Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ca Cervix - 2
Uploaded by
Egie Nugraha Fitriyan ApriyadiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ca Cervix - 2
Uploaded by
Egie Nugraha Fitriyan ApriyadiCopyright:
Available Formats
23-May-13
CERVICAL CANCER
PENDAHULUAN
Pembunuh no 1 di dunia Setiap tahunnya terdapat 400 ribu kasus baru cervical cancer, sebanyak 80 persen terjadi pada wanita yang hidup di negara berkembang Penyebabnya minimnya akses screening dan pengobatan.
BY : TETTI SOLEHATI, S.KP.,M.KEP
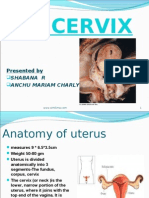
1: fallopian tube, 2: bladder, 3: pubic bone, 4: g-spot, 5: clitoris, 6: urethra, 7: vagina, 8: ovary, 9: sigmoid colon, 10: uterus, 11: fornix, 12: cervix, 13: rectum, 14: anus
23-May-13
STATISTICS
10,520 new
DEFINITION
Kanker
cases in the U.S. 3,900 will die 50% are diagnosed between ages 35 and 55. 20% at the age of 65 or over. Rarely occurs in women younger than 20
serviks adalah jenis kanker yang biasanya tumbuh lambat pada wanita dan mempengaruhi mulut rahim, yaitu bagian yang menyambungkan antara rahim dan vagina.
Perubahan
sel-sel serviks dinamakan proses metaplasia yang terjadi di daerah sambungan skuamosa kolumnar. Kanker ini dipengaruhi oleh aktivitas seksual.
23-May-13
TYPES
Three Types :
Adenocarcinomas
Cancer arising from
glandular epithelium
Squamous cell Carcinomas
Cancer of 80%
10% -
20%
flat epithelial cell to 90%
Mixed carcinoma
Features both
types
KLASIFIKASI
STAGE
Klasifikasi kanker serviks menurut International Federation Of Gynaecology and Obstetric (FIGO) adalah terdiri dari stage 0 sampai stage IV
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in Situ) In stage 0, cancer is found only in the first layer of cells lining the cerviks and has not invaded the deepertissues of the cervix. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ
Stage I cancer is found in the cerviks only. Stage I is divided into stages IA and IB, based on the amount of cancer that is found.
Stage IB:,
Stage 1A: A very small amount cancer that can only be seen with a microscope is found in the tissue of the cervix. Stage IA is divided into stages IA1 and IA2, based on the size of the tumor.
In stage
IA1, the cancer is not more than 3 millimeters deep and not more than 7 millimeters wide. In stage IA2, the cancer is more than 3 but not more than 5 millimeters deep, and not more than 7 millimeters wide.
cancer can only be seen with a microscope and is more than 5 millimeters deep or more than 7 millimeters wide, or can be seen without a microscope. Cancer that can be seen without a microscope is divided into stages IB1 and IB2, based on the size of the tumor stage 1B1, the cancer can be seen without a microscope and is not larger than 4 centimeters. stage 1B2, the cancer can be seen without a microscope and is larger than 4 centimeter
23-May-13
Stage II cancer has spread beyond the cervix but not to the pelvic wall (the tissues that line the part of the body between the hips) or to the lower third of the vagina. Stage II is divided into stages IIA and IIB, based on how far the cancer has spread.
Stage IIA:
Stage III cancer has spread to the lower third of the vagina, may have spread to the pelvic wall and/or has caused the kidney to stop working. Stage III is divided into stages IIIA and IIIB, based on how far the cancer has spread.
Stage IIIA: Cancer has spread to the lower third of the vagina but not to the pelvic wall. Stage IIIB Cancer has spread to the pelvic wall and/or the tumor has become large enough to block the ureters (the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder). This blockage can cause the kidneys to enlarge or stop working. Cancer cells may also have spread to lymph nodes in the pelvis.
Cancer has spread beyond the cervix to the upper two thirds of the vagina but not to tissues around the uterus. Stage IIB: Cancer has spread beyond the cervix to the upper two thirds of the vagina and to the tissues around the uterus.
