Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study - DHF
Uploaded by
MerrrksOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study - DHF
Uploaded by
MerrrksCopyright:
Available Formats
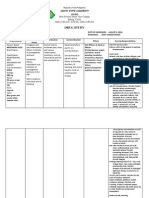
DRUG STUDY
DATE ORDERED & STARTED GENERIC NAME & TRADE/BRAND NAME JULY 21, 2013 PARACETAMOL 500mg/tab 1tab PO q4 Inhibits the synthesis of the prostaglandins that may serve as mediators or pain and fever, primarily in the CNS. I: Mild pain. Fever. C: Previous hypersensitivity; products containing alcohol, aspartame, saccharin, sugar, or tartrazine (FDC yellow dye#5) Severe Reduce fever and hypoglycemia, headache oliguria, urticaria Assess overall health status and alcohol usage before administering paracetamol. Pain: Assess type, location, and intensity prior to and 30-60min following administration Fever: Assess fever, note presence of associated signs (diaphoresis, tachycardia, and malaise) Evaluate hepatic, hematologic, and renal function periodically Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain and frank or occult blood in the stool and emesis. Monitor CBC Administer drug on empty stomach TEACH CLIENT Monitor for severe, persistent constipation Increase fluids, dietary bulk to relieve constipation PHARMACOLOGIC INDICATION AND ADVERSE ACTION OF DRUG CONTRAINDICATIONS EFFECTS OF THE DRUG DESIRED ACTION ON CLIENT NURSING RESPONSIBILIES
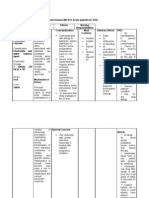
JULY 21, 2013 OMEPRAZOLE (Prilosec) 40mg NOW & OD TIV
Brings to an enzyme on gastric parietal cells in the presence of acidic gastric pH, preventing the final transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen.
I: Reduction of risk of GI bleeding in critically ill patients C: Hypersensitivity
Fatigue, dizziness, headache, abdominal pain
Reduce the risk of pain and GI bleeding
JULY 21, 2013 CEFUROXIME 500mg/tab 1tab BID PO
Interferes with bacterial cell-wall synthesis and division by binding to cell wall, causing cell to die. Active against gramnegative and grampositive bacteria, with expanded activity against gramnegative bacteria.
I: Moderate to severe infections, including those of skin, bone, joints, urinary or respiratory tract C: Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins or penicillins
Seizures, rashes, diarrhea, cramps, nausea
To reduce the development of drugresistant bacteria
Avoid liquids and foods that can cause gastric irritation : caffine-containing beverages, alcohol, certain fats, spices Assess allergy to cephalosporins Observe patient for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis Monitor vital signs, urine output, and laboratory results. Report abnormal findings. Instruct client to report any side effects from use of oral cephalosporin drugs Advise client the tablet should be swallowed whole.
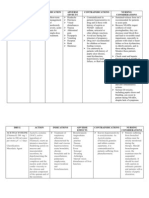
JULY 22, 2013
Binds to mu-opioid receptors. Inhibits reuptake of TRAMADOL + serotonin and PARACETAMOL norepinephrine in the 37.5mg/ 325mg tab CNS. BID PO
I: Moderate to moderately Dizziness, severe pain nausea, fatigue, C: Hypersensitivity headache, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, vomiting, anorexia, anxiety, confusion, insomnia, nervousness,
To decreased pain
Assess type, location, and intensity of pain before and 2-3 hr (peak) after administration. Assess BP & RR before and periodically during administration. Respiratory depression has not occurred with recommended doses. Assess bowel function routinely. Prevention of constipation should be instituted with increased intake of fluids and bulk and with laxatives to minimize constipating effects.
rash
Monitor patient for seizures. May occur within recommended dose range. Risk increased with higher doses and inpatients taking antidepressants, analgesics, or other durgs that decrese the seizure threshold. Maintain fluids and electrolytes Use sterile infusion set Assess patient's hydration status Regulate fluid as prescribed Monitor signs and symptoms of fluid volume excess and fluid volume deficit Monitor I&O Monitor IV site for infiltration or phlebitis TEACH CLIENT To recognize signs and symptoms of fluid volume excess and deficit How to measure I&O How to weigh himself /herself Use sterile infusion set Assess patient's hydration status Regulate fluid as prescribed Monitor signs and symptoms of fluid volume excess and fluid volume deficit Monitor I&O
JULY 21, 2013 D5NSS Each 100mL contains 5g of dextrose monohydrate and 300 mg of sodium chloride Hypertonic Solution
Hypertonic solutions contain a high concentration of solute relative to another solution( e.g. the cells cytoplasm) when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water diffuses out of the cell to shrivel.
