Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chilgoza pine nuts: Nutrient-rich Himalayan nuts
Uploaded by
munna777Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chilgoza pine nuts: Nutrient-rich Himalayan nuts
Uploaded by
munna777Copyright:
Available Formats
.
Chilgoza pine nuts and kernels.
Chilgoza pine nuts (Pinus gerardiana) is another distinct pine variety found in western Himalayan forests of Pakistan, India (Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh), and Afghanistan. Chilgoza pines have similar appearance as stone pines; featuring long slender, pointed kernels.
Health benefits of pine nuts Pine nuts are one of the calorie-rich edible nuts. 100 g of dry-kernels provide 673 calories. Additionally, they comprise of numerous health promoting phyto-chemicals, vitamins, antioxidants, and minerals. Their high caloric content chiefly comes from fats. Indeed, the nuts, especially rich in monounsaturated fatty acids like oleic acid (18:1 undifferentiated fat) that helps to lower LDL or "bad cholesterol" and increases HDL or "good-cholesterol" in the blood. Research studies suggest that Mediterranean diet, which contain good amounts of monounsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and antioxidants, helps to prevent coronary artery disease and strokes by favoring healthy blood lipid profile. Pine or cedar nuts contain essential fatty acid ( -6 fat), pinolenic acid. Recent research has shown its potential use in weight loss by curbing the appetite. Pinolenic acid triggers the release of hunger-suppressant enzymes cholecystokinin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the gut. In addition, pinolenic acid was thought to have LDL-lowering properties by enhancing hepatic LDL uptake. Like almonds, pines are an excellent source of vitamin E; contain about 9.33 mg per 100 g (about 62% of RDA). Vitamin E is a powerful lipid soluble antioxidant, required for maintaining the
integrity of cell membrane of mucus membranes and skin by protecting it from harmful oxygenfree radicals. Furthermore, like almonds and peanuts,pines too are free from gluten and therefore, are a popular ingredient in the preparation of gluten-free food formulas. Such formula preparations are, in fact, healthy alternatives in people with wheat food allergy and celiac disease. Pine nuts are an excellent source of B-complex group of vitamins such as thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, vitamin B-6 (pyridoxine) and folates. These vitamins work as co-factors for enzymes in cellular substrate metabolism inside the human body. Furthermore, pine nuts contain healthy amounts of essential minerals like manganese, potassium, calcium, iron, magnesium, zinc and selenium. At 8.802 mg per 100 g (about 383% of daily recommended intake), pines are one of the richest sources of manganese. Manganese is an all-important co-factor for antioxidant enzyme, superoxide dismutase. It is therefore, consumption of pines helps the body develop resistance against infectious agents and scavenge harmful oxygen-free radicals.
Pine nut oil has a delicate flavor with sweet aroma and is used in many traditional medicinal applications since ancient times. The main chemical components in pine oil are borneol, bornyl acetate, and -
phellandrene, -pinene and -pinene. Its emollient property helps to keep skin well protected from
dryness. It has also been used in cooking, and as carrier or base oil in traditional medicines in aromatherapy, in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry.
