Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Set 1
Uploaded by
Augene ToribioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Set 1
Uploaded by
Augene ToribioCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSESSMENT Subjective cues: kailangan talaga inaaalalayan na siya sa lahat ng ginagawa niya as verbalized by the caregiver of the patient.
DIAGNOSIS Self-Care Deficit in bathing/ hygiene dressing/ grooming, feeding and toileting related to neuromuscular impairment, secondary to cerebrovascular accident
PLANNING After 24 hours( 3 days) of nursing interventions, the patient will be able to demonstrate, perform and identify activities
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Assess abilities and level of deficit (0 to 4 scales) for performing ADLs. Avoid doing things for client that client can do for self, providing assistance as necessary.
RATIONALE Aids in anticipating and planning for meeting individual needs. These clients may become fearful and dependent, and although assistance is helpful in preventing frustration, it is important for client to do as much as possible for self to maintain selfesteem and promote recovery. May indicate need for additional interventions and supervision to promote client safety. Clients need empathy and to know caregivers will be consistent in their assistance.
IMPLEMENTATION Assessed abilities and level of deficit (0 to 4 scales) for performing ADLs. Avoided doing things for client that client can do for self, providing assistance as necessary.
EVALUATION Demonstrated techniques/lifes tyle changes to meet self-care needs. Performed selfcare activities within level of own ability. Identified personal/comm unity resources that can provide assistance as needed such grooming and picking up objects near bed.
Objective cues:
Limited range of motion Be aware of impulsive behavior or actions suggestive of impaired judgment. Maintain a supportive, firm attitude. Allow client sufficient time to accomplish tasks.
Checked impulsive behavior or actions suggestive of impaired judgment. Maintained a supportive, firm attitude. Allowed client sufficient time to accomplish tasks.
Provide positive feedback for efforts and accomplishments.
Enhances sense of self- Provided positive worth, promotes feedback for efforts and independence, and accomplishments. encourages client to continue endeavours.
25
Provide self-help devices, such as button or zipper hook, knife fork combinations, long-handled brushes, extensions for picking things up from floor, Assist and encourage good grooming and makeup habits.
Enables client to manage for self, enhancing independence and selfesteem; reduces reliance on others for meeting own needs; and enables client to be more socially active.
Provided self-help devices, such as button or zipper hook, knife fork combinations, longhandled brushes, extensions for picking things up from floor, Assist and encourage good grooming and makeup habits.
Encourage SO to allow client to do as much as possible for self.
Re-establishes sense of Encouraged SO to allow independence and client to do as much as fosters self-worth and possible for self. enhances rehabilitation process. Note: This may be very difficult and frustrating for the SO/caregiver, depending on degree of disability and time required for client to complete activity. Assessed clients ability to communicate the need to void and ability to use urinal or bedpan.
Assess clients ability to communicate the need to void and ability to use urinal or bedpan.
26
Client may have neurogenic bladder, be inattentive, or be unable to communicate needs in acute recovery
phase, but usually is able to regain independent control of these functions as recovery progresses.
Identify previous bowel habits and re-establish normal regimen. Increase bulk in diet. Encourage fluid intake and increased activity.
Assists in development of retraining program (independence) and aids in preventing constipation and impaction (long term effects).
Identified previous bowel habits and re-establish normal regimen. Increase bulk in diet. Encourage fluid intake and increased activity.
Self-Care Deficit Stroke (CVA) Nursing Care Plan (NCP) http://nurseslabs.com/self-care-deficit-stroke-nursing-care-plans/ Nurses pocket guide 11th edition by Doenges,Moorhouse& Murr
27
ASSESSMENT
DIAGNOSIS
PLANNING
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
IMPLEMENTATION
EVALUATION
Subjective cues: hindi na nya magalaw yung kaliwang kamay niyaas verbalized by the caregiver of the patient
Impaired physical mobility related to neuromuscular damage involvement
Long term: After 3 days of nursing intervention, client will be able to increase physical mobility Expected outcome Demonstrate resumption of activities
Begin range of motion of all extremities.
