Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Contraceptive Methods Guide
Uploaded by
murali_bharadwazOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Contraceptive Methods Guide
Uploaded by
murali_bharadwazCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of contraception o A method or a system which allows intercourse and yet prevents conception is called a contraceptive method.
Failure rate of any contraceptive method is described in terms of pregnancy rate per 100 woman years (Pearl index). o The calender method or the rhythm method o avoidance of sexual intercourse around ovulation o In a 28-day cycle ovulation normally occurs on the 14th day of the cycle ovulation may occur anytime between the 12th and 16th day (MCQ) Spermatozoa deposited in the female genital tract may survive for 24 hours ovum itself may live for 12 to 24 hours intercourse between the 11 th and 17th day may result in a pregnancy. (MCQ) o Safe period first day of the menstrual period until the 10th day of the cycle from the 18th to the 28th day(MCQ) o Risk period, from 3 days before ovulation to 3 days after ovulation. In a 35-day menstrual cycle ovulation will occur on the 21st day (that is 14 days before the next period) risk period is from day 18 to day 24. (MCQ) o Calendar method. Ogino-Knaus method fertile peiod is determined by subtracting 18 days from the shorest cycle and 10 days from the longest cycle which gives the first and the last day of fertile period, respectively. (MCQ) Failure rate : 25 pregnancies per 100 woman years. o Mucus method (billings or ovulation method). Under oestrogen influence the mucus increases in quantity becomes progressively more slippery and elastic until a peak is reached under the influence of progesterone after peak under estrogen influence ,mucus becomes thicker, scanty and dry until the onset of menses Intercourse is considered safe during the 'dry days' immediately after the menses until mucus is detected. T thereafter the couple must abstain until the fourth day after the 'peak (MCQ) o Temperature method. Progesterone is known to exert a thermogenic effect on the body. BBT chart will be biphasic in an ovulatory cycle day of temperature shift indicates the time of ovulation.
Abstinence during the fertile phase
o Symptothermal method. This combination method is more effective. The first day of abstinence is predicted either from the calender, by subtracting 21 from the length of the shortest menstrual cycle in the preceding 6 months, or first day mucus is detected, whichever comes first. (MCQ) The end of the fertile period is predicted by use of the 'basal body temperature' chart. The woman resumes intercourse 3 days after the thermal shift. o Withdrawal method (coitus interruptus) Failure rate : 25 per 100 woman years. (MCQ) The main cause of the failure is not that ejaculation occurs inside the vagina but that prostatic fluid secreted prior to ejaculation, frequently contains active spermatzoa. Breastfeeding o Regular breastfeeding with at least one feed at night is shown to prevent pregnancy for 6 months o failure rate of only 0.5 to 1.5%. (MCQ) Barrier methods o Condoms water-based spermicides should be used with latex condoms Because of irritation by latex in some women, non-latex polyurethane condoms are avail-able. (MCQ) They however slip and break easily and are more costly than the latex condoms. Latex condoms prevent STDs such as HIV less protective against STD transmitted from skin-to-skin contact such as human papilloma vims and herpes virus. Nirodh brand is distributed free of cost in the government hospitals in India. pregnancy rate of 10 to 14 per 100 woman years. (MCQ) Other uses of condom following vasecomy for 12 ejaculates(MCQ) in immunological infertility to prevent transmission of gonococcal, chlamydia, syphilis, trichomonad and fungal infection, HIV. (MCQ) o Spermicidal agents contain surfactants, such as nonoxynol-9, octoxynol and menfegol (MCQ) failure rate - 30 per 100 woman years. (MCQ) remain effective for 1 to 2 hours after the application. (MCQ) By causing irritation and abrasions in chronic use, they can cause vaginal ulceration and perhaps increase the risk of HIV spread rather than prevent it. Therefore, the sper-micidal agents should not be recommended to HIV couples. (MCQ) A new spermicidal cream, Tenofovir, prevents viral attachment to the vaginal mucosa and is non-irritant and is under development. (MCQ) o Ocdusive diaphragms