See the table below for in depth analysis of nutrients: Pine nuts, raw, Nutritional value per 100 g. (Source: USDA National Nutrient data base) Principle Nutrient Percentage Value of RDA
Energy Carbohydrates Protein Total Fat Cholesterol Dietary Fiber Vitamins Folates Niacin Pantothenic acid Pyridoxine
673 Kcal 34% 13.08 g 13.69 g 68.37 g 0 mg 3.7 g 10% 24% 228% 0% 10%
34 g 4.387 mg 0.313 mg 0.094 mg 0.227 mg 0.364 mg 29 IU 0.8 mg
9% 27%
6%
7%
Riboflavin
17%
Thiamin Vitamin A Vitamin C Vitamin E Electrolytes Sodium Potassium Minerals Calcium Copper Iron Magnesium Manganese
30% 1% 1%
9.33 mg 62%
2 mg 597 mg
0% 13%
16 mg 1.324 mg
1.5% 147%
5.53 mg 69% 251 mg 8.802 63% 383%
mg Phosphorus Selenium Zinc Phyto-nutrients Carotene- Crypto-xanthin Luteinzeaxanthin 17 g 0 g --575 mg 0.7 g 82% 1%
6.45 mg 58%
9 g
--
Selection and storage In the wild, fallen seeds are generally gathered beneath the trees. In the markets, one may find shelled as well as unshelled pine nuts displayed for sale. When you are buying whole, unshelled nuts, look at the nuts that feature bright brown color; compact and uniform in size, and feel heavy in hand and feature good metallic sound when poured down from a height. They should be free from cracks, mold, and spots and of rancid smell. Shelled and processed kernels are also put for sale in air-tight plastic bags in the stores. Always try to buy fresh nuts from authentic sources. Unshelled nuts have long shelf life and can be stored for many months. Shelled kernels deteriorate soon if exposed to warm, humid conditions. Therefore, store shelled nuts in airtight jars and store in the refrigerator.
Preparation and serving methods Raw whole pinon nuts are generally cut open at processing units using larger sheller machines. Smaller nut sheller equipment or hand held pliers usually are being used for domestic uses. Raw, whole pignoli nuts are generally broken open at the processing units using larger sheller machines. Smaller nut-sheller equipment or hand held pliers usually are being used for domestic uses. Here are some serving tips:
Pine nut cookie. Photo courtesy: Greencolander. Siberian pines generally enjoyed as they are. Additionally, they are also eaten roasted, salted or sweetened. They also used in granolas, biscuits, cookies, chocolates and crunch bar preparations. The nuts also used in salads especially sprinkled over fruit/vegetable salads. Pinon nuts are used in desserts, particularly sundaes and other ice cream based recipes. They feature frequently in meat, fish, and vegetable dishes. Pine nut oil is used in salad dressing and in cooking.
You might also like
- Protein Fats: Arizona Center For Integrative Medicine The University of ArizonaDocument2 pagesProtein Fats: Arizona Center For Integrative Medicine The University of ArizonaIN73% (15)
- Health & Food - UpdatedDocument11 pagesHealth & Food - Updatedecuamantis1No ratings yet
- Nutritional Values: Fat LossDocument19 pagesNutritional Values: Fat LossIvie de ClaroNo ratings yet
- The 28 All-Time Best Healing FoodsDocument64 pagesThe 28 All-Time Best Healing FoodsMardz100% (2)
- Amaranth - A Superfood Everyone Should Start StockDocument17 pagesAmaranth - A Superfood Everyone Should Start StockLes BennettNo ratings yet
- The Miracle of Nuts, Seeds and Grains: The Scientific Facts About Nutritional Properties and Medicinal Values of Nuts, Seeds and GrainsFrom EverandThe Miracle of Nuts, Seeds and Grains: The Scientific Facts About Nutritional Properties and Medicinal Values of Nuts, Seeds and GrainsNo ratings yet
