Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Management
Uploaded by
Nica Marie LumbaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Management
Uploaded by
Nica Marie LumbaCopyright:
Available Formats
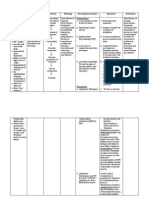
C. NURSING PROBLEM PRIORITIZATION PRIORITIZATION DIAGNOSIS Problem No.
1 Ineffective Airway Clearance 1 JUSTIFICATION Airway must be given the first attention as based on the rule of ABC which is Airway, Breathing and Circulation. In addition, difficulty of breathing can cause anxiety to the client that is why, immediate attention must be done. Addressing the problem to proper health care provider will give patent airway to the client. Oxygenation is a vital need for every cell, if there are any problems related to it can easily affect the functioning of the individual. Retained secretions can cause blockage of airway which will further cause difficulty of breathing(Fundamentals of Nursing 8th ed by Kozier and erbs p. 1299
Lack of action in this health care problem may cause leading to hypoxia of the lung tissue and a significant ventilation-perfusion mismatch
Problem No. 2 Impaired Gas Exchange 2
Problem No. 3 Ineffective Breathing Pattern 3
This demands immediate treatment/care and subsequent medical attention, as they can result in ineffective breathing pattern. This also needs attention as based on the rule of ABC which is Airway, Breathing and Circulation. This is an actual problem that needs to address. Lack of action in this health care problem may cause dyspnea which may later cause a bigger threat to the health of the patient. Difficult and labored in breathing during which the individual has a persistent, unsatisfied need for air and feel distressed. (Fundamentals of Nursing 8th ed by Kozier and erbs p. 549) CAP is the inflammation of the lung parenchyma due to offending organisms, inflammatory lung response will be stimulated leading to
Problem No. 4 Hyperthermia
Problem No. 5 Activity Intolerance 5
the release of chemical mediators that would increase blood flow to the lung tissues leading to erythema, swelling, pain, and increased body temperature that would reset the hypothalamus which is the major center for regulation of body temperature The onset of pneumonia is generally marked by fever, dyspnea, and shortness of breath and easy fatigability that may lead to inability to perform activities of daily living
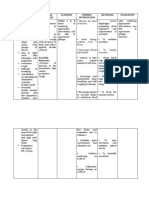
Problem No. 1 Ineffective Airway Clearance Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Cue: nahihirapan siyang huminga dahil sa plema yun yung sinabi sa akin nung nars as verbalized by the mother.
Objective cues :
Ineffective Airway CommunityShort Term : > Assess respiratory Clearance related to Acquired status: breath retained secretions in Pneumonia is the sounds, respiratory the bronchi ( inflammation of the After 5 hours rate, oxygen increased thick lung parenchyma saturation, note of Nursing mucous secretions) when the offending Interventions, abnormalities such and lung organism reaches the patient will as dyspnea, presence inflammation the alveoli via of cyanosis, use of expectorate leading to droplets or saliva in accessory muscles, mucous as accumulation of whi8ch goblet cells flaring of nostrils evidenced by mucous in the produces an productive alveoli outpouring fluid into cough, the alveoli. The effective > Assess anxiety organisms multiply coughing and and reassure patient
> Abnormal breathing patterns may signal worsening of condition: flaring of nostrils indicate a significant decline in respiratory status: assessment establishes baseline and monitor response to interventions
Short Term :
The patient shall be able to expectorate mucous as evidenced by productive cough effective coughing and breathing exercise
>appears weak
>pale palpebral conjunctiva
> rales on both lung lobes upon chest auscultation
> difficulty of breathing
> shortness of breath
> non- productive cough
>Tachypnea
in the serous fluid and the infection is spread. The organisms damage the host by their overwhelming growth and interference with lung function leading to massive accumulation of mucus. Disruption of the mechanical defenses of cough and ciliary motility leads to the colonization of the lungs and accumulation of secretions in the alveoli and bronchi leading to ineffective airway clearance as evidence by nonproductive cough etc. alveolar exudates tend to consolidate,
breathing exercise
presence
Long Term : > Place patient in high fowlers position and support overbed table as needed.