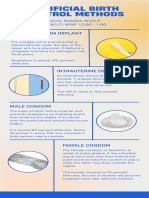
diaphragm liberally covered with spermicide can be inserted at any convenient time left in position for a minimum of 8 hours after coitus. (MCQ) It causes no discomfort no douching is required A refitting of the diaphragm is always required after childbirth, and this can be done about 6 to 8 weeks after confinement. (MCQ) The Dutch cap or diaphragm. ones in common use range between 65 and 80 mm fit obliquely in the vagina, stretcing from just behind the pubic ramus into the posterior fornix, thus covering the cervix. It is held in position by the tension of the spring rim Contraindications to use of diaphragm (MCQ) o prolapse, cystocele, rectocele because accurate fitting is not possible o recurrent urinary tract infection o allergy to rubber or spermicidal agent. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) o occur if the diaphragm is left in the vagina for a long period o caused by staphylococcal pyogenic infection. failure rate of the Dutch cap is about 4 to 6 per 100 woman years Cervical cap. It fits closely to the cervix suitable where the cervix is long and firm. When a woman has a prolapse of uterus and vagina, a cervical cap is preferred to the vaginal diaphragm. Chronic cervicitis, erosion and cervical laceration contraindicate its use. available in four sizes, varying from 22 to 31 mm Dumas cap It is a cup-shaped rubber with a thickened rim fits well into the vault of the vagina so that it encloses the cervix(MCQ) size varies from 55 to 75 mm diameter. Femshield (female condom). known as 'FEM' or Femidom It is a loose-fitting 15 to 17 cm long sheath made of polyurethane prelubricated(MCQ) It has the combined features of a diaphragm and a condom It covers the entire vagina, cervix as well as the external genitalia. It is highly protective against spread of STDs, and AIDS in particular(MCQ) It can be removed immediately after intercourse.
Today
(MCQ) Advantages of the Femshield (MCQ) o it is coital-independent and can be worn well in advance of the sexual act o it does not slip off easily, and the failure rate is expected to be low, o it is stronger than the condom and does not burst easily o it can be worn during the puerperal period unlike the diaphragm. Failure rate is 5 to 15 per 100 woman years. (MCQ) Femshield is expensive, costing 2 to 3 dollars per piece It is not re-usable
It is a mushroom-shaped polyurethane disposal sponge
contains 1 g of nonoxynol-9(MCQ) It can remain effective for 24 hours. (MCQ) Failure rate - 9 to 30 per 100 woman years(MCQ) expensive, coital-dependent may cause TSS if left over a long period. o Intrauterine contraceptive devices an effective, reversible and long-term method of contraception it does not require replacement for long periods it does not interfere with sexual activity. It is commonly made of polyethylene (MCQ) It is impregnated with barium sulphate to render it radiopaque so that the presence or absence of the device in the pelvis can be easily detected by radiograph. Biologically inert devices indude Lippes loop and Saf-T-Coil. They can be left in situ for several years, provided they cause no side effects Copper carrying devices copper wire of surface area 200 to 250 mm is wrapped round the vertical stem of a polypropylene frame. (MCQ) Copper T 200, Copper 7, Multiload Copper 250, CopperT380, CopperT220 and NovaT. have an effective life of about 3 to 5 years(MCQ) It is estimated that about 50 microgms of copper is eluted daily in the uterus. (MCQ) Paraguard o Copper T 380A (MCQ) o has a lifespan of 10 years. (MCQ) Nova T has silver added to the copper wire (MCQ) lifespan is 5 years. (MCQ) Progestasert and levonova. Progestasert
a T- shaped device carry 38 mg of progesterone in silicon oil reservoir in the vertical stem. (MCQ) It releases 65 micrograms of the hormone per day. (MCQ) Mechanism of contraceptive effect.
