Professional Documents
Culture Documents
O' Level Physics Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Yee Kai TanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
O' Level Physics Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Yee Kai TanCopyright:
Available Formats
O Level Physics Formula Sheet
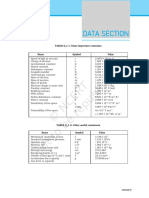
Measurements
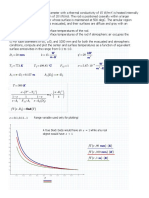
Base SI Units Kg m s A K mol Number Prefix n (10-9) (10-6) m (10-3) c (10-2) d (10-1) K (103) M (106) Average Speed s = d / t SI Unit for mass: Kilogram SI Unit for length: metre SI Unit for time: second SI Unit for current: Ampere SI Unit for Temperature: Kelvin SI Unit for Amount of substance: molar nano micro milli centi deci Kilo Mega For a body in rotational Principle of Moment Anticlockwise Moment equilibrium, = Clockwise Moment Sum of ACW Moment = sum of CW Moment
Pressure
Pressure F = A Pressure of liquid column P = hg P = Pressure F = Force over area, A A = Area P = Pressure = density, h = height of liquid column g = gravitational field strength. W = work done F= force d= distance in direction of force Work done per unit time, t Ek = Kinetic Energy m = mass v = velocity g = gravity =9.81 m/s h = height m = mass E1 = Total Energy Before E2 = Total Energy After Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be transformed or converted into other forms. P = pressure of fixed mass of gas V = volume occupies by fixed mass of gas T = Temperature of gas Subscript 1 = initial state Subscript 2 = final state
Energy, Work and Power
Work Done W = Fd Power P = W/t = Fv Kinetic Energy 1 = mv 2 2 Gravitational Potential Energy Ep = mgh Conservation of Energy E1 = E2
d = total distance travelled (area under speed-time graph) x = total displacement Average Velocity t = total time taken v = change in velocity v = x/t Velocity (slope of displacement-time graph) Acceleration Acceleration (slope of velocity-time graph) a = v/t v = u + at u = initial velocity v = final velocity x = ut + at2 t = time v2 = u2 + 2ax a = acceleration x = displacement h = height vfree fall = 2 g = gravitational constant = 9.81 m/s2
Kinematics
Dynamics
Kinetic Model of Matter
Ideal Gas Law PV T P1V1 = P2V2
Newtons First Law = 0 at equilibrium Newtons Second Law F= ma
Newtons Third Law
Resolving forces Fhorizontal = Fr cos Fvertical = Fr sin Weight w = mg Density m = V
A body continues to stay in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line as long as there is no net force/moment acting on the body. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. For every force object A acts on object B, object B will exert an equal and opposite force on object A giving rise to Reaction/Normal Forces Fr Fvertical Fhorizontal
Thermal Properties of Matter
Specific Heat Capacity c = Specific heat capacity (Energy required to raise the temperature of E = m c T 1kg of the object by 1 C) m = mass T = change in temperature. Lfusion = latent heat of fusion (Energy Latent Heat required to change 1kg of solid to For melting, liquid at the constant temp) E = m Lfusion Lvaporization = latent heat of vaporization (Energy required to For boiling, change 1kg of liquid to gas at the E = m Lvaporization constant temp) m = mass
Mass, Weight, Density
w = Weight m = mass g = gravitational field strength = density m = mass V = volume
General Wave Properties
Wave Velocity v=f Wave frequency 1 f=
T
v = velocity of a wave f = frequency = wavelength T = Period f = frequency
Turning effect of Force
M = Moment F = force d = distance from force to pivot
Moment of Force M=Fd
http://physictuition.blogspot.com
O Level Physics Formula Sheet
Light
Law of Reflection i = r i = angle of incidence r= angle of reflection Snells Law (refraction) n1Sin i = n2Sin r i = angle of incidence r = angle of refraction Critical angle n2 sin = n1 Normal i r Electric Power
2 P = VI = V2/R = I R
Practical Electricity
P = Power V = voltage R = resistance I = current E = energy output P = power t = time V = voltage I = current V = voltage N = number of coils I = current Subscript p = primary coil Subscript s = secondary coil