Minimizes loss of muscle tone promotes circulation and prevents contractures. Identify extension of damage
Begun range of motion of all extremities
Demonstrated resumption of activities Participated in ADLs
Assess extent of paralysis initially and on a regular basis.
Assessed extent of paralysis initially and on a regular basis.
Maintained muscle control Participated in the interventions rendered by the nurse
Objective cues: Limited range of motion Limited ability and difficulty to perform gross motor skills like extending and lifting the left arm Slowed movement
Maintain patient in functional Participate in ADLs position and body in alignment with extremities supported. Maintain or increase muscle control Able to participate in the interventions rendered by the nurse Support affected arm in a functional position with hand and arm slightly higher than level of the heart
Prevents contractures
Maintained patient in functional position and body in alignment with extremities supported. Supported affected arm in a functional position with hand and arm slightly higher than level of the heart
Promotes drainage and prevents edema and fibrosis
28
Change position every 2 hours, turning on unaffected side.
Minimizes edema
Changed position every 2 hours, turning on unaffected side.
Keep flat or slightly elevate head of the bed when on back. Involve family, caregiver and patient in exercise program.
Prevents hip Kept flat or slightly flexion contractures elevate head of the bed when on back. Enhances feeling of control and sense of involvement in situation where many factors are not in their control Involved family and patient in exercise program.
Nurses pocket guide 11th edition by Doenges, Moorhouse & Murr Nursing care plans by Doenges, Jefffries & Moorhouse
29
ASSESSMENT Objective cues: Disorientation to time, place, person Change in behavior pattern/usual response to stimuli; exaggerated emotional responses Poor concentration, altered thought processes Reported/measured change in sensory acuity: hypoparesthesia; altered sense of taste/smell Inability to tell position of body parts (proprioception)
DIAGNOSIS Disturbed sensory perception related to neurological trauma or deficit
PLANNING After 3 days of nursing interventions, the patient will: Regain/mainta in usual level of consciousness and perceptual functioning. Acknowledge changes in ability and presence of residual involvement. Demonstrate behaviors to compensate for/overcome deficits.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Assess for sensory awareness
RATIONALE Stimulus of hot or cold. Dull or sharp, awareness of motion and location of body parts.
IMPLEMENTATION Assessed for sensory awareness
EVALUATION After 3 days of nursing intervention, the patient Regained/maintained usual level of consciousness and perceptual functioning. Acknowledged changes in ability and presence of residual involvement. Demonstrated behaviors to compensate for/overcome deficits.
Talk to patient while giving care, telling them what has occurred.
Hearing seems to be the last sense lost and patient may receive information when still unconscious or unresponsive, provide auditory stimulation and a sense of being included in what is going on
Talked to patient while giving care, telling him what has occurred.
Reorient to time, place, and events when conscious
Will diminish sense of alienation and fear
Reoriented to time, place, and events when conscious
Altered communication patterns Motor incoordination
Assess type of sensory deficit present
Restriction of field of vision, symmetry of dilation, eye movement may be present
Assessed type of sensory deficit present
30
Arrange bed, personal Plan to take advantage of articles, and food functional vision trays and approach patient on unaffected side Describe where May have loss of ability to affected areas of body know the location of parts are when moving of body in space patient
Arranged bed, personal articles, and food trays and approach patient on unaffected side Described where affected areas of body are when moving patient
Provide tactile Touching is an important Provided tactile stimulation as care is part of caring and is a stimulation as care given. deep psychologic need is given. Disturbed Sensory Perception Stroke (CVA) Nursing Care Plan (NCP) http://nurseslabs.com/disturbed-sensory-perception-stroke-nursing-careplans/ Nurses pocket guide 11th edition by Doenges, Moorhouse & Murr Nursing care plans by Doenges, Jefffries & Moorhouse
31
ASSESSMENT Subjective cues: nahihirapan nga kami umintindi sa mga sinasabi niya,paminsan oo nalang kami ng oo as verbalized by the caregiver of the patient.
DIAGNOSIS Impaired verbal communication related to loss of facial or oral muscle tone control
PLANNING After 24 hours (3 days) of nursing interventions, the patient will establish method of communication in which needs can be expressed.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Provide alternative methods of communication like picture or visual cues, gestures or demonstration.
