Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spanish verb tenses worksheet
Uploaded by
Sylvia RodríguezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spanish verb tenses worksheet
Uploaded by
Sylvia RodríguezCopyright:
Available Formats
HOJA DE TRABAJO: REPASO DE TIEMPOS VERBALES Leer y trabajar de izquierda a derecha y por bloques
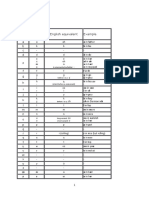
FORM PRESENT SIMPLE
(+) el V va como el Inf. sin to aunque + -(e)s en 3 p.s. (-) (?) el verbo (V) se pone en infinitivo sin to y el auxiliar (AUX ) es do o does Orden: (+) S + V (-) S + AUX + "not" + V (?) AUX + S + V ... ?
EXAMPLES
I go to school every day My mother goes to her office My mother doesn't go to school. I don't work. Do you speak English? Yes, I do. / No, I dont Does she study? No, she doesn't. I went to school yesterday. My mum didn't go to work yesterday. Did you see Mary yesterday? Yes, I did. / No, I didn't Con verbo regular:I watched TV yesterday. She didn't watch TV with me. Did she watch TV? Yes, she did. I am listening to music. You are not listening to me. Is she listening to you? Yes, she is./ No, she isn't. Ms ejemplos: We are playing football. My brother and I aren't studying French at school. Are you studying English now? I was listening to music yesterday afternoon. You weren't listening to me yesterday! Were you studying yesterday evening? Traduce todas las frases de los ejemplos de esta pgina. I will go to school tomorrow. They will not (won't) go to the concert tomorrow. My mother will study French next year. What will you be when you grow up? I`ll be a teacher. Will you marry me? Yes, I will. / No, I wont! I have finished. She hasn't finished yet. Have you finished? Today I've learnt the English tenses. My friends haven't found their walkman. What have you done today? Nothing!/ Lots of things!
Noticing...
Los V to be (= ser, estar) y to have (got) (= tener) britnico no siguen este esquema sino: I am here/Spanish/17 You are not Chinese Is Peter Polish? Yes, he is. / No, he isn't. Cul es la diferencia?
Recuerda: el pasado de to be es was/were y el de to have (got) es had. Misma estructura que arriba. Haz unas frases.
PAST SIMPLE
(+) si el verbo es regular, se aade -(e)d; si es irregular, ver la 2 col. Misma forma para todas las personas. (-) (?) el AUX es did (pasado de "do") y el V va en infinitivo sin to (porque el AUX ya nos dice que es pasado). Mismo orden que arriba.
En general, qu hay en comn con el Present Simple? Haz frases en este estilo: 1. Estudio. 2. No estudio. 3. Estudias? 4. Estudia. 5. No estudia. 6. Estudi. 7. No estudi. 8. Estudiaste?
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Aqu hay AUX en (+) (-) (?) y es to be (am, is, are ). Significa "estar". Como hay aux en todo, el V siempre va en gerundio (-ing). Orden: (+) S + AUX + V (-) S + AUX + "not" + V (?) AUX + S + V ...?
Cundo usaras el Present Simple y cundo el Present Continuous? Pon ejemplos en ingls.
PAST CONTINUOUS
Aqu tambin hay AUX en los tres tipos de frases y el V tambin va en gerundio. La diferencia es que el AUX va en pasado (was, were ). Se traduce: estaba/estuve, etc. + el gerundio del verbo princ.
En qu se diferencian los tiempos continuos de los tiempos simples ingleses? Explcalo y pon ejemplos en ingls.
"WILL" FUTURE
Sigue el mismo orden que los continuos. El AUX es siempre will y el verbo principal (V) es siempre un infinitivo sin to.
Respecto a la forma, qu tiene en comn este futuro con los tiempos simples y qu tiene en comn con los continuos? Pon ejemplos en ingls. Qu notas comparando las dos preguntas de los ejemplos? A qu tiempos es idntico en estructura de (+) (-) e (?)? En qu se diferencian? Escribe frases en Present Perfect y tradcelas.