- Vitamin ChartDocument5 pagesVitamin ChartHimNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 (Part-1) Nutraceuticals: B. Pharm 6 SemDocument49 pagesUnit-2 (Part-1) Nutraceuticals: B. Pharm 6 SemMamta Pant67% (3)
- Vox Latina The Pronunciation of Classical LatinDocument145 pagesVox Latina The Pronunciation of Classical Latinyanmaes100% (4)
- Express VPN Activation CodeDocument5 pagesExpress VPN Activation CodeButler49JuulNo ratings yet
- Detox Diet Book: The Detox Diet Guide for Detoxing for Health. Detox Cleanse for your Optimum Detoxification HealthFrom EverandDetox Diet Book: The Detox Diet Guide for Detoxing for Health. Detox Cleanse for your Optimum Detoxification HealthRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
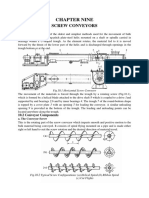
- Chapter 9 Screw ConveyorsDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Screw ConveyorsMarew Getie100% (1)
- P-H Agua PDFDocument1 pageP-H Agua PDFSarah B. LopesNo ratings yet
- ASTRO UserguideDocument1,054 pagesASTRO UserguideMarwan Ahmed100% (1)
- Chanukyuni ArthasastramDocument308 pagesChanukyuni Arthasastramebookks.blogspot.com100% (2)
- Boost Your Immunity with a Nutritious Diet and LifestyleDocument46 pagesBoost Your Immunity with a Nutritious Diet and Lifestylekcnit training100% (1)
- What Bananas Do To Your Body 0317Document21 pagesWhat Bananas Do To Your Body 0317Jawad KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Ambree's Meatless Patty: A Healthier AlternativeDocument9 pagesAmbree's Meatless Patty: A Healthier AlternativedalDALYNNo ratings yet
- Experience NutriliteDocument319 pagesExperience NutriliteNieRy FreelancerNo ratings yet
- Audit AP TestsDocument3 pagesAudit AP TestsSweet Emme100% (1)
- Final Reflective Essay by Georgi ShopovDocument7 pagesFinal Reflective Essay by Georgi ShopovMd Siddique UllahNo ratings yet
- Dates Nutrition FactsDocument9 pagesDates Nutrition FactsmaduraiicNo ratings yet
- COCOWAXDocument54 pagesCOCOWAXMark TomenesNo ratings yet
- 1989 Volvo 740 Instruments and ControlsDocument107 pages1989 Volvo 740 Instruments and Controlsskyliner538No ratings yet
- SOF IEO Sample Paper Class 4Document2 pagesSOF IEO Sample Paper Class 4Rajesh RNo ratings yet
- Peanuts Nutrition FactsDocument4 pagesPeanuts Nutrition Factspepz funnelNo ratings yet
- Eat Better Think Better Enjoy Better Live Better: Organo Snacks & Cereal IndustriesDocument4 pagesEat Better Think Better Enjoy Better Live Better: Organo Snacks & Cereal IndustriesKishor PariharNo ratings yet
- Ingredients BenifitsDocument18 pagesIngredients BenifitsManjit VishalNo ratings yet
- Health and Fitness DR Anna ChellappaDocument94 pagesHealth and Fitness DR Anna Chellappasjo05No ratings yet
- Benefits of SapotaDocument6 pagesBenefits of SapotaSukku DheevaNo ratings yet
- Watermelon Project by Gopi Kasi-1Document13 pagesWatermelon Project by Gopi Kasi-1Kasirao MScNo ratings yet
- Nuts - Printable Detailed Summary - 0Document6 pagesNuts - Printable Detailed Summary - 05ynicNo ratings yet
- Turmeric Nutrition FactsDocument40 pagesTurmeric Nutrition FactsUdhaya KumarNo ratings yet
- SoybeanDocument3 pagesSoybeandandy nhNo ratings yet
- Go Nuts Go Healthy: International Nut and Dried Fruit FoundationDocument12 pagesGo Nuts Go Healthy: International Nut and Dried Fruit FoundationfxpmtraderNo ratings yet