> Being unstable to breath causes anxiety and fear: the patient needs a calming presence: anxiety increases the demand for oxygen
Long Term :
After 2 days of Nursing Interventions, the patient will maintain airway patency as evidenced by clear breath sounds, absence of dyspnea, etc.
> Maximize chest excursion and subsequent movement of air
> Encourage expectoration of secretions and assess the viscosity amount and color of secretions
The patient will maintain airway patency as evidenced by clear breath sounds, absence of dyspnea, etc.
> Thickened secretions of Cap re more likely to occlude the airway: making this observation would allow for implementation if measures to thin and loosen the secretions
>Restlessness
increasingly difficult to expectorate.
> Assist the patient coughing and deep breathing
> Mobilizes secretions and prevent atelectasis
> Orthopnea > Increase fluid intake
> Flaring of nostrils
> Assists with liquefying secretions and enhancing ability to clear airways
> Decrease demand for oxygen > Provide for periods of rest and activity, assisting devices as needed
> Elevate head of bed/ change of position every 2 hours
> To maintain an open airway and to take advantage of gravity decreasing pressure on the diaphragm and enhancing drainage of
secretions.
> Assist respiratory therapist the administration of nebulizer
>This causes bronchiodilation to ease breathing
> Establish intravenous access as ordered
> Ensures a route for rapid- acting medications
> Assess arterial blood gases (ABG)
>ABG provide data for treatment regarding the lungs ability to oxygenate tissues
> Provide humidified oxygen as ordered to maintain O2
> Loosen secretions, making them easier to expectorate coughing: improves oxygenation
saturation >90%
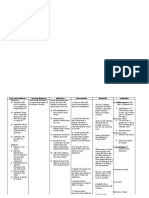
Problem No. 2 Impaired Gas Exchange Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Cue: Pansin ko lagi siyang parang hinihingal as
Impaired Gas Exchange related to
CommunityAcquired Pneumonia is defined as a lower
Short Term :
After 8hours
> Perform a complete respiratory assessment ;
> Because airway inflammation and mucous accumulation, pneumonia can cause
Short Term : The patient shall be relieved from dyspnea by
verbalized by the mother
Objective cue :
>difficulty of breathing
>nasal flaring
inflamed lung tissue and consolidatio n of mucous / ffluid in specific lung lobes preventing transfer of gases across the alveolar capillary cellular membrane
>shortness of breath/ exertional discomfort
>with presence of crackles on both lung lobes upon auscultation
> with non
respiratory tract infection of the lungs parenchyma with onset in the community or during thre first 2days of hospitalization. Pneumonia occurs when the offending organism stimulate inflammatory response the defense mechanism of the lung lo9se effectiveness and allow organisms to penetrate the sterile, lower respiratory tract, where inflammation develops. Inflammation occurs due to colonization of offending organization wherein there is the release of chemical
of Nursing Interventions, the patient will be relieved from dyspnea by participating in breathing exercises, effective coughing and use of oxygen as evidenced by absent of nasal flaring, shortness of breath, easy fatigability, etc.
