Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revision (Mm-Form 5) P2-Section B
Uploaded by
Ilman MohamadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision (Mm-Form 5) P2-Section B
Uploaded by
Ilman MohamadCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 1
Paper 2- Section B
Graphs of Function II
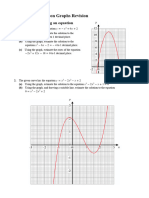
1) Table 2 shows the values of x and y which satisfy the equation
2
2 3 x x y + =
.
Jadual 2 menunjukkan nilai x dan nilai y yang memuaskan persamaan
2
2 3 x x y + = .
x 2
1
0 1 2 3 4 5
y 5
0 3 m 3 0 n 12
Table 2/ Jadual 2
(a) Calculate the values of m and n.
Hitung nilai m dan n. [2 marks/markah]
(b) For this part of the question, use graph paper. You may use a flexible curve rule.
Untuk ceraian soalan ini, gunakan kertas graf. Anda boleh menggunakan pembaris fleksibel.
Using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 2 units on the y-axis, draw the graph
of
2
2 3 x x y + = for 5 2 s s x .
Dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 1 unit pada paksi-x dan 2 cm kepada 2 unit pada paksi-y,
lukis graf
2
2 3 x x y + = bagi 5 2 s s x . [4 marks/markah]
(c) From your graph, find
Daripada graf anda, cari
(i) the value of y when x = 3.5
nilai y apabila x = 3.5.
(ii) the values of x when y = 2.
nilai-nilai x apabila y = 2.
[3 marks/markah]
(d) Draw a suitable straight line on your graph to find the values of x which satisfy the equation
0 3 6
2
= + x x for 5 2 s s x . State these values of x.
Lukis satu garis lurus yang sesuai pada graf anda untuk mencari nilai-nilai x yang memuaskan
persamaan 0 3 6
2
= + x x bagi 5 2 s s x . Nyatakan nilai-nilai x itu.
[3 marks/markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 2
2) a)Complete table below for the equation
x
y
24
= by writing down the values of y
when 2 . 1 = x and . 8 . 4 = x
Lengkapkan Jadual 1 di ruang jawapan bagi persamaan
x
y
24
= dengan menulis nilai-nilai y apabila
2 . 1 = x dan . 8 . 4 = x
x 1 1.2 2 3 4.8 6 8 10 12
y 24 12 8 4 3 2.4 2
[2 marks / 2 markah]
b) Using a scale of 2 cm to 2 units on the x-axis and 2 cm to 2 units on the y-axis, draw the graph of
x
y
24
= for
. 12 1 s s x
Dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 2 unit pada paksi-x dan 2 cm kepada 2 unit pada paksi-y,
lukis graf bagi
x
y
24
= bagi
. 12 1 s s x
[4 marks / 4 markah]
c) From your graph, find
Daripada graf anda, cari
(i) the value y when
. 5 . 2 = x
Nilai y apabila
. 5 . 2 = x
(ii) the value of x when y = 6.
Nilai x apabila y = 6.
[2 marks / 2 markah]
d) Draw a suitable straight line on your graph to find the values of x which satisfy the equation
0 20 2
24
= + x
x
for
. 12 1 s s x
State these values of x.
Lukis satu garis lurus yang sesuai pada graf anda untuk mencari nilai-nilai x yang memuaskan
persamaan bagi 0 20 2
24
= + x
x
bagi
. 12 1 s s x
Nyatakan nilai-nilai x itu.
[4 marks / 4 markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 3
3) a)Complete the Table 2 in the answer space for the equation
3 8 3
2
+ = x x y
a) Lengkapkan Jadual 2 di ruang jawapan bagi persamaan
3 8 3
2
+ = x x y
[2 markah]
x - 2 - 1 0 1 2 3 4 5
y 14 3 - 2 - 1 19 38
Table 2 / Jadual 2
(b) For this part of the question, use a graph paper. You may use a flexible curve
By using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 5 units on the y-axis, draw the
graph of
3 8 3
2
+ = x x y
for -2 x 5.
untuk ceraian soalan ini, gunakan kertas graf. Anda boleh menggunakan pembaris
fleksibel.
Dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 1 unit pada paksi-x dan 2 cm kepada 5 unit
pada paksi-y, lukiskan graf
3 8 3
2
+ = x x y
bagi -2 x 5.
( 4 marks )
(c) From the graph, find
Daripada graf anda, carikan
(i) The value of y when x = 4.2 and
nilai y apabila x = 4.2, dan
(ii) The value of x when y = 35
nilai x apabila y = 35.
( 2 marks )
(d) Draw a suitable line on your graph to find all the values of x which satisfy the equation
1 3 8 3
2
+ = + x x x
for -2 x 5. State these values of x.
Lukiskan satu garis lurus yang sesuai pada graf anda untuk mencari semua nilai x yang memuaskan
persamaan
1 3 8 3
2
+ = + x x x
bagi -2 x 5. Nyatakan nilai-nilai x itu.
( 4 marks)
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 4
4. (a) Complete Table 1 in the answer space for the equation y = 6 + 2x x
3 .
Lengkapkan Jadual 1 di ruang jawapan untuk persamaan y = 6 + 2x x
3 .
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
Answer:
(a) x -4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4
y 62 10 5 6 7 2
(b) For this part of the question, use the graph paper on the next page. You may use a
flexible curve ruler.
Untuk ceraian soalan ini, gunakan kertas graf yang disediakan pada halaman
sebelah. Anda boleh menggunakan pembaris fleksible.
By using a scale of 2 cm to represent 1 unit on the x-axis and a scale of 2 cm to represent 10
units on the y-axis, draw the graph of y = 6 + 2x x
3
for -4 x 4.
Dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm menunjukkan1 unit pada paksi-x dan 2 cm untuk
menunjukkan 10 unit pada paksi-y, lukiskan graf y = 6 + 2x x
3
bagi nilai x dalam julat -4
x 4.
[3 marks]
(c) From the graph, find
Daripada graf anda, carikan
(i) The value of y when x = 4.2 and
nilai y apabila x = 4.2, dan
(ii) The value of x when y = 35
nilai x apabila y = 35.
( 2 marks )
(d) Draw a suitable straight line on your graph to find values of x which satisfies the
equation x
3
+ 9 = 12x for -4 x 4. State the values of x.
Lukiskan satu garis lurus yang sesuai pada graf anda untuk mencari semua nilai x
yang memuaskan persamaan x
3
+ 9 = 12x bagi nilai x dalam julat -4 x 4.
Nyatakan nilai-nilai x itu.