RATIONALE Provide communication needs or desires based on individual situation or underlying deficit.
IMPLEMENTATION Provided alternative methods of communication like picture or visual cues, gestures or demonstration.
EVALUATION After 3 days of nursing interventions, the patient established method of communication in which needs can be expressed.
Anticipate and provide for patients needs. Objective cues: Difficulty producing speech Facial paralysis Muscle and facial tension Talk directly to patient. Speaking slowly and directly. Use yes or no question to begin with.
Helpful in decreasing frustration when dependent on others and unable to communicate desires.
Anticipated and provided for patients needs.
It reduces confusion or anxiety and having to process and respond to large amount of information at one time.
Talked directly to patient. Speaking slowly and directly. Use yes or no question to begin with.
32
Speak in normal tones and avoid talking too fast. Give patient ample time to respond.
Patient is not necessary hearing impaired and raising voice may irritate or anger the patient
Spoke in normal tones and avoided talking too fast. Gave patient ample time to respond.
Encourage family members and visitors to persist efforts to communicate with the patient.
It is important for family members to continue talking to the patient to reduce patients isolation ,promote establishment of effective communication and maintain sense of connectedness or bonding with the family.
Encouraged family members and visitors to persist efforts to communicate with the patient.
Impaired Verbal Communication Stroke (CVA) Nursing Care Plan (NCP) http://nurseslabs.com/impaired-verbal-communication-stroke-nursingcare-plans/ Nurses pocket guide 11th edition by Doenges, Moorhouse & Murr Nursing care plans by Doenges, Jefffries & Moorhouse
33
ASSESSMENT
DIAGNOSIS
PLANNING
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Establish rapport
RATIONALE
IMPLEMENTATION
EVALUATION
Objective cues: hemiplegia assess for muscle strength altered mental status restlessness changes in papillary Reactions difficulty in swallowing
Ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion r/t interruption of blood flow secondary to CVA
Short Term: After 8 hrs. Of NI, patient will be able to display decrease signs of ineffective tissue perfusion as evidence by gradual improvement of vital signs. Long Term: After 3 days of NI, patient will be able to gradually improve tissue perfusion AEB good capillary refill and pink conjunctiva.
To promote cooperation To have a baseline data, assess changes in neurologic status
Established rapport
Monitor vital signs
Monitored vital signs
Short Term: Patient displayed a decrease signs of tissue perfusion
Check capillary refill and conjunctiva for paleness Elevate head of bed to 30 as ordered Advise patient to have enough rest
To determine blood circulation
Checked capillary refill and conjunctiva for paleness Elevated head of bed to 30 as ordered Advised patient to have enough rest
Long Term: Patient shall have gradually improved tissue perfusion AEB good capillary refill and pink conjunctiva
To promote circulation Enough rest is needed to conserve energy
Avoid neck flexion and extreme hip/knee extension Provide and maintain oxygen as ordered
To avoid obstruction of arterial and venous blood flow Aids in difficulty of breathing
Avoided neck flexion and extreme hip/knee extension Provided and maintain oxygen as ordered
34
Perform GCS monitoring as ordered
To detect changes indicative of worsening or improving condition
Performed GCS monitoring as ordered
Administer medications To promote as ordered wellness
Administered medications as ordered
Nurses pocket guide 11th edition by Doenges, Moorhouse & Murr Nursing care plans by Doenges, Jefffries & Moorhouse
35
Drug Study Drug Generic Name: Atorvastatin Calcium Major Action Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, an early step in cholesterol Brand Name: Lipitor biosynthesis Indications Contraindications Nursing Responsibilities -Use only after diet and
Adjunct to diet to reduce LDL -Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive cholesterol, total cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and triglyceride levels and to increase HDL cholesterol
to drug and in those with active liver disease other nondrug therapies or unexplained persistent elevations of transaminase levels. - Use cautiously in patients with history of liver disease or heavy alcohol use. - Withhold or stop drug in patients at risk for renal failure cause by rhadomyolysis resulting from trauma; in serious, acute conditions that suggest myopathy; and in major surgery, severe acute infections, hypotension, uncontrolled seizures, or severe metabolic, endocrine, or electrolyte disorders. rove ineffective. Patient should follow a standard low-cholesterol diet before and during therapy. - Drug may be given as a single dose at any time of day, with or without food. - Watch for signs of myositis.