Cmo se contraen los auxiliares? Pon ejemplos. Por qu estn subrayadas unas palabras de los ejemplos?
PRESENT PERFECT
(Pretrito perfecto) Sigue el mismo orden que los dems en (+) (-) (?). El AUX es el verbo "to have" en presente (have, has) y el V va en participio: -(e)d, si es regular; 3 col. si es irregular.
You might also like
- The Simple Present Tense Is UsedDocument8 pagesThe Simple Present Tense Is UsedskbbatamNo ratings yet
- Tiempos VerbalesDocument30 pagesTiempos VerbalesjhadhsgasdasdNo ratings yet
- 16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument9 pages16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisNurul May ApriyaniNo ratings yet
- Learn the Simple Present TenseDocument19 pagesLearn the Simple Present TenseJavier Gustavo Chuco ChucoNo ratings yet
- 000 - Unidad 1 - InglésDocument31 pages000 - Unidad 1 - InglésAnonymous 3D8vtRNo ratings yet
- English Unit 1 - 6: Nama: Neysa Kelas: Viii E No Absen: 32Document8 pagesEnglish Unit 1 - 6: Nama: Neysa Kelas: Viii E No Absen: 32Jessica GultomNo ratings yet
- Presente Simple, Group 1Document12 pagesPresente Simple, Group 1Scarlet Rossemary Bueno IntriagoNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Part A FormDocument5 pagesSimple Present: Part A Formveronika wienaNo ratings yet
- Learn Simple Present, Past, Future TensesDocument4 pagesLearn Simple Present, Past, Future TensesIswaraiswaraNo ratings yet
- Presente Continuo: Estructura Verbal AfirmaciónDocument14 pagesPresente Continuo: Estructura Verbal AfirmaciónmatiasNo ratings yet
- ElecDocument15 pagesElecfaith_khp73301No ratings yet
- Present Simple and Continuous ExercisesDocument4 pagesPresent Simple and Continuous ExercisescarmencitacristeaNo ratings yet
- Inglês - Médio - Módulo 3Document24 pagesInglês - Médio - Módulo 3biancaNo ratings yet
- Guia de Sextos Del 20 Al 24 de AbrilDocument13 pagesGuia de Sextos Del 20 Al 24 de AbrilSamuNo ratings yet
- Kejadian. Didalam Bahasa Indonesia Tidak Ada Perubahan Kata Kerja YangDocument42 pagesKejadian. Didalam Bahasa Indonesia Tidak Ada Perubahan Kata Kerja YangmiftaNo ratings yet
- The Quest For The Holy VerbDocument13 pagesThe Quest For The Holy VerbLotte WynantsNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap HTD-HTTDDocument12 pagesBai Tap HTD-HTTDLê ThủyNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument24 pagesEnglish GrammarjorgeNo ratings yet
- The Indicative - Verbul A Fi Conjugat La Toate Timpurile VerbaleDocument9 pagesThe Indicative - Verbul A Fi Conjugat La Toate Timpurile VerbalePif GretaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-7 of Oxford Practice GrammarDocument23 pagesUnit 4-7 of Oxford Practice GrammarHarjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present Tense Explained: Forms, Usage and ExamplesDocument8 pagesThe Simple Present Tense Explained: Forms, Usage and ExamplesNOOR AZNINo ratings yet
- Inglés: Universidad Nacional Del Centro Del PerúDocument30 pagesInglés: Universidad Nacional Del Centro Del Perúwilll reyyNo ratings yet
- Simple Past-29 Mayo 2017Document32 pagesSimple Past-29 Mayo 2017Anita de BorbonNo ratings yet
- Curs EnglezaDocument81 pagesCurs EnglezaSilviu CarstinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 16b - BasicDocument6 pagesLesson 16b - BasicMichael MccormickNo ratings yet
- Simple Present PresentationDocument7 pagesSimple Present PresentationJacke ArizalaNo ratings yet
- Lectia I Timpurile Modului Indicativ NegativDocument52 pagesLectia I Timpurile Modului Indicativ Negativdan marianNo ratings yet
- Engleza CursDocument100 pagesEngleza CursElena ProsaNo ratings yet
