Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics
Uploaded by
ashrafraziCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics
Uploaded by
ashrafraziCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics 2204 Multiple Choice Questions for Review Work and Power: 1.
If youre trying to find work on an angle you must find the _________ of the angle? a) Tan b) Sec c) Sin d) Cos 2. If Goku sprints and tackles a large metal crate doing 18002 J of work over the course of 2 secs, what is his power level? a) 4500 watts b) 36004 watts c) 9001 watts d) <9000 watts 3. Which of the following situations doesnt have any work done? a) A truck pulling a trailer along the road b) A waiter carrying a tray to a table c) A soccer player kicks a ball across the field d) A bodybuilder lifts a barbell above his head 4. If you increase the distance you move an object would happen to the power? a) It would increase b) It would decrease c) It would not change d) There will only be a change in work 5. A 5.00 Kg block is moved 5.00m using 70.0J of work. What net force is acting against the block, if the coefficient of friction is 0.15? a) 6.06 b) 6.006N c) 0.60N d) 6.60N D C BAD 1. How much work is done to move a 100.0 kg box 5.00m? a)500J b) 5.00 X 102 J c)50J d)250. J 2. Power is defined as. a) The rate at which work is done c) To push someone a given distance b) The strength of a person d) The ability to do work
3. 5N of force is being applied to an object, but the object does not move. How much work is being done? a)5J b)0.5J c) 0W d)no work is being done, 0J 4. A force of 60.0N [30o N of W] is being applied to an object travelling at a constant speed [W] over 50.0m. How much work is being done?
a)2.60X103J c)3000J
b) 2.61X102J d)2.60J
5. A 324-kg piano slides 5.16 m down a 30 deg incline and is kept from accelerating by a man who is pushing back on it parallel to the incline. The effective coefficient of friction is 0.40.Find the work done by gravity. a) 8192.016J c) 9000J b) 8190J d) 8100J
Kinetic and Potential Energy: 1. What is the formula for gravitational potential energy? a. GPe= mgh b. Gpe=mv2 c. Gpe=abc d. Gpe=mg-h 2. What does V stand for in the equation KE= (MV^2)/2 a. Height b. Volts c. Velocity d. Power 3. If an object that had a mass of 15.0kg and is 20.0m above the earth, whats its gravitational potential energy? a. 2940N b. 2940J c. 2.940J d. 29.40J 4. A very fast bullet has a mass of 2.0g and its kinetic energy is 2000.J while it flies through the air, what is its velocity? a. 1400 m/s b. 1400 m/s^2 c. 1420 m/s d. 1400 n/m 5. A roller coaster at an amusement park begins at its highest peak at 100.m. The mass of the roller coaster is 200.kg. In the middle of the ride when the roller coaster is at 40.0m above the earth what is the coasters velocity? a. 34.3m/s c. 647 m/s b. 34.0m/s d. 71.0m/s Answers A, C, B, A, A. 1. When is an objects gravitational energy equal to zero? a. h=42 b. h=67 c. m=10 d. h=0 2. What happens to the kinetic energy of an object if the velocity is quadrupled? a. 4 times more. b. 16times. c. 8 times. d. 24 times. 3. A box moving across a frictionless surface has 35J of kinetic energy and a velocity of 1.5m/s, what is its mass? a. 40kg. b. 2.6kg c. 31kg. d. 31.1kg
4. A soccer ball rolls off a shelf that is 4.0m high. When it bounces it retains 65% of its energy. How high will it reach after the first bounce? a. 2.6m b. 2.4m c. 41m d. 3.0m 5. In the circus a person with a mass of 67kg is fired out of a cannon, using a spring. The spring has a spring constant of 5.0*104n/m. The spring is compressed 1.2m how high does the clown fly? a. 47m b. 109999m c.6789m d. 55m
Hookes Law and Simple Harmonic Motion 1. A mass is hung from a spring with a spring constant of 120 N/m, and displaces 21cm. What is the elastic potential energy of the spring. a. 2.65 J b. 3.65J c. 1512J d. 26500J 2. If the displacement of a spring (x) is doubled, how much would its potential energy change? a. It would not change b. it would increase 4x c. it would increase 2x d. it would decrease 2x 3. If a mass of 400g is hanged from a spring with a spring constant of 30 N/m, how far will it stretch? a. 15cm b. 13cm c. 14cm d. 15m 4. Does a spring which is not in its elastic region obey Hookes law? a. Depends on the spring b. Yes c. No d. Only if a mass is hung 5. A 1m high spring that is standing up has a mass of 100g dropped on it from a height of 3m. The spring has a spring constant of 90 N/m. How far will the spring compress? a. 1m b. 10cm c. .65m d. 50 cm answer key: a b b c c. 1. What does Simple Harmonic Motion describe? a) The oscillations of springs and their tendency to return to the equilibrium point. b) The linear relationships of springs in the inelastic region. c) The friction acting on springs in the absence of air. d) That there are powerful forces working on springs at the equilibrium point.
