Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OpticsExam2 Practice
Uploaded by
Jane WinnerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
OpticsExam2 Practice
Uploaded by
Jane WinnerCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYS 3190, Applied Optics Exam #2 Practice Exam Dr.
John Sohl
Name: No Time Limit, Score: _____(/50)
Math tables, calculator, ruler, 8.5 X 11 note sheet allowed. Instructions: You MUST show all work to get full credit, if I can't read it I'll assume that it is wrong. Circle your final answer. By affixing your name to this exam you certify that you have not and will not talk to anyone about the exam prior to the A Due date.@ If you need more space, use the back of the sheet and make a note on the front to direct me there.
0 = 8.8542 10-12 C2 N-1 m-2, 0 = 4 10-7 kg m A-2 s-2, c = 3 108 m/s, h = 6.626 X 10-34 J s 1. (10 pts) Light of continuously variable wavelength illuminates normally a thin oil (index of 1.30) film on a glass surface (nglass = 1.50). Extinction of the reflected light is observed to occur at wavelengths of 525 and 675 nm in the visible spectrum. Determine the thickness of the oil film and the orders of the interference.
2. (4 pts) When one mirror of a Michelson interferometer is translated by 0.0114 cm, 523 fringes are observed to pass the crosshair of the viewing telescope. Calculate the wavelength of the light.
3. (6 pts) The plates of a Fabry-Perot interferometer have a reflectance coefficient of r = 0.99. Calculate the minimum (a) resolving power and (b) plate separation that will accomplish the resolution of the two components of the H-alpha doublet of the hydrogen spectrum whose separation is 9.472 GHz at 6563 .
4. (6 pts) The indices of refraction for the fast and slow axes of calcite (CaCO3) with 589.3 nm light are 1.4864 and 1.6584 respectively. (a) What is the thickness of a zeroth-order QWP?
(b) If a multiple-order calcite plate 0.998 mm thick functions as a QWP, what is its order?
5. (4 pts) At a particular wavelength the index of refraction for isotropic (non-crystalline) quartz is 1.548. What is Brewsters angle for a ray of light incident from fresh water where n=1.333? (I.e., the quartz is submerged in water.)
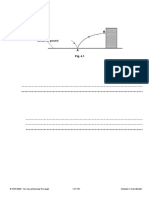
6. (10 pts) The Tactical High Energy Laser (THEL) Demonstrator for shooting down missiles using a laser beam has an aperture of 58 cm and operates at a wavelength of 2.0 microns. The maximum range is estimated to be approximately 5 km. While the exact power output is classified, it is common knowledge that this H-F (hydrogen fluoride) laser probably operates with a power output of about 100-kW. (By the way, the THEL costs about $8,000 per shot and can do about 60 shots between refurbishments and refueling. Another application is for shooting down fighter jets. Currently THEL is about the size of 4 or 5 mobile homes.) (a) What is the radius of the laser spot at the maximum range of 5 km?
(b) What is the irradiance of the beam at this location?
Images from the THEL program which is a US government funded Israeli military weapons program:
7. (10 pts) The Jarrel-Ash 0.25-meter spectrograph in the lab provides a minimum of 0.2 first order resolution anywhere in the visible spectrum (400 to 700 nm). The ruled width of the grating is 5.0 cm. (a) Determine the minimum number of grooves required.
(b) If the diffraction pattern is focused 25-cm from the grating, what is the linear separation of a 0.2 interval in the vicinity of = 550 nm?
Bonus Problem (6 points) An echelle grating is ruled over 12 cm of width with 8 grooves/mm and is blazed at 63. Determine for a Littrow configuration the following: (a) The range of orders in which the visible spectrum (400 to 700 nm) appears.
(b) The resolving power and minimum resolvable wavelength interval at 550 nm.