- Modul 2 Jobs and RoutinesDocument17 pagesModul 2 Jobs and RoutinesElla SiooNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Regular FormsDocument9 pagesSimple Past Regular FormsTifany PereiraNo ratings yet
- English - Modul 2 TensesDocument46 pagesEnglish - Modul 2 TensesM Aswin SebayangNo ratings yet
- Ôn THPTQGDocument252 pagesÔn THPTQGMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Ôn THPTQGDocument252 pagesÔn THPTQGUyển Mai TăngNo ratings yet
- Present Tense SimpleDocument35 pagesPresent Tense SimpleLara PopNo ratings yet
- Unidad II Ing-: CUAM "Cuestión de Excelencia"Document27 pagesUnidad II Ing-: CUAM "Cuestión de Excelencia"Miguel PerezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Grammar AppendixDocument32 pagesUnit 1: Grammar AppendixlleizaloNo ratings yet
- Present Simple - Present ProgressiveDocument32 pagesPresent Simple - Present ProgressiveJéssica Katherine Santoyo VillegasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 20: Costache Reli-CătălinaDocument22 pagesLesson 20: Costache Reli-CătălinaMiha MihaelaNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Exercises Present Simple TenseDocument1 page6th Grade Exercises Present Simple TenseOana GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Letter Phonetic Symbol English Equivalent Example A B C D e F G H I J K L M N o P Q R S T U V W X y Z Æ ØDocument26 pagesLetter Phonetic Symbol English Equivalent Example A B C D e F G H I J K L M N o P Q R S T U V W X y Z Æ ØOsman MehmedovicNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2Document35 pagesMeeting 2Marvin KnbNo ratings yet
- PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE GUIDEDocument35 pagesPRESENT SIMPLE TENSE GUIDEMaria MayelaNo ratings yet
- Atividade de InglêsDocument7 pagesAtividade de InglêsBia alvaresNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument64 pagesTENSESsaputraardi1793No ratings yet
- Lesson 5a Tenses LessonDocument86 pagesLesson 5a Tenses LessonWane DavisNo ratings yet
- B. Inggris I - Simple Present and Present ProgressiveDocument17 pagesB. Inggris I - Simple Present and Present ProgressiveAgriel ArsadelNo ratings yet
- Grammar Units 4,5,6,7,8 PDFDocument11 pagesGrammar Units 4,5,6,7,8 PDFrosibeth78No ratings yet
- Simpe Present Vs Simple PastDocument10 pagesSimpe Present Vs Simple PastJuieta MelisaNo ratings yet
- KP English HomeDocument14 pagesKP English Homepy27hlNo ratings yet
- Essential Grammar and Vocabulary IndexDocument61 pagesEssential Grammar and Vocabulary IndexMontse Morillo100% (2)
- Simple PastDocument27 pagesSimple PastAlainHuniorAracaAracaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense and ExercisesDocument9 pagesSimple Present Tense and ExercisesPapa Martelo MarteloNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense Explained: Rules, Forms and ExamplesDocument9 pagesSimple Present Tense Explained: Rules, Forms and ExamplesEdi YuniNo ratings yet
- Name: Shara Tauladania Class: 1B Keperawatan NIM: PO72201201696 MK: English Supervisor: Wahyu Eni Setyohari, M.PDDocument6 pagesName: Shara Tauladania Class: 1B Keperawatan NIM: PO72201201696 MK: English Supervisor: Wahyu Eni Setyohari, M.PDShara TauladaniaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense in English - Grammar LessonDocument7 pagesPresent Simple Tense in English - Grammar LessonVerónica PilcoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bhs InggrisDocument8 pagesTugas Bhs InggrisSarma MarlinangNo ratings yet
- Tiempos verbales activos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #1From EverandTiempos verbales activos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #1No ratings yet