2. In 1660, who discovered Hookes Law and what did it describe? a) Roger Hooke. It describes the property of a material to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically and then, upon unloading to have this energy recovered. b) Harry Hooke. It describes the deformation of a material undergoing non-reversible changes of shape in response to applied forces. c) Robert Hooke. It describes the property of springs that causes them to return to the equilibrium point in the absence of friction. d) John Needham. It describes the relationship between springs and their stretch. 3. According to Hookes Law to find k (k=F/x), if x is doubled how is k affected? a) Quadrupled b) Doubled c) One Half d) One Quarter 4) What is the relationship of springs in the inelastic region? a) F=kx b) F=ma c) k=F/x d) None of the above. 5) In F=kx, what is x? a) The displacement of the springs top from its end. b) The displacement of the springs end from its equilibrium position. c) The distance the mass at the end of the spring travels. d) None of the above. 1)a 2)c 3)c 4)d 5)b
Law of Conservation of Energy: 1. What is the Work-Energy Theorem? a) Force = Mass x Acceleration b) KE = mv2 c) Work = Ek d) Power = Work Time 2. How is Efficiency found? a) Finding the Useful Output Energy. b) Finding the Total Input Energy. c) (Useful Output Energy Total Input Energy) x 100% d) (Total Input Energy x Useful Output Energy) x 100% 3. What is the Efficiency of a Crane the uses 6.00x105 J of Energy, to lift 500.0 kg a vertical distance of 20.0 m? a) 60.3% b) 45.93% c) 17.36% d) 16.3% 4. What is the Total Mechanical Energy of a 1000.0 kg rollercoaster traveling at 10.0 m/s with a height of 6.0 m? a) 108 800 J b) 96 000 J c) 100 101 J d) 108 600 J 5. A kitten of mass 240 g is moving through the air at 20.0 m/s, with a GPE of 70 J, with what speed will the kitten hit the ground? a) 30.0 m/s b) 31.4 m/s c) 20.5 m/s d) 32.0 m/s Answer Key 1: 1. c) 2. c) 3. d) 4. a) 5. b)
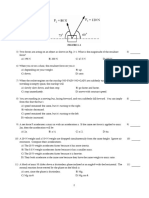
Which of the following statements is TRUE: a) The total energy of a closed system never stays the same b) Energy cannot be created or destroyed c) The form/type of energy can never change d) Energy can be created Which one of the following is an example o f a non-conservative force? A) Elastic spring force B) Electrical force C) Kinetic frictional force D) Gravitational force A roller coaster car with a mass of 265.3 kg starts from a height of 114.9 meters above the ground just before rolling down the frictionless track. Using conservation of energy, find the speed of the car just as it reaches the ground. a) b) C) d) A ball of mass 0.50 kg is tossed upward into the air. When it leaves your hand, it has a kinetic energy of 138 Joules. How high do the ball go. (Ignore air resistance) a)28m b)30m c)25m d)27m
You might also like
- Unit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsDocument57 pagesUnit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsLissa Hannah100% (1)
- Physics Lesson 2 MCQ - AnsDocument5 pagesPhysics Lesson 2 MCQ - AnsUma SundarNo ratings yet
- Midterm Spring 09Document3 pagesMidterm Spring 09rubel_lincNo ratings yet
- FWM Prefinals 2023Document5 pagesFWM Prefinals 2023kumarardash86No ratings yet
- Physics Practice Problems: Work and EnergyDocument5 pagesPhysics Practice Problems: Work and EnergysaparullahNo ratings yet
- Student's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Document2 pagesStudent's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Nam Anh Nguyễn HữuNo ratings yet
- Test 07 Energy 05dkDocument13 pagesTest 07 Energy 05dkLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Physics Test PrepDocument4 pagesPhysics Test PrepEhsan ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Chapter#6Document11 pagesQuestion Bank For Chapter#6krishnam rajuNo ratings yet
- Physics Test Bank For Grade 8Document12 pagesPhysics Test Bank For Grade 8Jeff SuarezNo ratings yet