I: For replacement or maintenance of fluid and electrolytes C: Hypersensitivity
JULY 22, 2013 D5LR Lactated Ringers Solution with 5%Dextrose Hypertonic
Hypertonic solutions contain a high concentration of solute relative to another solution( e.g. the cells cytoplasm) when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water
I: Treatment for persons needing extra calories who cannot tolerate fluid overload. Treatment for shock. C: Hypersensitivity
Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance
Solution
diffuses out of the cell to shrivel.
Monitor IV site for infiltration or phlebitis TEACH CLIENT To recognize signs and symptoms of fluid volume excess and deficit How to measure I&O How to weigh himself/herself
You might also like
- Nursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboDocument7 pagesNursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboAlexa Abidin Oldenborg100% (8)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- PN Pharmacology Online Practice 2014 BDocument5 pagesPN Pharmacology Online Practice 2014 BTee Wood67% (3)
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Cavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidDocument3 pagesCavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyjennachristy03100% (3)
- Icu Drug StudyDocument7 pagesIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFritzie Beatrice NomusNo ratings yet
- TB medications overviewDocument7 pagesTB medications overviewANNIE SHINE MAGSACAYNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- CHH Drug Study Week 2Document25 pagesCHH Drug Study Week 2maryxtine24No ratings yet
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyCrystal Joy MisaNo ratings yet
- Drug StuyJJASGHDocument7 pagesDrug StuyJJASGHJan Pierre RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Mesalamine MercaptopurineDocument15 pagesDrug Study On Mesalamine Mercaptopurineسوما الشمريNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoDocument10 pagesAmpicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingNo ratings yet
- CHH Drug Study Week 3Document21 pagesCHH Drug Study Week 3maryxtine24No ratings yet
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocument19 pagesAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- LM, KLDocument5 pagesLM, KLVictor CondeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Dosage GuideDocument3 pagesChlorpromazine Dosage GuideChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyKrishelle Kate PannigNo ratings yet
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsElisa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesChlorpromazine Drug StudyPeyjey100% (1)
- Ditropan Drug CardDocument2 pagesDitropan Drug CardBenNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument31 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesiamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocument12 pagesDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCarson BirthNo ratings yet
- Patient profile and drug studiesDocument8 pagesPatient profile and drug studiesEspiridionNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument6 pagesDrug NameAnnette Aquino GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicDocument7 pagesGeneric Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- FaciitisDocument17 pagesFaciitisdalaginding clophNo ratings yet
- Albuterol Drug StudyDocument7 pagesAlbuterol Drug StudyMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- DRUG and IVF StudyDocument4 pagesDRUG and IVF StudyJohanna Camelle Insong MonteronNo ratings yet
- Total Parenteral NutritionDocument6 pagesTotal Parenteral Nutritionpam23lozadaNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug AnaDocument4 pagesCefuroxime Drug AnaCarpz DarpzNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and DosageDocument6 pagesDrug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and Dosageسبوكاي100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyClarkEstacioNo ratings yet
- PreeclampsiaDocument179 pagesPreeclampsiaJohn Wilbert Birung100% (3)
- Paracetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyDocument9 pagesParacetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Tolbutamide: Orinase, Orinase Diagnostic, Apo-Tolbutamide, Novo-ButamideDocument4 pagesTolbutamide: Orinase, Orinase Diagnostic, Apo-Tolbutamide, Novo-ButamideALFATH REFYANUSNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studyzbestgurl100% (1)
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieNo ratings yet
- Drug and NCPDocument15 pagesDrug and NCPgeelawlietNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: GENERIC NAME: Acetaminophen TRADE NAME: TylenolDocument3 pagesDrug Study: GENERIC NAME: Acetaminophen TRADE NAME: TylenolLinda AdamsonNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure Mechanical VentilationDocument37 pagesRespiratory Failure Mechanical Ventilationawakepull312No ratings yet
- Mindmap - CholinergicDocument1 pageMindmap - CholinergicMerrrksNo ratings yet