respiratory rate, fluid in the lungs and participating in rhythm, chest increase the work of breathing expansion, ease of breathing, resulting in exercise, effective breathing, use of impaired gas exchange. coughing and use accessory muscles, These assessment of oxygen as pursed lip provide data use for evidenced by breathing, breath planning absence of nasal sounds, mucous flaring, shortness Interventions and expectoration, of breath, easy assessing progress. perioral cyanosis, fatigability. Etc. Sputum cultures identify tachypnea, dyspnea, pulse oximetry and the causative organisms, arterial blood gases monitor laboratory demonstrate decreased and diagnostic oxygen concentration, procedures such as chest x-ray will confirm sputum cultures, the presence of fluid in complete blood the lungs or areas of count, arterial blood Long Term : consolidation gases, etc. The patient shall have an improved ventilation and adequate oxygenation of lung tissue as evidenced by normal arterial blood gases, clear
Long Term :
After 1 to 3 days of Nursing
> Obtain subjective data from the patient or significant other, including history of chronic respiratory disease and history
> knowledge of the patient respiratory status contributes to information that can assist in determination
productive cough
> easy fatigability
>Tachycardia
> abnormal rate rhythm, depth of breathing
>Restlessness
>Confusion
>fever
O 2
mediators, attraction of neutrophils, accumulation of fibrinous exudates, red blood cells and macrophages. These would in turn trigger erythema swelling, edema and stimulation of nerve fibers, leading to pain. Goblet cells will increase mucus production in attempt to dilute amd wash away offending organisms out of the respiratory tract. Inflamed fluid-filler alveolar sacs cannot exchange O2 and CO2 effectively leading to hypoxia of the lung tissue and a significant ventilation-
Interventions, the patient will have an improved ventilation and adequate oxygenation of lung tissue as evidenced by normal arterial blood gases, patient will have a clear breath sounds, absence of purulent discharge
of smoking
> Assist patient to semi fowlers position
other factors that may have contributed to pneumonia or influence its treatment
Breathing sounds, absence of purulent discharges, etc.
> Sitting upright allows the diaphragm to descend, resulting in easier breathing >Take temperature every 4 hours > Infectious processes can cause an increase body temperature > Provide comfort measures change linen or clothing
>Following temperature spikes, linen and clothing may become saturated with perspiration
> Encourage adequate fluid intake to 2000
> Helps thin and liquefy secretions
perfusion mismatch s a t u r a t i o n o f l e s s t h a n 9 0 %
cc/day
> Assess mucous amount, color consistency.
>Helps to detect improving status of pneumonia, amount should be decreasing and viscosity should be thinning following interventions; green, brown or purulent mucus indicate continued presence of pneumonia
>Coughing and deep breathing cause alveoli to open and loosen mucous to help clear the airways >Encourage coughing and deep breathing with mucous expectoration
>Loosen mucous plugs thus increasing are available for gas
exchange > Provide chest physiotherapy postural drainage, chest percussion and vibration > To maintain airway patency > Elevate head of bed >Promotes optimal chest expansion and drainage of secretion
> Encourage frequent position changes
> Helps limit oxygen needs/ consumption > Encourage adequate rest and limit activities to with in patient tolerance. Promote calm and restful environment
> Administer
oxygen as ordered >Pneumonia increased mucous production and fluid retention in lungs which decreases adequate gas exchange; supplemental oxygen provides additional oxygen for tissue oxygenation
>Helps to stop the proliferation of microorganisms >Administer antibiotic as ordered and monitor for side effects. A d o
Problem No. 3 Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Cue: Nahihirapang huminga ang baby ko., as verbalized by the mother
O=Patient Manifested the following :
Ineffective breathing pattern related to thick tenacious secretions in the bronchi due to inflammatio n of lung tissue
>difficulty of breathing
>shortness of breath on exertion, paleness
CommunityAcquired is a disease process involving inflammation of lung tissue. It typically results when microorganisams enter the normally sterile lungs from the nasopharynx and produces inflammation of the lung parenchyma. Because of the inflammation of the alveoli are filed with fluid and mucus and oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange cannot take place at a alveolar capillary cellular membrane level due to blood flow decreases
Short Term :
After 4 hours of Nursing Interventions, the patient shall have a normal respiratory rate, rhythm, depth and reports a shortness of breath as evidence by decrease RR from 38 cpm to 16-20 cpm
> Assess respiratory system by noting respiratory rate, depth chest expansion, breath sounds, arterial blood gases, etc.