Classification: Antilipidemics
levels in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia
Dosage: 40 mg tab Route: Oral Frequency: Once a day
36
Generic Name: Fluoxetine Hydrochloride
Unknown. Thought to be linked to drugs inhibition of
>Depression, obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD) > Depression in elderly patients >Maintenance therapy for depression in stabilized patients
-Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug and in those taking MAO inhibitors within 14 days of starting therapy. MAO inhibitors shouldnt be started within 5 weeks of stopping fluoxetine therapy. avoid using thioridazine with fluoxetine or within a minimum of 5 weeks after stopping fluoxetine.
-Use antihistamines or topical corticosteroids to treat rashes or pruritus. - watch for weight change during therapy, particularly in underweight or bulimic patients.
Brand Name: Prozac
CNS neuronal uptake of serotonin
Classification: Antidepressants
>Short-term treatment of
panic disorder with or without -use cautiously in patients at high risk for agoraphobia suicide and in those with history of diabetes mellitus; seizures; mania; or hepatic, renal, or CV disease.
Dosage: 20mg 1 tab Route: Oral Frequency: Once a day
> Depression caused by bipolar disorder >Cataplexy >Alcohol dependence
37
Generic Name: Tramadol Hydrochloride
Unknown. A centrally-acting synthetic analgesic
>Moderate to moderately severe pain
>Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or other opioids, and in those with acute intoxication from alcohol, hypnotics, centrally acting analgesics, opiids, or pschotropic drugs. Serious hypersensitivity reactions can occur, usually after the first dose. Patients with history of anaphylactic reaction to codeine and other opioids may be at increased risk.
-Reassess patients level of pain at least 30 minutes after administration. -Monitor bowel and bladder function. Anticipate need for laxative. -for better analgesic effect, give drug before onset of intense pain. -monitor patients at risk for seizures. Drug may reduce seizure threshold. -Monitor patient for drug dependence.
Brand Name: Ultram
compound not chemically related to opioids. Thought
Classification: Opioid Analgesic
to bind to opioid receptors and inhibit reuptake of
Dosage: 50mg 1 tab Route: Oral Frequency: Once a day( as needed for pain)
norepinephrine and serotonin.
38
Generic Name: Isosorbide Dinitrate
Not completely known. Thought to reduce cardiac
Acute angina attacks; to prevent situations that may cause angina attacks.
>Contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to nitrates and in those with severe hypotension, angleclosure glaucoma, increased intracranial pressure, shock, or acute MI with low left ventricular filling pressure. > Use cautiously in patients with blood volume depletion or mild hypotension.
>To prevent tolerance, a nitrate-free interval of 8 to 12 hours per day is recommended. >Monitor blood pressure and intensity and duration of drug response. >Drug may cause headaches, especially at beginning of therapy. Dosage may be reduced temporarily, but tolerance usually develops.
Brand Name: Isordil
oxygen demand by decreasing preload and afterload. Drug
Classification: Antianginal
also may increase blood flow through the collateral
Dosage: 5mg 1 tab Route: Sublingual Frequency: Once a day( as needed for chest pain)
coronary vessels.
39
Laboratory Results HEMOCHROME Test WBC Leukocytes Result 5.5x10^9/L Reference 4.0-11.0 Interpretation Normal Implications If increased, may indicate an infection. If decreased, greater susceptibility to infection. RBC- Erthrocytes 3.94x10^12/L 4.50-6.50 Decreased Results from abnormal loss of erythrocyte, lack of needed elements or hormones for erythrocyte production. Hgb- Hemoglobin 118.8g/L 130-180 Decreased Results from blood loss, haemolytic anemia, and bone marrow suppression. Htc- Hematocrit 0.333L/L 0.400-0.500 Decreased Might be due to overhydration, true decrease in the number of RBC(more common). PLt-Platelet 150-400 344x10^9/L Normal If increased, embolism may develop. If decreased, hemorrhagic disorder.
