Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab App
Uploaded by
Erika Perez AlvarezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab App
Uploaded by
Erika Perez AlvarezCopyright:
Available Formats
Rhyanne Faye Asuncion
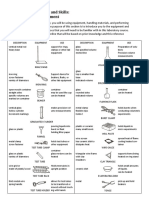
Common Laboratory Apparatus
APPARATUS 1. BEAKER Beakers are generally cylindrical in shape, with a flat bottom and a lip for pouring. A simple container for stirring, mixing and heating liquids commonly used in many laboratories.
2. Test tube
Test tube also known as a culture tube or sample tube, is a common piece of laboratory glassware consisting of a finger-like length of glass or clear plastic tubing, open at the top, usually with a rounded U-shaped bottom. Hold a small experiment, which would be used to conduct an investigation.
3. Florence flask
Florence flask has a round body with a single long neck and with either a round or a flat bottom. It can be used as a container to hold solutions of chemicals. It is designed for uniform heating and ease of swirling; it is produced in a number of different glass thicknesses to stand different types of use.
4. Erlenmeyer flask
Erlenmeyer flask also known as a conical flask, is a widely used type of laboratory flask which features a flat bottom, a conical body, and a cylindrical neck. Erlenmeyer flasks are suitable for heating liquids. The small neck reduces evaporative losses compared to a beaker, while the flat bottom of the conical flask makes it unlikely to tip over and spill.
5. Graduated cylinder
Graduated cylinder is a piece of laboratory equipment used to accurately measure the volume of a liquid. Water displacement can be used to find out the volume of a solid. Graduated cylinders are generally more accurate and precise for this purpose than flasks and beakers.
6. Funnel
Funnel is a pipe with a wide, often conical mouth and a narrow stem. It is used to channel liquid or fine-grained substances into containers with a small opening. Without a funnel, spillage would occur.
7. Evaporating dish
Evaporating dish is a laboratory device for evaporation of solids and supernatant fluids, and sometimes to their melting point. Evaporating dishes are used to evaporate excess water - or other solvents - to ensure that a concentrated solution or the dissolved substance is left behind.
8. Crucible and cover
A crucible is a ceramic container capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, whilst the cover is designed to prevent heat escaping from the crucible itself. Crucibles are used for a range of purposes, and are particularly common amongst chemists for the chemical analysis of various substances.
9. Bunsen burner
Bunsen burner a device for combining a flammable gas with controlled amounts of air before ignition; it produces a hotter flame than would be possible using the ambient air and gas alone.
10. Iron Ring with iron clamp
An iron ring holds glassware such as a funnels or other objects, like the wire gauze or clay triangle for heating with a Bunsen burner. Often, the iron ring will be attached to an iron stand. An iron clamp is a piece of laboratory equipment used to hold things and is placed in an iron stand to elevate other equipment.
11. Iron stand
Iron stand a metal rod attached to a heavy metal base. The heavy base keeps the stand stable, and the vertical metal rod allows for easy height adjustment of the iron ring/clamp. (A tripod can sometimes be used in place of an iron stand.)
12. Test tube holder
The test tube holder obviously is designed to hold test tubes. However, it can be used to hold pipettes and stirring rods, etc. as well.
13. Test tube brush
Test tube brush is a device, made with nylon bristles attached to a twisted-wire shaft, used to knock the bottoms out of test tubes. It is a brush that is long and narrow to clean the inside of glassware, in particular test tubes.
14. Wire gauze
The use of wire gauze in an experiment is to place under the container holding the liquid, which is being heated by the Bunsen burner, so that the container doesn't have direct contact with the flame.
15. Tripod
Tripod is three-legged equipment, generally used as a platform of some sort. This lab equipment is used to support and hold various flasks, beakers and other glass ware when not in use and also during experiments.
16. Spatula
Spatula is used to take and handle small quantities of solid chemicals. It is used like a spoon or an instrument for scooping material out of a container.
17. Stirring rod
Stirring rod is a piece of laboratory equipment used to mix chemicals and liquids for laboratory purposes. They are usually made of solid glass, about the thickness and slightly longer than a drinking straw.