- Medical News TodayDocument13 pagesMedical News TodayremusgramaNo ratings yet
- Nutrients in Banana PeelsDocument4 pagesNutrients in Banana PeelsShanine Faye BacsainNo ratings yet
- BING KelompokDocument30 pagesBING KelompokMF17No ratings yet
- Medicinal HerbsDocument15 pagesMedicinal Herbsjoatham octavioNo ratings yet
- Nutritive ValueDocument25 pagesNutritive Valuedhruvamishra100% (2)
- Fruits Processing Preservation Recipes PDFDocument20 pagesFruits Processing Preservation Recipes PDFGourav TailorNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Sun Flower SeedsDocument20 pagesBenefits of Sun Flower SeedsMohd Idris MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A: Sweet Potatoes 28,000 International UnitsDocument14 pagesVitamin A: Sweet Potatoes 28,000 International UnitsTina Avergonzado AmbaNo ratings yet
- Grapefruit: Name: Grapefruit Scientific Name: Citrus Paradisi Family: RutaceaeDocument20 pagesGrapefruit: Name: Grapefruit Scientific Name: Citrus Paradisi Family: Rutaceae12tribeNo ratings yet
- 9 Evidence-Based Health Benefits of AlmondsDocument4 pages9 Evidence-Based Health Benefits of AlmondsMaria TahreemNo ratings yet
- Principles of Normal Nutrition: Santiago T.K. de Leon, Jr. RND, MAHED, PSM-FPMDocument56 pagesPrinciples of Normal Nutrition: Santiago T.K. de Leon, Jr. RND, MAHED, PSM-FPMAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- My Plate (Plan Meal) 2021Document18 pagesMy Plate (Plan Meal) 2021Jastine Miguel EGUIANo ratings yet
- Cancer20201206 Bonus Answer To Cancer DR Nalini Chilkov Anti Cancer Checklist Notes 4pages ICA+Fullscript+Bundles+and+Diet+Checklist+v1Document4 pagesCancer20201206 Bonus Answer To Cancer DR Nalini Chilkov Anti Cancer Checklist Notes 4pages ICA+Fullscript+Bundles+and+Diet+Checklist+v1AgnesNo ratings yet
- NutraceuticalDocument32 pagesNutraceuticalMayank Tandon100% (4)
- 1st Clinical PostingDocument109 pages1st Clinical PostingThyroxine AchieverNo ratings yet
- C 4 StafflessonplanDocument3 pagesC 4 Stafflessonplanapi-515538459No ratings yet
- Espinosa, Kristine M. Bsn-IDocument5 pagesEspinosa, Kristine M. Bsn-ICamille EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Wellness Newsletter Fall 2013Document7 pagesWellness Newsletter Fall 2013lrbrennanNo ratings yet
- Fruits, Benefits, Processing, Preservation and Pineapple RecipesDocument21 pagesFruits, Benefits, Processing, Preservation and Pineapple RecipesMARIANELLA ASTUDILLO GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Detoxify For Healthy LivingDocument15 pagesDetoxify For Healthy LivingUmesh SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Nutraceuticals: Let Food Be Your MedicineDocument34 pagesNutraceuticals: Let Food Be Your MedicinesivaNo ratings yet
- All Product Handbook EnglishDocument21 pagesAll Product Handbook EnglishAnnapoorani ManiNo ratings yet
- Healthy Balanced DietDocument5 pagesHealthy Balanced DietBao HuiiNo ratings yet
- Food PyramidDocument9 pagesFood PyramidMEN'S ARENANo ratings yet
- All ProductTraning Guide - EnglishDocument44 pagesAll ProductTraning Guide - EnglishSunil Sharma75% (4)
- Nutraceutical IntoductionDocument34 pagesNutraceutical IntoductionAjeet Kumar100% (1)
- Plant Based Protein SeminarDocument41 pagesPlant Based Protein SeminarRitika ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Concept StatementDocument4 pagesConcept Statementkyla PalugaNo ratings yet