[5 marks]
[5 markah]
TABLE 1
JADUAL 1
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 5
5. (a) Complete Table 1 in the answer space for the equation 30 12
3
+ = x x y by writing down
the values of y when x = 2 and x = 2.5.
Lengkapkan Jadual 1 di ruang jawapan bagi persamaan 30 12
3
+ = x x y dengan menulis
nilai-nilai y apabila x = 2 dan x = 2.5.
[2 marks]
[2 markah
x - 4.5 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 2.5
y -7.125 39 41 30 19 14
(b) For this part of the question, use the graph paper provided on page 16.
You may use a flexible curve rule.
Untuk ceraian soalan ini, gunakan kertas graf yang disediakan pada halaman 16.
Anda boleh guna pembaris fleksibel.
Using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 5 units on the y-axis, draw the graph of
30 12
3
+ = x x y for 5 . 2 5 . 4 s s x .
Menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 1 unit di paksi-x dan 2 cm kepada 5 unit pada paksi-y, lukis graf
bagi 30 12
3
+ = x x y untuk
5 . 2 5 . 4 s s x
.
[4 marks]
[4 markah]
(c) From the graph in 12(b), find
Dari graf 12(b), cari
(i) the value of y when x = 1.5
nilai y apabila x = 1.5
(ii) the value of x when y = 25 [2 marks]
nilai x apabila y = 25 [2 markah]
(d) Draw a suitable straight line on the graph in 12(b) to find all the values of x which satisfy the
equation 0 10 17
3
= + x x for 5 . 2 5 . 4 s s x . State these values of x.
Lukis satu garis lurus yang sesuai pada graf di 12(b) untuk mencari semua nilai x yang
memuaskan persamaan 0 10 17
3
= + x x untuk 5 . 2 5 . 4 s s x . Nyatakan nilai-nilai x itu.
[4 marks]
[4 markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 6
6.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 7
7.
8. (a) Complete Table 1 in the answer space for the equation
18 13
3
+ = x x y
. [2]
(b) By using the scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 5 units on the y-axis , draw the
graph of
18 13
3
+ = x x y
for 4 x 4. [4]
(c) From your graph, find
(i) the value of y when x = 1.5,
(ii) the value of x when y = 25. [2]
(d) Draw a suitable straight line on your graph to find all the values of x which satisfy the
equation
3
11 2 x x =
for 4 x 4.
State these values of x. [4]
x -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4
y 6 3
6
30 1
8
6 6 30
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 8
9.
10.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 9
11.
x - 3 -2 -1 0 1 2 2.5
y 24 5 -3 -4 -18.625
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 10
13. a) Complete the Table 1 for the equation
x
y
4
= .
X -4 -2.5 -1 -0.5 0.5 1 2 3.2 4
y 1 1.6 8 -8 -4 -1.25 -1
Table 1[2 marks]
b) By using a scale of 2cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2cm to 2 units on the y-axis, draw the graph of
x
y
4
= for -4 x 4.[5 marks]
c) From your graph, find
i. the value of y when x = 1.8
ii. the value of x when y = 3.4
[2 marks]
d) Draw a suitable straight line on your graph to find all the values of x which satisfy the equation
3 2
4
+ = x
x
for -4 x 4. State these values of x.
[3 marks]
14.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 11
Statistics
1. Table 3 shows the frequency distribution of the heights of 90 students in a school.
Jadual 3 menunjukkan taburan kekerapan bagi tinggi 90 pelajar di sebuah sekolah.
Height (cm)
Tinggi (cm)
Frequency
Kekerapan
140-144 4
145-149 10
150-154 18
155-159 21
160-164 17
165-159 10
170-174 6
175-179 4
Table 3/ Jadual 3
(a) Using the data in Table 3, complete Table 3 .
Dengan menggunakan data dalam Jadual 3, lengkapkan Jadual 3.
Midpoint
Titik tengah
Upper boundary
Sempadan atas
Cummulative frequency
Kekerapan longgokan
142 144.5
179.5 90
[3 marks/markah]
(b) Calculate the estimated mean height, in cm, of the students and give the answer correct to two
decimal places.
Hitung min anggaran tinggi dalam cm, bagi pelajar-pelajar itu dan beri jawapan betul kepada dua
tempat perpuluhan.
[3 marks/markah]
(c) For this part of the question, use the graph paper.
Untuk ceraian soalan ini, gunakan kertas graf.
Using a scale of 2 cm to 5 cm on the horizontal axis and 2 cm to 10 students on the vertical axis, draw
an ogive for the data.
Dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 5 cm pada paksi mengufuk dan 2 cm kepada 10 pelajar
pada paksi mencancang, lukis satu ogif bagi data itu.
[5 marks/markah]
(d) From your ogive in 14 (c), find the median.
Daripada ogif anda di 14 (c), cari median. [1 marks/markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 12
2. The data below shows the masses, to the nearest kg, of a group of students.
Data di bawah menunjukkan jisim, betul kepada kg terdekat, bagi sekumpulan pelajar.
(a) Based on the data, complete Table 2 in the answer space.
Berdasarkan data itu, lengkapkan Jadual 2 di ruang jawapan.
[3 marks / 3 markah]
(b) Based on Table 2 in (a), calculate the estimated mean mass of the students.
Berdasarkan Jadual 2 di (a), hitung min anggaran jisim bagi pelajar-pelajar.
[3 marks / 3 markah]
(c) Using a scale 0f 2 cm to 5kg on the horizontal axis and 2 cm to 1 student on the vertical axis,
draw a frequency polygon for the data.
Dengan menngunakan skala 2 cm kepada 5 kg pada paksi mengufuk dan 2 cm kepada 1 orang
pelajar pada paksi mencancang, lukis satu polygon kekerapan bagi data tersebut.
[5 marks / 5 markah]
(d) Based on the frequency polygon in 14 (c), state the number of students whose mass is more
than 30 kg.
Berdasarkan polygon kekerapan di 14 (c), nyatakan bilangan pelajar yang berjisim lebih daripada
30 kg.
[1 mark / 1 markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 13
3. The Table 2 above shows the frequency distribution of the mass of fishes caught in a study.
Jadual 2 menunjukkan kekerapan bagi pengagihan jisim ikan yang ditangkap dalam suatu kajian.
(a) Complete Table 3 in the answer space.
Lengkapkan Jadual 3 pada ruang jawapan.
[3 marks] / [3 markah]
TABLE 3 / Jadual 3
(b) Based on your table in (a), state the modal class. [1 mark]
Berdasarkan jadual anda di (a), nyatakan kelas mod. [1 markah]
(c) For this part of the question, use a graph paper..
By using a scale of 2 cm to 10 grams on the horizontal axis and 2 cm to 20 fishes on the vertical
axis, draw an ogive for the data.