40
Leucocyte Formula Lymphocytes
Reference 20-45
Result% 23
Interpretation Normal
Implications If increased, with infections, viral and bacterial, hepatitis. If decreased, with aplastic anemia, immunodeficiency such as AIDS.
Monocytes
0-10
10
Normal
If Increased, chronic granulomatous inflammation (TB, syphilis), ulcerative colitis, systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, hematologic neoplasms might be present. If decreased, monocytopenia results and it is generally not a clinical problem.
Neutrophils
40-75
65
Normal
If increased, neutrophilia hematologic marked malignancy. If decreased, neutronpenia.
Eosinophils
0-6
Normal
If increased, allergy, parasitic disease, collagen disease, sub-acute infections may occur.
41
If decreased due to stress, use of some medications ( epinephrine, thyroxine) Basophils 0-1 1 Normal If marked increase, presence of allergic reactions, myxedema, chronic haemolytic anemias. If decreased, basopenia is generally not a clinical problem. Clinical Chemistry Creatinine Reference 59-104umol/L Result 49.1umol/L Interpretation Decreased Implications Seen in conditions characterized by muscle wasting.
42
You might also like
- The Art of Healthy Eating KidsDocument122 pagesThe Art of Healthy Eating KidsSenka SkenderovicNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument39 pagesAnxiety DisordersAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Comprehensive Case Study 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Comprehensive Case Study 1api-546355462No ratings yet
- Seven Principles of Building ResilienceDocument7 pagesSeven Principles of Building ResiliencemilosvblNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Notes SummaryDocument9 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Notes Summarysorryandreosayanisalreadytaken100% (28)
- Music and MoodDocument5 pagesMusic and MoodNatalia TríasNo ratings yet
- LM Outline ManagementDocument15 pagesLM Outline ManagementAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesHealth Teaching PlanLester Dalanon100% (1)
- Teva PharmaceuticalDocument17 pagesTeva PharmaceuticalGanesh VedhachalamNo ratings yet
- Firstaid ModuleDocument143 pagesFirstaid Moduleretni wulandariNo ratings yet
- History Taking in JaundiceDocument2 pagesHistory Taking in Jaundiceshanyiar100% (5)
- Post Partum ExamDocument4 pagesPost Partum ExamAhby Vitug de Luna100% (1)
- Impaired Social Interaction Related To Fear of Being Scrutinized and Embarrassed by OthersDocument9 pagesImpaired Social Interaction Related To Fear of Being Scrutinized and Embarrassed by Othersnathalie cotengNo ratings yet
- IMCI Knowledge Post-Test Answer KeyDocument8 pagesIMCI Knowledge Post-Test Answer KeyCarissa De Luzuriaga-BalariaNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Financing in IndiADocument86 pagesHealthcare Financing in IndiAGeet Sheil67% (3)
- Milieu TherapyDocument4 pagesMilieu TherapyManu Sethi100% (1)
- Everyone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument4 pagesEveryone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Assess mental status with this psychiatric nursing MSE guideDocument4 pagesAssess mental status with this psychiatric nursing MSE guideChien Lai R. BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Document6 pagesNursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Elaine Dionisio TanNo ratings yet
- NCP Alzheimers DiseaseDocument2 pagesNCP Alzheimers DiseaseShawn TejanoNo ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument5 pagesPsych NCPJannen Casas100% (3)
- Community Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesDocument15 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Practice Questions With RationalesFelice Lamzon Labrador100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For DepressionDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan For DepressionCatherineNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvDocument8 pagesSubmitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvCharisa Simbajon100% (1)
- Care Plan 27Document10 pagesCare Plan 27Oroma TobiasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Client with Altered Thought ProcessDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Client with Altered Thought ProcessOphelia Ross Omaña TutanesNo ratings yet
- Acute Confusion Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesAcute Confusion Nursing Diagnosisasmika danaNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep Pattern in Bipolar ClientDocument2 pagesDisturbed Sleep Pattern in Bipolar ClientJermaine Anne MadayagNo ratings yet
- NCP Alcoholic NeuropathyDocument5 pagesNCP Alcoholic NeuropathyPeachy Marie Anca100% (1)