o Hormone released in the uterus forms a thick plug of mucus at the cervical os which prevents penetration by the sperms Menstrual problems like menorrhagia and dysmenorrhoea noticed with Copper T are less with this device (40% reduction). (MCQ) Requires yearly replacement Levonova o Contains 60 mg of levonorgestrel (LNG) o releases the hormone in very low doses (20 micrograms/day). (MCQ) o It is longer-acting (5 years) (MCQ) o It has a low pregnancy rate of 0 to 3 per 100 woman years(MCQ) o incidence of ectopic pregnancy is sixfold to nine-fold higher in women who do become pregnant as compared to failures amongst Copper T users. (MCQ) o It can be safely recommended for nursing mothers. (MCQ) Mirena o contains 52 mg LNG(MCQ) o elutes 20 microgram daily. (MCQ) o It can be retained for 5 years(MCQ) o It has a failure rate of 0.1 to 0.4 per 100 woman years Frameless IUCD IUCD under trial. contains several copper cylinders tied together on a string anchored 1 cm deep into fundus IUCDs are a good contraceptive choice for Low risk of STD Multiparous woman (MCQ) Monogamous relationship Desirous of long-term reversible method of contraception, but not yet desirous of permanent sterilization Unhappy or unreliable users of oral contraception or barrier contraception. Uses of IUCD As a contraceptive
Postcoital contraception (emergency contraception) Following excision of uterine septum, Asherman's syndrome(MCQ) Hormonal IUCD (Mirena) in o menorrhagia and dysmenorrhea(MCQ) o hormonal replacement therapy in menopausal women(MCQ) o In a woman on tamoxifen for breast cancer, it can be used to counteract endometrial hyperplasia. (MCQ) Contraindications of IUCD Suspected pregnancy Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) lower genital tract infection Presence of fibroidsbecause of misfit(MCQ) Menorrhagia and dysmenorrhoea, if Copper T is used Severe anaemia Diabetic women who are not well controlledbecause of slight increase in pelvic infection(MCQ) Heart diseaserisk of infection(MCQ) Previous ectopic pregnancy(MCQ) Preferably avoid its use in unmarried and nulliparous patient because of the risk of PID and subsequent tubal infertility(MCQ) LNG IUCD in breast cancer (MCQ) Abnormally shaped uterus, septate uterus(MCQ) Mechanism of action The presence of a foreign body in the uterine cavity renders the migration of spermatozoa difficult. A foreign body within the uterus provokes uterine contractility through prostaglandin release It increases the tubal peristalsis (MCQ) the fertilized egg is propelled down the fallopian tube more rapidly than in normal it fertilized egg reaches the uterine cavity before the development of chorionic villi and thus is unable to implant. The device in situ causes leucocytic infiltration in the endometrium. (MCQ) Copper T o elutes copper which brings about certain enzymatic and metabolic changes in the endometrial tissue which are inimical to the implantation of the fertilized ovum. (MCQ) Progestogen-carrying device o causes alteration in the cervical mucus which prevents penetration of sperm, in addition to its local action. o It also causes endometrial atrophy(MCQ) o It prevents ovulation in about 40%.(MCQ)
Complications(MCQ) Immediate o Difficulty in insertion o Vasovagal attack o Uterine cramps Early o Expulsion (2 to 5%) o Perforation (1 to 2%) o Spotting, menorrhagia (2 to 10%) o Dysmenorrhoea (2 to 10%) o Vaginal infection o Actinomycosis Late o PID-2 to 5%. o IUCD does not prevent transmission of HIV. o Pregnancy 1 to 3 per 100 woman years (failure rate) o Ectopic pregnancy o Perforation o Menorrhagia o Dysmenorrhoea. IUCD can be inserted in HIV-positive woman on medication. (MCQ) Long-term follow-up of women wearing IUCD has shown no ill effects on systemic diseases. There is no evidence that the device predisposes to either cervical or endometrial cancer. Perforation can occur at the time of insertion, particu-larly during puerperium rare with withdrawal than push-in technique(MCQ) Menorrhagia is controlled with NSAID drugs. Expulsion may occur in 5 to 15% due to small size of IUCD common during the puerperal period or following MTP of a large gestation size. (MCQ) PID occurs usually in the 4 weeks of insertion Actinomycosis is an infection commonly associated with IUCD. Misplaced IUCD the tail of the IUCD is not seen through the os causes are(MCQ) o uterus has enlarged through pregnancy o thread has curled inside the uterus o perforation has occurred o IUCD is buried in the myometrium o it has been expelled