- Cheesy EggDocument13 pagesCheesy EggGetstop SmokingNo ratings yet
- TIens ProductsDocument12 pagesTIens ProductsGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Mindful Nutrition - Food To Eat in AbundanceDocument10 pagesMindful Nutrition - Food To Eat in AbundancePamela SaundersNo ratings yet
- Eating Right For Your DiabetesDocument6 pagesEating Right For Your Diabeteskanishka upadhyayNo ratings yet
- ACES - Malunggay InfoDocument12 pagesACES - Malunggay Infonepp1963No ratings yet
- C. Researching Lipids Peanut Butter: Weight LossDocument4 pagesC. Researching Lipids Peanut Butter: Weight LossAlea PutiNo ratings yet
- Temp ControllerDocument1 pageTemp Controllermunna777No ratings yet
- Chakravarthi AakuDocument1 pageChakravarthi Aakumunna777No ratings yet
- Circular Motion WS1Document1 pageCircular Motion WS1munna777No ratings yet
- RohitDocument2 pagesRohitmunna777No ratings yet
- 6783 - List of Socially and Educationall BackwardClasses NewDocument8 pages6783 - List of Socially and Educationall BackwardClasses Newmunna777No ratings yet
- RohitDocument2 pagesRohitmunna777No ratings yet
- Suresh Raina - Indian CricketerDocument2 pagesSuresh Raina - Indian Cricketermunna777No ratings yet
- 30 Smart Cities CutDocument1 page30 Smart Cities Cutmunna777No ratings yet
- MythalirajDocument1 pageMythalirajmunna777No ratings yet
- Circular Motion WS1 PDFDocument2 pagesCircular Motion WS1 PDFmunna777No ratings yet
- Suresh Raina - Indian CricketerDocument2 pagesSuresh Raina - Indian Cricketermunna777No ratings yet
- Suresh Raina - Indian CricketerDocument2 pagesSuresh Raina - Indian Cricketermunna777No ratings yet
- MythalirajDocument1 pageMythalirajmunna777No ratings yet
- 30 Smart Cities CutDocument1 page30 Smart Cities Cutmunna777No ratings yet
- Sony Camera Manual PDFDocument40 pagesSony Camera Manual PDFmunna777No ratings yet
- BB PlansDocument1 pageBB Plansmunna777No ratings yet
- EBook Create CheyyadamDocument9 pagesEBook Create Cheyyadammunna777No ratings yet
- MythalirajDocument1 pageMythalirajmunna777No ratings yet
- Sunil Varma Is An Indian Actor From The: Telugu Film Industry Comic Relief Filmfare Awards Nandi Awards S. S. RajamouliDocument1 pageSunil Varma Is An Indian Actor From The: Telugu Film Industry Comic Relief Filmfare Awards Nandi Awards S. S. Rajamoulimunna777No ratings yet
- Types of Radioactive Emissions: Alpha, Beta, Gamma & X-RaysDocument2 pagesTypes of Radioactive Emissions: Alpha, Beta, Gamma & X-Raysmunna777No ratings yet
- Rashmi Gautam: Indian actress known for Telugu, Tamil filmsDocument1 pageRashmi Gautam: Indian actress known for Telugu, Tamil filmsmunna777No ratings yet
- Rajinikanth (Born Shivaji Rao Gaekwad 12 December 1950) Is An Indian Film ActorDocument1 pageRajinikanth (Born Shivaji Rao Gaekwad 12 December 1950) Is An Indian Film Actormunna777No ratings yet
- Types of Radioactive Emissions: Alpha, Beta, Gamma & X-RaysDocument2 pagesTypes of Radioactive Emissions: Alpha, Beta, Gamma & X-Raysmunna777No ratings yet
- Telugu Tamil Assistant Director Srinu Vaitla Bapu RJ Filmfare Critics Award For Best Actor - South Bhale Bhale MagadivoyDocument1 pageTelugu Tamil Assistant Director Srinu Vaitla Bapu RJ Filmfare Critics Award For Best Actor - South Bhale Bhale Magadivoymunna777No ratings yet
- Konidela Kalyan Babu (Born 2 September 1971) ,: Akkada Ammayi Ikkada Abbayi Tholi PremaDocument1 pageKonidela Kalyan Babu (Born 2 September 1971) ,: Akkada Ammayi Ikkada Abbayi Tholi Premamunna777No ratings yet