Stage IV cancer has spread to the bladder, rectum, or other parts of the body. Stage IV is divided into stages IVA and IVB, based on where the cancer is found. Stage IVA: Cancer has spread to the bladder or rectal wall and may have spread to lymphnodes in the pelvis. Stage IVB: Cancer has spread beyond the pelvis and pelvic lymph nodes to other places in the body, such as the abdomen, liver , intestinal tract, or lungs.
PATHOFISIOLOGY
Karsinoma serviks mulai timbul dibatas antara epitel yang melapisi ektoserviks dan endoserviks, kanalis serviks yang disebut sebagai scuamocolumnar junction Pada awal perkembangnnya kanker serviks tidak memberi tanda-tanda dan keluhan. Pada pemeriksaan dengan spekulum, tampak sebagai porsio yang mengalami peradangan
23-May-13
Umumnya fase prainvasif berkisar antara 1015 tahun. Penyebaran terjadi secara limfogen yaitu melalui pembuluh getah bening. Meninggalnya penderita kanker serviks disebabkan oleh pendarahan yang eksesif dan gagal ginjal menahun akibat uremia oleh karena obstuksi ureter di tempat ureter masuk ke dalam kandung kemih
ETIOLOGI
human
papilloma virus (HPV) type 16, 18) mayoritas Other possible risk factor s include the following: Giving birth to many children. Having many sexual partners.
Having first
sexual intercourse at a young age. Smoking cigarettes. Oral contraceptive use ("the Pill"). Weakened immune system Defisiensi vit A,C, Beta caroten, as folat
MANIFESTASI KLINIK
Pra
ca tdk menimbulkan gejala
Low
socioeconomic status Diethylstilbestrol (DES) Family history
Ca
: Terdapat keputihan berlebihan, berbau busuk, dan tidak sembuhsembuh. Adanya pendarahan tidak normal, karena ca menyerang jaringanjaringan di sekitarnya.
23-May-13
Meningkatnya
pendarahan selama
Nyeri
menstruasi. Terjadi pendarahan di luar siklus menstruasi dan setelah hubungan seks. Kesulitan atau nyeri dalam perkemihan
selama berhubungan seks. Nyeri di daerah panggul Pendarahan pada masa pra atau paska menopause
PREVENTION
Bila kanker sudah mencapai stadium 3 ke atas, maka akan terjadi pembengkakan di berbagai anggota tubuh, seperti di paha, betis, tangan dan sebagainya.
Avoiding the risk factors Especially HPV Help for low-income women Having the Pap Test 3 years after first vaginal intercourse or by age 21. Have test annually
23-May-13
DIAGNOSIS
pap smear biopsi X-ray CT- scan USG MRI
Papsmear sebaiknya dilakukan setahun sekali bagi yang sudah melakukan hubungan seks. Bagi wanita yang berusia di atas 30 tahun dan telah melakukan Pap smear selama tiga kali berturut-turut dan hasil didapatkan normal, maka pap smear dapat dilakukan setiap dua atau tiga tahun sekali.
THREATMENT
Three types of standard treatment are used:
Invasive
Surgery Preinvasive cervical cancer Cryosurgery Laser surgery Conization
cervical cancer hysterectomy Removal of the body of the uterus and cervix. Radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection Removal of entire uterus, surrounding tissue, upper part of the vagina, and lymph nodes from the cervix.
Simple
23-May-13
Radiation therapy Chemotherapy
Penatalaksanaan medis terhadap klien kanker serviks tergantung dari stadium
Stadium Ib dan IIa - histerektomi radikal dengan limfadenektomi pelvis. Pasca bedah dilanjutkan dengan radiasi, tergantung ada tidaknya sel tumor dalam kelenjar limfe regional yang diangkat.
Stadium IIb dan III untuk terapi primer adalah radioterapi. Kombinasi dari kemoterapi dan radiasi sebagai upaya untuk memperbaiki laju penyembuhan, karena banyak klien mempunyai metastasis jauh yg tidak nampak.