- True False ReadingsDocument6 pagesTrue False ReadingsSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Cae Speaking Questions Part 1 StyleDocument3 pagesCae Speaking Questions Part 1 StyleSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- 3rd Conditional Conversation PracticeDocument1 page3rd Conditional Conversation PracticeViki RincónNo ratings yet
- FCE Spotlight Paper 3 and Answer Key PDFDocument16 pagesFCE Spotlight Paper 3 and Answer Key PDFAlenka Pla OlahNo ratings yet
- Units 6 / 23 - Phrasals Verbs: Make Do Have TakeDocument1 pageUnits 6 / 23 - Phrasals Verbs: Make Do Have TakeSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Renzo - GrammarDocument18 pagesRenzo - GrammarSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- InversionDocument3 pagesInversiondeliailona555No ratings yet
- Listening Part 1Document5 pagesListening Part 1Sylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Conditionals WorksheetDocument2 pagesConditionals WorksheetSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Verbs Exam Worksheet 30671Document2 pagesVerbs Exam Worksheet 30671Sylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Use of English FirstDocument6 pagesUse of English FirstSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- 8.3 USE ENGLISH ANSWERSDocument5 pages8.3 USE ENGLISH ANSWERSSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- FIIL IN THE GAPS - Jealous Guy Lyrics - STUDENTSDocument1 pageFIIL IN THE GAPS - Jealous Guy Lyrics - STUDENTSSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Match Proverbs and MeaningsDocument3 pagesMatch Proverbs and MeaningsSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios SelectividadDocument4 pagesEjercicios SelectividadSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Engl1080 Eap 6 Portfolio 2Document8 pagesEngl1080 Eap 6 Portfolio 2Sylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Reduced relative clauses explainedDocument11 pagesReduced relative clauses explainedSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Jealous Guy Lyrics - STUDENTSDocument1 pageJealous Guy Lyrics - STUDENTSSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Practising Cae Speaking Part 4Document8 pagesPractising Cae Speaking Part 4Sylvia Rodríguez100% (1)
- Key Word Transformation ExpressionsDocument2 pagesKey Word Transformation ExpressionsjelliclekatzenNo ratings yet
- A Compound AdjectiveDocument2 pagesA Compound AdjectiveCoatl SchlangeNo ratings yet
- Part A. Directions: Complete Each Question or Sentence With Should Have or Could Have, and A Main Verb. (10 Points)Document2 pagesPart A. Directions: Complete Each Question or Sentence With Should Have or Could Have, and A Main Verb. (10 Points)Sylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Relatives 3º EsoDocument2 pagesRelatives 3º EsoSylvia Rodríguez100% (1)
- Exercice SDocument10 pagesExercice SSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Answers Exam 8 JanDocument2 pagesAnswers Exam 8 JanSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Conditionals (Download)Document6 pagesConditionals (Download)Sylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- c1 Test TypologyDocument3 pagesc1 Test TypologySylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Or DenarDocument1 pageOr DenarSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Action VerbsDocument2 pagesAction VerbsFahmi NoorNo ratings yet
- Present Simple ContinuousDocument5 pagesPresent Simple ContinuousEnglish StationNo ratings yet
- Muk's Guide To Everything He Learned From TashaDocument44 pagesMuk's Guide To Everything He Learned From TashabeveriaaNo ratings yet
- New Framework 2Document129 pagesNew Framework 2Laura MujicaNo ratings yet