- WORK ENERGY AND POWER NEET questionsDocument3 pagesWORK ENERGY AND POWER NEET questionsGanesh MogaveeraNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS XI WORK, POWER & ENERGY CHAPTER REVIEWDocument1 pagePHYSICS XI WORK, POWER & ENERGY CHAPTER REVIEWraffia mahakNo ratings yet
- TB Chapter5Document18 pagesTB Chapter5Jerry HuntNo ratings yet
- Gravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeDocument11 pagesGravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeJohnNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPhysics Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsRachel Du PreezNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Document13 pagesWork and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Mansoor Al TunijiNo ratings yet
- Force, Motion and EnergyDocument18 pagesForce, Motion and EnergyTushitaNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section, All Question Carry Equal MarksDocument4 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section, All Question Carry Equal Markssulayajanny100% (1)
- Chapter (1) Revision QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter (1) Revision Questionssosoayman484No ratings yet
- 4th Unit McqsDocument33 pages4th Unit McqsManav LekhiNo ratings yet
- Ex3mech 2019Document8 pagesEx3mech 2019Nasim RazaviNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Pre Annual Physics Set 1 QPDocument8 pagesClass 11 Pre Annual Physics Set 1 QPSanjukta ChandaNo ratings yet
- (Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education) : General InstructionsDocument24 pages(Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education) : General Instructionsdeetchu10No ratings yet
- Work - Energy - PowerDocument9 pagesWork - Energy - PowermaryNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument20 pagesPhysicsAnthony HugillNo ratings yet
- Class X Unit 1 AKDocument6 pagesClass X Unit 1 AKAshaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11Document9 pagesPhysics 11NasimaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems for Test #2 Chapters 5-8 PhysicsDocument3 pagesPractice Problems for Test #2 Chapters 5-8 PhysicsAntoine S. NdiayeNo ratings yet
- Army Public School and College Khanewal: Schedule Test 2 (CHP 3 & 4)Document2 pagesArmy Public School and College Khanewal: Schedule Test 2 (CHP 3 & 4)Muhammad sajjadNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws and Momentum Reading QuizDocument58 pagesNewton's Laws and Momentum Reading QuizAltammar13No ratings yet
- Mechanical Advantage For Inclined PlaneDocument25 pagesMechanical Advantage For Inclined PlaneJune AlapaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Practice ExercisesDocument4 pagesAP Physics 1 Practice Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Gaurav Burhade's Mechanics Problems and SolutionsDocument14 pagesGaurav Burhade's Mechanics Problems and SolutionsmansikakaniNo ratings yet
- Question Bank MCQ AnswersDocument15 pagesQuestion Bank MCQ AnswersPriyeshNo ratings yet
- The Energy Stored in Coal IsDocument2 pagesThe Energy Stored in Coal IsNayab seharNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetDocument9 pagesAP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetEAGLEFORCE06No ratings yet
- Work, Power and Energy Worksheet SolvedDocument3 pagesWork, Power and Energy Worksheet SolvedKobiXDNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Practice Test 2Document18 pagesAP Physics 1 Practice Test 2John BoswellNo ratings yet
- Question 412291Document8 pagesQuestion 412291Nikhil PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Engg Mech Unit 3Document4 pagesEngg Mech Unit 3Piyush BhandariNo ratings yet
- Intro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixADocument63 pagesIntro Physics Instructors Guide Semester1 AppendixAGfour Maserati50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Test QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Test QuestionsBestswimmer2011No ratings yet