Normal i r n2 = refractive index 2 Normal c n1 = refractive index 1 n1 = refractive index 1
Electrical Energy E = Pt = (VI)t
Electromagnetism
Transformer Vp Np = Vs Ns (ideal transformer) VPIP = VsIs Right hand grip
(special case of Snells law where r = 90) Refractive Index c = v (n of air 1) Magnification hi di = = ho do Current I = Q / t Ohms Law Resistance R=V/I Resistance of a wire R = L/A
n2 = refractive index 2 c = speed of light in vacuum. v = speed of light in medium Higher reflective index of a medium means light travel slower in the medium M = magnification h = height d = distance from lens Subscript i = image Subscript o = object Current = rate of flow of charges Q = Charge t=time V = voltage, R = resistance I = current = resistivity L = length of wire A = cross sectional area
Flemings Right Hand Rule
Current of Electricity
Flemings Left Hand Rule
D.C. Circuits
Kirchoffs 1st Law Iin = Iout V = E. M. F Conservation of charges. Iin = Sum of current going into a junction Iout = Sum of current going out of a junction V = Sum of potential difference V across all components in a circuit E.M.F = Voltage supplied by the power supply.
I R1 R2 R3
Kirchoffs 2nd Law
Resistance in Series Rtotal = R1 + R2 + R3 Resistance in Parallel 1 1 1 1 = + + R total R1 R 2 R 3
Prepared by etuitionx (http:/physictuition.blogspot.com)
V R1 R2 R3
References
1. PHYSICS Ordinary Level (Syllabus 5058) 2. Education Haven (http://matchtutor.com.sg)
http://physictuition.blogspot.com
You might also like
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 pagesPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics EquationsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Physics EquationsMisterBlueSkyNo ratings yet
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 pagesPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 SummaryDocument8 pagesPhysics 11 SummaryJ100% (5)
- Physics Important ConceptsDocument2 pagesPhysics Important Conceptsazhar aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Work and Power NotesDocument17 pagesChapter 16 Work and Power NotesAishath WaheedaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Motion Through Speed, Velocity and AccelerationDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Motion Through Speed, Velocity and AccelerationSel FortichNo ratings yet
- SPH4U Assignment 1 PDFDocument3 pagesSPH4U Assignment 1 PDFLeah SparksNo ratings yet
- AS - A 2 Revesion Formula Sheet Edexcel IALDocument3 pagesAS - A 2 Revesion Formula Sheet Edexcel IALMahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- Ged Earth Science Test 1bDocument12 pagesGed Earth Science Test 1bapi-301605346No ratings yet
- Physics Formula BookletDocument8 pagesPhysics Formula BookletramexistsNo ratings yet
- WWW - Ib.academy: Study GuideDocument95 pagesWWW - Ib.academy: Study GuideGag PafNo ratings yet
- 14 - Waves General Waves and Wave Intensity - 14Document4 pages14 - Waves General Waves and Wave Intensity - 14dil19860209No ratings yet
- Topic 10 Fields (HL) - IB PhysicsDocument1 pageTopic 10 Fields (HL) - IB PhysicsFortNite KIDNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics (2020)Document15 pagesGrade 10 Physics (2020)Mikail MoorajNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulae List (IGCSE)Document6 pagesPhysics Formulae List (IGCSE)saimee77No ratings yet
- Module 2 DynamicsDocument47 pagesModule 2 DynamicsTaha Kafil-HussainNo ratings yet
- GED Physics Note4 (Electricity and Magnetism)Document6 pagesGED Physics Note4 (Electricity and Magnetism)Shahadat Hussain ParvezNo ratings yet
- 3.13 - Vectors WorksheetDocument2 pages3.13 - Vectors Worksheetdilsharakavi100% (1)
- Practice Sat Questions: Chapter 11 / Triangles 135Document5 pagesPractice Sat Questions: Chapter 11 / Triangles 135Mark GalstianNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetMomin BabarNo ratings yet
- SPH3U1 Exam Review NotesDocument26 pagesSPH3U1 Exam Review Notesrahihot100% (1)