- 6 Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pages6 Nursing Care Plan 1Denise Louise PoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Special ChildrenDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Special Childrenharas_dcsaisNo ratings yet
- Head NurseDocument11 pagesHead Nursejannet20No ratings yet
- FHP & NCP - FractureDocument14 pagesFHP & NCP - FractureFrancis AdrianNo ratings yet
- NCP SchizDocument12 pagesNCP SchizKristine Reyes - MerleNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDocument6 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: - DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment On GERD PatientDocument8 pagesPhysical Assessment On GERD PatientRobert Medina100% (1)
- Nursing ManagementDocument11 pagesNursing ManagementAnjelika Eurelle Caliboso MapiliNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument3 pagesDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJoenna GaloloNo ratings yet
- Burns - Skin Integrity, ImpairedDocument2 pagesBurns - Skin Integrity, Impairedmakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- HoplessnessDocument16 pagesHoplessnessHamza IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument11 pagesCase StudyRadenroro Atih Utari RizkyNo ratings yet
- Emj Cases : Questions For Case 1Document8 pagesEmj Cases : Questions For Case 1Azmyza Azmy100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For GlaucomaEmiey Rara100% (1)
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocument6 pagesImpaired Verbal CommunicationLaura Sansonetti100% (1)
- Psych NCPDocument1 pagePsych NCPEliza Joy Franco RNNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMa Virginia Nathalia CreerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan CVADocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan CVALhyn MacogayNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNo ratings yet
- NCP (Or) ThyroidectomyDocument3 pagesNCP (Or) ThyroidectomyChiz CorreNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationErjohn Vincent Lim100% (1)
- Mental Health Case StudyDocument11 pagesMental Health Case Studyapi-453449063No ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPmsinsanoNo ratings yet
- Chicken-Pox Concept MapDocument4 pagesChicken-Pox Concept MapElle0% (1)
- Process RecordingDocument7 pagesProcess RecordingKim ApuradoNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Caring for a Patient with Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument3 pagesAssessing and Caring for a Patient with Alzheimer's Diseaseria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- Drug-Study-Ncp-And-Fdar - Sir WencyDocument21 pagesDrug-Study-Ncp-And-Fdar - Sir WencyBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07No ratings yet
- Health Teaching of Patients With Tuberculosis TreatmentDocument34 pagesHealth Teaching of Patients With Tuberculosis TreatmentFarhanaRahimNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPBon BonNo ratings yet
- Retinopathy of PrematurityDocument15 pagesRetinopathy of Prematuritymarissa ulkhairNo ratings yet
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Altered Renal Perfusion CRFDocument4 pagesAltered Renal Perfusion CRFKristel Anne Nillo ZepolNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationMG PolvorosaNo ratings yet
- NCP For IHDDocument19 pagesNCP For IHDMasyitah Farahin100% (2)
- Assessing and Managing Sleep DeprivationDocument2 pagesAssessing and Managing Sleep DeprivationDavid Brillo100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management for Stroke PatientsDocument4 pagesNursing Management for Stroke PatientsAna Louise BatallaNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching: Health Perception and MaintenanceDocument7 pagesHealth Teaching: Health Perception and MaintenanceBeRnAlieNo ratings yet
- Self-Care Deficit Nursing InterventionsDocument29 pagesSelf-Care Deficit Nursing InterventionsYna VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NCP GrandcaseDocument5 pagesNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Oncology Toribio Augene SecFDocument9 pagesOncology Toribio Augene SecFAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Water Borne DiseasesDocument16 pagesWater Borne DiseasesAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- AugeneDocument3 pagesAugeneAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia GonorrheaDocument3 pagesChlamydia GonorrheaAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- CTDocument4 pagesCTAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- 23 IMCI Chart Booklet Timor LesteDocument34 pages23 IMCI Chart Booklet Timor LesteAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Favirab administration guidelines for rabies prophylaxisDocument4 pagesFavirab administration guidelines for rabies prophylaxisAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Disaster NursingDocument10 pagesDisaster NursingAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Summary of Ross's EthicsDocument2 pagesSummary of Ross's EthicsAugene Toribio100% (1)