A plain radiograph or pelvic ultrasound is used to diagnose If it is inside, the uterine sound or another IUCD inserted in the uterine cavity will show on radiograph its proximity to the misplaced IUCD and perforation can be diagnosed Abnormal shape or location of IUCD on radiograph indicates likely perforation. Hysteroscopy is useful not only to locate it but also for its retrieval If the IUCD is in the uterine cavity, it can be retrieved with Shirodkar's hook, a curette or through a hysteroscope. In case of perforation, a laparotomy is needed, because Copper T causes adhesions to the omentum or a gut and cannot be retrieved easily through a laparoscope. Pregnancy. occurs with IUCD in situ in 1 to 3 per 100 woman years. If this happens, it is important to do ultrasound and rule out ectopic pregnancy(MCQ) The uterine pregnancy can cause severe infection It is therefore mandatory to remove the IUCD if the tail is visible through the os. While doing so, the risk of abortion should be explained to the woman. If the thread of the IUCD is not seen, termination of pregnancy is offered, not because IUCD has any teratogenic effect but because the risk of uterine infection is considerable. (MCQ) Ectopic pregnancy It occurs in 1:30 pregnancies in woman wearing IUCD. because IUCD has a local contraceptive action on the uterus and prevents a uterine pregnancy but does not protect against tubal or ovarian pregnancy Progestasert has the highest incidence of ecto-pic pregnancy (six to nine times more than Copper T). (MCQ) PID also contributes to the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy. Advantages of IUCD It is coital-independent. (MCQ) newer IUCDs being as effective as oral contraceptives. hree per cent failure rate at the end of 1 year is reduced to less than 1% at the end of 5 years. There is no user failure. (MCQ) o There is no evidence of reduced fertility following its removal. o About 75% women conceive within 6 months of its removal
almost 90% conceive within a year. (MCQ) There are no systemic ill effects, unlike oral contraceptives No adverse effect on lactation is observed. Copper T is inserted free of cost in government hospitals in India. (MCQ)
You might also like
- Barrier Methods and Natural Family PlanningDocument16 pagesBarrier Methods and Natural Family PlanningMy StoryNo ratings yet
- Family Planning Methods GuideDocument51 pagesFamily Planning Methods GuideJessa MaeNo ratings yet
- Artificial Family Planning Methods ExplainedDocument33 pagesArtificial Family Planning Methods ExplainedJullienne Ysabelle AngNo ratings yet
- CONTRACEPTION TeachingDocument46 pagesCONTRACEPTION TeachingsaufisafingiNo ratings yet
- Type of Family Planning Natural Family PlanningDocument4 pagesType of Family Planning Natural Family Planningboyet101No ratings yet
- Permanent ContraceptionDocument8 pagesPermanent ContraceptionJean Mae DesquitadoNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Contraceptive DevicesDocument15 pagesIntrauterine Contraceptive DevicesAditya Malladi100% (1)
- CONTROL PREGNANCY METHODSDocument2 pagesCONTROL PREGNANCY METHODSJo Anne CTarrayNo ratings yet
- Gynecology: Three Minimally Invasive Procedures You Need to Know About For: Permanent Birth Control, Heavy Menstrual Periods, Accidental Loss of Urine Plus: Modern Hormone Therapy for the Post Menopausal WomenFrom EverandGynecology: Three Minimally Invasive Procedures You Need to Know About For: Permanent Birth Control, Heavy Menstrual Periods, Accidental Loss of Urine Plus: Modern Hormone Therapy for the Post Menopausal WomenNo ratings yet
- IUD Types, Designs & EffectivenessDocument33 pagesIUD Types, Designs & EffectivenessAmit Belekar100% (1)
- Permanent Methods of Contraception (Surgical Sterilization) : VasectomyDocument7 pagesPermanent Methods of Contraception (Surgical Sterilization) : VasectomyEmAr ExNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument6 pagesFamily PlanningMZ LimNo ratings yet
- Procedures in OBGDocument8 pagesProcedures in OBGKanak Soni100% (1)
- Midwifery - SterlizationDocument39 pagesMidwifery - SterlizationEsha KuttiNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - MOW (Medical Oprative Women) Tubectomy and IUDDocument13 pagesGroup 3 - MOW (Medical Oprative Women) Tubectomy and IUDIrfinaNo ratings yet