Stadium IVa dan IVb radiasi untuk meredakan perdarahan dari vagina, kandung kemih, atau rektum. Karena terdapat metastasis yang jauh maka kemoterapi sering digunakan tetapi hanya bersifat paliatif.
You might also like
- 1 CervixDocument12 pages1 Cervixzianab aliNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument6 pagesCervical CancerCnette S. LumboNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Cancers by EasterDocument19 pagesReproductive System Cancers by EasterIGA ABRAHAM100% (1)
- Benign and Malignant Tumors of CervixDocument37 pagesBenign and Malignant Tumors of CervixFirifan DiribaNo ratings yet
- Pathologic Types: o o o oDocument2 pagesPathologic Types: o o o orexzordNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument11 pagesChapter ISeptian RahaNo ratings yet
- en Dome Trial CarcinomaDocument31 pagesen Dome Trial Carcinomadr_asalehNo ratings yet
- Group Health EducationDocument20 pagesGroup Health EducationBrijesh Yadav100% (1)
- Cancer of The CervixDocument68 pagesCancer of The CervixSandra mugunzvaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer: Dr. Vijay PrakashDocument23 pagesCervical Cancer: Dr. Vijay PrakashVijay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Prognosis: Rectal CancerDocument3 pagesPrognosis: Rectal CancerAlizza Therese Severo AnzanoNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Church PresentationDocument48 pagesCervical Cancer Church Presentationbande_adegboyegaNo ratings yet
- 4580-Article Text-8427-1-10-20210504Document14 pages4580-Article Text-8427-1-10-20210504model frameNo ratings yet
- Septiya Agestin Cahyaningrum - Malignancy in Reproductive Health System - WordDocument30 pagesSeptiya Agestin Cahyaningrum - Malignancy in Reproductive Health System - WordSepty KawaiNo ratings yet
- Endometrial CancerDocument34 pagesEndometrial CancertyasdwiarumNo ratings yet
- CA Cervix NewDocument54 pagesCA Cervix NewBi PinNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument5 pagesCaseBles B. MercadoNo ratings yet
- OUTPUT SabellanoDocument18 pagesOUTPUT SabellanoNedeve OznedNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cancer AlvezaDocument13 pagesOvarian Cancer AlvezaYa Mei Li100% (1)
- Malignant Ovarian TumourDocument46 pagesMalignant Ovarian Tumourahmed shorshNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer OverviewDocument22 pagesCervical Cancer OverviewnyseaNo ratings yet
- Milla Kviatkovsky, OMS-III, April 2013Document23 pagesMilla Kviatkovsky, OMS-III, April 2013api-210786702No ratings yet
- Proiect EnglezaDocument20 pagesProiect EnglezaRenata BendeNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - BREAST CANCER - Case StudyDocument29 pagesGroup 1 - BREAST CANCER - Case StudyCONTRERAS, ALIANNA IRISHNo ratings yet
- Ca OvaryDocument27 pagesCa OvaryMuhammad AbeeshNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument36 pagesCervical CancerDebabrata SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Presented By-Deeksha Sharma B.SC (Hons) Nursing 3 YearDocument35 pagesCase Presentation: Presented By-Deeksha Sharma B.SC (Hons) Nursing 3 YearMinakshi MawariNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Surgery in IndiaDocument9 pagesCervical Cancer Surgery in Indiadkumar1986No ratings yet
- Powerpoint: Breast CancerDocument89 pagesPowerpoint: Breast Cancerj.doe.hex_8780% (5)
- Bab Ii Tinjauan PustakaDocument7 pagesBab Ii Tinjauan PustakaDMdewiNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument53 pagesCervical Cancerthamizh555No ratings yet
