Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acquisition
Uploaded by
Nor AmiraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acquisition
Uploaded by
Nor AmiraCopyright:
Available Formats
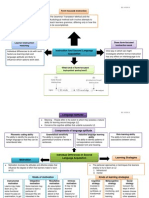
Acquisition The act of contracting or assuming or acquiring possession of something; "the acquisition of wealth"; "the acquisition of one company
by another" Acquiring, getting - the act of acquiring something; "I envied his talent for acquiring"; "he's much more interested in the getting than in the giving" The definition of an acquisition is the act of getting or receiving something, or the item that was received. Language acquisition is the process by which humans acquire the capacity to perceive and comprehend language, as well as to produce and use words and sentences to communicate. Learning Measurable and relatively permanent change in behavior through experience, instruction, or study. Whereas individual learning is selective, group learning is essentially political its outcomes depend largely on power playing in the group. Learning itself cannot be measured, but its results can be. Acquiring new, or modifying and reinforcing existing, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, or preferences and may involve synthesizing different types of information. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals and some machines. Progress over time tends to follow learning curves. Learning is not compulsory; it is contextual. It does not happen all at once, but builds upon and is shaped by what we already know. To that end, learning may be viewed as a process, rather than a collection of factual and procedural knowledge. Learning produces changes in the organism and the changes produced are relatively permanent. Human learning may occur as part of education, personal development, schooling, or training. It may be goal-oriented and may be aided by motivation. The study of how learning occurs is part of neuropsychology, educational psychology, learning theory, and pedagogy.
Language Language is the human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, and a language is any specific example of such a system. The scientific study of language is called linguistics. The method of human communication, either spoken or written, consisting of the use of words in a structured and conventional way Estimates of the number of languages in the world vary between 6,000 and 7,000. However, any precise estimate depends on a partly arbitrary distinction between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken or signed, but any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli, for example, in graphic writing, braille, or whistling.
First Language A first language (also native language, mother tongue, arterial language, or L1) is the language(s) a person has learned from birth or within the critical period, or that a person speaks the best and so is often the basis for sociolinguistic identity. In some countries, the terms native language or mother tongue refer to the language of one's ethnic group rather than one's first language. Sometimes, there can be more than one mother tongue, (for example, when the child's parents speak different languages). Those children are usually called bilingual.
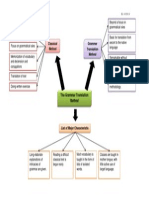
Method
By contrast, a second language is any language that one speaks other than one's first language.
A way of doing something, especially a planned or established way A means or manner of procedure, especially a regular and systematic way of accomplishing something: a simple method for making a pie crust; mediation as a method of solving disputes. Orderly arrangement of parts or steps to accomplish an end: random efforts that lack method. The procedures and techniques characteristic of a particular discipline or field of knowledge: This field course gives an overview of archaeological method.
Approach
Way of dealing with a situation or problem:we need a whole new approach to the job An initial proposal or request made to someone:the landowner made an approach to the developer [in singular] the action of coming near or nearer to someone or something in distance or time:the approach of winter
Technique Theory A set of statements or principles devised to explain a group of facts or phenomena, especially one that has been repeatedly tested or is widely accepted and can be used to make predictions about natural phenomena. The branch of a science or art consisting of its explanatory statements, accepted principles, and methods of analysis, as opposed to practice The systematic procedure by which a complex or scientific task is accomplished. A practical method, skill, or art applied to a particular task
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Facts About GeminiDocument5 pagesThe Facts About Geminitehejahe100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- House Tree Person AssessmentDocument5 pagesHouse Tree Person Assessmentnicklan100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Hidden PersuadersDocument16 pagesHidden PersuaderspetrucciNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Washington State Juvenile Court Assessment Manual, Version 2.1Document146 pagesWashington State Juvenile Court Assessment Manual, Version 2.1Washington State Institute for Public PolicyNo ratings yet
- DepEd-Learning-Activity-Sheets-LAS-CESC Week 1Document7 pagesDepEd-Learning-Activity-Sheets-LAS-CESC Week 1roselyn100% (1)
