocument64 pagesMechanics of FluidsShiva U100% (2)
- Chem Class XI ch.01Document7 pagesChem Class XI ch.01Navin KumarNo ratings yet
- Vaimanika-Sastra and Flying VimanasDocument3 pagesVaimanika-Sastra and Flying VimanasAleksander StrukeljNo ratings yet
- Driven Pile Design Methods in Weak Rock: September 2017Document7 pagesDriven Pile Design Methods in Weak Rock: September 2017Anonymous I8nZsDqlmhNo ratings yet
- The IsochroneDocument6 pagesThe IsochronePriscilla RochaNo ratings yet
- Multi-physics Simulation with CST STUDIO SUITEDocument43 pagesMulti-physics Simulation with CST STUDIO SUITESanjay_Tadepal_9503No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physical WorldDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Physical WorldPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Master Thesis - César Sebastián Silva ProañoDocument154 pagesMaster Thesis - César Sebastián Silva ProañoSebastián Silva100% (1)
- Design of flat glass plates with 4 edges simply supported and uniform loadingDocument1 pageDesign of flat glass plates with 4 edges simply supported and uniform loadingSHANIL051No ratings yet
- Applied Reactor Technology - Henryk Anglart PDFDocument204 pagesApplied Reactor Technology - Henryk Anglart PDFdogclutchNo ratings yet
- Theory 1Document191 pagesTheory 1Joseph Arben Agus100% (1)
- Teori Pile Geo5Document27 pagesTeori Pile Geo5Rivana AyuningrumNo ratings yet
- XVI - Magneticpropertiesofmanganese ContainingsolidsolutionsofbismuthorthoniobateBiNiO4Document7 pagesXVI - Magneticpropertiesofmanganese ContainingsolidsolutionsofbismuthorthoniobateBiNiO4Chukwuebuka UgochukwuNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Life Assessment of Bolted Connections: Aliou Badara Camara, Fabienne PennecDocument8 pagesFatigue Life Assessment of Bolted Connections: Aliou Badara Camara, Fabienne Pennecprraaddeej chatelNo ratings yet
- Residual Life Assessment of 110 KV XLPE CableDocument9 pagesResidual Life Assessment of 110 KV XLPE CableJesúsNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability of Road EmbankmentDocument7 pagesSlope Stability of Road Embankmentpraveen latharNo ratings yet
- NumericalsDocument6 pagesNumericalsaditya dhapodkarNo ratings yet
- Elemen Struktur Baja-III. COMPRESSION STRUCTUREDocument27 pagesElemen Struktur Baja-III. COMPRESSION STRUCTUREirfananda hutomoNo ratings yet
- Diagramme LogP-H - T-S À ImprimerDocument2 pagesDiagramme LogP-H - T-S À ImprimerRiad OualiNo ratings yet
- Cbse 12th Term 2 Mathematics Question Paper 2022Document3 pagesCbse 12th Term 2 Mathematics Question Paper 2022JayNo ratings yet
- Undamped Free VibrationDocument7 pagesUndamped Free VibrationMD Atiqur Rahman Faisal100% (2)
- Experimental Comparison of Single and Multistage Air Compressor EfficienciesDocument11 pagesExperimental Comparison of Single and Multistage Air Compressor EfficienciesJohn barry CorpuzNo ratings yet