- ch.3,4,5 2 7Document6 pagesch.3,4,5 2 7qwesghwqedfgNo ratings yet
- Work SheetDocument3 pagesWork SheetMikî Mań0% (1)
- SCI Second Exam 101BDocument3 pagesSCI Second Exam 101BSalma MohamedNo ratings yet
- Review ProblemsDocument2 pagesReview ProblemsLương Thị Quỳnh PhượngNo ratings yet
- Work Power EnergyDocument9 pagesWork Power EnergySawthang RaiNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 2 PDFDocument8 pagesPractice Exam 2 PDFDavid WeitzelNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Review 2Document11 pagesDiagnostic Exam Review 2France Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument10 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionAlejandro Torrico MorenoNo ratings yet
- PHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesPHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsAaisha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 3 Practice Test Dynamics5Document5 pagesPhysics Unit 3 Practice Test Dynamics5StephanieNo ratings yet
- 11TH Physics Model QPDocument3 pages11TH Physics Model QPermaharajanNo ratings yet
- Phys2325 Final Exam Ch10-16Document4 pagesPhys2325 Final Exam Ch10-16schelankoNo ratings yet
- NCERT Physics Class XI Question PaperDocument7 pagesNCERT Physics Class XI Question PaperRachel SmithNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tones and Styles AparnaDocument7 pagesTones and Styles Aparnaapi-3854593No ratings yet
- Solar PV Power Plant: - Dr. Rohit Verma - National Power Training Institute - Sector-33, FaridabadDocument120 pagesSolar PV Power Plant: - Dr. Rohit Verma - National Power Training Institute - Sector-33, FaridabadashrafraziNo ratings yet
- GraphTricks PDFDocument8 pagesGraphTricks PDFashrafraziNo ratings yet
- On Testingof CTDocument19 pagesOn Testingof CTashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems 4Th Edition Simon Haykin With Solutions ManualDocument1,397 pagesCommunication Systems 4Th Edition Simon Haykin With Solutions ManualTayyab Naseer100% (3)
- Xam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Document419 pagesXam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Mohammed Farhad77% (13)
- Designing of PV 2Document55 pagesDesigning of PV 2ashrafrazi100% (1)
- On Testingof CTDocument19 pagesOn Testingof CTashrafraziNo ratings yet
- AC PPT Power Sector ReformsDocument56 pagesAC PPT Power Sector ReformsashrafraziNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument66 pagesCapacitorsashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Module 10: Differential Protection of Bus, Transformer and Generator: Transformer ProtectionDocument11 pagesModule 10: Differential Protection of Bus, Transformer and Generator: Transformer ProtectionNithin Kumar K SNo ratings yet
- I.C EngineDocument18 pagesI.C EngineashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Isomerism Coordination ChemistryDocument9 pagesIsomerism Coordination ChemistryLala NurfalahNo ratings yet
- Gauss'S Law: Chapter - 30Document6 pagesGauss'S Law: Chapter - 30rajpersonalNo ratings yet
- Single Page Integral Table PDFDocument2 pagesSingle Page Integral Table PDFMehmet Helva100% (2)
- Faraday"s LawDocument12 pagesFaraday"s LawashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Gauss's LawDocument14 pagesGauss's LawashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument15 pagesAlternating CurrentashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Single Page Integral Table PDFDocument2 pagesSingle Page Integral Table PDFMehmet Helva100% (2)
- Ch02 AtomicNucleusDocument8 pagesCh02 AtomicNucleusPrichindel MorocanosNo ratings yet
- E.M WavesDocument22 pagesE.M WavesashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundDocument17 pagesCoordination CompoundRohit Mehta0% (1)
- Kinetics PDFDocument22 pagesKinetics PDFPallab MallickNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eiaght - Chemical EquiDocument33 pagesChapter Eiaght - Chemical EquiAhmed Saeed100% (2)