18. Mortar and pestle
Mortar and Pestle is a tool used to crush, grind, and mix solid substances. The substance to be ground is placed in the mortar and ground, crushed or mixed with the pestle.
19. Medicine dropper
Medicine dropper is an instrument used to measure small amount of liquids, usually in milligrams.
20. Test tube rack
Test tube rack is a convenient and necessary piece of laboratory equipment for the storage of test tubes.
21. Laboratory thermometer
Laboratory thermometer is a device that measures temperature or temperature gradient using a variety of different principles.
22. Microscope
Microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. There are many types of microscopes, the most common and first to be invented is the optical microscope which uses light to image the sample.
23. Burette
Burette is a vertical cylindrical piece of laboratory glassware with a volumetric graduation on its full length and a precision tap. It is used to dispense known amounts of a liquid reagent in experiments.
24. Platform balance
The platform balance is a form of equal-arm balance in which two flat platforms are attached to the top side of the beam, one at each end.
25. Alcohol lamp
Alcohol lamp is usually found in biology laboratory where they do inoculations of bacteria cultures. It heats the wire loop on a stick that they use to spread the bacteria on the growth medium, which will prevent contamination to the cultures.
You might also like
- Laboratory Apparatus: Submitted By: Ma. Francesca Louise C. BaldemorDocument5 pagesLaboratory Apparatus: Submitted By: Ma. Francesca Louise C. BaldemorDaniel HaleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ApparatusDocument8 pagesChemistry ApparatusLian Tuliao67% (15)
- List of Apparatus For Quiz LabDocument8 pagesList of Apparatus For Quiz LabLiah MercadoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument37 pagesLaboratory Apparatusalancstnd67% (3)
- Chemistry Laboratory EquipmentsDocument11 pagesChemistry Laboratory EquipmentsEliutario IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab ApparatusDocument3 pagesChemistry Lab ApparatusMark Luigi Babol100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry Solution Stopcock: 4. Pipettes and AspiratorDocument2 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Solution Stopcock: 4. Pipettes and AspiratorCheska BustosNo ratings yet
- Functions of Laboratory Apparatus Finished Sa Wakas HhuhuhuDocument8 pagesFunctions of Laboratory Apparatus Finished Sa Wakas HhuhuhuMawi BargayoNo ratings yet
- Appendix A List and Uses of ApparatusDocument3 pagesAppendix A List and Uses of ApparatusayraNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word 97 - 2003 DocumentDocument8 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word 97 - 2003 Documentgraceymeg_reyesNo ratings yet
- 1.analytical Balance Description:: MG Dust Vented Balance Safety EnclosureDocument10 pages1.analytical Balance Description:: MG Dust Vented Balance Safety EnclosureJeck AbañoNo ratings yet
- Lab MicroscopeDocument6 pagesLab MicroscopeJenny Lyn GesmundoNo ratings yet
- 50 Laboratory Apparatuses Biochemistry: OCTOBER 31, 2020Document14 pages50 Laboratory Apparatuses Biochemistry: OCTOBER 31, 2020Allen TandocNo ratings yet
- Lab EquipmentsDocument15 pagesLab EquipmentsNazam NabeelaNo ratings yet
- LabaparDocument2 pagesLabaparWilhelm DagumanNo ratings yet
- Know Your Lab Equipments: Test TubeDocument9 pagesKnow Your Lab Equipments: Test TubeWelly Boss HwiNo ratings yet
- Ingles Laboratory Apagas LaboratorioDocument11 pagesIngles Laboratory Apagas LaboratorioGraciela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Echeml Chemistry For Engineers - LaboratoryDocument2 pagesEcheml Chemistry For Engineers - LaboratoryJulieAnne DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Chem181: Chemistry For Engineers - Laboratory First Semester, AY 2020-2021 (Cluster 1) Activity No. 1 Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument5 pagesChem181: Chemistry For Engineers - Laboratory First Semester, AY 2020-2021 (Cluster 1) Activity No. 1 Common Laboratory ApparatusMaxine de la TorreNo ratings yet
