Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gig04 6
Uploaded by
LTE002Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gig04 6
Uploaded by
LTE002Copyright:
Available Formats
Website: www.ags-hk.
org
GROUND INVESTIGATION GUIDELINES 04.6 SOFT GROUND TUNNELLING
What do we need to know?
Finalise tunnel alignment Selection of most appropriate tunnelling method Assess the rates of advance Design the permanent lining Assess the affects on buildings, utilities, other tunnels etc Design of temporary works including shafts Information Required Proposed Tunnel Alignment & Access Shaft Locations Geological Model + Potential Geotechnical Hazards + Hydrogeological Profile Source Scheme Plans Field Mapping API Site Reconnaissance Notes: (1) This GIG focuses on soft ground tunnelling. For tunnels comprising rock reference should may be made to GIG 4.4. (2) Investigation of contaminated soils is not covered under this GIG. Notes: (1) As much appropriate information as possible should be obtained and assessed. (2) The geological model should be reviewed and the databases added to as more information is received. Desk study of Geological Maps Existing GI & Geophysics Records Existing building structures sensitive to settlement Existing Utilities Existing Tunnels Existing Mineworkings Existing buried structures (Eg. old sea walls, piles) Site Reconnaissance Desk study of utility records, topographic survey plans, as built records
Appropriate G.I. Methods - Field
What is Required? Develop Geological Model Bedrock level Rock & soil types Layer thickness Weathering profile Overburden thickness Fault zones Investigation of Potential Geological Hazards e.g. Corestones, fault zones, old seawalls, cavities Develop Hydrogeological Profile Perched water table Piezometric levels G.I. Methods Drillholes with regular sampling & SPT tests. Supplemented by CPT and/or geophysical methods (seismic/radar/resistivity/gravity) as appropriate. What is Required? N value for soil classifications, correlation with other parameters & use directly in empirical analysis (granular soils) Undrained shear strength, Cu (soft clays) -E h, OCR, G,mV, (soils/weak rocks) In Situ Test ResuIts
h, G, OCR, mv (soils/weak rocks)
G.I. Methods
SPT Test
In situ vane shear test Pressuremeter
Additional `targeted vertical, inclined and even horizontal drillholes. Also probing (e.g. for seawalls). Install and monitor piezometers (vibrating wire, pneumatic or Casagrande) and standpipes. Sampling in boreholes: In clays - pistons or undisturbed samples In sands - SPT liners In decomposed rock and Fill Mazier samples In bedrock - rotary coring
Dilatometer
F s,q c , for soil classification, correlation with other parameters and in empirical analysis (soils) Permeability
Static cone penetration testing Variable & constant head tests (soil) packer tests (rock) Test borehole with a gas meter Borehole televiewer / impression packer
Recover material for laboratory testing
Presence of gas & type of gas Rock discontinuity orientations & detailed discontinuity log
Notes : (1) Based on US National Committee on Tunnelling Technology study for better results increase scope of SI to 1.5 linear metre of borehole per route metre tunnel alignment 3% of cost of tunnelling civil works for ground investigation
Appropriate G.I. Methods - Field Instrumentation
What is Required? Baseline monitoring of building structure defects and subsequent change G.I. Methods Crack gauges & meters Settlement markers (surface settlement), extensometers (sub- surface layer settlement)
Appropriate G.I. Methods - Field Mapping & Logging
What is Required? TCR, SCR, RQD, Fracture Index, discontinuity description G.I. Methods Logging of rock samples Additional Engineering Geological Mapping where good rock exposure Identification of cohesive and none cohesive soils and their description Splitting and Logging of soil samples