- Cognitive PsychologyDocument7 pagesCognitive PsychologyAshu KoolNo ratings yet
- H Schroeppel-Advanced PerceptionDocument56 pagesH Schroeppel-Advanced PerceptionFaithful100% (2)
- Research StudyDocument31 pagesResearch StudyArris Gawe100% (4)
- Humss Disiplines Week 10 New 111Document174 pagesHumss Disiplines Week 10 New 111Jonathan Gecomo Garin100% (2)
- Gender and Physical EducationDocument243 pagesGender and Physical EducationherkamayaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Career Guidance Grade 11Document35 pagesMODULE 6 Career Guidance Grade 11Ronel M. Buid100% (1)
- Nursing ProcessDocument16 pagesNursing ProcessNader Smadi100% (10)
- Grammar Translation MethodDocument1 pageGrammar Translation MethodNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Tongue TwisterDocument1 pageTongue TwisterNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Second Language AcquisitionDocument2 pagesSecond Language AcquisitionNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Tongue TwisterDocument1 pageTongue TwisterNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Overview of Learning StylesDocument11 pagesOverview of Learning StylesNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Dividing by 10: Can You Use The Calculator To Help You Learn How To Divide by 100?Document1 pageDividing by 10: Can You Use The Calculator To Help You Learn How To Divide by 100?Nor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2Nor AmiraNo ratings yet
- ISL WEEK 1 (I) & (Iii) WIDADocument9 pagesISL WEEK 1 (I) & (Iii) WIDANor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Why Save Endangered Specie1Document2 pagesWhy Save Endangered Specie1Nor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Academic Essay: Knowing How To Live AloneDocument8 pagesAcademic Essay: Knowing How To Live AloneNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Cut and Paste The Animals From The Brochure. Write The Phrase For Each Animals Pasted and You Can Use The Words Given in The BoxDocument4 pagesCut and Paste The Animals From The Brochure. Write The Phrase For Each Animals Pasted and You Can Use The Words Given in The BoxNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Group Members: 1. Amar Safwan 2. Nor Amira 3. Bendly Roy: Strengths WeaknessesDocument3 pagesGroup Members: 1. Amar Safwan 2. Nor Amira 3. Bendly Roy: Strengths WeaknessesNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Write Four Sentences About The Animal in Space Provided. You Are Given 5 Minutes To Complete This TaskDocument1 pageWrite Four Sentences About The Animal in Space Provided. You Are Given 5 Minutes To Complete This TaskNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- III HarmerDocument5 pagesIII HarmerNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Tick (/) For The Right Answer: Conjunctions Exercise 1Document11 pagesTick (/) For The Right Answer: Conjunctions Exercise 1Nor AmiraNo ratings yet
- III HarmerDocument5 pagesIII HarmerNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Same and SimilarDocument15 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Same and SimilarNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- AbacusDocument41 pagesAbacusNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Golden RatioDocument6 pagesGolden RatioNor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Hamad Ismail, Summative Assignment #1Document4 pagesHamad Ismail, Summative Assignment #1hammiiid IsmailNo ratings yet
- 1st Grade Friendship LessonDocument2 pages1st Grade Friendship Lessonapi-242270654No ratings yet
- Negation - Sigmund FreudDocument3 pagesNegation - Sigmund FreudAndrea Denisse Castillo GonzálezNo ratings yet
- L3 Barriers To CommunicationDocument36 pagesL3 Barriers To CommunicationVedansha SinghalNo ratings yet
- 1 Prof Ed 20Document10 pages1 Prof Ed 20Marvin GalanoNo ratings yet
- An Autobiography Is More Than Just A Literary GenreDocument6 pagesAn Autobiography Is More Than Just A Literary GenreEmma PreciousNo ratings yet
- In Our Families and Faith CommunitiesDocument1 pageIn Our Families and Faith CommunitiesroshelleNo ratings yet
- What I Have Learned: Activity 4 EssayDocument1 pageWhat I Have Learned: Activity 4 EssayJordan Lance LazagaNo ratings yet
- Ojt Evaluation Form 2022 2023Document2 pagesOjt Evaluation Form 2022 2023Ocubillo Froilan D.No ratings yet
- Ewc 661 ProposalDocument9 pagesEwc 661 ProposalLuqman AriefNo ratings yet
- Memorandum Project ProposalDocument2 pagesMemorandum Project Proposalapi-270738730No ratings yet
- Matrix - Combative Sports - Wellness - KipaoDocument3 pagesMatrix - Combative Sports - Wellness - KipaoANNE JELENE KIPAONo ratings yet
- UTS Module 1 - For PrintingDocument38 pagesUTS Module 1 - For PrintingKristine CruzNo ratings yet
- (Ebook) Creative Problem Solving - Brain Power ConsultingDocument42 pages(Ebook) Creative Problem Solving - Brain Power ConsultingBozzorNo ratings yet
- BSC2 Long Exam ReviewerDocument2 pagesBSC2 Long Exam ReviewerArwin Kyle De LeonNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 Handling Emotional EmployeesDocument2 pagesCase Study 1 Handling Emotional EmployeesRitik RanaNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Activity Intolerancekeiii_21No ratings yet
- Title - The Janitor - How An Unexpected Friendship Transformed A CEO and His Company (Todd Hopkins & Ray Hilbert)Document2 pagesTitle - The Janitor - How An Unexpected Friendship Transformed A CEO and His Company (Todd Hopkins & Ray Hilbert)Kimberly VillanuevaNo ratings yet