(c) The free spectral range assuming the shortest wavelength present is 350 nm.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Tomorrow Is WaitingDocument8 pagesTomorrow Is WaitingsrplsmskNo ratings yet
- OpticsHW Ch11KeyDocument12 pagesOpticsHW Ch11KeyJane Winner100% (1)
- OpticsHW Ch12KeyDocument4 pagesOpticsHW Ch12KeyJane WinnerNo ratings yet
- Lec27 - Tissue Engineering - CaseStudies PDFDocument10 pagesLec27 - Tissue Engineering - CaseStudies PDFJane WinnerNo ratings yet
- OpticsExam2 Practice KeyDocument5 pagesOpticsExam2 Practice KeyJane WinnerNo ratings yet
- Lec19 Surface Modification PDFDocument10 pagesLec19 Surface Modification PDFJane WinnerNo ratings yet
- Lec8 Hydrogels PDFDocument52 pagesLec8 Hydrogels PDFJane WinnerNo ratings yet
- Lab Polarization PDFDocument4 pagesLab Polarization PDFJane WinnerNo ratings yet
- Chitin Antimicrobial Activity: Biomacromolecules, 2007, 8 (5), PP 1359-1384Document23 pagesChitin Antimicrobial Activity: Biomacromolecules, 2007, 8 (5), PP 1359-1384Jane WinnerNo ratings yet
- Lec8 Hydrogels PDFDocument52 pagesLec8 Hydrogels PDFJane WinnerNo ratings yet
- Lab Polarization PDFDocument4 pagesLab Polarization PDFJane WinnerNo ratings yet
- 2012 Nike Football Clinic 4Document2 pages2012 Nike Football Clinic 4Bruno ChuNo ratings yet
- Listado de Vehiculos para ChatarrizaciónDocument658 pagesListado de Vehiculos para ChatarrizacióntaycotcNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Social WorkDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Social WorkSheherbano TariqNo ratings yet
- 5 Energy ManagementDocument1 page5 Energy ManagementDibyo SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Physics Exam Qs StudentDocument7 pagesAtomic Physics Exam Qs StudentfitzttNo ratings yet
- Role of Women in Urban and Rural AreasDocument3 pagesRole of Women in Urban and Rural AreasUmair AltafNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Project (Electochemistry)Document10 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Project (Electochemistry)Raghvendra Pandey0% (1)
- Optics and Lasers in EngineeringDocument5 pagesOptics and Lasers in EngineeringsenthilNo ratings yet
- 1 CE155 - Introduction To EstimatingDocument14 pages1 CE155 - Introduction To EstimatingAlbert SaludNo ratings yet
- EPR in Waste ManagementDocument11 pagesEPR in Waste Managementdorexp17No ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Exam Questions 69 QuestionsDocument145 pagesQuantum Physics Exam Questions 69 QuestionsVedant BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Lino PresentationDocument14 pagesLino Presentationapi-356807903No ratings yet
- The Mystic Class 11 Updated Psionics For 5eDocument36 pagesThe Mystic Class 11 Updated Psionics For 5eShaadJackNo ratings yet
- Everyday Conversation 3CDocument10 pagesEveryday Conversation 3Cjiyoon KimNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know First: No Luck RequiredDocument8 pagesWhat You Need To Know First: No Luck RequiredEvangielyn ArenasNo ratings yet
- How Do I Upgrade From Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 To Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7Document12 pagesHow Do I Upgrade From Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 To Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7Shailendra MathurNo ratings yet
- Intro To Threads PDFDocument4 pagesIntro To Threads PDFNANDINI BNo ratings yet
- 2000 - VAICTM-an Accounting Tool For IC Management - Ante PulicDocument13 pages2000 - VAICTM-an Accounting Tool For IC Management - Ante PulicIklima RahmaNo ratings yet
- Negative Effects of Social Media AddictionDocument2 pagesNegative Effects of Social Media AddictionTubagus Fikih AriansyahNo ratings yet
- How To Write Master Thesis AbstractDocument8 pagesHow To Write Master Thesis Abstractidmcgzbaf100% (2)
- Approach SlabDocument2 pagesApproach SlabMahmood Mufti100% (1)
- File ListDocument17 pagesFile ListAndre CunhaNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument6 pagesSubject-Verb AgreementCheryl AquinoNo ratings yet
- Goodman and Gilman's Sample ChapterDocument17 pagesGoodman and Gilman's Sample Chapteradnankhan20221984No ratings yet
- QUIZ ENGCOM 2 - Week 4Document2 pagesQUIZ ENGCOM 2 - Week 4Amin sanNo ratings yet
- ICMA2011 DigestDocument160 pagesICMA2011 DigestPREEDAIENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- Antheil - Piano Sonata No 4Document29 pagesAntheil - Piano Sonata No 4TateCarson100% (1)
- Original PDFDocument37 pagesOriginal PDFAhmadS.Alosta50% (2)
- Karl Storz Endoscopy-America v. Stryker Et. Al.Document9 pagesKarl Storz Endoscopy-America v. Stryker Et. Al.Patent LitigationNo ratings yet