- Laboratory EquipmentsDocument16 pagesLaboratory EquipmentsedomanpcNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMIST-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesGENERAL CHEMIST-WPS OfficeYra kyranNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument17 pagesLaboratory Apparatuszena100% (1)
- Lab Apparatuses and Equipment's Uses and DescriptionsDocument5 pagesLab Apparatuses and Equipment's Uses and Descriptionsumen chronsterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ApparatusDocument8 pagesChemistry ApparatusLJ AbancoNo ratings yet
- Identification of Laboratory 1Document15 pagesIdentification of Laboratory 1kimberlymapagalNo ratings yet
- 50 Common Laboratory Apparatus and Their Uses With PicturesDocument4 pages50 Common Laboratory Apparatus and Their Uses With PicturesDESMOND EZIEKENo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument11 pagesLaboratory ApparatusThe Unknown MusicNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory Apparatus Names and UsesDocument4 pagesCommon Laboratory Apparatus Names and UsesjammyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Apparatus With DefinitionDocument7 pagesLaboratory Apparatus With DefinitionArgyll ArgyllsNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub Chemistry-Apparatus PDFDocument8 pagesIdoc - Pub Chemistry-Apparatus PDFAshrafNo ratings yet
- Eng Chem (4068) - Lab Act1 - Francisco, Andrew Chester Aliano.Document5 pagesEng Chem (4068) - Lab Act1 - Francisco, Andrew Chester Aliano.MemeowwNo ratings yet
- Lab ApparatusDocument6 pagesLab ApparatusRandolf AsiaNo ratings yet
- CHEM2212 - ESTANOCO - SAMUEL.M. - Activity 1 LABORATORY EQUIPMENTDocument6 pagesCHEM2212 - ESTANOCO - SAMUEL.M. - Activity 1 LABORATORY EQUIPMENTSam EstanocoNo ratings yet
- Glossary PHARMACY AND LABORATORYDocument3 pagesGlossary PHARMACY AND LABORATORYNataly Balbin TarmeñoNo ratings yet
- W1 L5 - Laboratory ApparatusDocument23 pagesW1 L5 - Laboratory ApparatusSaba OsamahNo ratings yet
- Mon Lab ApparatusDocument11 pagesMon Lab ApparatusJustin MenorasNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Apparatus and Its FunctionDocument4 pagesLaboratory Apparatus and Its FunctionTrese ShanelleNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus & GlasswaresDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity 1 Common Laboratory Apparatus & GlasswaresRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument6 pagesBiochemistrykentdanieltulod87No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument6 pagesSciencenwekemunachimso.nNo ratings yet
- JVC Laboratory Activity 1Document34 pagesJVC Laboratory Activity 1Jade CagsawaNo ratings yet
- CrucibleDocument10 pagesCrucibleAlegna PalenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Week 1 Lesson 2Document3 pagesGrade 8 Week 1 Lesson 2alleynekenisha5No ratings yet
- Lab EquipmentDocument8 pagesLab EquipmentMathew YoyakkyNo ratings yet
- Lab ApparatusDocument29 pagesLab ApparatusEpoditmas SeyerNo ratings yet
- 02 Unit 1. Common Laboratory GlasswaresDocument59 pages02 Unit 1. Common Laboratory GlasswaresKevin Mark IlaganNo ratings yet
- CHEM Lab ApparatusDocument4 pagesCHEM Lab ApparatusHannah Gwynette SamonteNo ratings yet
- Acn Laboratory ApparatusDocument40 pagesAcn Laboratory ApparatusAlma Cecilia QuiaoNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment BSCrim Organic - AutosavedDocument130 pagesLab Equipment BSCrim Organic - Autosavedangelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesDocument11 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 1 - Common Laboratory ApparatusesJuliane JaynNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 Introduction To BiochemistryDocument5 pagesWEEK 1 Introduction To BiochemistryCosmic PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory ApparatusDocument21 pagesCommon Laboratory ApparatusMaria Kristelle Alejandro PaltaoNo ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument10 pagesApparatusJohann Darnley100% (1)
- Maintaining Accuracy and PrecisionDocument6 pagesMaintaining Accuracy and PrecisionAkshit ParmarNo ratings yet