- Konidela Kalyan Babu (Born 2 September 1971) ,: Akkada Ammayi Ikkada Abbayi Tholi PremaDocument1 pageKonidela Kalyan Babu (Born 2 September 1971) ,: Akkada Ammayi Ikkada Abbayi Tholi Premamunna777No ratings yet
- Anushka Shetty Biography - Indian Actress Known for Telugu, Tamil FilmsDocument1 pageAnushka Shetty Biography - Indian Actress Known for Telugu, Tamil Filmsmunna777No ratings yet
- Rajinikanth (Born Shivaji Rao Gaekwad 12 December 1950) Is An Indian Film ActorDocument1 pageRajinikanth (Born Shivaji Rao Gaekwad 12 December 1950) Is An Indian Film Actormunna777No ratings yet
- Anushka SharmaDocument1 pageAnushka Sharmamunna777No ratings yet
- WFP-Remote Household Food Security Survey Brief-Sri Lanka Aug 2022Document18 pagesWFP-Remote Household Food Security Survey Brief-Sri Lanka Aug 2022Adaderana OnlineNo ratings yet
- Duet Embedded Memories and Logic Libraries For TSMC 28HP: HighlightsDocument5 pagesDuet Embedded Memories and Logic Libraries For TSMC 28HP: HighlightsmanojkumarNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 15 06202Document28 pagesSustainability 15 06202Somesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- CEA-2010 by ManishDocument10 pagesCEA-2010 by ManishShishpal Singh NegiNo ratings yet
- CONTACT DETAILS HC JUDGES LIBRARIESDocument4 pagesCONTACT DETAILS HC JUDGES LIBRARIESSHIVAM BHATTACHARYANo ratings yet
- Schedule For Semester III, Class of 2021Document7 pagesSchedule For Semester III, Class of 2021Jay PatelNo ratings yet
- KEC115/6/7x: Ac Generator Short Circuit and Over Current GuardDocument4 pagesKEC115/6/7x: Ac Generator Short Circuit and Over Current GuardRN NNo ratings yet
- Construction Internship ReportDocument8 pagesConstruction Internship ReportDreaminnNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 STS4021 SS VL2019201000258 Reference Material I 11-Jul-2019 CAT1-4021-Integ-AS PDFDocument14 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 STS4021 SS VL2019201000258 Reference Material I 11-Jul-2019 CAT1-4021-Integ-AS PDFjahnavi rajuNo ratings yet
- Ecma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Document2 pagesEcma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Anil JindalNo ratings yet
- Ballari City Corporation: Government of KarnatakaDocument37 pagesBallari City Corporation: Government of KarnatakaManish HbNo ratings yet
- Pakage PAU (Fruits)Document70 pagesPakage PAU (Fruits)Gary Bhullar57% (7)
- DesignWS P1 PDFDocument673 pagesDesignWS P1 PDFcaubehamchoi6328No ratings yet
- Assignment - Stocks and CBDocument2 pagesAssignment - Stocks and CBGhulam HassanNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Computer With Their FunctionsDocument19 pagesParts of A Computer With Their FunctionsJaried SumbaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word Documentshubhangiw17No ratings yet
- Business Law & TaxationDocument3 pagesBusiness Law & TaxationD J Ben UzeeNo ratings yet
- Going to the cinema listening practiceDocument2 pagesGoing to the cinema listening practiceMichael DÍligo Libre100% (1)
- Dxgbvi Abdor Rahim OsmanmrDocument1 pageDxgbvi Abdor Rahim OsmanmrSakhipur TravelsNo ratings yet
- Sles-55605 C071D4C1Document3 pagesSles-55605 C071D4C1rgyasuylmhwkhqckrzNo ratings yet
- Course Code: Hrm353 L1Document26 pagesCourse Code: Hrm353 L1Jaskiran KaurNo ratings yet