- Module 9Document12 pagesModule 9Augene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - 50 MCQDocument10 pagesModule 8 - 50 MCQAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument2 pagesCHNAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Toribio Augene Pedia2Document3 pagesToribio Augene Pedia2Augene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Oncology Toribio Augene SecFDocument9 pagesOncology Toribio Augene SecFAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Oncology Toribio Augene SecFDocument9 pagesOncology Toribio Augene SecFAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Water Borne DiseasesDocument16 pagesWater Borne DiseasesAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Summary of Ross's EthicsDocument2 pagesSummary of Ross's EthicsAugene Toribio100% (1)
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of The United NationsDocument4 pagesThe Food and Agriculture Organization of The United NationsAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Water Borne DiseasesDocument16 pagesWater Borne DiseasesAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia GonorrheaDocument3 pagesChlamydia GonorrheaAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - RevisedDocument10 pagesDrug Study - RevisedAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- PsychopathologyDocument2 pagesPsychopathologyAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY - Drug Study - RevisedDocument10 pagesCASE STUDY - Drug Study - RevisedAugene ToribioNo ratings yet
- Resume Gholamreza MahmoodiDocument3 pagesResume Gholamreza Mahmoodiarian tejaratNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of thyroid dysfunctionDocument32 pagesPrevalence of thyroid dysfunctiondalip kumarNo ratings yet
- Beggs Stage 1 - Ortho / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument33 pagesBeggs Stage 1 - Ortho / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Automation of Mechanical VentilationDocument12 pagesAutomation of Mechanical VentilationjuanNo ratings yet
- MRI Monitoring System Provides Safety and MobilityDocument4 pagesMRI Monitoring System Provides Safety and MobilityAchiyat WinataNo ratings yet
- All Models W ExplanationDocument63 pagesAll Models W Explanationpayal1407No ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Surgery of Inferior Oblique Muscle EctopiaDocument5 pagesClinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Surgery of Inferior Oblique Muscle EctopiaMuhammad Imam NoorNo ratings yet
- Fatal Airway Obstruction Due To Ludwig'sDocument6 pagesFatal Airway Obstruction Due To Ludwig'sRegina MugopalNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Equality ToolkitDocument64 pagesBenefits of Equality ToolkitBasic Rights OregonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Hema Priya AdityanNo ratings yet
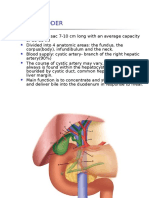
- Gallbladder and Bile Duct Anatomy, Function and DiseasesDocument16 pagesGallbladder and Bile Duct Anatomy, Function and DiseasesKadenceFreya-Charisse G PosadasBulintao100% (2)
- 45 PDFDocument8 pages45 PDFChika FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Standard Case Report Checklist and Template For AuthorsDocument5 pagesStandard Case Report Checklist and Template For AuthorsArief MunandharNo ratings yet
- Baker v. Dalkon Sheild, 156 F.3d 248, 1st Cir. (1998)Document10 pagesBaker v. Dalkon Sheild, 156 F.3d 248, 1st Cir. (1998)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Fphar 12 768268Document25 pagesFphar 12 768268Araceli Anaya AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- 108 Names of DhanvantariDocument7 pages108 Names of DhanvantaricantuscantusNo ratings yet
- Vivekananda Kendra NRL HospitalDocument29 pagesVivekananda Kendra NRL HospitalVivekananda Kendra100% (1)
- Pneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenDocument1 pagePneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenPrincess Gutierrez RositaNo ratings yet
- Review of drug-induced gingival overgrowthsDocument14 pagesReview of drug-induced gingival overgrowthsRobins DhakalNo ratings yet
- Supine Cervical Traction After Anterior Cervical Diskectomy and FusionDocument4 pagesSupine Cervical Traction After Anterior Cervical Diskectomy and FusionOscar NgNo ratings yet
- Joint Disorders - Ay NewDocument46 pagesJoint Disorders - Ay NewPraisingson SyiemliehNo ratings yet
- Elderly Care IndiaDocument3 pagesElderly Care IndiakasurvarNo ratings yet