Monitoring of ground settlement
Notes:(1) For piezometers/standpipes refer to GI Methods Field (Above)
Appropriate G.I. Methods - Laboratory Testing - Soils
What is Required? Soil classification (Atterberg Limits, W, ) G.I. Methods Index tests
Appropriate G.I. Methods - Laboratory Testing - Rocks
What is Required? Rock classification (w, Strength (UCS) ) G.I. Methods Index tests Unconfined compressive strength Point load test Petographic analysis Abrasivity tests (Cerchar Abrasivity, Paddle Test)
Appropriate G.I. Methods - Laboratory Testing - Water
What is Required? Aggressiveness of ground water to concrete G.I. Methods Tests for SO4 & pH
Parameter for settlement analysis (Cc, Cv, eo, mv) and permeability Soil strength (Cu, C, ) & also stiffness
Oedometer Test/Rowe cell Strength (Point Load Index) Triaxial tests Assessment of abrasiveness to TBM cutter
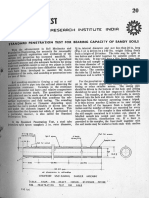
Schematic G.I. Layout for a Soft Rock Tunnel (Section)
Note : (1) Movement monitoring required for all affected structures. (2) For clarity instrumentation not shown (with the exception of piezometers)
GIG04.6
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- CS 2000iDocument88 pagesCS 2000iBintang MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Pump Affinity Laws GuideDocument3 pagesPump Affinity Laws Guidesubramanyanvenkat6185No ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques QuizDocument1 pageSampling Techniques QuizNicole Magluyan Garcia100% (4)
- Important Statistics FormulasDocument12 pagesImportant Statistics FormulasSNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument42 pagesCentrifugal Pumprumabiswas853100% (2)
- Thesis Writing: Dr. Tamara O'Connor Dr. Mark MatthewsDocument38 pagesThesis Writing: Dr. Tamara O'Connor Dr. Mark MatthewsNelson Algones100% (1)
- Hazard Identification of ConstructionDocument29 pagesHazard Identification of ConstructionPintu Jaiswal100% (1)
- EarthingDocument40 pagesEarthingmamoun_hammad7917No ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger VibrationDocument3 pagesHeat Exchanger VibrationTim KuNo ratings yet
- Biomass To Ethanol ProcessDocument132 pagesBiomass To Ethanol ProcessLTE002No ratings yet
- Ettv - BcaDocument56 pagesEttv - BcaHo Chee YongNo ratings yet
- Bridges - Asia-22-25 02 10Document84 pagesBridges - Asia-22-25 02 10LTE002100% (1)
- Daily Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson PlanNover Keithley Sicay MenteNo ratings yet
- YZ - 10 Intumescent CoatingDocument26 pagesYZ - 10 Intumescent CoatingLTE002No ratings yet
- YYJ - Stiff - 2003 Caternary Action - Steel BeamDocument29 pagesYYJ - Stiff - 2003 Caternary Action - Steel BeamLTE002No ratings yet
- YZ - 11 Intumescent Coating ModellingDocument39 pagesYZ - 11 Intumescent Coating ModellingLTE002No ratings yet
- ZH - 09 Steel ConnectionDocument65 pagesZH - 09 Steel ConnectionLTE002No ratings yet
- ZH - 09 Steel ConnectionDocument65 pagesZH - 09 Steel ConnectionLTE002No ratings yet
- Oxygen RequirementsDocument22 pagesOxygen RequirementsLTE002No ratings yet
- Bio Gas Burner 1Document21 pagesBio Gas Burner 1saadullah_siddiqui6076No ratings yet
- Soil WashingDocument19 pagesSoil WashingLTE002No ratings yet
- ZH - 2005 RCDocument99 pagesZH - 2005 RCLTE002No ratings yet
- Building Digest 20Document4 pagesBuilding Digest 20LTE002No ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographDocument21 pagesGas ChromatographLTE002No ratings yet
- Fire Sprinklers PDFDocument28 pagesFire Sprinklers PDFChristopher BrownNo ratings yet
- MethaneDocument24 pagesMethaneLTE002No ratings yet
- Toxicity of BiodieselDocument53 pagesToxicity of BiodieselLTE002No ratings yet