[4 marks]
Untuk ceraian soalan ini, gunakan kertas graf.
Dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 10 gram pada paksi mengufuk dan 2 cm kepada 20
ekor ikan pada paksi mencancang, lukiskan satu ogif bagi data itu.
[4 markah]
(d) Based on the ogive in (c)
Berdasarkan ogif anda di (c),
(i) find the inter quartile range.
Nyatakan beza antara kuartil,
[3 marks] / [3markah]
(ii) hence, explain briefly the meaning of third quartile.
Seterusnya, terangkan dengan ringkas maksud kuartil ketiga.
[1 mark] / [1markah]
Mass of fishes (g)
Jisim ikan (g)
Upper Boundary
Sempadan atas
Frequency
Kekerapan
Cumulative
frequency
Kekerapan
longgokan
40 49 0
50 59 3
12
22
34
60
44
20
5
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 14
4. The data in Table 2 shows the score obtained by 45 students in Mathematics quiz.
Data dalam Jadual 2 berikut menunjukkan markah yang diperoleh oleh sekumpulan 45
pelajar bagi suatu kuiz Matematik.
15 20 36 23 33 30 28 9 12
22 28 34 5 43 14 24 36 18
12 9 36 10 8 40 23 28 17
18 22 43 10 11 10 18 22 28
36 39 33 22 18 19 15 28 18
(a) Using the data in table 1 and class interval of 5 marks, complete the table in the answer space
provided.
Dengan menggunakan data-data dalam jadual 1 dan dengan mengambil selang
kelas dengan saiz 5 markah, lengkapkan jadual yang disediakan di ruang jawapan
yang disediakan.
Score
Skor
Frequency
Kekerapan
Midpoint
Titik Tengah
Upper Boundaries
Sempadan Atas
5 9 4
10 - 14 7
Jumlah = 45
[4 marks]
(b) Calculate the mean mark of the group.
Hitungkan min markah bagi kumpulan di atas.
[3 marks]
(c) For this part of the question, use the graph paper on the next page.
Untuk bahagian ini, gunakan kertas graf yang disediakan pada halaman sebelah
Using a scale of 2 cm to 5 marks on the x-axis and 2 cm to 1 student on the y-axis.
Draw a histogram to represent this data.
Dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 5 markah pada paksi-x dan 2 cm kepada
1 orang pelajar pada paksi-y. Lukiskan sebuah histogram bagi menggambarkan
data-data tersebut.
[3 marks]
(d) Using your histogram or otherwise calculate the percentage of student who score less
than 25 marks.
Dengan menggunakan histogram atau dengan cara lain, hitungkan peratus pelajar yang
memperolehi markah kurang daripada 25 markah.
[2 marks]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 15
5. Table 2 shows the distribution of the height of 40 students in a school.
Jadual 2 menunjukkan taburan kekerapan bagi tinggi 40 orang pelajar di sebuah sekolah
(a) State the modal class for the data in the Table 2
Nyatakan kelas mod bagi data yang diberi dalan Jadual 2 [1 mark]
(b) (i) Construct a cumulative frequency table for the data in Table 2
Binakan satu jadual kekerapan longgokan bagi data dalam Jadual 2
Height (cm)
Tinggi (cm)
Frequency
Kekerapan
Upper boundary
Sempadan atas
Cumulative
frequency
Kekerapan
longgokan
135 139 2
140 144 5
145 149 8
150 154 10
155 159 7
160 164 4
165 169 3
170 174 1
[3 marks]
(ii) For this part of the question, use the graph paper.
Untuk ceraian soalan ini, guna kertas graf.
Using the scale of 2 cm to 5 cm on the x-axis and 2 cm to 5 students on the y-axis, draw
an ogive for the data.
Dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 5 cm pada paksi x dan 2 cm kepada 5 orang
pelajar pada paksi-y, lukiskan satu ogif bagi data di atas.
[5 marks]
(c) From the graph, find
Daripada graf itu, carikan
(i) median
(ii) interquartile range
julat antara kuartil
[3 marks]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 16
6. The data in Diagram 14 shows the marks scored by 40 students in
a Co-curricular Evaluation.
Data dalam Rajah 14 menunjukkan markah bagi 40 orang pelajar dalam
Penilaian Kokurikulum.
33 42 72 57 43 67 83 65 79 85
75 58 45 75 68 78 49 76 63 43
82 65 74 56 78 51 35 84 55 69
92 32 63 94 52 85 68 59 88 77
Diagram 14
Rajah 14
(a) (i) Based on the data, complete Table 14 in the answer space provided
on page 24.
Berdasarkan data itu, lengkapkan Jadual 14 pada ruang jawapan
yang disediakan halaman 24.
[4 marks / markah]
(ii) Based on Table 14 in 14(a), calculate the estimated mean of the mark
scored by a student.
Berdasarkan Jadual 14 di 14(a), hitung min anggaran markah bagi
seorang murid.
[3 marks / markah]
(b)
By using the scale of 2 cm to 10 marks on the horizontal axis and
2 cm to1 student on the vertical axis, draw a histogram based on Table 14.
Dengan menggunakan skala 2 cm kepada 10 markah pada paksi
mengufuk dan 2 cm kepada 1 pelajar pada paksi mencancang, lukis satu
histogram berdasarkan Jadual 14.
[4 marks / markah]
(c) Based on a histogram in 14(b), state the number of students who scored
more than 70 marks for the Co-curricular Evaluation.
Berdasarkan histogram di 14(b), nyatakan bilangan murid yang
mendapat markah lebih daripada 70 di dalam Penilaian Kokurikulum.
[1 mark / markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 17
7.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 18
8. The data in diagram below shows the time, in minute, taken by 30 students to solve some
trigonometry problems.
(a) Using data in diagram above and a class interval of 5 minutes, complete table in the
answer space. [3 marks]
(b) Based on the table ,
(i) find the modal class,
(ii) calculate the mean time taken by the students. [4 marks]
(c) For this part of the question, use the graph paper provided.
By using a scale of 2 cm to 10 minutes on the horizontal axis and 2 cm to 1
students on the vertical axis, draw a frequency polygon based on the table .
[5marks]
Answer:
a)
Time (minutes) Frequency Midpoint
35-39
40-44
b) i) Modal class =
ii) Mean =
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 19
9. The data in Diagram 14 shows the marks scored by 40 students in a Co-curricular
Evaluation.