> Any of this abnormalities would indicate the studies of the respiratory system and progression of disease; also establishes a baseline comparison
Short Term :
> Assist Patient in assuming a highfowlers position or position of choice such as leaning forward or over bed table
>maximizes thoracic cavity space, decreases pressure from diaphragm and abdominal organs and facilitates use of accessory muscles
The patient shall have a normal respiratory rate, rhythm, depth of breathing and relief from shortness of breath as evidence by decrease RR from 38 cpm to 16-20 cpm
Long Term :
> Increase oral fluids to 2000-3000 ml/day as tolerated
>help to improve hydration status and decrease secretions.
After 2 days
> Provide chest
> mobilizes thick
> nonproductive cough
> with presence of rales on both lung lobe upon chest auscultation easily fatigability
(deceased perfusion of blood in the lungs)and leukocytes and fibrin consolidate in the affected part of the lung due to a decreased blood flow there is a decreased supply of oxygen to other tissues leading to ineffective breathing pattern
of Nursing Interventions, the patient shall be free from any signs and symptoms of hypoxia as evidenced by normal ABG, etc.
physiotherapy, bronchial tapping, vibration, etc.
secretions, and facilitates clearing of lung fields. Long Term :
>Assist with activities of daily living as required
>patient with pneumonia may lack sufficient oxygen reserves to perform activites; even eating may cause severe dyspnea
The patient shall be free from any signs and symptoms of hypoxia as evidenced by normal ABG, etc.
>severe dyspnea
> Teach patient how to decrease shorthness of breath by restructuring activities
> Knowing how to control shortness of breath will help cope and have optimal functioning
>Teach pulmonary hygiene; prevention of spread of infection
> Preventing spread of infection and subsequent
hospitalization >Provide humidified low flow of oxygen as ordered >Provide some supplemental oxygen to improve oxygenation and to make secretions less viscous
>Administer bronchodilators and expectorants
>Enhances expectoration of secretions of previously ineffective cough
> Administer antibiotics as ordered
>Helps to prevent or eradicate infections to reduce secretions and to end to inflammation
You might also like
- NCP AirwayDocument2 pagesNCP AirwayjlucandoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearancejancel_bollaNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- NCP CopdDocument4 pagesNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDocument3 pagesAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Document9 pagesRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document1 pageChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBKath TalubanNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Impaired Breathing PatternDocument1 pageImpaired Breathing PatternHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for PneumoniaFARAH MAE MEDINANo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- BPN NCPDocument6 pagesBPN NCPJoart EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument5 pagesPneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentcrisolandNo ratings yet
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 page(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahNo ratings yet
- Angel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAngel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisSalvaje CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Medical Management For PneumoniaDocument2 pagesMedical Management For PneumoniaSue Elaine100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Peritonsillar AbscessDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Peritonsillar AbscessKevin Leo Lucero AragonesNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaNo ratings yet
- NICU Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNICU Nursing Care Planlorence_cachoNo ratings yet
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmirose Fatima TagabNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)CHRISTIE MONTANO0% (1)
- HTP of AsthmaDocument1 pageHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention (Epiglottitis Disease)Document2 pagesNursing Intervention (Epiglottitis Disease)Marianne Rose HernandezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Progress Notes for Sanaa Anwar TahirDocument2 pagesNursing Progress Notes for Sanaa Anwar TahirROXANNE V. LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanAnnahNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Risk of AspirationDocument6 pagesAssessing and Managing Risk of AspirationaianrNo ratings yet