- PH MeasurementsDocument12 pagesPH MeasurementsLTE002No ratings yet
- 32438Document154 pages32438vasakaNo ratings yet
- High PerformanceDocument3 pagesHigh PerformanceLTE002No ratings yet
- Otis About ElevatorsDocument14 pagesOtis About ElevatorsRajeshkragarwalNo ratings yet
- I. Introduction, Purpose, and Study LayoutDocument17 pagesI. Introduction, Purpose, and Study LayoutLTE002No ratings yet
- Cal Methodology - Energy Saving - Electrical - HouseholdDocument15 pagesCal Methodology - Energy Saving - Electrical - HouseholdLTE002No ratings yet
- Trigger Sprayer Dynamic Systems ModelDocument5 pagesTrigger Sprayer Dynamic Systems ModelLTE002No ratings yet
- Simulation of High-Speed FillingDocument13 pagesSimulation of High-Speed FillingLTE002No ratings yet
- 833 Anaerobic Digestion ParametersDocument4 pages833 Anaerobic Digestion ParametersLTE002No ratings yet
- Dissertation Photography TopicsDocument4 pagesDissertation Photography TopicsWhatShouldIWriteMyPaperOnCincinnati100% (1)
- RationalizingDocument8 pagesRationalizingb3ltaNo ratings yet
- SIM-UTA: Evaluating Reorganization Scenarios in A Healthcare OrganizationDocument24 pagesSIM-UTA: Evaluating Reorganization Scenarios in A Healthcare OrganizationPerseu PadreDe MacedoNo ratings yet
- Cambodia's Postgraduate Students: Emerging Patterns and TrendsDocument13 pagesCambodia's Postgraduate Students: Emerging Patterns and TrendsPUSAT PEMBANGUNAN AKADEMIKNo ratings yet
- Stat211 062 02 E1Document9 pagesStat211 062 02 E1Annia CodlingNo ratings yet
- Volume 82Document601 pagesVolume 82CH NarimaneNo ratings yet
- Review of Six Sigma Approach Methodology, Obstacles and BenefitsDocument5 pagesReview of Six Sigma Approach Methodology, Obstacles and Benefitsjustin ambroseNo ratings yet
- S.4 Chi-Square Tests - STAT ONLINEDocument1 pageS.4 Chi-Square Tests - STAT ONLINEJude MetanteNo ratings yet
- 8614 1 BacDocument14 pages8614 1 Bacusman razaNo ratings yet
- IirlpnormDocument2 pagesIirlpnormSudeepta MondalNo ratings yet
- Kotler MM 14e 05 IpptDocument16 pagesKotler MM 14e 05 IpptShanti PutriNo ratings yet
- The Normal Approximation for DataDocument28 pagesThe Normal Approximation for DataAlper MertNo ratings yet
- Action Research Seyoum and TedyDocument27 pagesAction Research Seyoum and Tedysiyoum negashNo ratings yet
- Experimental Research Designs - Types, Examples & MethodsDocument18 pagesExperimental Research Designs - Types, Examples & MethodsHéctor CancholaNo ratings yet
- 08 - Bottom Stability AnalysisDocument7 pages08 - Bottom Stability AnalysisDang Dinh ChiNo ratings yet
- DABURDocument15 pagesDABURPrerna Joshi100% (1)
- An Exploratory Inquiry Into The Psychological Biases in Financial Investment Behavior PDFDocument11 pagesAn Exploratory Inquiry Into The Psychological Biases in Financial Investment Behavior PDFShahban ktkNo ratings yet
- Sampling Methods LectureDocument2 pagesSampling Methods LectureBaste BaluyotNo ratings yet
- HW 6Document5 pagesHW 6Mansi JainNo ratings yet
- Example Term Paper On Public AdministrationDocument4 pagesExample Term Paper On Public Administrationea59a2k5100% (1)
- Special MCQs NOTES THZ Session 2 Pranav PopatDocument11 pagesSpecial MCQs NOTES THZ Session 2 Pranav Popatsaurabhk4106No ratings yet
- Age and Gender Impact on Magazine SubscriptionsDocument5 pagesAge and Gender Impact on Magazine Subscriptionshaider_simple71No ratings yet
- Bullwhip Effect in Supply Chain For Perishable Product (A Systematic Literature Review)Document8 pagesBullwhip Effect in Supply Chain For Perishable Product (A Systematic Literature Review)JihanNo ratings yet
- A Qualitative Study Examining The Effects of PolygynyDocument71 pagesA Qualitative Study Examining The Effects of PolygynyAnonymous jlLBRMAr3ONo ratings yet