- GED Physics Notes on Energy Forms and TransfersDocument5 pagesGED Physics Notes on Energy Forms and TransfersShahadat Hussain Parvez100% (1)
- Answers To Test Yourself Questions: Topic 6Document5 pagesAnswers To Test Yourself Questions: Topic 6Abel CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MomentumDocument6 pagesChapter 6 MomentumAbdulaziz AlMuallimNo ratings yet
- Igcse 43 Work&PowerDocument39 pagesIgcse 43 Work&PowerHany ElGezawy67% (3)
- Dokumen - Tips - Physics Module 1 Kinematics Note It It Essential in Kinematics Problems ToDocument14 pagesDokumen - Tips - Physics Module 1 Kinematics Note It It Essential in Kinematics Problems ToTaha Kafil-Hussain100% (2)
- Definitions and Questions Paper 1Document47 pagesDefinitions and Questions Paper 1ThabeloNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Công Phạm BáNo ratings yet
- Physics - Unit 1 (Mechanics)Document49 pagesPhysics - Unit 1 (Mechanics)hippohorse100% (1)
- CH 4 - OW - (B) SuperpositionDocument59 pagesCH 4 - OW - (B) Superpositionsonali_krishNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula ListDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula ListMomeena Nouman100% (1)
- Physics Forces Impulse Momentum QuizDocument21 pagesPhysics Forces Impulse Momentum QuizSam Hnatiuk0% (1)
- Gcse Physics Equations Sheet As1 As2 Ph2Document2 pagesGcse Physics Equations Sheet As1 As2 Ph2hadigy1001No ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument9 pagesIGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionKasunDilshanNo ratings yet
- PHYS 211 Exam 1 Sample 2 With Key PDFDocument11 pagesPHYS 211 Exam 1 Sample 2 With Key PDFAndrew TrolioNo ratings yet
- Physics - K.A. Tsokos - Seventh Edition - Cambridge 2023Document561 pagesPhysics - K.A. Tsokos - Seventh Edition - Cambridge 2023Janya Polavarapu100% (1)
- IB Physics Data and FormulasDocument5 pagesIB Physics Data and FormulasfossacecaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes (Physics)Document65 pagesChapter 1 Notes (Physics)ronniego100% (2)
- WavesDocument30 pagesWavesExotic EagleNo ratings yet
- H2 Physics Formulae and Definitions: MeasurementDocument7 pagesH2 Physics Formulae and Definitions: MeasurementChong Yi AnNo ratings yet
- Vector Worksheet 10 AnsDocument13 pagesVector Worksheet 10 AnsMegan GohNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Turning Effect of Forces)Document4 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Turning Effect of Forces)Sharuvindan Nair100% (1)
- Chapter 01 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument4 pagesChapter 01 Physical Quantities and UnitsPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- 4ph1 1pr Que 20220610Document32 pages4ph1 1pr Que 20220610Faozia AbidaNo ratings yet
- Physics Equation TablesDocument6 pagesPhysics Equation TablesSangram NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Year 10 IGCSE Science SyllabusDocument1 pageYear 10 IGCSE Science SyllabusRigen AlamNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 - Deformation of SolidsDocument8 pagesTopic 8 - Deformation of Solidsargh67% (3)
- Kinematics (Teachers)Document33 pagesKinematics (Teachers)Rajiv BiswasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Kinematics KeyDocument6 pagesWorksheet On Kinematics KeyelenaNo ratings yet
- 0625 Igcse Physics 22Document237 pages0625 Igcse Physics 22Vinod R100% (1)
- IB Physics Topic 2Document18 pagesIB Physics Topic 2wee100% (1)
- Wave Calculations Speed Frequency WavelengthDocument3 pagesWave Calculations Speed Frequency WavelengthTrixia AlbaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Autonomous Educational Organization Nazarbayev Intellectual SchoolsDocument49 pagesPhysics: Autonomous Educational Organization Nazarbayev Intellectual SchoolsAbylai Tashtan100% (1)
- Phy Formula ListDocument2 pagesPhy Formula ListtingsengNo ratings yet
- O-Level-Physics-Formula-Sheet 1 PDFDocument3 pagesO-Level-Physics-Formula-Sheet 1 PDFGeofrey100% (4)
- Category: Physics FormulasDocument24 pagesCategory: Physics FormulasKalpana ShankarNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) Ronewing949No ratings yet