- Research - Long Version 2Document87 pagesResearch - Long Version 2Erika LlorenNo ratings yet
- Material To Read ContraceptionDocument12 pagesMaterial To Read Contraception8kx6rvg5p6No ratings yet
- Female SterilizationDocument6 pagesFemale Sterilizationjkj;jjNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentDocument3 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentJuviely PremacioNo ratings yet
- Contraception 2017Document85 pagesContraception 2017pt.mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Plan EducativoDocument17 pagesPlan EducativoNahomi CottoNo ratings yet
- Contraceptive MethodsDocument40 pagesContraceptive MethodsMa. Lourdes CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Contraception 1. Permanent ContraceptionDocument7 pagesMethods of Contraception 1. Permanent ContraceptionCaurrine MonsaludNo ratings yet
- Chapter 133Document16 pagesChapter 133Saloni SaloniNo ratings yet
- DR Jehan Hamadneh Consultant Gynecology Endocrinology and Reproductive MedicineDocument181 pagesDR Jehan Hamadneh Consultant Gynecology Endocrinology and Reproductive MedicineNur Aliya IshakNo ratings yet
- Vasectomy Reversals Expensive and Not Guaranteed; Tubal Ligation Also Considered PermanentDocument7 pagesVasectomy Reversals Expensive and Not Guaranteed; Tubal Ligation Also Considered PermanentEmAr ExNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project: TopicDocument13 pagesBiology Investigatory Project: TopicRaj SahuNo ratings yet
- Contraception and Family Planning_102215Document99 pagesContraception and Family Planning_102215bazuu mbwegzeNo ratings yet
- Contraception LectureDocument31 pagesContraception LectureDilushi sujikala silvaNo ratings yet
- Cervical IncompetenceDocument28 pagesCervical IncompetenceHoney May Rollan Vicente100% (1)
- DocumentDocument9 pagesDocumentsangtradesNo ratings yet
- Family Planning FinalDocument30 pagesFamily Planning FinalJHONESSA LAYOSNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Artificial MethodDocument19 pagesGroup 4 Artificial MethodDonah Marie Dumago AtanacioNo ratings yet
- Copper-T Insertion ProcedureDocument5 pagesCopper-T Insertion Procedurepriyanka100% (2)
- Permanent ContraceptionDocument33 pagesPermanent Contraceptionshyama seerviNo ratings yet
- The Process of Reproduction and Sexual Health and HygieneDocument28 pagesThe Process of Reproduction and Sexual Health and HygieneMila MagistradoNo ratings yet
- Contraceptive methods guide under 40 charactersDocument13 pagesContraceptive methods guide under 40 charactersJasper Padilla CaranyaganNo ratings yet
- Induction of Labor Methods and IndicationsDocument31 pagesInduction of Labor Methods and IndicationsDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Contraception Methods: 1. Long-Acting Reversible ContraceptionDocument5 pagesContraception Methods: 1. Long-Acting Reversible ContraceptionFaith MarfilNo ratings yet
- Iucdseminar 140127130253 Phpapp02Document37 pagesIucdseminar 140127130253 Phpapp02Imaylani S. SitanggangNo ratings yet
- 10 The Role of Routine Cervical Length Screening in Selected High - and Low-Risk Women For Preterm Birth PreventionDocument6 pages10 The Role of Routine Cervical Length Screening in Selected High - and Low-Risk Women For Preterm Birth PreventionWailea Faye SalvaNo ratings yet
- Permanent Family Planning MethodsDocument5 pagesPermanent Family Planning MethodsRALPH ELVIN MACANLALAYNo ratings yet
- Contraception Methods GuideDocument5 pagesContraception Methods GuideJemiline OlbocNo ratings yet
- What Is Microsurgical Tubal Ligation Reversal?Document2 pagesWhat Is Microsurgical Tubal Ligation Reversal?Andy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Akdr Pasca Post PartunDocument25 pagesAkdr Pasca Post PartundwiNo ratings yet
- Handout Maternity Nursing ContraceptionDocument2 pagesHandout Maternity Nursing ContraceptionPaul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (1)
- ContraceptionDocument2 pagesContraceptionlucyharrison778No ratings yet
- Contraception Is Not A New Idea.: Contraception (Birth Control Methods and Techniques)Document2 pagesContraception Is Not A New Idea.: Contraception (Birth Control Methods and Techniques)Ivan Dennis SalupanNo ratings yet
- Permanent Family PlanningDocument36 pagesPermanent Family PlanningNilakshi Barik MandalNo ratings yet