(a) (i) Based on the data, complete Table 14 [4]
Marks
Markah
Mid-point
Titik tengah
Frequency
Kekerapan
31 40 355
(ii) calculate the estimated mean of the mark scored by a student. [3]
(b) By using the scale of 2 cm to 10 marks on the horizontal axis and 2 cm to1 student on the
vertical axis, draw a histogram [4]
(c)Based on a histogram in 14(b), state the number of students who scored more than 70 marks for the
Co-curricular Evaluation. [1]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 20
Plans and Elevations
1) a) Diagram below shows a solid consisting of a cuboid and a half-cylinder which is joined at the
plane GHJK. The base ABCD is on a horizontal plane and JH = 4cm.
Draw to a full scale, the plan of the solid. [3 marks]
b) A solid right prism is joined to the solid in diagram a) at the vertical GFCV. The combined solid is
shown in the diagram below. Trapezium PVTS is the uniform cross section of the prism and PQRS
is an inclined plane and V is the midpoint of DC. The base BCTUWVDA lies on a horizontal plane
whereby CT = 2cm and PG = 3cm.
Draw to full scale,
i) the elevation of the combined solid on a vertical plane parallel to AB as viewed from X.
[5 marks]
ii) the elevation of the combined solid on a vertical plane parallel to BC as viewed from Y.
[4 marks]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 21
2) You are not allowed to use graph paper to answer this question.
a) Diagram 8(i) shows a right prism with rectangular base ABCD on a horizontal
table. The surface AEHILD is its uniform cross-section. The rectangle IJKL is an
inclined plane. The rectangle EFGH is a horizontal plane. The edges AE , BF, CK,
DL, GJ and HI are vertical edges. Given EH = FG = 3 cm.
Draw in full scale, the elevation of the solid on a vertical plane parallel to DC as
viewed from P. [4 marks]
b) A half-cylinder is joined to the solid in the Diagram 8(i) at the plane CDLK to form
a combined solid as shown in Diagram 8(ii).
Draw to full scale,
(i) the plan of the combined solid,
[4 marks]
(ii) the elevation of the combined solid on a vertical plane parallel to AD as viewed from Q.
[4 marks]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 22
3. You are not allowed to use graph paper to answer question.
(a) Diagram 8(i) shows a solid right prism with rectangular base ABCD on a horisontal
table. The surface ABGF is the uniform cross-secsion of the prism. Rectangle ABCD
and EFGH are horizontal planes. Rectangle ADEF is an inclined plane. BG and CH
are vertical edges .
DIAGRAM 8(i)
Draw full scale, the elevation of the solid on a vertical plane parallel to EF as viewed
from X . [ 3 marks ]
(b) Diagram 8(ii) shows a solid consisting of a prism and a cuboid which are joined at the horizontal plane
EFGH. Given that GF = 5cm .
DIAGRAM 8(ii)
Draw to full scale,
(i) the plan of the solid,
[4 marks]
(ii) the elevation of the remaining solid on a vertical plane parallel to AD as
viewed from Y [5 marks]
B
F
G
H
C
D
E
A
8 cm
4cm
5cm
4cm
X
4 cm
2 cm
8 cm
4 cm
4 cm
6 cm
B
F
G
H
J
C
I
D
E
A
K
L
N
M
Y
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 23
4.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 24
5. (a) Diagram 15(i) shows a solid with rectangular base ADEK on horizontal plane. ABJK is trapezium. DC, EF and
HL are vertical edges, LF = 2 cm. Rectangle CFLM is a horizontal plane and BMHJ is an inclined plane
Draw full scale, the plan of the solid. [3]
(b) A half-cylinder solid of diameter GN = 6 cm is joined to the solid in diagram 15(ii) at the plane EFLHNR.
The combined solid is shown in Diagram 15 (ii).
Draw full scale,
(i) the elevation of the combined solid on a vertical plane parallel to DE as viewed from P. [4]
(ii) the elevation of the combined solid on a vertical plane parallel to AD as viewed from Q.[5]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 25
6.
7.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 26
8.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 27
9. You are not allowed to use graph paper to answer this question.
Anda tidak dibenarkan menggunakan kertas graf untuk menjawab soalan ini.
(a) Diagram 7(i) shows a solid right prism with a square base ABJK on a horizontal plane. The
surface ABCDE is the uniform cross section of the prism. AE and BC are vertical edges. The
rectangle CDGH is an inclined plane and DEFG is a horizontal plane.
Rajah 7(i) menunjukkan sebuah pepejal prisma tegak bertapak segi empat sama ABJK pada satah
mengufuk. Permukaan ABCDE ialah keratan rentas seragamnya. Tepi AE dan BC adalah tegak.
Segi empat tepat CDGH ialah satah condong dan segi empat tepat DEFG ialah satah mengufuk.
Diagram 7(i)/ Rajah 7(i)
Draw to full scale, the elevation of the solid on a vertical plane parallel to AB as viewed from X.
Lukis dengan skala penuh, dongakan gabungan pepejal itu pada satah mencancang yang selari
dengan AB sebagaimana dilihat dari X.
[3 marks/markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 28
(b) A solid cube is removed from the solid in Diagram 7(i). The remaining solid is shown in Diagram
7(ii). The square PQRS is a horizontal plane. DR, MS and NP are vertical edges. DR = 3 cm and
QR = 3 cm.
Sebuah pepejal kubus dikeluarkan daripada pepejal dalam Rajah 7(i). Pepejal yang tinggal
adalah seperti dalam Rajah 7 (ii). Segi empat sama PQRS ialah satah mengufuk. Tepi DR, MS
dan NP adalah tegak. DR = 3 cm dan QR = 3 cm.
Diagram 7(ii)/ Rajah 7(ii)
Draw full scale,
Lukis dengan skala penuh,
(i) the plan of the remaining solid.
dongakan pepejal yang tinggal itu.
[4 marks/markah]
(ii) the elevation of the remaining solid on a vertical plane to KA as viewed from Y.
dongakan pepejal yang tinggal itu pada satah mencancang yang selari dengan KA
sebagaimana dilihat dari Y.
[5 marks/markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 29
10.(a) Diagram 8.1 shows a solid right prism with a rectangular base ABHG on a
horizontal plane . The surface ABCDE is the uniform cross-section of the prism . AE
and BC are vertical edges . Rectangle EDKF is a horizontal plane and rectangle
DCJK is an inclined plane .
Rajah 8.1 menunjukkan sebuah pepejal berbentuk prisma tegak dengan tapak segi empat
tepat ABHG terletak pada suatu satah mengufuk . Permukaan ABCDE ialah keratin
rentas seragam prisma itu . Tepi AE dan BC adalah tegak . Segi empat tepat EDKF ialah
satah mengufuk dan segi empat tepat DCJK ialah satah condong .
Diagram 8.1
Rajah 8.1
Draw full scale , the plan of the solid.
Lukis dengan skala penuh , pelan pepejal itu.