- Solid State PhysicsDocument86 pagesSolid State Physicsshima1987No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsashrafraziNo ratings yet
- 16506physics Set B 17Document5 pages16506physics Set B 17ashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SlidesDocument99 pagesChemistry Slideswjohnson_3No ratings yet
- 2013 SP 12 Chemistry 06Document6 pages2013 SP 12 Chemistry 06ashrafraziNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Free Body DiagramDocument10 pagesFree Body Diagramjames arajaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS TUTORIALDocument22 pagesPHYSICS TUTORIALAten AzharNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Advantage of Inclined PlaneDocument4 pagesMechanical Advantage of Inclined PlaneShuja MarwatNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Simple MachinesDocument2 pagesIntroduction to Simple MachinesAaron Hoback100% (2)
- Unit 7. MachinesDocument8 pagesUnit 7. MachinesCasajardinmania JaenNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Question. (5% Each)Document6 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Question. (5% Each)Crayon0401No ratings yet
- Helping Mr. Cruz move a refrigerator with simple machinesDocument1 pageHelping Mr. Cruz move a refrigerator with simple machinesJoanna Marie VillamarNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1-Engineering StaticsDocument5 pagesLab Report 1-Engineering StaticsAndhika UtamaNo ratings yet
- Algodoo LessonsDocument30 pagesAlgodoo LessonsMickey HD100% (2)
- Physics 40a Final Exam ReviewDocument4 pagesPhysics 40a Final Exam ReviewRexRu100% (1)
- 2005 May Paper 2Document12 pages2005 May Paper 2Hubbak Khan100% (7)
- Adxl : Instruction ManualDocument24 pagesAdxl : Instruction ManualAnonymous tkrhtNfsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 7Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 7Swarnava SanyalNo ratings yet
- Linde Operator Manual (3538043001) 353-02D H50 Through H80-900 0303-US (353 - 02 - 0702gb)Document130 pagesLinde Operator Manual (3538043001) 353-02D H50 Through H80-900 0303-US (353 - 02 - 0702gb)Rat Sorina50% (6)
- PhysicsDocument46 pagesPhysicsGian Peñaflor67% (3)
- 3rd Quarter LAS in Science 6Document4 pages3rd Quarter LAS in Science 6Michael Edward De VillaNo ratings yet
- Md2 Plates No 4 Wire RopesDocument1 pageMd2 Plates No 4 Wire RopesDaniel Tanus MararangNo ratings yet
- Mechanics (ALL)Document146 pagesMechanics (ALL)P1koNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 Friction - Solutions PDFDocument9 pagesTutorial 4 Friction - Solutions PDFBharat SaiNo ratings yet
- 4 Chapter PDFDocument8 pages4 Chapter PDFSouryadipta MajumdarNo ratings yet
- FRICTION FORCES AND EQUILIBRIUMDocument18 pagesFRICTION FORCES AND EQUILIBRIUMPriyankaMishraNo ratings yet
- Science Law-Q3-Week-5-6-7Document6 pagesScience Law-Q3-Week-5-6-7Prince Jallie Bien GuraNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Gravity Power GenerationDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Gravity Power Generationpuzolunyzyg2100% (1)
- (Antim Yudh) - Namo Sir - 22febDocument55 pages(Antim Yudh) - Namo Sir - 22febNamo KaulNo ratings yet
- m1 Dynamics Connected ParticlesDocument17 pagesm1 Dynamics Connected ParticlesAjmalMansoorNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of Energy - KeyDocument7 pagesLaw of Conservation of Energy - KeyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Air TrackDocument9 pagesAir TrackSara MorsiNo ratings yet
- Advance Staad by SarojDocument90 pagesAdvance Staad by SarojSAROJ BISWAS100% (3)
- Sub Code: ME8292 Sub Name: Engineering Mechanics Max - Marks:100 Duration: 3 Hrs Branch: Mechanical Engg. Year/Sem: I / II Answer All QuestionsDocument3 pagesSub Code: ME8292 Sub Name: Engineering Mechanics Max - Marks:100 Duration: 3 Hrs Branch: Mechanical Engg. Year/Sem: I / II Answer All QuestionssivashanmugamNo ratings yet