- Family Planning Methods/ Contraceptive Methods/nurses Education/ B.Sc. NursingDocument129 pagesFamily Planning Methods/ Contraceptive Methods/nurses Education/ B.Sc. NursingSameekshaNo ratings yet
- The Different Types ofDocument5 pagesThe Different Types ofJuanillo AllyssaNo ratings yet
- Cervical IncompetenceDocument30 pagesCervical IncompetenceSignor ArasNo ratings yet
- 1 CervixDocument12 pages1 Cervixzianab aliNo ratings yet
- PERPETUAL HELP MEDICAL CENTER-BIÑAN DEPARTMENT OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY FAMILY PLANNINGDocument9 pagesPERPETUAL HELP MEDICAL CENTER-BIÑAN DEPARTMENT OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY FAMILY PLANNINGKim Adarem Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- Clinical Findings: ACOG - Cervical Insufficiency As "Document5 pagesClinical Findings: ACOG - Cervical Insufficiency As "lllNo ratings yet
- Natural and Barrier MethodsDocument14 pagesNatural and Barrier Methodsshubham waleNo ratings yet
- Birth Control Methods BayoDocument3 pagesBirth Control Methods BayoRamsis Pimentel BayoNo ratings yet
- Natural and Artifical Methods of ContraceptionDocument21 pagesNatural and Artifical Methods of ContraceptionJoanne Ico MagnayeNo ratings yet
- Artificial Method (Hormonal Method)Document45 pagesArtificial Method (Hormonal Method)Ninfa Lansang100% (1)
- All You Need to Know About Neck Threadworms and Your Itchy HorseFrom EverandAll You Need to Know About Neck Threadworms and Your Itchy HorseNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5Document7 pagesQuiz 5murali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document6 pagesQuiz 3murali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum Structure and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCerebellum Structure and Functionsmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Auditory System PathwayDocument2 pagesAuditory System Pathwaymurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document8 pagesQuiz 2murali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Depressed Skull FractureDocument6 pagesDepressed Skull Fracturemurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Lesions of The Spinal CordDocument7 pagesLesions of The Spinal Cordmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document6 pagesQuiz 3murali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document8 pagesQuiz 1murali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Arteries, and Their Divisions. Arteries Fuse To Form The Basilar ArteryDocument6 pagesVertebral Arteries, and Their Divisions. Arteries Fuse To Form The Basilar Arterymurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy and StructuresDocument5 pagesBrain Anatomy and Structuresmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Medullar Oblongata (Myelencephalon) Gastrointestinal MotilityDocument10 pagesMedullar Oblongata (Myelencephalon) Gastrointestinal Motilitymurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- AIIMS May 2013Document11 pagesAIIMS May 2013murali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- AIIMS May 2013 Expalnations Ignore But CheckDocument16 pagesAIIMS May 2013 Expalnations Ignore But Checkmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- AIIMS May 2013 Expalnations Transfer FileDocument32 pagesAIIMS May 2013 Expalnations Transfer Filemurali_bharadwaz0% (1)
- Depressed Skull FractureDocument6 pagesDepressed Skull Fracturemurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Celiac Disease: A Comprehensive Review of Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument3 pagesCeliac Disease: A Comprehensive Review of Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Managementmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Aiims May Transfer File 5Document7 pagesAiims May Transfer File 5murali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- 33 Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pages33 Polycystic Kidney Diseasemurali_bharadwaz100% (1)
- Programmed Cell Death MechanismsDocument5 pagesProgrammed Cell Death Mechanismsmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Programmed Cell Death MechanismsDocument5 pagesProgrammed Cell Death Mechanismsmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Red Cells or White Cells.: g/100 Ml. (MCQ)Document7 pagesRed Cells or White Cells.: g/100 Ml. (MCQ)murali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- 16 AmlDocument5 pages16 Amlmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- 23 Multiple MyelomaDocument3 pages23 Multiple Myelomamurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- 16 C CLLDocument2 pages16 C CLLmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- 11 Inheritance PatternsDocument9 pages11 Inheritance Patternsmurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- 33 Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pages33 Polycystic Kidney Diseasemurali_bharadwaz100% (1)