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(b) Another solid right prism with trapezium AGUV as the uniform cross-section is
joined to the prism in Diagram 15.1 at the vertical plane ARSG . The composite solid
is as shown in Diagram 15.2 . The base ABHGUV lies on a horizontal plane . VQ
and UP are vertical edges and AGU = GUV = 90
o
Sebuah pepejal lain berbentuk prisma tegak dengan trapezium AGUV sebagai keratin
Rentas seragamnya dicantumkan kepada prisma dalam Rajah 15.1 pada satah
mencancang ARSG . Gabungan pepejal adalah seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah
14.2 . Tapak ABHGUV terletak pada suatu saatah mengufuk . Tepi VQ dan UP adalah
tegak dan AGU = GUV = 90
o
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 30
Draw full scale,
Lukis dengan skala penuh,
(i) the elevation of the composite solid on a vertical plane parallel to AB as viewed
from X.
dongakangabungan pepejal itu pada satah mencancang yang selari dengan AB
sebagaimana dilihat dari X.
[4 marks]
[4 markah]
(ii) the elevation of the composite solid on a vertical plane parallel to UV as viewed
from Y.
dongakan gabungan pepejal itu pada satah mencancang yang selari dengan UV
sebagaiman dilihat dari Y.
[5 marks]
[5 markah]
Diagram 8.2
Rajah 8.2
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 31
Transformation III
1. The following diagram shows the quadrilaterals ABCD, EFGH and JKLM drawn on a Cartesian Plane
a) Transformations R is a rotation of 90 anticlockwise about the centre (0, 2). Transformation T is a
reflection in the straight line x = 2. State the coordinates of the image of point A under each of the
following transformations:
(i) TR,
(ii) R
2
.
(b) EFGH is the image of ABCD under the combined transformation MN. Describe in full,
(i) the transformation M,
(ii) the transformation N.
(c) JKLM is the image of EFGH under an enlargement at centre (3, 0).
(i) State the scale factor of the enlargement.
(ii) Given that EFGH represents a region of area 112 m
2
, calculate the area, in m
2
, of the region
represented by JKLM.
2. Diagram 6 shows trapeziums ABCD , LM NP , RSNT and EFGH drawn on a Certesian plane.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 32
Rajah 6 menunjukkan trapezium ABCD , LM NP , RSNT dan EFGH yang dilukis di atas satah Cartesan.
DIAGRAM 6
RAJAH 6
(a) Diberi bahawa : V ialah pantulan pada garis x = 3.
W ialah translasi
4
3
| |
|
\ .
:
Nyatakan koordinat imej bagi titik F di bawah penjelmaan berikut :
(i) VW
(ii) WV [ 2 marks]
[2 markah]
(b) Trapezium LMNP ialah imej bagi trapezium ABCD di bawah penjelmaan X dan
trapezium RSNT ialah imej bagi trapezium LMNP di bawah penjelmaan Y.
(i) Huraikan selengkapnya penjelmaan X dan penjelmaan Y.
(ii) Huraikan selengkapnya satu penjelmaan tunggal yang setara dengan
penjelmaan YX.
[6 markah]
(c) Trapezium EFGH ialah imej bagi trapezium ABCD di bawah satu pembesaran.
(i) Nyatakan faktor skala dan pusat pembesaran itu.
(ii) Diberi luas trapezium EFGH ialah 50 cm
2
, hitungkan luas trapezium ABCD.
[4 markah]
3.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 33
Diagram 7
Rajah
(a) Penjelmaan T ialah translasi
2
4
| |
|
\ .
dan penjelmaan P ialah pantulan pada
paksi-y.
Nyatakan koordinat imej bagi
(i) titik A di bawah translasi T,
(ii) titik D di bawah pantulan P,
(iii) titik B di bawah gabungan penjelmaan TP.
[4 markah
(b) EFGH ialah imej bagi ABCD di bawah satu penjelmaan V dan JKLM ialah imej
bagi EFGH di bawah satu penjelmaan W.
Huraikan selengkapnya penjelmaan V dan penjelmaan W.
[6 marks]
Diberi luas EFGH ialah 4 cm
2
, hitungkan luas, dalam cm2 , JKLM.
[2 markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 34
4. a) Transformation P is a reflection in the line . k y = Transformation R is an anticlockwise rotation of
90 about the centre ( 0, 2). Transformation T is a translation
|
|
.
|
\
|
4
2
.
(i) Point (6, 4) is the image of point (6,-2) under the transformation P. State the value of k.
Titik (6,4) ialah imej bagi titik (6, -2) di bawah penjelmaan P. Nyatakan nilai k.
(ii) Find the coordinates of the image of point (1, 5) under the following combined transformations:
Cari koordinat imej bagi titik (1, 5) di bawah gabungan penjelmaan berikut:
(i) T
2
(ii) TR
[5 marks / 5 markah]
(b) (i) Diagram 7 shows three pentagons, ABCDE, FGHIJ and KLMNF, drawn on a cartesan plane.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan tiga pentagon, ABCDE, FGHIJ dan KLMNF, dilukis pasa suatu satah Cartesan.
DIAGRAM 7
RAJAH 7
KLMNF is the image of ABCDE under a combined transformation VU.
KLMNF ialah imej bagi ABCDE di bawah gabungan penjelmaan VU.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 35
Describe in full the transformation
Huraikan selengkapnya penjelmaan
(a) U (b) V
ii) Given that the pentagon KLMNF represents a region with an area of 37.5 m
2
, calculate the area, in
m
2
, of the shaded region.
Diberi bahawa pentagon KLMNF mewakili rantau dengan luas 37.5 m
2
, hitung luas, dalam m
2
,
kawasan yang berlorek.
[7 marks / 7 markah]
5. Diagram 6 shows quadrilaterals ABCD, PQRS and PTUV drawn on a Cartesian plane.
Rajah 6 menunjukkan sisiempat ABCD, PQRST dan PTUV dilukis pada suatu satah Cartesan.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 36
(a) Transformation M is a translation
4
3
| |
|
\ .
. Transformation N is a reflection in the line y x = . State
the coordinates of the image of point D under each of the following transformations:
Transformasi M ialah translasi
4
3
| |
|
\ .
. Transformasi N ialah pantulan pada garis y x = . Nyatakan
koordinat imej bagi titik D di bawah setiap transformasi berikut:
(i) M,
(ii) NM.
[3 marks/markah]
(b) (i) PTUV is the image of ABCD under the combined transformation JK. Describe in full,
transformation K and transformation J.
PTUV ialah imej bagi ABCD di bawah gabungan transformasi JK. Huraikan selengkapnya,
transformasi K dan transformasi J.