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- NCP For FeverDocument2 pagesNCP For FeverSherwin B. CaytapNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nanda Diagnoses Goals InterventionsDocument4 pagesAsthma Nanda Diagnoses Goals InterventionsZinya RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- BronchiectasisDocument40 pagesBronchiectasisyana jaeNo ratings yet
- NCP #2Document4 pagesNCP #2Nutz TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The BronchiDocument9 pagesChronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchiinamaliit100% (1)
- Competencymr McdougalcopdDocument17 pagesCompetencymr Mcdougalcopdmac_rymrt7569No ratings yet
- Bronchitis 170709131740Document28 pagesBronchitis 170709131740Viji MNo ratings yet
- Active Cycle of Breathing TechniquesDocument6 pagesActive Cycle of Breathing Techniqueskarl24No ratings yet
- Far Eastern University: Basic Concepts of Oxygenation: RespiratoryDocument6 pagesFar Eastern University: Basic Concepts of Oxygenation: RespiratoryJoiesammae Mitzi OreNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management - 112Document67 pagesNursing Care Management - 112Ong KarlNo ratings yet
- Instructional Design - SampleDocument9 pagesInstructional Design - SampleNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- 8th Lec Updated Determinants of Learning Ch. 4Document42 pages8th Lec Updated Determinants of Learning Ch. 4Nica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- First PagenDocument3 pagesFirst PagenNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- NameDocument2 pagesNameNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Gawad KalasagDocument8 pagesGawad KalasagNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Inflammatory Response SyndromeDocument33 pagesSystemic Inflammatory Response SyndromeNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- TimeDocument2 pagesTimeNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Marking A New BeginningDocument1 pageMarking A New BeginningNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- THESIS Official PaperDocument43 pagesTHESIS Official PaperNica Marie Lumba100% (1)
- Endings Are BeginningsDocument2 pagesEndings Are BeginningsNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- ElectiveDocument20 pagesElectiveNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- PT # Profile Health and Kidney Disease AGE Gender Civil Status Occupation Monthly Income Highest Educational Attainment Co-Morbidity 1Document20 pagesPT # Profile Health and Kidney Disease AGE Gender Civil Status Occupation Monthly Income Highest Educational Attainment Co-Morbidity 1Nica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- The Retreat Has Helped Me To Fall More Deeply in Love With GodDocument2 pagesThe Retreat Has Helped Me To Fall More Deeply in Love With GodNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Designing Software Project ArchitectureDocument268 pagesDesigning Software Project ArchitectureNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Layers of The SkinDocument4 pagesLayers of The SkinNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Eb NNDocument1 pageEb NNNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- KARDEX: Organizing Client Health DataDocument1 pageKARDEX: Organizing Client Health DataNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Shades of Aces: by Jamaica Louise MacalinoDocument3 pagesShades of Aces: by Jamaica Louise MacalinoNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- EbeesDocument2 pagesEbeesNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- EbeesDocument2 pagesEbeesNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CommunityDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CommunityNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- NameDocument2 pagesNameNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Mohillo Labs Part 2Document3 pagesMohillo Labs Part 2Nica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State U names Nursing notes advisersDocument1 pageBulacan State U names Nursing notes advisersNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Mohillo Labs Part 2Document3 pagesMohillo Labs Part 2Nica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Eb NNDocument1 pageEb NNNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- BSU College Nursing Pub Recognition AppDocument1 