- The New FIGO Staging For Carcinoma of The Vulva, Cervix, Endometrium, and SarcomasDocument9 pagesThe New FIGO Staging For Carcinoma of The Vulva, Cervix, Endometrium, and SarcomasAji PatriajatiNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma Uterus - Amita MaheshwariDocument42 pagesCarcinoma Uterus - Amita MaheshwariMochammad Rizal AttamimiNo ratings yet
- Explanation: Mass in The Axilla Metastasis Level 3 Axillary DissectionDocument51 pagesExplanation: Mass in The Axilla Metastasis Level 3 Axillary DissectionHasan ManghiNo ratings yet
- ONCOLOGICAL GYNECOLOGY - Malignant Tumors of The Vagina and Modalities of TreatmentDocument9 pagesONCOLOGICAL GYNECOLOGY - Malignant Tumors of The Vagina and Modalities of TreatmentVesna AntovskaNo ratings yet
- Pathology: Human PapillomavirusDocument15 pagesPathology: Human Papillomavirussandeepv08No ratings yet
- G. Yagci, S. Cetiner, M. Dede, O. GunhanDocument3 pagesG. Yagci, S. Cetiner, M. Dede, O. GunhanAnonymous pNIzA5No ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument28 pagesCervical CancerAngetile KasangaNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CA 450918 SHDocument52 pagesOvarian CA 450918 SH180045No ratings yet
- Ca Cervix: Shabana R Anchu Mariam CharlyDocument53 pagesCa Cervix: Shabana R Anchu Mariam CharlySuci Rahayu EvashaNo ratings yet
- Colposcopy: Cervical Cancer Is Cancer of The Cervix (Lowermost Opening of The Uterus in TheDocument4 pagesColposcopy: Cervical Cancer Is Cancer of The Cervix (Lowermost Opening of The Uterus in TheMayuri SwamiNo ratings yet
- Ca OvarioDocument13 pagesCa OvarioDaniel MálagaNo ratings yet
- 9.cancer of The Female Genital Tract.Document58 pages9.cancer of The Female Genital Tract.vichramNo ratings yet
- Cervical CancerDocument4 pagesCervical CancerMarjorie Mae R. HerreraNo ratings yet
- Gynaecological CancersDocument4 pagesGynaecological CancerssdfNo ratings yet
- Case Study g3p3 Am Shift Guzman LusungDocument38 pagesCase Study g3p3 Am Shift Guzman Lusungxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Tumor PayudaraDocument53 pagesTumor PayudaraBeivyNo ratings yet
- Final Handouts (Cervica Cancer)Document3 pagesFinal Handouts (Cervica Cancer)lisette_sakuraNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer FIXDocument29 pagesBreast Cancer FIXaryaniNo ratings yet
- Tutor 4 - CA ServiksDocument98 pagesTutor 4 - CA ServiksJessica Amelia100% (1)
- Malignant Ovarian TumourDocument42 pagesMalignant Ovarian TumourJones MarinaNo ratings yet
- Pra VeenDocument88 pagesPra VeenPraveen PraviiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Tract MalignanciesDocument30 pagesReproductive Tract Malignanciesjeelani saima100% (3)
- Cancer of The CervixDocument14 pagesCancer of The CervixJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Referat RahmanDocument27 pagesReferat Rahmannasution7No ratings yet
- Cervix Uteri1Document5 pagesCervix Uteri1twiggy484No ratings yet
- Cancer Research ProjectDocument10 pagesCancer Research ProjectRosemary CullingworthNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer BMJDocument4 pagesCervical Cancer BMJMaria Camila Ortiz UsugaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi &embriology Git (Compatibility Mode)Document6 pagesAnatomi &embriology Git (Compatibility Mode)Putri Ayu Prima DewiNo ratings yet
- Siti Yuyun Rahayu Fitri, S.KP., M.SiDocument30 pagesSiti Yuyun Rahayu Fitri, S.KP., M.SiMentari WardhaniNo ratings yet
- Paradigma Keperawatan RevDocument21 pagesParadigma Keperawatan RevMentari WardhaniNo ratings yet
- Komunikasi Dalam Pelayanan KesehatanDocument41 pagesKomunikasi Dalam Pelayanan KesehatanMentari WardhaniNo ratings yet
- Urinary EliminationDocument80 pagesUrinary EliminationMentari WardhaniNo ratings yet
- Bowel EliminationDocument137 pagesBowel EliminationMentari WardhaniNo ratings yet