- 17 Lung CancerDocument3 pages17 Lung Cancermurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- 16 E Hairy Cell LukemiaDocument2 pages16 E Hairy Cell Lukemiamurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle and HormonesDocument30 pagesMenstrual Cycle and HormonesGALPAO MELISSANo ratings yet
- Fpp-Obstetric & Gynaecology ProcedureDocument8 pagesFpp-Obstetric & Gynaecology ProcedureNurul FarhanahNo ratings yet
- Causes of infertility in UAE females: A cross-sectional studyDocument88 pagesCauses of infertility in UAE females: A cross-sectional studyOhmed KhiljiNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Women Reproduction SystemDocument52 pagesPhysiology of Women Reproduction Systemram kumarNo ratings yet
- Tog 12150Document10 pagesTog 12150saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- DR - Moslim Obs & Gyn Answers GuideDocument124 pagesDR - Moslim Obs & Gyn Answers GuideMandark0009100% (5)
- Anatomy Female GenitaliaDocument70 pagesAnatomy Female GenitaliaHeni KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- INFERTILITY Purnima SeminarDocument9 pagesINFERTILITY Purnima SeminarBhanesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Organ GuideDocument19 pagesFemale Reproductive Organ Guidemistry100% (1)
- Disorders of Sexual FunctioningDocument5 pagesDisorders of Sexual FunctioningDhaneanne Marie ChanNo ratings yet
- Session #45 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document6 pagesSession #45 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Pessary in Women With SymptomaticDocument8 pagesVaginal Pessary in Women With SymptomaticNina VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument22 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingAde JuandaNo ratings yet
- 7.recent Advances in Contraceptive TechnologyDocument25 pages7.recent Advances in Contraceptive TechnologyVeena Dalmeida100% (1)
- Prevalence of Cervicitis in Dairy Cows and Its EffDocument8 pagesPrevalence of Cervicitis in Dairy Cows and Its EffАнастасія ПоліщукNo ratings yet
- Mestrual CycleDocument16 pagesMestrual CycleMaria Elaiza CortesNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemLucille BallaresNo ratings yet
- Approach To Vaginal Discharge in ChildrenDocument12 pagesApproach To Vaginal Discharge in ChildrensujataNo ratings yet
- The FIGO Recommendations On Terminologies and Definitions For Normal and Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument8 pagesThe FIGO Recommendations On Terminologies and Definitions For Normal and Abnormal Uterine BleedingAchmad KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Libro de Endocrino y FertilidadDocument684 pagesLibro de Endocrino y FertilidadClaudia Mercedes Alonso Cuevas100% (1)
- AUB Williamgyne4e PDFDocument35 pagesAUB Williamgyne4e PDFS BooNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Normal Menstrual Cycle - UpToDateDocument10 pagesPhysiology of The Normal Menstrual Cycle - UpToDateAacv CvNo ratings yet
- Aub Updated-1 PDFDocument87 pagesAub Updated-1 PDFEvelyn Pamela Espinoza Morales100% (2)
- Cervical ErosionDocument19 pagesCervical ErosionYogesh ValaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of the OvaryDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of the OvaryJay PaulNo ratings yet
- EndometriosisDocument2 pagesEndometriosisIrham KasyfulNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Structures and FunctionsDocument9 pagesFemale Reproductive System Structures and FunctionsReign SaplacoNo ratings yet
- Tingkat Pematangan OositDocument11 pagesTingkat Pematangan OositHendrik_NurfitriantoNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual Cycle: For Science Grade 5Document12 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle: For Science Grade 5Rhodora Rendon OrizonteNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Menstrual CycleDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Menstrual CycleMICHAEL JR FERNANDO100% (1)