pageBSU College Nursing Pub Recognition AppNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies For Nurse EducatorsDocument3 pagesTeaching Strategies For Nurse EducatorsNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Attendance Sheet BSN 4-A Date: Name Sign-In Signature Sign-Out SignatureDocument1 pageAttendance Sheet BSN 4-A Date: Name Sign-In Signature Sign-Out SignatureNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- 3D Area Clearance Strategies for Roughing ComponentsDocument6 pages3D Area Clearance Strategies for Roughing ComponentsMohamedHassanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finite Element Methods (2001) (En) (489s)Document489 pagesIntroduction To Finite Element Methods (2001) (En) (489s)green77parkNo ratings yet
- FST Handbook 2014-Final Copy 1 PDFDocument382 pagesFST Handbook 2014-Final Copy 1 PDFDelvon DownerNo ratings yet
- Phenomenological of in Church and TV WorshipDocument18 pagesPhenomenological of in Church and TV WorshipCindy TirtaNo ratings yet
- WK 43 - Half-Past-TwoDocument2 pagesWK 43 - Half-Past-TwoKulin RanaweeraNo ratings yet
- Home Brewing Log Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesHome Brewing Log Sheet PDFStefanita0% (1)
- Caterpillar Ep15krtDocument37 pagesCaterpillar Ep15krtIvan MajikNo ratings yet
- Daftar Spesifikasi Teknis Pembangunan Gedung Kantor BPN BojonegoroDocument6 pagesDaftar Spesifikasi Teknis Pembangunan Gedung Kantor BPN BojonegoroIrwin DarmansyahNo ratings yet
- Who will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisDocument12 pagesWho will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisbhasker sharmaNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument24 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentOktaviana Sari Dewi100% (1)
- Sto - Cristo Proper Integrated School 1 Grading Grade 9 Science Table of SpecializationDocument2 pagesSto - Cristo Proper Integrated School 1 Grading Grade 9 Science Table of Specializationinah jessica valerianoNo ratings yet
- LKC CS Assignment2Document18 pagesLKC CS Assignment2Jackie LeongNo ratings yet
- Feline DermatologyDocument55 pagesFeline DermatologySilviuNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Beam DesignDocument13 pagesReinforced Concrete Beam Designmike smithNo ratings yet
- Final Decision W - Cover Letter, 7-14-22Document19 pagesFinal Decision W - Cover Letter, 7-14-22Helen BennettNo ratings yet
- Project On Stones & TilesDocument41 pagesProject On Stones & TilesMegha GolaNo ratings yet
- ProtectionDocument160 pagesProtectionSuthep NgamlertleeNo ratings yet
- Antennas Since Hertz and MarconiDocument7 pagesAntennas Since Hertz and MarconiTaiwo Ayodeji100% (1)
- OpenROV Digital I/O and Analog Channels GuideDocument8 pagesOpenROV Digital I/O and Analog Channels GuidehbaocrNo ratings yet
- ROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDocument20 pagesROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDan George IIINo ratings yet
- JY Series Single-Phase Capacitor Induction MotorsDocument1 pageJY Series Single-Phase Capacitor Induction MotorsAditya PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- SOR 8th Ed 2013Document467 pagesSOR 8th Ed 2013Durgesh Govil100% (3)
- Interactive Architecture Adaptive WorldDocument177 pagesInteractive Architecture Adaptive Worldhoma massihaNo ratings yet
- Maureen L. Walsh - Re-Imagining Redemption. Universal Salvation in The Theology of Julian of NorwichDocument20 pagesMaureen L. Walsh - Re-Imagining Redemption. Universal Salvation in The Theology of Julian of NorwichAni LupascuNo ratings yet
- Xii Neet Chemistry Mcqs PDFDocument30 pagesXii Neet Chemistry Mcqs PDFMarcus Rashford100% (3)
- HVCCI UPI Form No. 3 Summary ReportDocument2 pagesHVCCI UPI Form No. 3 Summary ReportAzumi AyuzawaNo ratings yet
- Chain Surveying InstrumentsDocument5 pagesChain Surveying InstrumentsSachin RanaNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Challenges For Firms To Operate in The Hard-Boiled Confectionery Market in India?Document4 pagesDiscuss The Challenges For Firms To Operate in The Hard-Boiled Confectionery Market in India?harryNo ratings yet
- Effect of Some Algal Filtrates and Chemical Inducers On Root-Rot Incidence of Faba BeanDocument7 pagesEffect of Some Algal Filtrates and Chemical Inducers On Root-Rot Incidence of Faba BeanJuniper PublishersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Energy Transfers: I) Answer The FollowingDocument3 pagesChapter 16 - Energy Transfers: I) Answer The FollowingPauline Kezia P Gr 6 B1No ratings yet