[6 marks/markah]
(ii) Given the shaded region QTUVSR represents a region with an area of 78 cm
2
,
calculate the area, in cm
2
, of the region represented by PQRS.
Diberi kawasan berlorek QTUVSR mewakili kawasan dengan luasnya 78 cm
2
,
kirakan luas bagi kawasan yang diwakili oleh PQRS, dalam cm
2
.
[3 marks/markah]
6.
Diagram 6/Rajah 6
2 O 2 4 6 8
10
8
6
4
2
C
D
B
A
S
R
Q
P
V
U
T
y
x
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 37
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 38
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 39
7.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 40
8.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 41
9.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 42
10.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 43
11.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 44
Earth As a Sphere
1. Diagram 9 shows the locations of point P ( 58
o
S , 100
o
E ) , and point V (58
o
N , 30
o
E ) on the
surface of the earth . O is the centre of the earth . PQ is the diameter of the common parallel of latitude
58
o
S .
Rajah 9 menunjukkan kedudukan titik P (58
o
S , 100
o
T) dan titik V (58
o
N , 30
o
T) pada
permukaanbumi , O ialah pusat bumi . PQ ialah diameter selarian latitude sepunya
58
o
S .
(a) State the longitude of Q
Nyatakan longitude bagi Q.
[ 2 marks ]
(b) Calculate the shortest distance , in nautical miles , from P to Q measured along
the surface of the earth .
Hitung jarak terpendek,,dalam batu nautika, ,dari P ke Q diukur disepanjang permukaan
bumi .
[ 2 marks]
(c) Calculate the distance , in nautical mile , from V due east to P measured along
the common parallel of latitude .
hitung jarak , dalam batu nautika , dari V arah ke timur ke P diukur sepanjang selarian
latitude sepunya .
[ 3 marks]
(d) Point R lies 3960 nautical miles due north of P . An aeroplane took off from
P and flew due north to R . The flight took 8 hours .
Titik R terletak 3960 batu nautika ke utara P . Sebuah kapal terbang berlepas dari P arah
Ke utara ke R . Tempoh penerbangan ialah 8 jam .
(i) Calculate the latitude of R
Hitung latitude bagi R .
(ii) Calculate the average speed , in knot , of the aeroplane from P to R .
Hitung purata laju , dalam knot , kapal terbang itu dari P ke R .
[5]
Diagram 9
Rajah 9
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 45
2. P, Q and R are three points on the surface of the earth. PQ is a diameter of the earth
with P located at (50
o
S , 78
o
E ) while R is 3500 nautical miles due north of P.
P, Q dan R adalah tiga titik di permukaan bumi. PQ ialah diameter bumi dengan
kedudukan P ialah (50
o
B, 78
o
T ), sementara R terletak 3500 batu nautika ke Utara P.
(a) Find
Carikan
(i) the position of Q [2 marks]
kedudukan Q [2 markah]
(ii) latitude of R [2 marks]
latitud R [2 markah]
(b) Calculate the shortest distance between Q and R
Hitungkan jarak terpendek, dalam batu nautika , dari Q ke R.
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(c) W is due east of R with a longitude of 130
o
E. An aeroplane took off from P
and flew due north to R. It then changed its direction and flew due east until it
reach W. The whole journey took 15 hours and 41 minutes.
Calculate the average speed of the aeroplane.
W terletak ke timur R dengan longitude 130
o
T. Sebuah kapal terbang
berlepas dari P dan terbang arah ke utara ke R. Kemudian ia mengubah
haluan ke timur sehingga ke W. Keseluruhan perjalanan menganbil masa 15
jam dan 41 minit. Hitungkan purata laju kapal terbang itu.
[5 marks]
[5 markah]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 46
3. P, Q and R are three points on the surface of the earth. PQ is a diameter of the earth
with P located at (50
o
S , 78
o
E ) while R is 3500 nautical miles due north of P.
P, Q dan R adalah tiga titik di permukaan bumi. PQ ialah diameter bumi dengan
kedudukan P ialah (50
o
B, 78
o
T ), sementara R terletak 3500 batu nautika ke Utara P.
(a) Find
Carikan
(i) the position of Q [2 marks]
kedudukan Q
(ii) latitude of R [2 marks]
latitud R
(b) Calculate the shortest distance between Q and R
Hitungkan jarak terpendek, dalam batu nautika , dari Q ke R.
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(c) W is due east of R with a longitude of 130
o
E. An aeroplane took off from P
and flew due north to R. It then changed its direction and flew due east until it
reach W. The whole journey took 15 hours and 41 minutes.
Calculate the average speed of the aeroplane.
W terletak ke timur R dengan longitude 130
o
T. Sebuah kapal terbang
berlepas dari P dan terbang arah ke utara ke R. Kemudian ia mengubah
haluan ke timur sehingga ke W. Keseluruhan perjalanan menganbil masa 15
jam dan 41 minit. Hitungkan purata laju kapal terbang itu.
[5 marks]
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 47
4. P(56
0
S, 94
0
E) , Q (56
0
S, 49
0
E), R and V are four points on the surface of the earth. PR is a diameter
of the parallel of latitude 56
0
S.
P(56
0
S, 94
0
E) , Q (56
0
S, 49
0
E), R dan V adalah empat titik pada permukaan bumi. PR ialah diameter
selarian latitude 56
0
S.
(a) State the location of R.
Nyatakan kedudukan bagi R.
[ 3 marks / 3 markah]
(b) Calculate the shortest distance, in nautical miles, from P to R measured along the surface of the
earth.
Hitung jarak terpendek, dalam batu nautika, dari P ke R diukur sepanjang permukaan bumi.
[2 marks / 2 markah]
(c) Calculate the distance, in nautical miles, from P due west to Q measured along the parallel of latitude.
Hitung jarak, dalam batu nautika, dari arah P arah barat ke Q diukur sepanjang selarian latitude
sepunya.
[ 3 marks/ 3 markah]
(d) An aeroplane took off from Q and flew due north to V. The average speed of the flight was 540 knots
and the time taken was 8
4
1
hours.
Sebuah kapal terbang berlepas dari Q arah ke utara ke V. Purata laju penerbangan itu ialah 540 knot
dan masa yang diambil untuk penerbangan itu ialah 8
4
1
jam.
Calculate / Hitung
(i) the distance, in nautical mile, from Q to V measured along the meridian.
jarak, dalam batu nautika, dari Q ke V diukur sepanjang meridian.
(ii) the latitude of V.
Latitude bagi V.
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 48
5. J (77S, 70E) and K are two points on the surface of the earth. JK is the diameter of the earth and JL
is the diameter of a parallel of latitude.