- 1976-Li, Charles N. & Sandra A. Thompson-Subject and Topic A New Typology of Language PDFDocument33 pages1976-Li, Charles N. & Sandra A. Thompson-Subject and Topic A New Typology of Language PDFOscarHeNo ratings yet
- Showing Direct Contrast: WhileDocument28 pagesShowing Direct Contrast: WhileAlridah SyahfitriNo ratings yet
- Kaushanskaya V L Kovner R L Kozhevnikova o N I DR A Grammar PDFDocument324 pagesKaushanskaya V L Kovner R L Kozhevnikova o N I DR A Grammar PDFDasha GrebenschikovaNo ratings yet
- SyntaxDocument5 pagesSyntaxStela Valentinova100% (1)
- The Present Perfect Tense: EmptiedDocument1 pageThe Present Perfect Tense: Emptieddiegobonilla74No ratings yet
- Adjective Order Rules for Multiple DescriptorsDocument12 pagesAdjective Order Rules for Multiple DescriptorsFuture LearningNo ratings yet
- Present Unreal Conditional: Would + Can Could Would + Shall Should Would + May MightDocument2 pagesPresent Unreal Conditional: Would + Can Could Would + Shall Should Would + May MightEduardoJoseSaletaSanchez100% (1)
- 101 U1Document27 pages101 U1qwesghwqedfgNo ratings yet
- English TipsDocument21 pagesEnglish TipsLaura HallNo ratings yet
- Academic Word List: Sublist 5: Sheldon SmithDocument32 pagesAcademic Word List: Sublist 5: Sheldon SmithHafiza GuliyevaNo ratings yet
- 10 ECCE 1 - Teacher's Book Derivative ChartsDocument10 pages10 ECCE 1 - Teacher's Book Derivative ChartsPremanandaNo ratings yet
- The Style of Official and Business Documents: Specific Lexical and Grammatical FeaturesDocument11 pagesThe Style of Official and Business Documents: Specific Lexical and Grammatical FeaturesDiana ShuxratovnaNo ratings yet
- Tibetan Language PDFDocument72 pagesTibetan Language PDFDiana Nicoleta100% (1)
- Sessi 12Document4 pagesSessi 12Abdul HalimNo ratings yet
- Syriac Verb Paradigms Draft AnalyzedDocument22 pagesSyriac Verb Paradigms Draft Analyzedthe_doctor1990100% (1)
- Meeting 1 - Introduction To Linguistics For TeachersDocument63 pagesMeeting 1 - Introduction To Linguistics For TeachersSommerledNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement For Web 7 2019Document20 pagesSubject Verb Agreement For Web 7 2019dianela fionaNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice GuideDocument2 pagesActive and Passive Voice GuideIlyana HaniNo ratings yet
- Learn Malayalam in 30 Days Through English 9789352781355Document223 pagesLearn Malayalam in 30 Days Through English 9789352781355Mohammad Tahir KhanNo ratings yet
- GRE Word List With Synonyms and AntonymsDocument96 pagesGRE Word List With Synonyms and AntonymsAQ HassanNo ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP THI HÌNH THÁI HỌC REVISION FOR THE FINAL TESTDocument31 pagesÔN TẬP THI HÌNH THÁI HỌC REVISION FOR THE FINAL TESTHồng Hà BùiNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice ExplainedDocument3 pagesPassive Voice Explainedanon_805613190No ratings yet
- Lexicology of modern English languageDocument293 pagesLexicology of modern English languageТанюшка Ткачук50% (2)
- Grammar - Word Phrase Clause Sentence 1Document17 pagesGrammar - Word Phrase Clause Sentence 1Bib SaleemNo ratings yet
- Using Nouns and Pronouns As Predicate NominativesDocument9 pagesUsing Nouns and Pronouns As Predicate NominativesChristine DianeNo ratings yet
- The English Language: and The 8 Parts of SpeechDocument18 pagesThe English Language: and The 8 Parts of SpeechRenDenverL.DequiñaIINo ratings yet
- Must/mustn't, have to/don't have to form and meaningDocument3 pagesMust/mustn't, have to/don't have to form and meaningQuỳnh Anh LêNo ratings yet
- Describing Trends Using Prepositions in IELTS WritingDocument7 pagesDescribing Trends Using Prepositions in IELTS WritingDeniz TokgozNo ratings yet