- KumiDocument29 pagesKumimonike07No ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusesDocument4 pagesLaboratory ApparatusesBlake MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument44 pagesLaboratory ApparatusJerneth Nyka FloresNo ratings yet
- Lab EquipmentsDocument10 pagesLab Equipmentschouroukbelkacemi236No ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Mysteries, Fun Laboratory Tools! Chemistry for Kids - Children's Analytic Chemistry BooksFrom EverandChemistry Lab Mysteries, Fun Laboratory Tools! Chemistry for Kids - Children's Analytic Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Stress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8From EverandStress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8No ratings yet
- Sample Containers For Gamma SpectometryDocument8 pagesSample Containers For Gamma SpectometrySilver BlazeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory: Group 1Document51 pagesChemistry Laboratory: Group 1Rachel Ann De LeonNo ratings yet
- Thomaplast I (English)Document116 pagesThomaplast I (English)Reichelt ChemietechnikNo ratings yet
- Sodium MetabisulphiteDocument2 pagesSodium MetabisulphiteImran AnwarNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment Lab Equipment: Keep Our Lab AreaDocument10 pagesLab Equipment Lab Equipment: Keep Our Lab AreaPaul Doronila100% (1)
- Temperature Change in Solid X and y With Aluminum FoilDocument4 pagesTemperature Change in Solid X and y With Aluminum Foilapi-345353769No ratings yet
- Using A Bunsen Burner Air Hole Position Colour of FlameDocument2 pagesUsing A Bunsen Burner Air Hole Position Colour of FlameoscarbecNo ratings yet
- MK-09 Packing ListDocument7 pagesMK-09 Packing ListShureendran Muniandy RajanNo ratings yet
- Thickness and Density of Sprayed Fire-Resistive Material (SFRM) Applied To Structural MembersDocument5 pagesThickness and Density of Sprayed Fire-Resistive Material (SFRM) Applied To Structural MembersBeymerBustamanteMejía100% (2)
- Laboratory Equipment and Skills: Recognizing Lab EquipmentDocument2 pagesLaboratory Equipment and Skills: Recognizing Lab EquipmentDinesh ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment Powerpoint 1Document50 pagesLab Equipment Powerpoint 1Dylan Brhyce Esparagoza100% (1)
- Softening PointDocument8 pagesSoftening PointMauricio CruzNo ratings yet
- 942 15Document1 page942 15Gia Trish100% (2)
- Lab Report 1Document4 pagesLab Report 1AntonCrowley6660% (1)
- Common Laboratory EquipmentDocument5 pagesCommon Laboratory EquipmentTobey Arevalo PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- PM IS 8887 cmd2Document9 pagesPM IS 8887 cmd2Anurag ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Chief Chemical EngineerDocument4 pagesChief Chemical EngineerMario KonsachristianNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Equipment ListDocument15 pagesLaboratory Equipment Listdeepak925No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument9 pagesChemistryJessamyn DimalibotNo ratings yet
- Heat Number in MilkDocument17 pagesHeat Number in MilkLaura MarcelaNo ratings yet
- Penyediaan Larutan KimiaDocument11 pagesPenyediaan Larutan KimiaIna InaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Chemistry 10 - 7Document4 pagesLab Report Chemistry 10 - 7api-256986280No ratings yet
- Corning QuideDocument141 pagesCorning Quidepacho916No ratings yet
- End User: Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia: NO Category Items Specifications BrandDocument50 pagesEnd User: Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia: NO Category Items Specifications BrandwarieNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety and EquipmentDocument33 pagesLab Safety and EquipmentGábor PatakiNo ratings yet
- Buyers GuideDocument32 pagesBuyers GuideFord cellNo ratings yet
- Schott GlassDocument48 pagesSchott GlassmickstaNo ratings yet
- Fisher Scientific Catalogue 2018Document240 pagesFisher Scientific Catalogue 2018morton1472No ratings yet
- Physical Chem 1 (Combined)Document35 pagesPhysical Chem 1 (Combined)Yit JuanNo ratings yet
- Glassware CalibrationDocument2 pagesGlassware CalibrationRoger ManzanarezNo ratings yet