J (77S, 70E) dan K adalah dua titik pada permukaan bumi. JK ialah diameter bumi dan JL
ialah diameter selarian.
(a) Mark the position of K and L in Diagram 9.
Tandakan kedudukan K dan L pada Rajah 9.
[2 marks/markah]
(b) State the position of K.
Nyatakan kedudukan K.
[2 marks/markah]
(c) Calculate the shortest distance, in nautical miles, from J to L measured along the surface
of the earth.
Hitungkan jarak terpendek, dalam batu nautika, dari J ke L, diukur sepanjang permukaan
bumi.
[3 marks/markah]
(d) A jet plane took off from J due west to L and then flew due north to K. The average speed
for the whole flight was 1500 knots.
Sebuah kapal jet berlepas dari J arah ke barat ke L dan kemudian terbang arah ke utara
ke K.
Calculate
Hitungkan
(i) the distance , in nautical miles, from J to L measured along the parallel of latitude,
jarak, dalam batu nautika, dari J ke L diukur sepanjang selarian latitude,
(ii) the total time, in hours, taken for the whole flight.
jumlah masa, dalam jam, diambil seluruh penerbangan itu.
[5 marks/markah]
Answer/Jawapan:
(a)
O
N
J
S
0
o
-
Diagram 9/Rajah 9
Mathematics-CYL@2011 Page 49
6.
You might also like
- Emaya2012maths SPMDocument25 pagesEmaya2012maths SPMJane Lee Xin RuNo ratings yet
- Graph of FunctionsDocument12 pagesGraph of Functionswanis11No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 II Graphs of Functions EnrichmentDocument12 pagesChapter 11 II Graphs of Functions EnrichmentksganNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 2 Graphs of Functions IIDocument2 pagesForm 5 Chapter 2 Graphs of Functions IIWilliam Teo75% (4)
- Revision Module Midterm Maths Form 5Document19 pagesRevision Module Midterm Maths Form 5Lyna NaderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 II Graphs of Functions Enhanced Ah Died ItDocument9 pagesChapter 11 II Graphs of Functions Enhanced Ah Died Itkartini_kadirNo ratings yet
- 3na Graphs 2Document8 pages3na Graphs 2John GohNo ratings yet
- MODULE 10-Graphs of FunctionsDocument13 pagesMODULE 10-Graphs of Functionsidaman2905No ratings yet
- Module 10 Graf FunctionDocument10 pagesModule 10 Graf FunctionHelen PappuNo ratings yet
- Islamia English School, Abu Dhabi.: Grade 9 Graphs Revision Chapter - 5Document2 pagesIslamia English School, Abu Dhabi.: Grade 9 Graphs Revision Chapter - 5attooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Graphs of Functions (Practice Form 3) : 1. in The Figure Shown, When X 4, The Value of y IsDocument10 pagesChapter 8: Graphs of Functions (Practice Form 3) : 1. in The Figure Shown, When X 4, The Value of y Isunknown :)No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Graphs of Functions (Practice Form 3) : 1. in The Figure Shown, When X 4, The Value of y IsDocument10 pagesChapter 8: Graphs of Functions (Practice Form 3) : 1. in The Figure Shown, When X 4, The Value of y Isunknown :)No ratings yet
- A PaperDocument29 pagesA PaperÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- 3exp Functions and Graphs 1Document3 pages3exp Functions and Graphs 1John GohNo ratings yet
- Graf FungsiDocument14 pagesGraf FungsikhairulabidininstarNo ratings yet
- Graphs RevisionDocument15 pagesGraphs Revisionzylon.d.liteNo ratings yet
- Calculus Review Packet NovemberDocument23 pagesCalculus Review Packet NovemberagwenexusNo ratings yet
- Islamia English School, Abu Dhabi.: Grade 9 Graphs Chapter - 5Document2 pagesIslamia English School, Abu Dhabi.: Grade 9 Graphs Chapter - 5attooNo ratings yet
- School Holiday ModuleDocument3 pagesSchool Holiday ModuleBye Zuera OthmanNo ratings yet
- GraphDocument17 pagesGraphDarwin ManoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Graphs of Functions Ii: 11.1: Linear FunctionDocument30 pagesChapter 2: Graphs of Functions Ii: 11.1: Linear FunctionksganNo ratings yet
- 2011 IJC Prelims P1 PDFDocument6 pages2011 IJC Prelims P1 PDFmath3matics3No ratings yet
- Math Revision WorksheetDocument6 pagesMath Revision WorksheetNausaf AhmedNo ratings yet
- ANSWER ALL Questions All Working Must Be Clearly ShownDocument3 pagesANSWER ALL Questions All Working Must Be Clearly Shownrajal11No ratings yet
- Straight Line Graphs Yr 10 11 HigherDocument21 pagesStraight Line Graphs Yr 10 11 HigherchrisNo ratings yet
- A76 Graphical Solutions With FunctionsDocument11 pagesA76 Graphical Solutions With FunctionsAkafNo ratings yet
- Quad FN Worksheet 4Document7 pagesQuad FN Worksheet 4jan12th2004No ratings yet
- Powerpoint QuadraticsDocument129 pagesPowerpoint QuadraticsDominic SavioNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Add MathsDocument11 pagesForm 4 Add MathsEve EvNo ratings yet
- 2exp Functions Graphs 2Document3 pages2exp Functions Graphs 2John GohNo ratings yet
- Topical Test 4 Additional Mathematics, Form 5 Answer All The Questions. (40 Marks)Document3 pagesTopical Test 4 Additional Mathematics, Form 5 Answer All The Questions. (40 Marks)Xian RouNo ratings yet
- revision WorksheetDocument10 pagesrevision WorksheetJumana ElkhateebNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Functions 1Document2 pagesGraphs of Functions 1Risaudin BaharNo ratings yet
- Freshman Algebra Midterms ReviewerDocument7 pagesFreshman Algebra Midterms Reviewerstix_n_stonedNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Graphs of Functions 2Document123 pages2.0 Graphs of Functions 2juriah binti ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Linear Inequalities: Diagram 1Document4 pagesLinear Inequalities: Diagram 1amerudin bin abul rahimNo ratings yet
- 1st Mid-Term Test (Add Maths f4)Document5 pages1st Mid-Term Test (Add Maths f4)Jarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- Matematik Tingkatan 4Document8 pagesMatematik Tingkatan 4n_rajay84100% (1)
- Curved GraphsDocument5 pagesCurved GraphsboostoberoiNo ratings yet