- Physics Formulas & SI UnitDocument14 pagesPhysics Formulas & SI Unitönemsiz biriNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) RAitazaz AhsanNo ratings yet
- 2009 Gan Eng Seng SCH Sec 4 e Maths 2nd Prelim Exam Paper 1 With AnswersDocument16 pages2009 Gan Eng Seng SCH Sec 4 e Maths 2nd Prelim Exam Paper 1 With AnswersYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument46 pagesIGCSE Chemistry NotesRenée ReimiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes v1.6 ExtraDocument20 pagesChemistry Notes v1.6 Extraarj77No ratings yet
- 4exp SChem P3 2012 PrelimDocument18 pages4exp SChem P3 2012 PrelimYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Exam 2012: Physics and Chemistry MCQsDocument9 pagesPreliminary Exam 2012: Physics and Chemistry MCQsYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Science Chemistry Preliminary 2 2011 Marking Scheme Paper 3Document8 pagesScience Chemistry Preliminary 2 2011 Marking Scheme Paper 3Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 4E&5NA SC (Chem) Prelim P3 10 Ans LDocument10 pages4E&5NA SC (Chem) Prelim P3 10 Ans LYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- R WeidenfellerDocument2 pagesR WeidenfellerYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Prelim 2 Paper 1 Answer SchemeDocument1 pagePrelim 2 Paper 1 Answer SchemeYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Prelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)Document14 pagesPrelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Kranji Prelim09 5116 P1 - With KeysDocument9 pagesKranji Prelim09 5116 P1 - With KeystopcatNo ratings yet
- 4exp SChem P3 2012 PrelimDocument18 pages4exp SChem P3 2012 PrelimYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Test No. Test Observations Remarks: /black Solid FormedDocument3 pagesTest No. Test Observations Remarks: /black Solid FormedYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- BSS2012 Prelim Exam Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesBSS2012 Prelim Exam Marking SchemeYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Prelim 2 Paper 1 Answer SchemeDocument1 pagePrelim 2 Paper 1 Answer SchemeYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Prelim Scichem P5 2012Document2 pagesPrelim Scichem P5 2012Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision NotesDocument20 pagesQuick Revision NotesYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Science Chemistry Preliminary 2 2011 Marking Scheme Paper 3Document8 pagesScience Chemistry Preliminary 2 2011 Marking Scheme Paper 3Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Prelim Scichem P5 2012Document2 pagesPrelim Scichem P5 2012Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- BP Prelim05 5152 P1Document10 pagesBP Prelim05 5152 P1Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- MHSS Prelim06 5152 P1Document8 pagesMHSS Prelim06 5152 P1Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 0653 s13 GT Science-CombinedDocument2 pages0653 s13 GT Science-CombinedYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Westwood 4NA Prelim2010 P3 MCQDocument10 pagesWestwood 4NA Prelim2010 P3 MCQYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases & SaltsDocument19 pagesAcids Bases & SaltsMuhammadAbutalibKazmiNo ratings yet
- Coastal Systems and Processes: Types of WavesDocument2 pagesCoastal Systems and Processes: Types of WavesYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Metals (Key Points and Q&A)Document7 pagesMetals (Key Points and Q&A)wakakkaNo ratings yet
- 4 E5 NSci Phy Prelim IIP12012 AnswersDocument1 page4 E5 NSci Phy Prelim IIP12012 AnswersYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Pure Geog P1 AnsDocument27 pagesPure Geog P1 AnsYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 2010 Prelim2 ScChem 4E5N.P1Document15 pages2010 Prelim2 ScChem 4E5N.P1Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- 2012 Sec 4Ex/5NA Science (Physics) Prelim ANSWERDocument4 pages2012 Sec 4Ex/5NA Science (Physics) Prelim ANSWERYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Schäffer - 1996 - Second-Order Wavemaker Theory For Irregular Waves - Ocean Engineering-AnnotatedDocument42 pagesSchäffer - 1996 - Second-Order Wavemaker Theory For Irregular Waves - Ocean Engineering-AnnotatedSherlin Prem Nishold S oe13d015No ratings yet