- Vision and Hearing ScreenDocument1 pageVision and Hearing ScreenMerrrksNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases GuideDocument15 pagesCommunicable Diseases GuidesnpjavierNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment - AnemiaDocument14 pagesPhysical Assessment - AnemiaMerrrks100% (1)
- GallbladderDocument1 pageGallbladderMerrrksNo ratings yet
- HEPATOBLASTOMADocument2 pagesHEPATOBLASTOMAMerrrksNo ratings yet
- Patho - HepatoblastomaDocument2 pagesPatho - HepatoblastomaMerrrksNo ratings yet
- Essential Guide to Spinal Cord Injury Types and LevelsDocument6 pagesEssential Guide to Spinal Cord Injury Types and LevelsMerrrks100% (1)
- Reduce Risk of Injury for Weak Elderly PatientDocument1 pageReduce Risk of Injury for Weak Elderly PatientMerrrksNo ratings yet
- Mindmap - CholinergicDocument1 pageMindmap - CholinergicMerrrksNo ratings yet
- Linguistic EthnographyDocument3 pagesLinguistic EthnographyMerrrks100% (1)
- 30 Years Old Family History of Diabetes Mellitus Calorie DietDocument1 page30 Years Old Family History of Diabetes Mellitus Calorie DietMaricarcar1No ratings yet
- MiddleadulthoodDocument2 pagesMiddleadulthoodMerrrksNo ratings yet
- Tissue Map2Document2 pagesTissue Map2MerrrksNo ratings yet
- Albert BanduraDocument2 pagesAlbert BanduraMerrrksNo ratings yet
- Models of Communicato N GuideDocument9 pagesModels of Communicato N GuideMerrrksNo ratings yet
- Poultry Vaccination SeminarDocument16 pagesPoultry Vaccination SeminarRishiNo ratings yet
- NHRA-PPR - Drug Price List - 06-10-2016Document595 pagesNHRA-PPR - Drug Price List - 06-10-2016Um AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Core Pharmacology ConceptsDocument3 pagesIntroduction to Core Pharmacology ConceptsZahid Bashir BhattiNo ratings yet
- Axcel IncentiveDocument12 pagesAxcel Incentivegracious pharmacy 2No ratings yet
- PARIET 20mg - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (Emc)Document9 pagesPARIET 20mg - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (Emc)Abdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Linezolid: Antibiotic ClassDocument2 pagesLinezolid: Antibiotic ClassEdison Patricio Vallejo PasquelNo ratings yet
- AUGMENTIN Injection: What Is in This LeafletDocument5 pagesAUGMENTIN Injection: What Is in This LeafletPragneshNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis: Guide: DR P Bhosle Student: DR BharatDocument22 pagesMyasthenia Gravis: Guide: DR P Bhosle Student: DR BharatDr.Asif ButtNo ratings yet
- Formulative Pharmacy and BiopharmaceuticsDocument16 pagesFormulative Pharmacy and BiopharmaceuticsJafrine100% (1)
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument53 pagesAntimalarial DrugsAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Protocol: RegimenDocument6 pagesChemotherapy Protocol: RegimenAlexandra AndronescuNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressants: Pharmacology TeamDocument26 pagesImmunosuppressants: Pharmacology TeamZaina MasriNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance ManagementDocument14 pagesCorporate Governance ManagementGautamNo ratings yet
- GIT PharmacologyDocument35 pagesGIT PharmacologyDANSAA LATIINo ratings yet
- Lercanidipine Drug StudyDocument16 pagesLercanidipine Drug StudylenecarglbnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Psychoactive Drugs: Classification and HistoryDocument24 pagesChapter 1 - Psychoactive Drugs: Classification and HistoryrayNo ratings yet
- Doze AntibioticeDocument6 pagesDoze AntibioticeMocanu Cristina-Viorica100% (1)
- PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY - AntihistaminesDocument283 pagesPHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY - AntihistaminesGianniNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Calculations: Abbreviations Commonly Used in DosageDocument3 pagesDrug Dosage Calculations: Abbreviations Commonly Used in DosageShannen Kix OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Malaysia PharmaceuticalDocument371 pagesMalaysia Pharmaceuticalching leeNo ratings yet
- PROIECT Managementul Activitatii de Traducator. Malear IrinaDocument11 pagesPROIECT Managementul Activitatii de Traducator. Malear IrinaOffice Hydro-CarpatiNo ratings yet
- FOLFOX Chemotherapy Protocol for Colorectal CancerDocument8 pagesFOLFOX Chemotherapy Protocol for Colorectal CancerNurul Kamilah SadliNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan HandoutDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching Plan HandoutJoey AbalorioNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole PoDocument5 pagesMetronidazole PoFlower Flower FlowerNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocument1 pagePhenytoin Drug StudyRoland Yuste100% (3)
- Obat - BMDocument50 pagesObat - BMNovita PermataNo ratings yet
- February Journal 2020Document36 pagesFebruary Journal 2020rammvr05No ratings yet
- Bird Anesthesia: Standard Operating Procedure #121Document4 pagesBird Anesthesia: Standard Operating Procedure #121nofan rickyawanNo ratings yet
- SleepDocument3 pagesSleepBSN 2-2 Espiritu Melody Mae DNo ratings yet