- Assignment CcordinateDocument1 pageAssignment CcordinateAnirban DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Addmath IsDocument37 pagesAddmath IsYusuf WahabNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Monthly Test March 2016Document10 pagesAdd Maths Monthly Test March 2016Armadaramor ShiNo ratings yet
- Math HL Revision PackDocument21 pagesMath HL Revision Packpoocamaccotta100% (4)
- MTM4 - DDX - Test2 - 2020 Increase FontDocument15 pagesMTM4 - DDX - Test2 - 2020 Increase FontMathKeysNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document25 pagesLecture 8Gia Huy LạiNo ratings yet
- Chap23 - 380-391Document12 pagesChap23 - 380-391jfarrell_ie5767No ratings yet
- Marks) : Pada Graf Di Ruangan Jawapan Lorekkan Rantau Yang Memuaskan Ketiga-Tiga Ketaksamaan - Markah)Document11 pagesMarks) : Pada Graf Di Ruangan Jawapan Lorekkan Rantau Yang Memuaskan Ketiga-Tiga Ketaksamaan - Markah)IrinePallNo ratings yet
- Linear LawDocument29 pagesLinear LawsusansoonNo ratings yet
- Math FT S1 G10 SGS 2023Document7 pagesMath FT S1 G10 SGS 2023noorlailyNo ratings yet
- Edexcel C3 PaperADocument3 pagesEdexcel C3 PaperAwinstonNo ratings yet
- 1 (A) Complete Table 1 in The Answer Space For The EquationDocument4 pages1 (A) Complete Table 1 in The Answer Space For The EquationWilson OngNo ratings yet
- Functions (Graphs of Functions)Document13 pagesFunctions (Graphs of Functions)Dileep NaraharasettyNo ratings yet
- Maths f4 Pp2 QnsDocument14 pagesMaths f4 Pp2 QnsElvis KemboiNo ratings yet
- Form 5 - Maths - Chapter 2Document38 pagesForm 5 - Maths - Chapter 2Rajeshvaramana Venkataramana50% (2)
- Graphs of Exponential Functions (Worksheet) No.2Document4 pagesGraphs of Exponential Functions (Worksheet) No.2Kevin SmallNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Document12 pagesCSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Anthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Praktis 1: Nama: - KelasDocument10 pagesPraktis 1: Nama: - Kelasmohamedamin96No ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Buku Teks Fizik T4 KSSM PDFDocument297 pagesBuku Teks Fizik T4 KSSM PDFIlman Mohamad69% (48)
- Fizik K1 KedahDocument29 pagesFizik K1 KedahIlman MohamadNo ratings yet
- Skema Sains P2Document6 pagesSkema Sains P2Ilman MohamadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.1 (Smtai 09) .Document5 pagesLesson 4.1 (Smtai 09) .Ilman MohamadNo ratings yet
- Compensating For Doc. Number: MTD-0802 888.668.8743 Technical Document Tilt, Hard Iron and Soft Iron EffectsDocument15 pagesCompensating For Doc. Number: MTD-0802 888.668.8743 Technical Document Tilt, Hard Iron and Soft Iron EffectsmojimiraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Computer Graphics Theory and Practice Using OpenGL and MayaDocument297 pagesPrinciples of Computer Graphics Theory and Practice Using OpenGL and MayaVpn UserNo ratings yet
- Classical Electromagnetism - FitzpatrickDocument227 pagesClassical Electromagnetism - FitzpatrickTarwin WinNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics For The Managerial Life and Social Sciences 6th Edition Tan Test BankDocument10 pagesApplied Mathematics For The Managerial Life and Social Sciences 6th Edition Tan Test Bankshannonhuertamwsxzkgijf100% (12)
- Operating Mode JOGDocument36 pagesOperating Mode JOGALEXANDRU ZANOAGA100% (1)
- Geometric Properties of The Cross-Section Parameter Value: V, y V, ZDocument2 pagesGeometric Properties of The Cross-Section Parameter Value: V, y V, ZARYANo ratings yet
- 9 Cartesian System of CoordinatesDocument15 pages9 Cartesian System of Coordinatesaustinfru7No ratings yet
- Sinclair Uim SDT sdv5 enDocument41 pagesSinclair Uim SDT sdv5 enyayoteNo ratings yet
- Final PPT of Tracing of Polar CurvesDocument66 pagesFinal PPT of Tracing of Polar CurvesNidhi Rai100% (2)
- Math10 - Q2 - Week 9Document16 pagesMath10 - Q2 - Week 9Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- LibreOffice Calc Guide 6Document20 pagesLibreOffice Calc Guide 6Violeta XevinNo ratings yet
- Physics LabDocument44 pagesPhysics Labsal27adamNo ratings yet
- Math 5 Line GraphDocument32 pagesMath 5 Line GraphSHARON MANUEL100% (1)
- CSS Module-Melc 1-3 Grade 11Document22 pagesCSS Module-Melc 1-3 Grade 11Rina Brucal-DimayugaNo ratings yet
- CK12 CalculusDocument457 pagesCK12 CalculussamrandaNo ratings yet
- 2D 2 ReferenceDocument454 pages2D 2 ReferenceratNo ratings yet
- Anotha 111432Document33 pagesAnotha 111432AnoNo ratings yet
- ME424 201516 Unit4Document56 pagesME424 201516 Unit4venkateshNo ratings yet
- Maneuvering Board ManualDocument148 pagesManeuvering Board ManualAlex Cr100% (1)
- AS Practice Paper M8Document6 pagesAS Practice Paper M8saNo ratings yet
- Swd-Csa-A23.3-04 (Etabs2013)Document81 pagesSwd-Csa-A23.3-04 (Etabs2013)BJERNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 05 Oriented Core and Rock Mass ClassificationDocument16 pagesTutorial 05 Oriented Core and Rock Mass ClassificationDEMETRIONo ratings yet
- Pattern Grading)Document2 pagesPattern Grading)zoomerfins2267% (3)
- Buckling Analysis Connecting Rod PDFDocument8 pagesBuckling Analysis Connecting Rod PDFAnonymous NFsIMHyfLtNo ratings yet
- Generic 6-DOF Added Mass Formulation For Arbitrary Underwater VehiclesDocument51 pagesGeneric 6-DOF Added Mass Formulation For Arbitrary Underwater VehiclesebwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 I Transformation I, II ENHANCEDocument14 pagesChapter 2 I Transformation I, II ENHANCETan Kui GekNo ratings yet
- Development of Transition PiecesDocument37 pagesDevelopment of Transition PiecesElancheran RengaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Scatter GraphsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Scatter GraphsJonathan Robinson100% (2)
- Force Vectors: Cien 3144 Structural Theory 1 Ensc 20043 Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument53 pagesForce Vectors: Cien 3144 Structural Theory 1 Ensc 20043 Statics of Rigid BodiesAndrei AlidoNo ratings yet