- P30 Unit Three Diploma ReviewDocument30 pagesP30 Unit Three Diploma ReviewhelloNo ratings yet
- Power Grid Earthing CertificatesDocument40 pagesPower Grid Earthing Certificatesshanmugam.sNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased Arrays - 1-10Document10 pagesFundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased Arrays - 1-10Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Mullion AnalysisDocument4 pagesMullion AnalysisganeshNo ratings yet
- MOTOR BASES FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONSDocument8 pagesMOTOR BASES FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONSbogdanalaciNo ratings yet
- Burmister Three Layer TheoryDocument10 pagesBurmister Three Layer TheoryT K Rao100% (5)
- Circus-Trick Science - How To Balance Anything - Science ProjectDocument12 pagesCircus-Trick Science - How To Balance Anything - Science ProjectjimenaNo ratings yet
- Buried Pipe - CalcstressDocument17 pagesBuried Pipe - CalcstressAnjani PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics - Rod in CylinderDocument5 pagesThermal Physics - Rod in CylinderLUIS HUMBERTO MARTINEZ PALMETHNo ratings yet
- Lelm 316Document20 pagesLelm 316neerajNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Thermoelectric EffectDocument16 pagesLecture On Thermoelectric EffectjacobNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter 4 Solid State PhilipsDocument10 pagesSolutions Chapter 4 Solid State PhilipsmiesvamaNo ratings yet
- Rheology of The Earth's Mantle: A Historical Review: Gondwana Research July 2010Document30 pagesRheology of The Earth's Mantle: A Historical Review: Gondwana Research July 2010MarcosGouveaNo ratings yet
- VSEPR Theory5Document18 pagesVSEPR Theory5Inaya ImranNo ratings yet
- Examples of Physics Homework Help: Solved Mechanical Energy Conservation ProblemsDocument4 pagesExamples of Physics Homework Help: Solved Mechanical Energy Conservation ProblemsJeff HardyNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE STRESS IN GEOTHERMAL PIPING SYSTEMDocument15 pagesANALYSIS OF PIPELINE STRESS IN GEOTHERMAL PIPING SYSTEMAbdul Haris SiregarNo ratings yet
- Som Unit - 1.1.2 Prismatic Bar With FosDocument1 pageSom Unit - 1.1.2 Prismatic Bar With FosNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Control of Deflection of Concrete Structures - AciDocument13 pagesControl of Deflection of Concrete Structures - AciSayuriAgustinNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Science ResearchDocument9 pagesSpiritual Science Research5joanNo ratings yet
- Colorimeter and Fully Auto Analyzer - Group HDocument35 pagesColorimeter and Fully Auto Analyzer - Group HAjish jo100% (1)
- 2022-JEE Main-5 Question PaperDocument14 pages2022-JEE Main-5 Question PaperAchint Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Decrease in Level of Sound Pressure and Sound IntensityDocument1 pageDecrease in Level of Sound Pressure and Sound IntensitySreeNo ratings yet
- Notes Potential Flow Around CylinderDocument4 pagesNotes Potential Flow Around CylinderMohit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Universal Current SensorsDocument21 pagesUniversal Current SensorsKarthik SD67% (6)
- Computational StructuralENGG PDFDocument1,244 pagesComputational StructuralENGG PDFFAIZ100% (2)
- Racqb 2Document7 pagesRacqb 2ratchagaraja0% (1)
- Heat Transfer of Non-Newtonian Fluids in Circular Micro-TubeDocument14 pagesHeat Transfer of Non-Newtonian Fluids in Circular Micro-TubeGaurav KhamesraNo ratings yet
- Lab Ideal Gas LawDocument2 pagesLab Ideal Gas LawblackwellbertNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Flow MeterDocument3 pagesMagnetic Flow Meterniazakhtar100% (1)